Detailed description of the study
Triglycerides are simple fats (lipids) that provide energy to cells during fasting or intense physical activity. An increase in their level in the blood is one of the reasons for the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver, and pancreas.
Triglycerides come from foods or are formed in the liver and fat cells. Those that come with food are absorbed in the small intestine and, as part of large transport molecules (chylomicrons), are transported through the lymphatic vessels into the plasma.
Triglycerides are used by muscles and other tissues as an energy substrate. Some is stored in adipose tissue, the other is in the plasma, mainly in combination with proteins - a complex called very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) is formed. The amount of triglycerides changes throughout the day. It rises in the blood half an hour to an hour after eating due to the formation of chylomicrons.
With excess nutrition, there is an increased formation of fatty acids by fat cells, and they accumulate in the liver. This leads to increased formation of triglycerides, which are released into the blood as part of VLDL.
Errors in nutrition are the main cause of lipid metabolism disorders. Excessive consumption of saturated and trans fats (butter, fatty meats, confectionery), alcohol, and simple sugars increase the content of triglycerides in the blood.
Determining the amount of triglycerides helps to identify primary and secondary disorders of lipid metabolism (hypertriglycemia). Such conditions increase the risk of diseases of the heart and blood vessels, as well as the liver and pancreas, so timely diagnosis helps to take preventative measures.
Primary hypertriglyceridemias are hereditary diseases. They are very rare and are associated with a genetically determined disruption of the enzymes that are involved in lipid metabolism. This leads to the accumulation of chylomicrons in the blood.
Secondary ones arise against the background of other diseases - diabetes mellitus, disorders of the thyroid gland, kidneys. Due to an imbalance of lipids, fatty plaques begin to be deposited in the walls of blood vessels, and atherosclerosis develops. Atherosclerotic plaques cause narrowing and blockage of blood vessels, which leads to thrombosis, strokes, and heart attacks. In the liver and pancreas, against the background of hypertriglyceridemia, fat deposits are detected, which can impair the function of the organ and lead to the development of hepatitis and pancreatitis.
Factors such as lack of exercise, excess weight, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to an increase in the amount of triglycerides in the blood plasma.
Measuring triglyceride levels is an important test in the diagnosis of pathology of the heart and blood vessels, liver and pancreas. Timely detection of triglyceride metabolism disorders along with other indicators of lipid metabolism helps prevent many diseases.
Features of hypertriglyceridemia in men
The level of triglycerides in men increases with age. Due to the higher content of cholesterol and TG, men more often than women suffer from early coronary heart disease, brain disease, strokes, and myocardial infarction.
Elevated triglycerides in men of all ages are most often a consequence of poor nutrition and bad habits. Other common causes are diabetes, previous myocardial infarction, and kidney disease. Older men with gout have high TG levels.
References
- Diagnosis and correction of lipid metabolism disorders for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis. Eurasian Association of Cardiologists National Society for the Study of Atherosclerosis (NOA), 2020. - 61 p.
- Alves-Bezerra, M., Cohen, D. Triglyceride metabolism in the liver, 2021. - Vol. 8(1). — P. 1-8.
- ESC/EOA recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of dyslipidemia, 2016. - 71 p.
- Ershova, A.I., Ivanova, A.A., Aksenova Yu.O. and others. Secondary hyperlipidemia: etiology and pathogenesis, 2021. - 113 p.
