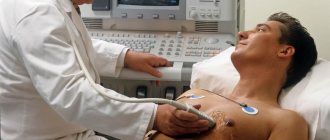
Ultrasound diagnostics is based on the property of sound waves to pass through tissue and be reflected from the surfaces they encounter. The movement of sound waves is carried out in a certain, specified direction with a certain strength and frequency. If media with different densities are encountered along the path of ultrasound, this is displayed on the screen. Air in the intestinal tract (GIT) is the main cause of interference during research. In order to avoid the occurrence of this problem, high-quality preparation for ultrasound diagnostics is necessary, generally aimed at reducing gas formation in the intestines.
At the International Center for Health Protection, the attending physician, when referring you for an examination, will definitely tell you how to properly prepare for an ultrasound. If you decide to be examined yourself, read the preparation rules.
What is duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta and its visceral branches
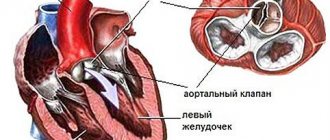
The abdominal aorta represents its descending part, located in the retroperitoneal space.
The muscles of the spine and abdominal organs are also located there. Visceral branches are represented as small arteries extending towards the internal organs, including the kidneys, spleen, intestines, and so on.
Duplex scanning is a method of ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal aorta and its visceral branches.
IMPORTANT: The word “duplex” itself has English roots; it can be translated as double or split.
This technique has two modes, which include conventional scanning and Doppler ultrasound. Ultrasound helps to see internal organs and tissues in black and white. Using the scanning mode, the thickness of the walls, their diameter, the formation of blood clots and the course of blood vessels are viewed.
Thanks to Doppler ultrasound, the doctor can assess the intensity of the blood, measure its pressure and direction.
Principle of operation
Content:
- Principle of operation
- Scan classification
- Indications and contraindications
- Preparatory process
- Decoding the result
- Benefits of Duplex Scanning
Scanning a specified part of a large segment of the cardiovascular system is just one of many methods for confirming or refuting a number of ailments. But it is precisely this that is considered one of the most productive, as it is based on a couple of reliable mechanisms for obtaining the necessary information.
The first option provides a basis from the observations of Mr. Doppler, who was an Austrian physicist. In honor of him, the technique was named Dopplerography. The main principle is based on the difference in the resulting frequency when taking into account the distance from the sensor to the particles. With its help, it is possible to evaluate the elements located inside the vessels: red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets, and the liquid plasma part.
By adjusting the frequency of incoming ultrasonic vibrations, the doctor will be able to check not only the presence of blood flow, but also its speed and direction.
The second component of the technique is the so-called “B-mode”. Typical ultrasonic spectrum diagnostics operate using high-frequency pulses. When reflected from the part being studied, they are captured by the apparatus.
Based on the results obtained, it is possible to record possible pathologies that occur in the vascular structure of potentially affected walls. The technology allows you to monitor changes in real time, provided that a two-dimensional image is transmitted.
Together, this guarantees a high-quality and complete assessment of the anatomy of the cardiovascular system and hemodynamics. No other modern methods can provide such accuracy.
What does a duplex scan of the abdominal aorta show?
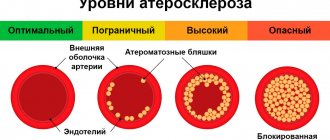
Damage to the walls of blood vessels occurs as a result of atherosclerotic vascular damage, which also accompanies the formation of plaques and narrowing of the vessel.
Because of this, the incoming blood volume decreases and ischemia of the area that feeds the narrowed vessel is formed. In the opposite situation, an aneurysm is formed, most often it affects the abdominal aorta and less often its visceral branches.
An aneurysm implies an expansion of blood vessels by one and a half times or more. The accepted maximum diameter, within the normal range, is 2 centimeters; when dilated to 3 centimeters, an aneurysm is diagnosed. It can be true or false.
REFERENCE: A true aneurysm has a full wall consisting of 3 layers, while a false aneurysm does not have such a wall.
