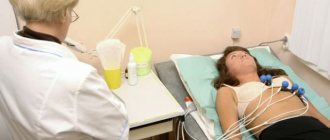
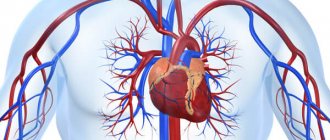
Cardiac echocardiography is an effective technique for visualizing the structures of the heart and heart valve to identify pathological functional and morphological changes. Diagnostics with ultrasonic waves helps to evaluate the functioning of the organ over time, to see on the display the contraction of the heart muscle and the functioning of the valve. Ultrasound examination is possible at any age: the technology is non-invasive, safe, and has virtually no contraindications. In addition, the method is informative and allows you to get results in just a few minutes.
In what situations should you undergo a cardiac ultrasound?
- Changes in ECG indicators.
- Heart murmurs.
- A slight increase in body temperature in the absence of inflammatory processes in the throat, nose, ear or kidneys.
- Arrhythmia.
- An x-ray of the heart showed a change in its shape and size, as well as in the vessels extending from it.
- Hypertension.
- Predisposition to hereditary heart diseases.
- Possible changes in cardiac structures.
- Fainting, swelling, shortness of breath, dizziness.
- Pain in the left half of the chest and behind the sternum.
- Risk of heart tumors.
- After myocardial infarction.
- Effusion pericarditis.
- Angina pectoris.
- Diagnosis of cardiomyopathy and its type.
- To detect true or false cardiac aneurysm.
It is extremely important to carry out this procedure after a myocardial infarction to determine how many muscle cells have died.
ECG and ultrasound of the heart should be performed by people in stressful situations, experiencing severe emotional and physical stress.
EchoCG has no age restrictions. It is prescribed to children if a congenital heart defect or a change in its structure is suspected, which often occurs during the period of active growth of the child.
EchoCG is prescribed for pregnant women, because allows you to identify heart defects in the fetus in the womb. The procedure is painless and does not cause harm.
Heart ultrasound is a mandatory procedure during pregnancy if:
- There was a history of spontaneous abortions.
- Diabetes.
- Hereditary predisposition to heart disease.
- In the 1st and 2nd trimester, the woman was forced to take antiepileptic drugs and antibiotics.
- The analysis revealed high titers of antibodies to rubella, or the woman had it during pregnancy.
Fetal echocardiography is prescribed at 18-22 weeks. Children undergo it when the above symptoms appear.
How to prepare for an ultrasound for children and adults
General rules for preparing for an ultrasound:When going to us for an ultrasound, you do not need to take with you a diaper for bedding and napkins to remove the gel after the procedure. Our ultrasound room is equipped with everything necessary to ensure that the ultrasound diagnostic session is comfortable and pleasant for you and your child.
Dress your child so that you can easily access the examination area.
If your scheduled ultrasound requires preparation, follow all instructions carefully. This will allow you to obtain the most complete information about the condition of the organs.
No special training required:
- Ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography);
- Ultrasound of the hip joints;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- Ultrasound of the thymus (thymus) - you only need to know the weight and height of the child at the time of the study;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland - you only need to know the weight and height of the child at the time of the study;
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes;
- Ultrasound of the salivary glands;
- Vascular ultrasound;
- Ultrasound of muscles;
- Ultrasound of soft tissues;
- Ultrasound of the scrotum;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands - performed in the first 10 days of the menstrual cycle;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys - with normal weight; if you are overweight and have increased gas formation in the intestines, the same preparation is required as for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Requires preliminary preparation:
- Ultrasound of the liver;
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder;
- Ultrasound of the spleen;
- Ultrasound of the pancreas;
- Ultrasound of the adrenal glands;
- Ultrasound of the stomach;
- Ultrasound of the bladder;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
Preparation for ultrasound of the liver and other abdominal organs (spleen, gallbladder, pancreas):
The main task here is to get rid of gases in the intestines. In preparation for an ultrasound scan of the liver, spleen and other abdominal organs, 3-4 days before the appointed date, it is necessary to exclude gas-forming foods from the diet (raw vegetables rich in fiber; fruits; legumes; black bread; whole milk; carbonated drinks; high-calorie confectionery products - cakes, pastries, etc.). If the body is prone to increased gas formation, it is recommended to take enterosorbents and enzyme preparations: activated carbon, festal, mezima-forte, espumizan. It is prohibited to undergo a gastro- and/or colonoscopy before an ultrasound scan. An abdominal ultrasound is performed on an empty stomach, so you should refrain from eating 8–12 hours before the procedure.
Preparation for liver ultrasound in infants:
If an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is performed on a baby, then the task is simplified. Feed your baby as usual.