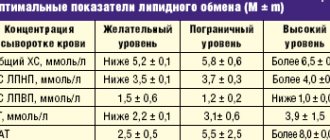
Normal levels of triglycerides in the blood of women and men
| Patient age | |
| Under ten years old | M 0.340 - 1.130 |
| F 0.40 - 1.240 | |
| From ten to fifteen years | M 0.360 - 1.410 |
| F 0.420-1.480 | |
| About fifteen to twenty years old | M 0.420 - 1.670 |
| F 0.440 - 1.40 | |
| Twenty to twenty-five years old | M 0.50 - 2.270 |
| F 0.410 - 1.480 | |
| Twenty-five to thirty years old | M 0.520 - 2.810 |
| F 0.420 - 1.630 | |
| Thirty to thirty-five years old | M 0.560 - 3.010 |
| F 0.440 - 1.70 | |
| From thirty-five to forty years old | M 0.610 - 3.620 |
| F 0.450 - 1.990 | |
| Forty to forty-five years old | M 0.620 - 3.610 |
| F 0.510 - 2.160 | |
| Forty-five to fifty years old | M 0.650 - 3.70 |
| F 0.520 - 2.420 | |
| Fifty to fifty-five years old | M 0.650 - 3.610 |
| F 0.590 - 2.630 | |
| Fifty-five to sixty years old | M 0.650 - 3.230 |
| F 0.620 -2.960 | |
| From sixty to sixty-five years old | M 0.650 - 3.290 |
| F 0.630 - 2.70 | |
| From sixty-five years old | M 0.620-2.940 |
| F 0.680 - 2.710 |
It should be noted that the norm of triglycerides in the blood of women after 50 years increases and approaches the “male norm” due to the onset of menopause and changes in hormonal levels.
- Reactive arthritis in a child, have you ever encountered this?
Why might their level be increased?
Short-term deviations from the norm of approximately 0.2 - 0.3 mmol/l are not something critical. This most often occurs after a heavy snack with a lot of fatty foods.
But within 1–2 hours, the body independently normalizes the balance of tringlycerides in the blood, activating the processes of their breakdown into energy.
Why do triglycerides increase? There can be many reasons, but the most common among them are:
- non-compliance with a healthy diet (abuse of fatty, sweet, and alcohol);
- problems with the functioning of the endocrine system (imbalance of hormones responsible for regulating metabolism);
- taking certain medications (directly affecting the functioning of the hormonal system).
Elevated triglyceride levels can also occur during pregnancy. This is not a deviation, it is not dangerous, but it is advisable to periodically consult a doctor on this matter to monitor the condition of the pregnant woman herself and her unborn child.
Conclusion
You can lower your triglyceride levels by changing your diet, maintaining a moderate weight, and exercising regularly.
You should also avoid refined carbohydrates, added sugars and saturated fats. Replacing them with low-sugar fruits and vegetables, whole grains and fatty fish can reduce triglyceride levels and the risk of obesity and cardiovascular disease.
It is important for the doctor to decide whether this approach is enough to make a difference or whether medications will be necessary. You should definitely contact your doctor to find out which approach is most appropriate.
Other Triglyceride Lowering Options
In addition to dietary changes, your doctor may also recommend the following to lower triglyceride levels:
- Physical Activity: The AHA recommends at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity at least 5 days per week for a total of at least 150 minutes per week.
- Achieving a moderate weight: According to the AHA, losing 5 to 10% weight results in a 20% reduction in triglyceride levels.
- Taking omega-3 fatty acids : Research suggests that omega-3s may prevent and treat hypertriglyceridemia.
- Taking niacin: Studies have shown that niacin, also known as niacin, may help lower triglyceride levels.
- Taking fibrates: Evidence also suggests that fibrates are effective in lowering triglyceride levels.
Choose your drinks carefully
Drink water instead of sweetened drinks. Even bottled juices can be high in sugar. Beverages often contribute significantly to total carbohydrate and sugar intake. Fruit drinks, soft drinks, and other sugar-sweetened beverages are among the major sources of added sugars in the diet.
Alcohol also has a direct effect on triglyceride levels in some people. People seeking to lower triglyceride levels should avoid drinking alcohol. Avoiding drinks containing added sugar can significantly reduce your overall calorie intake. Instead of high-sugar drinks, people can choose low-calorie drinks such as water or tea. On a hot day, instead of reaching for a cold drink, try adding some fruit juice to a glass of sparkling water.
Drugs that increase triglyceride levels
Some medications increase triglyceride levels. According to a study conducted in 2021, these include:
- oral estrogens
- corticosteroids
- retinoic acid derivatives
- beta blockers
- thiazide diuretics
- protease inhibitors
- bile acid sequestrants
- antipsychotic drugs
- cyclosporine and tacrolimus
- L-asparaginase
- interferon alpha-2b
- cyclophosphamide
You should not stop taking the drug without talking to your doctor first, as this may be dangerous. If you have concerns about the side effects of this medicine, you should seek professional medical advice.
4.What are the risks and what could interfere with the analysis?
What are the risks of testing for triglycerides and cholesterol?