An aneurysm is dangerous for a number of reasons, first of all, it can compress surrounding tissues, and there is also a threat of rupture and thrombosis.
Using this study, it is also checked whether the wall of the aorta or another arterial vessel is dissecting. What happens when there is a defect in the muscular layer of the artery.
And all these dangerous processes inside the abdominal cavity can be seen during duplex scanning, which means treatment can be prescribed on time. In addition, this is a completely painless and harmless process for the body.
Preparation for ultrasound examination
- Eliminate from your diet all foods that can cause gas in the gastrointestinal tract three days before the test. These include cabbage, milk, raw vegetables, fruits and legumes. Also, in order to reduce the level of flatulence in your body, take 4 tablets (capsules) of Espumisan twice a day.
- Before the study, do not eat food at night. You should come to the doctor on an empty stomach, and your last meal should be at least 6 hours ago.
- On the day you are scheduled for the test, you are not allowed to take any medications. It is mandatory to use 2 tablets (capsules) of Espumisan. However, there are exceptions to this rule, for example, seriously ill people are allowed to take medications, but only with the permission of a doctor.
- "Espumizan" can be replaced with any sorbents that are prescribed directly by your doctor.
- Among the patients for whom exceptions are allowed are diabetics, hypertensive patients and other seriously ill patients who are required to use pharmaceuticals.
Indications for duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta
Duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta is performed in the following cases:
- The presence of cerebrovascular disease (headache, dizziness), arterial hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and osteochondrosis;
- The presence of varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, phlebothrombosis, postthrombophlebitis disease;
- The presence of atherosclerosis, endarteritis and diabetic arterial angiopathy;
- The presence of atherosclerosis of the visceral branches of the abdominal aorta (including blood vessels, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract);
- With aneurysm of the vessels of the abdominal aorta and other parts;
- In case of vascular injury;
- To monitor the vessels of the abdominal aorta before surgery;
- To monitor the vessels of the abdominal aorta after surgery;
- For the purpose of conducting a screening examination (to identify asymptomatic forms of diseases);
- For the purpose of conducting a preventive examination of the abdominal cavity.
Indications and contraindications
Since the aorta is the largest arterial vessel, the health of the heart muscle will completely depend on its functioning. It originates in the left ventricle. The closer to the base the pathology is detected, the stronger the consequences will be.
Typically, cardiologists are referred to scan the aortic arch along with its branches. In their conclusions to issue a referral, they rely on current tests, as well as complaints from the victim. Among them, the most common symptoms are:
- headache;
- noise in ears;
- vision problems;
- deterioration of coordination.
All of the above are consequences of problems with the activity of the main artery of the body. Thus, a headache is a consequence of a chronic or acute cessation of stable blood flow to the brain. If the organ does not receive enough oxygen, it will suffer from hypoxia. Outwardly this manifests itself as tinnitus.
When cerebral circulation suffers, this guarantees abnormalities in the functioning of the frontal and occipital lobes. They are responsible for vision, which can decrease significantly over time.
Impaired coordination of movements is explained by metabolic disorders. The latter directly depend on the developing ischemia of the cerebellum and precentral gyrus.
Another striking sign is a weakening pulse in the hands. There are many reasons to explain this, but most often the culprit is stenosis of the subclavian artery. Additionally, this is indicated by freezing of the upper extremities or even their partial numbness.
If the patient has previously undergone an initial examination, the doctor may notice a systolic arterial murmur in the vessels that separate from the aortic arch. In the presence of a narrowed lumen, the flow acquires characteristic noise.
But most often people come to see a cardiologist for more trivial reasons:
- pain in the heart area;
- dyspnea;
- tachycardia.
This may indicate overload of the aorta or complications in the activity of its valve. To exclude the worst scenarios, the doctor suggests undergoing a duplex analysis.
But even the absence of visible symptoms does not mean that a person is completely healthy. In some cases, specialists prefer to be extra vigilant by sending their patients to such a clinical trial. Those at risk are those who:
- are within retirement age;
- are obese;
- lead a sedentary lifestyle.