Preparation for DECHG (dynamic echocholecystography) or ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of function:
The method consists of studying the volume of the gallbladder before and after taking a choleretic breakfast. The study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach; you should refrain from eating 8-12 hours before the procedure. Considering the need for such a long “hunger break,” it is more convenient to plan this study in the morning.
There is no need to bring sour cream, yogurt, or chocolate. Our clinic uses the drug hofitol as a choleretic breakfast, which allows for a more accurate assessment of the motor-evacuation function of the gallbladder.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the bladder:
Directly on the day of the ultrasound, 40 minutes before the start of the diagnosis, you need to drink half a liter of unsweetened and still water or tea. As soon as the desire to relieve yourself appears, the best moment comes to conduct research.
Preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder with determination of the volume of residual urine is carried out in a similar way. This procedure takes place in two stages: first, a classic ultrasound of the bladder is performed, then the patient is asked to visit the toilet, after which the study is repeated, paying attention to how much urine remains in the bladder, that is, whether it is fully emptied.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the bladder in an infant is easier: it will be enough to feed or drink the child 15–20 minutes before the start of the procedure.
Preparing for a prostate ultrasound:
Ultrasound of the prostate is performed through the abdomen (transabdominal access) or through the rectum (transrectal access). The bladder is also examined transrectally in very obese men. When preparing for an ultrasound of the prostate, which will be performed through the abdominal wall, all preparatory measures will be similar to those used for examining the bladder.
For TRUS of the prostate gland, when the sensor, “dressed” in a condom to protect against infections, is inserted into the rectum, there is no need to fill the bladder with fluid. Preparation for such a study involves only a light dinner the night before and a cleansing enema an hour before the start of the scan.
Preparation for ultrasound of the stomach:
Preparation for an ultrasound of the stomach is simple: do not eat for 6–8 hours and bring with you 200–400 ml of clarified juice (apple, apple-grape). After the doctor scans the empty stomach with a sensor, the child will drink the stored juice through a straw or bottle, and the diagnostician will observe how the liquid flows from the esophagus into the stomach. Water also allows visualization of the lower esophagus.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the stomach in infants does not imply such a long break between feedings. It will be enough to wait 3–3.5 hours, as with an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Preparing for a pelvic ultrasound:
Preparing for a pelvic ultrasound for boys:
Ultrasound of the scrotum in boys does not require preparation; it is enough to carry out the usual hygienic care of the external genitalia before the procedure. You should come to a prostate ultrasound with a full bladder. Preparation for this study is carried out according to the same scheme as preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder (see above).
Preparation for pelvic ultrasound for girls:
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages in girls is performed only transabdominally (through the abdominal wall) and with a full bladder. Preparation is carried out in the same way as preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder (see above).
Preparing a newborn for a screening ultrasound at 1–1.5 months:
A routine screening ultrasound is prescribed for each baby at the age of 1–1.5 months and necessarily includes ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography), kidneys and hip joints. All three ultrasounds can be performed in one session. No preparation needed.
Additionally, it is recommended to conduct an ultrasound of the thymus gland (thymus), heart and abdominal organs. The baby does not need to prepare for all these studies.
If you have scheduled tests or any other procedures at our center on the same day, start your visit with ultrasound diagnostics. To obtain clear and reliable results from a pediatric ultrasound, it is important that the child feels calm and relaxed.
Methods for performing echocardiography of the heart
- M – method (one-dimensional). With its help, the dimensions of the heart chambers and the work of the ventricles during their contraction are accurately determined. The indicators are presented in the form of a graph.
- B – method (two-dimensional). Allows you to see tumors, blood clots and aneurysms. With its help, the thickness of the heart walls and valves is measured, and the degree of contractility of the ventricles is determined.
- Electrocardiography with Doppler. The procedure is necessary to diagnose heart defects and other serious disorders.
Ultrasound can be performed through the esophagus or during periods of active physical activity.
Echocardiography through the esophagus is prescribed in situations such as:
- Infectious endocarditis.
- Routine examination before installation of an artificial valve.
- After a stroke and in cases of cerebral circulation disorders and atrial fibrillation.
- Cardio version.
- Defect of the septum between the atria.
- The impossibility of traditional ultrasound of the heart. This occurs in the presence of costal ossification and other disturbances in the structure of the chest.
It is prohibited to perform cardiac echocardiography through the esophagus if there is:
- Varicose veins of the esophagus.
- Strong gag reflex.
- Radiation therapy of the esophagus.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in acute form.
- Enlarged hernia on the diaphragm.
- Gastric and intestinal bleeding.
- Intestinal perforation.
- Spasms, tumors, intestinal diverticula.
- Pathological mobility of the cervical spine.