Possible risks of blood testing for cholesterol and triglycerides may only be associated with the blood collection itself. In particular, the appearance of bruises at the puncture site and inflammation of the vein (phlebitis). Warm compresses several times a day will relieve phlebitis. If you are taking blood thinning medications, you may bleed at the puncture site.
What can interfere with the analysis of cholesterol and triglycerides?
Testing for cholesterol and triglycerides may be interfered with by:
- Taking medications such as diuretics, corticosteroids, androgens, tranquilizers, estrogens, contraceptives, antibiotics, vitamin B3;
- Physical overload – infection, previous surgery, heart attack;
- Eating 9-12 hours before the test;
- Diseases such as hypothyroidism, diabetes, liver and kidney diseases;
- Abuse of alcohol or drugs, or sudden cessation of their use;
- Pregnancy.
Examples of Triglyceride Lowering Products
The AHA recommends focusing on certain foods to help manage triglyceride levels. Foods that may help lower triglyceride levels include:
- Low fructose vegetables: These include leafy greens, squash, pumpkin, green beans and eggplant.
- Low fructose fruits: such as berries, kiwis and citrus fruits.
- Fiber-rich whole grains: brown rice, whole grain bread, quinoa, oats, barley and buckwheat.
- Fatty fish : salmon, herring and sardines.
- Low-fat dairy products: These include milk, yogurt and cheese.
Additionally, the AHA advises:
- limit added sugar to no more than 10% of total daily calories
- limit carbohydrate intake to 50–60% of daily calories
- keep the fat content in the diet to 25–35% of the total diet
- reduce or avoid alcohol intake
Lower triglycerides and a new diet!
In order to reduce high triglycerides in the blood, it is extremely important to bring order to your diet. What does this look like in practice? First of all, you will definitely have to develop your own culinary skills, since you will have to give up some “store-bought” food products - temporarily, while others - forever! And also add new dishes that are very healthy for the body, but “NOT profitable” for mass sales. So, what can and cannot be eaten if you have high triglycerides? Which foods should you add to your diet and which should you exclude? Let's start with the last one.
Eliminate refined sugar!
In order to lower triglycerides in the blood, first of all, give up “sweets”. Especially “store-bought” ones, which contain an impressive amount of ingredients aimed not at human health, but at increasing shelf life. And that means the sales period. Despite the fact that sugar, as one of the main components for making sweets, tastes very pleasant, it is one of the representatives of “toxic food”.
Especially refined sugar, i.e. industrial/processed, having as many as 5 carbohydrate atoms in its structure. “Thanks to” this circumstance, along with this “wrong” sugar (absolutely devoid of minerals, vitamins and other useful substances), our body receives many “empty” calories, which are converted into excess triglycerides. Quickly accumulates and is difficult to remove from the body.
Thus, if you have high triglyceride levels (in order to reduce it - quickly and effectively) say to “sweets”: a firm NO! And the next time you go to the store, pay special attention to all products that contain ingredients (on the labels) that end in “OSA”. This includes sucrose (the above/mentioned “disguised” refined sugar), as well as fructose (natural/natural/“proper” sugar), lactose, maltose and dextrose.
After reducing the level of triglycerides to adequate values, your daily intake of “right” sugars (it is better to avoid “wrong” sugars forever) should not exceed 5-10% of the total calories. That is, approximately, no more than 100 kcal in “sweets” for women and 150 kcal for men. No more than 100-150 gr. (per day) mangoes, grapes, blackberries, bananas, pineapples, overripe watermelons and pears. Recommended gifts of nature (for people with “problematic” triglycerides) are tomatoes, citrus fruits, strawberries, avocados, melon and apricots.
Reducing the amount of carbohydrates!
To lower triglycerides (towards normal), you need to reduce the consumption of foods high in carbohydrates (especially refined ones). Their most striking representatives are baked goods baked from premium white flour (i.e., the beloved white bread). Although, sometimes, even white rice or semolina porridge can also increase the level of TG in the blood (or negatively affect their normalized amount). Be sure to consult your doctors!