You should not exclude from the list people who are prone to cardiovascular diseases due to heredity. Also, a profile examination cannot be avoided by those who have already had their diagnosis confirmed. Patients should undergo periodic scans to monitor progress in treatment if they have:
- Aneurysm of the aortic arch. The disease involves the expansion of the walls, which first provokes a weakening of their elasticity, and then a sudden rupture.
- Nonspecific aortoarteritis, which has a second name - Takayasu's disease. The pathology involves growths of the cardiac vessel according to the granulomatous pattern. Over time, it causes a narrowing of the lumen and subsequent disturbances in the hemodynamic spectrum of action.
- Hypertension. Increased blood pressure several times increases the risk of developing a heart attack or stroke in relation to completely healthy citizens.
- Atherosclerosis. Avoiding complex medical terminology, the disease is characterized by the formation of intravascular plaques that block the passage of blood.
But the list of contraindications for the duplex technique is extremely short. It covers only types of shock along with collapse, as well as terminal stage oncology. This also included cardiac and respiratory failure, which are in the decompensation phase.
Methodology
Duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta is performed to identify the cause of pain in the abdominal cavity, or as a preventative measure at the request of the client.
To perform a duplex scan, you will need to remove clothes above the waist, lower your pants or skirt to provide the doctor with free access and lie on the couch with your back.
Then the doctor applies a special gel to the abdominal cavity, thanks to which the device’s sensor moves better over the skin and more accurately registers sound waves.
ATTENTION: If necessary, you may need to speed up your breathing or, on the contrary, hold it.
The time required for the study is 10-30 minutes, depending on the complexity of the case.
Scan classification
Dopplerography for the aortic arch provides two main categories that are similar to each other. This is about:
- mapping;
- energy type.
But the second version is considered more suitable for studying vessels smaller than the aorta, so it is used much less often.
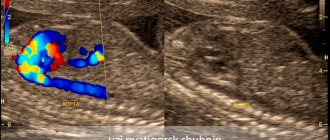
When mapping, technologies are used to color the studied blood flow in two colors. Red is responsible for indicators of the approach of blood elements to the sensitive sensor. The lighter the shade, the higher the speed of movement of the particles under study. And the blue color indicates the direction coming from the sensor.
When using the ultrasound method, you can also use one of two modes to choose from, based on current suspicions:
- B-mode;
- M-mode.
The first variation involves continuous production and reception of waves. Due to such a thorough study of the problem area, it is possible to study the volume on an ongoing basis.
The second approach is non-permanent, which works great if you just want to find the affected area.
Where to do duplex scanning in Moscow
We invite you to undergo research at Diamed. The clinics have original equipment for ultrasound diagnostics. High accuracy of the result is achieved by qualified specialists - we employ doctors of the highest category, candidates of medical sciences. Extensive experience in the field of duplex scanning allows our specialists to record minimal deviations from the norm and diagnose diseases in the early stages.
Based on the results of the study, immediately after the procedure, patients receive a detailed description with comprehensive information about their health status. You will receive all the necessary information and images for a visit to a specialist if health problems are detected. The doctor will recommend you a specialist who will treat you.
What will the transcript of an abdominal ultrasound show?
T.N. Marambey July 24, 2021 Ultrasound examination
First, let's look at what this ultrasound shows.
Behind the anterior wall of the abdomen there is a large space - the abdominal cavity. There are quite a few organs located in it, which an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity will show. This:
- stomach
- intestines
- pancreas
- liver
- bile ducts: intra- and extrahepatic
- spleen
- gallbladder
- kidneys
- adrenal glands
- abdominal part of the aorta and its branches
- lymph nodes
- lymphatic trunks and vessels
- division of the autonomic nervous system
- nerve plexuses.