Rules for preparing and conducting echocardiography through the esophagus:
- Stop eating and drinking at least 4 hours before the ultrasound
- Pull out dentures and gastric tube
- Before the procedure, the patient's mouth and throat are irrigated with lidocaine.
- The patient lies on his left side, a mouthpiece is inserted into his mouth and an endoscope is carefully inserted into the esophagus, through which ultrasonic waves penetrate
- The procedure takes from 15 to 20 minutes and is recorded on video.
Preparation for the procedure
If urgent diagnosis is necessary, an ultrasound of the heart can be performed without prior preparation. However, in order for the results to be as correct as possible, it is better to prepare. It is important to tell your doctor about the medications you are taking. The doctor will take this point into account and, perhaps, adjust the medication intake for a while. The day before the test, avoid drinking alcohol, tea and coffee. If you have thick hair on your chest, shave it off. Try not to smoke two to three hours before Echo-KG. Don't rush into the office right away. Sit in the hall for 10-15 minutes, relax, calm down after walking along the street.
Ultrasound is the fastest way to confirm or refute the presence of pathology of the heart and large vessels, which has a high safety profile. The result is issued immediately after the examination by a doctor. The doctor has the opportunity to prescribe appropriate treatment, give recommendations on the regimen, physical activity and nutrition on the day of the examination.
← All articles
In what cases is stress echocardiography prescribed?
- To diagnose coronary artery disease.
- To assess the extent to which narrowed coronary arteries in patients with coronary artery disease affect their quality of life and exercise endurance.
- To assess the degree of blood supply to the myocardium.
- To monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
- Uncomplicated heart attack or chronic ischemic heart disease.
- Risk of negative consequences during complex operations.
It is prohibited to perform echocardiography with stress if:
- Acute myocardial infarction (less than a month).
- Aortic aneurysm of dissecting type.
- Respiratory, cardiac, renal and liver failure.
- Blockage of blood vessels by blood clots.
The normal ultrasound of the heart with a load is considered to be:
- Evenly moving walls of the left ventricle (LV) during exercise.
- Decrease in end-systolic volume (ESV).
- Raising the exile faction.
- Absence of disturbance in the functioning of the walls during movement, if a disturbance was recorded at rest.
- Increase in wall thickening in systole.
Negative indicators are an enlarged right ventricle (RV), the appearance of new areas with inactive walls, and a decrease in the ejection fraction to 35%.
What does an ultrasound of the heart show?
The resulting parameters allow you to determine:
- hypertrophy of the LV walls;
- regurgitation of blood through the valves;
- tumors, blood clots, scars, aneurysms;
- blood flow condition;
- valve condition;
- degree of myocardial contractility;
- size of the heart cavities;
- state of the LV pumping function in a dynamic state.
It is considered normal if:
- there is no fluid in the pericardium;
- the size of the final section of the pulmonary artery is within 1.8-2.4 cm; trunk - up to 3 cm;
- ejection fraction is 55 – 60%;
- the volume of the pancreas at the final stage of relaxation of the heart (diastole) ranges from 0.9 to 2.5 cm;
- thickness of the interventricular septum in the final stage of diastole from 0.5 to 1.12 cm
- the final section of the aorta in diameter is 2 – 3.7 cm
- the thickness of the posterior wall of the LV at the final stage of relaxation of the heart (diastole) varies from 0.6 to 1.12 cm
- the change in the movement of the posterior wall of the LV towards contraction (systole) is 0.91 – 1.41 cm
- the size of the LV cavity in the final stage of relaxation (diastole) ranges from 3.51 to 5.7
- cardiac output (MCV) must be no less than 3.5 and no more than 7.5 l/min
- cardiac index ranges from 2 to 4.1 l/m2
- the diameter of the terminal part of the pulmonary artery is from 1.8 to 2.4 cm, its trunk is up to 3 cm
- the blood flow speed through the carotid artery is 22 cm/s with an error of +-5 cm/s
- there are no manifestations of regurgitation and dysfunction of the papillary muscles, growth on all valves.
The degree of discrepancy with normal values is determined by a sonologist, but the final diagnosis is made by a cardiologist taking into account the information received and based on other symptoms. The disease cannot be diagnosed by ultrasound alone.
General recommendations for ultrasound
To properly conduct an ultrasound examination, general rules must be followed. They are:
- if there are open wounds, it is better to postpone this procedure for another time;
- It is not recommended to smoke three days before the procedure;
- diagnostics are always carried out on an empty stomach;
- It is better to take special medications that eliminate gas formation 2-3 days before the procedure;
- It is better to wear clothes that are easy to remove during the procedure.
Using ultrasound, you can examine the thyroid gland, eyes, scrotum, and joints. And here no special preparatory measures are required.
Publication date: 2019-08-11