WE RECOMMEND YOU TO READ:
foods that increase fat (lipid) levels
What is the right thing to do? First of all, replace white bread with gray bread (made from rye flour / coarsely ground) if you do not have problems with high acidity. If you have them, then eat pasta! Next, by reducing (or eliminating) “carbohydrate” foods, increase or completely replace them with “protein” foods! Having a lower glycemic index, which means they are more slowly digested, absorbed and “metabolized” by our body! This results in minimal and slower increases in lipid (including triglycerides) and blood sugar levels. LEAN ON THE SQUIRRELS!
YOU MAY NEED:
table - what you can and cannot eat with high lipid levels
We take strict control of fats!
The next step to quickly and effectively lower triglyceride levels is to control the “names” and amount of fats you eat daily. It would seem that “fat is fat in Africa too.” But no! Again, in pursuit of profits, some companies use trans fats to make their products (margarine, spreads, hydrogenated vegetable oils, etc.). Thanks to which, goods can be stored for a long time and not lose their shape and taste even with temperature changes (which is very important during long-distance transportation of products to points of sale).
In addition, margarine or sandwich spreads are much cheaper than natural butter. And the taste is almost the same. Which suited both producers and consumers for a couple of decades. Until scientists found out that these ingredients (i.e., hydrogenated fats and oils) - both in their pure form (on a sandwich), as well as in everyone’s favorite fast food or donuts - literally kill the body. Not only by record-breaking levels of “bad” cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, but also by increasing the risks of a number of cancers.
That is why, completely give up all foods containing trans fats, without returning to them even when your (fat) lipid levels are completely normalized. However, never categorize absolutely all fats with the same brush. Because some of them are very important for our health. They are called: MONO- or POLY-UNsaturated fats. The first one is olive oil! Popular examples of others are sunflower oil, flaxseed oil, fish oil and walnut oil.
Separately, it is worth highlighting fish oil, rich in OMEGA-3 fatty acids. At their core, these are “good” fats that are capable of “knocking out” “bad” fats from our bodies. Thus, if you eat fatty fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel or alkabor tuna) twice a week, you will very quickly notice how quickly your triglyceride levels have decreased. Very good results are noticeable after about 10-12 weeks. If you are allergic to fish, then an alternative option on the menu is salads made from mixed greens (particularly leafy vegetables) with the addition of flaxseed oil and chopped walnuts. The latter also contain PUFAs, i.e. polyunsaturated OMEGA 3 fatty acids.
Fatty fish, walnuts, flax seeds and avocados not only reduce triglycerides, but also reduce the risk of breast cancer (in women).
Add more fiber to your diet
BE SURE to include foods containing (in large quantities) fiber in your menu. Those. coarse water-soluble and insoluble dietary fiber. As for the latter, due to their ability to perfectly absorb liquids, they turn into a kind of gel/shaped mass, which not only cleanses the intestines of toxins, but also “sculpts” fats onto itself. Thus, reducing the amount of “extra” lipids (including triglycerides) in our body.
In addition, fiber normalizes intestinal function (minimizing putrefactive processes, thereby saving us from cancer), and also acts as a “regulator” of blood sugar and cholesterol levels. As for the last advantage, water-soluble dietary fiber is responsible for this. The best option: use both. Daily fiber intake for men and women: 35-50 g. Just drink more water!
The champions in fiber content are wheat bran (43 g/100 g of product). Next come: dried apricots (18 g/100 g), dried apples (14.9 g/100 g), raisins (9.6 g/100 g), gray bread (8 g/100 g), nuts (4.0 g/100 g). Other recommended foods (to reduce excess triglycerides) are beans, cabbage, carrots, beets, tomatoes, peas, apricots, boiled pasta, greens (dill, parsley, lettuce). And also buckwheat, oatmeal and pearl barley porridge - DAILY! Another significant benefit of fiber is that it makes you feel full. And this is important when you have to heroically give up some bread/bakery products.
What about meat?!
To normalize high triglyceride levels, completely avoid meat by-products (i.e., internal organs of animals and birds), except for beef liver (up to 80 grams per week). And temporarily replace “red” meat with “white” / poultry / EXCEPT duck and goose (only without the skin). If the situation improves (in consultation with your doctors), add ONLY lean beef, veal or lamb to your diet. Naturally, you will have to forget about pork, lard, bacon, salts, smoked sausages and other (supposedly) “delights” of life for a very long time! And this is for the better!