The abdominal cavity is lined with two layers of a thin membrane - the peritoneum. It is this inflammation that is called peritonitis and is a life-threatening condition. The organs are covered in different ways by the peritoneum: some are wrapped in it, some do not even touch it, but are located within the boundaries outlined by it. Conventionally, the cavity is divided into the abdominal cavity itself and the retroperitoneal space. The latter includes the bottom of the list of organs, starting with the kidneys.
All these organs - both the abdominal cavity and the space behind the peritoneum - are examined during an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. This study can detect the presence of structural damage, inflammation, pathological formations, enlargement or reduction of the organ, and disruption of its blood supply. Ultrasound does not see how a sick or healthy organ copes with its functional responsibilities.
What does ultrasound give? The study helps to find the cause of the disease in such cases:
- pain or discomfort in the abdomen
- bitterness in the mouth
- feeling of a full stomach
- intolerance to fatty foods
- increased formation of gases
- frequent bouts of hiccups
- feeling of heaviness in the right or left hypochondrium
- jaundice
- high blood pressure
- lower back pain
- fever not due to a cold
- weight loss not related to diets
- belly enlargement
- as control over the effectiveness of treatment of pathologies of the digestive system
- and also as a routine examination, including for existing anomalies of organ development, cholelithiasis.
Pathology determined by ultrasound
What does abdominal ultrasound diagnose? Using this study, the following diseases can be identified:
1. From the gallbladder side:
- acute and chronic cholecystitis
- empyema of the bladder
- gallstone pathology
- during a choleretic breakfast, the motor function of the bladder can be assessed
- developmental anomalies (kinks, septa).
2. From the liver:
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- abscesses
- tumors, including metastases
- hepatosis
- "stagnation" in the liver due to cardiopulmonary diseases
- fatty liver change.
3. From the kidneys and urinary system:
- kidney tumors
- "wrinkled bud"
- pyelonephritis
- narrowing of the ureters
- stones and “sand” in the kidneys.
4. From the side of the spleen, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity reveals:
- cysts
- tumors
- abscesses
- heart attacks
- organ enlargement in infectious and parasitic diseases
5. From the pancreas:
- cysts
- tumors
- abscesses
- stones in the ducts
- signs of acute and chronic pancreatitis.
6. Ultrasound reveals free fluid in the abdominal cavity
7. From the abdominal part of the aorta or its branches, an aneurysm and its dissection, vasoconstriction may be visible
8. From the side of the retroperitoneal lymph nodes, their enlargement and homogeneity of structure are visible
How to understand the research results
To do this, consider the ultrasound form (protocol). It indicates points that relate to each organ separately.
Liver
Interpretation of abdominal ultrasound in relation to this organ includes:
| Parameter | What is written on the form | Normal ultrasound findings in adults |
| Dimensions of the entire organ | Normal, decreased, increased (underline as appropriate) | Norm |
| right | The numbers are indicated in cm for each item | Up to 12.5 |
| left | Up to 7 | |
| caudate | 30-35 | |
| Oblique-vertical dimension (OVR) of the right lobe | Numbers in mm | Up to 150 mm |
| Outlines | It is emphasized whether they are even or not | Smooth |
| Capsule | It is emphasized whether it is differentiated or not, thickened or not | Differentiated, not thickened |
| Left lobe thickness | Number in mm | 50-60 |
| Right lobe thickness | 120-125 | |
| Echostructure of parenchyma | Emphasized, normal, increased or decreased | Norm |
| Focal formations | Yes or no | Must not be |
| Portal vein | Size in mm | Up to 14 mm |
| Vascular pattern | Depleted, normal or enhanced | Ordinary |
| Inferior vena cava | Size in mm | Anechoic, diameter 20 mm |
| Hepatic veins of the first order | Size in mm | Up to 1 mm |
Decoding the results
- Fatty hepatosis is indicated by an increase in the echo density of the organ in the form of small foci. The edge of the liver is rounded. In the final stages, due to compaction of the organ, it is impossible to see the portal vessels.
- With cirrhosis of the liver, its enlargement and dilation of the portal and splenic veins are visible. The lower edge of the organ will also be rounded, the contours will be uneven. The increase in echo density in this case will be large-focal. Free fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites) is also determined.
- If an increase in size, rounding of the edges, as well as expansion of the vena cava and the absence of narrowing during inspiration are described, this indicates congestion in the liver due to cardiac or pulmonary disease.
- If lesions are described in which there is a violation of the normal echostructure, this may indicate malignant or benign tumors, cysts or abscesses.
In the video, a specialist talks about errors that occur during ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
Gallbladder
Ultrasound norm based on the results of examination of this organ:
- Shape: various – pear-shaped, cylindrical.
- Dimensions: width 3-5 cm, length 6-10 cm.
- Volume: 30-70 cubic meters cm.
- Walls: up to 4 mm thick.
- Formations in the lumen: normally there are none.
- Acoustic shadow from formations: this applies to stones and bladder tumors. Based on the presence of this shadow, the types of stones are deciphered (they come in different compositions).
- Whether they move or not: the stones are usually movable, but can be soldered to the wall or be large in size. Based on this and some other signs, one can judge whether the formation is a tumor.
Signs of gallbladder pathology
- In acute cholecystitis, thickening of the organ wall is noted, and the dimensions can be normal, reduced or enlarged. The wall may also be described as a "double contour" and the presence of fluid around the bladder indicates that local peritonitis has already developed and urgent surgery is needed.
- Thickening of the wall will also occur with chronic cholecystitis. The contour in this case is clear and dense.
- In conclusion, various deformations of the organ can be described. This is not a disease, but a structural feature.
- If echo-negative objects are described that leave an acoustic shadow, while the wall of the bladder is thickened and the contour is uneven, we are talking about calculous cholecystitis. In this case, the expansion of the bile ducts indicates that the stone is blocking the exit of bile.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the bile ducts
Normally, on ultrasound, the bile ducts have the following characteristics:
- common bile duct: diameter 6-8 mm
- intrahepatic ducts: should not be dilated
Norms of the pancreas on ultrasound
- There should be no additional education.
- head: up to 35 mm
- body: up to 25 mm
- tail: about 30mm
- contour: smooth
- echostructure: homogeneous
- echogenicity: neither reduced nor increased
- Wirsung duct: 1.5-2 mm
- education: normally there are none.
A decrease in the echo density of the gland indicates acute pancreatitis, an increase in it indicates chronic pancreatitis or cancer. The expansion of the Wirsung duct also indicates chronic inflammation. The “favor” of cancer is indicated by a segmental increase in size and unevenness of the contour of the gland, depression on the surface of the liver, as well as displacement or compression of the inferior vena cava or aorta.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the spleen
- Dimensions: length – up to 11 cm, thickness – up to 5 cm, longitudinal section – up to 40 sq. cm
- splenic index: no more than 20 cm2
- structure: normally – homogeneous
- splenic vein at the hilum.
- You can see an increase in the size of the organ. This is associated with both certain blood diseases and liver diseases (such as cirrhosis) or infectious diseases.
- Densified (less often, less dense) tissue indicates a splenic infarction, that is, that as a result of thrombosis or injury, the death of some part of the organ occurred.
- Ultrasound also allows you to see a rupture of the spleen, which usually occurs either with a severe injury or with a minor bruise, but in the case of an enlarged organ.
Ultrasound of hollow organs (stomach, small, large and rectal intestines)
It only indicates whether there is a symptom of an “affected organ” (there should not be one) and whether there is fluid deposition in the intestinal lumen (this should not happen either).
If an ultrasound scan of the kidneys was also performed, then a description of this organ is also included in the conclusion of the study. The results of an ultrasound examination of the kidneys are normal:
- width: 5-6 cm
- length – about 11 cm
- organ thickness: 4-5 cm
- kidney parenchyma - no more than 23 mm thick
- the pelvis should not be dilated
- There should be no structures in the lumen of the pelvis and ureters.
Lymphatic structures with ultrasound imaging
Ultrasound of the retroperitoneal lymph nodes normally suggests the following conclusion: “Lymph nodes are not visualized.” That is, if they are of normal size, ultrasound “does not see” them. An increase in these immune organs indicates either an infectious disease present in the abdominal cavity or a malignant formation. In the latter case, they can increase due to the fact that cancer cells of the hematopoietic system “live” in them, as well as with metastases of any nearby organ tumor.
Sonologist's conclusions
At the conclusion of the ultrasound, the sonologist (ultrasound doctor) indicates the presence of pathology: he describes what the echo signs look like. If in the referral the doctor indicates that it is necessary to conduct an examination for some disease, but the ultrasound did not visualize it (for example, calculous cholecystitis), then there may be the phrase “Echo signs of the disease were not identified.” The final diagnosis is made only by the doctor who refers you for examination.
Who needs to undergo Doppler ultrasound of the abdominal vessels
This examination, which is also called Doppler ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound) of the abdominal vessels, is often performed together with ultrasound. The patient's sensations are not differentiated and are not more harmful than ultrasound. It allows you to evaluate the anatomy and characteristics of blood circulation in vessels such as:
- abdominal aorta
- common hepatic artery
- iliac arteries
- celiac trunk
- splenic artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- portal vein of the liver and its branches
- inferior vena cava.
Ultrasound of the vessels of the abdominal cavity makes it possible to timely identify early abnormalities in the vessels, identify and evaluate the degree of increase in pressure in the portal vein (with cirrhosis, “congestive” liver), and evaluate the result of implantation of a vena cava filter.
Ultrasound of the abdominal aorta and its branches helps in the diagnosis of:
- fainting states
- frequent headaches
- epileptic seizures
- high blood pressure
- repeated strokes (sometimes blood clots can “fly off” from this large vessel)
- leg pain
- potency disorders
- aortic aneurysm
- atherosclerotic lesions
- vasoconstriction
- anomalies in the development of large vessels.
Duplex scanning
Vascular examination during ultrasound using modern equipment almost always includes duplex angioscanning. This is the “gold standard” in assessing blood circulation in the venous vessels. It allows you to identify pathological blood flow, obstructions to blood flow, assess their location, extent and severity.
With this type of study, the sonologist receives a color two-dimensional image of the abdominal vessels, where red indicates the movement of blood towards the sensor, and blue, on the contrary, away from the sensor. Based on the intensity of the red and blue colors, the doctor draws conclusions about the speed of blood flow in any part of the vascular system.
Additional Study Details
Reviews about ultrasound are mostly positive: the study is painless, harmless, and very informative. The negative point is that before the procedure you need to carefully prepare so that gases in the intestines (“flatulence phenomena”) do not interfere with the correct diagnosis.
How much does it cost to conduct this research? A complete examination of all organs (including the kidneys and urinary system) with duplex angioscanning is estimated by clinics at an average of 2000-2500 rubles. An examination of individual organs with an assessment of the blood flow in them costs about 800-1000 rubles.
Thus, interpretation of abdominal ultrasound should be carried out by a specialist, taking into account not only the “norm” numbers, but also based on clinical manifestations. The above values will help you understand a little about the pathology identified in you, but the final assessment should be given by a specialist therapist or gastroenterologist.
We also looked here: ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, interpretation is normal, they don’t see fluid on ultrasound, form for ultrasound of gastrointestinal organs, splenic vein is normal in adults
← All articles
Indications for the procedure
The main indication for ultrasound of the abdominal aorta is considered to be an aneurysm - a local protrusion of the aortic wall in the abdominal region. The condition is considered urgent and requires removal of the aneurysmal sac with the installation of a synthetic prosthesis or endoprosthetics. An ultrasound of the abdominal aorta is recommended if the following complaints and symptoms appear:
- periodic or constant throbbing pain on the left or around the navel, which radiates to the lower back, groin or legs;
- pain in the lower extremities and lameness;
- frequent headaches and dizziness, pulsation in the back of the head and temples;
- persistent increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- “floaters” in the eyes when turning the head;
- feelings of heaviness and fullness in the stomach;
- nausea, belching and vomiting;
- bloating;
- tendency to constipation.
Preparatory process
To prepare for the scan, you simply need to exclude factors that may blur the clinical picture. This includes pharmacological drugs that are designed to help during the course of treatment:
- hypertension;
- heart block;
- angina pectoris.
But only the doctor should note the medicine, since sometimes it is easier to postpone the procedure by a couple of days than to interrupt a pre-agreed therapeutic program in the middle of treatment.
It is also worth holding off on drinking coffee, which can affect your blood pressure.
The procedure begins with the patient being placed on a couch with a cushion placed under his head. Next, the doctor lubricates the sensor with gel, which is designed to improve the conductivity of incoming ultrasonic waves through the subcutaneous fat layer.
The doctor will have to visually assess the area under study in order to correctly distribute the ascending and descending parts, as well as the arc and extensions in the thoracic region. The calculation is made based on the fact that the arc has three branches:
- brachiocephalic trunk, located on the right;
- common carotid artery;
- left subclavian artery.
Using the anatomical principle of zone separation, the condition of the vascular network is assessed using a transducer sensor. To get a clearer picture, the expert can switch examination modes.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
Structural subdivision of Polikarpov Alley Polikarpov 6k2 Primorsky district
- Pionerskaya
- Specific
- Commandant's
Structural subdivision of Zhukov Marshal Zhukov Ave. 28k2 Kirovsky district
- Avtovo
- Avenue of Veterans
- Leninsky Prospekt
Structural subdivision Devyatkino Okhtinskaya alley 18 Vsevolozhsk district
- Devyatkino
- Civil Prospect
- Academic
For detailed information and to make an appointment, you can call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
Dopplerography (duplex, ultrasound, Doppler) of the abdominal vessels is usually recommended by a doctor. Examination of the vessels from the inside and the blood flow in them is necessary for a specialist to diagnose the pathology of internal organs:
- Liver (cirrhosis, hepatitis, tumors);
- Spleen (blood diseases);
- Gallbladder (congenital malformations, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, neoplasms, polyps).
More information about the Doppler method
Doppler of abdominal vessels includes examination of the abdominal aorta and its branches, iliac arteries, celiac trunk, common hepatic and splenic arteries, superior mesenteric artery, inferior vena cava, portal venous system.
The specialist evaluates each of these vessels according to their diameter and patency, the condition of the valves, the thickness of the walls of the arteries and veins, and the compliance of these indicators with the norm.
Important! Duplex of abdominal vessels shows their condition in real time!
Using ultrasound, the doctor measures the parameters of blood flow and its changes and difficulties: narrowing of the lumens, spasms, the presence of blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques and their sizes.
What influences the success of the procedure?
In addition to the quality of the equipment and the professionalism of the specialist who conducts the study, there are several other important factors that can affect the possibility of high-quality visualization.
First of all, this concerns a person’s body weight. Flatulence and shortness of breath may also affect the results. Therefore, it is extremely important to properly prepare for this study.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons:
Possibilities of abdominal ultrasound
- Assessment of the condition, speed and direction of blood flow in the veins and arteries of the abdominal cavity;
- Detection of early vascular changes (thrombosis, stenosis - that is, narrowing of the arteries);
- Diagnosis of aneurysms;
- Pathologies of the diaphragm;
- Increased pressure in the portal vein;
- Evaluation of the results of therapy and implantation;
- Determination of indications for surgery;
- Detection of blood supply disorders to the abdominal organs.
In addition, vascular duplex is prescribed if it is impossible to determine changes in internal organs using standard ultrasound diagnostics; to confirm the diagnosis (for example, vascular ischemia of the gastrointestinal tract).
Doppler ultrasound is an important diagnostic procedure for assessing the effectiveness of collateral (roundabout) blood flow, which sometimes occurs when the main arteries are blocked.