Reasons for increased and decreased indicators
If there is a significant deviation from the TG norms, this indicates metabolic disorders and the development of diseases of various types. Increased content may have the following reasons:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (ischemia, hypertension, atherosclerosis);
- disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system;
- gout;
- decreased thyroid function;
- obesity, chronic alcoholism;
- increased sugar levels;
- glucose absorption disorders;
- renal failure.
Systematically elevated TG levels (without proper treatment) can be fraught with the development of diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, and myocardial infarction. In such a situation, cholesterol and blood sugar should also be controlled.
Elevated levels of triglycerides in the blood can trigger the development of diabetes.
Low values are less common. When studies have confirmed reduced levels, the following pathologies can be suspected:
- chronic forms of lung diseases;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- poor nutrition;
- damage to kidney tissue;
- myasthenia gravis;
- ischemic stroke.
If abnormal triglyceride levels are detected during testing, action should be taken as soon as possible. If left untreated, the situation can get out of control.
What does high and low fat mean?
When a person's triglycerides are elevated, it is a sign of many serious illnesses and health problems. The main reasons that contribute to the growth of lipids are the use of medications with a high content of hormones. These could be oral contraceptives, drugs to restore hormonal levels, pregnancy, menopause and adolescence. These reasons are not clinical, i.e. such an increase in triglycerides is justified by their intake from the outside.
If all these factors are absent, then the reasons for high lipid levels should be sought in disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
These include:
- high blood pressure (hypertension);
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels (heart attack, ischemia, etc.);
- atherosclerosis;
- cerebral thrombosis;
- viral hepatitis;
- overweight or anorexia.
Also, triglycerides can increase with genetic abnormalities, excess calcium, diseases of the endocrine system, pancreatitis of various forms and in people suffering from alcoholism. Low levels are observed with poor nutrition, vitamin deficiency, excess vitamin C, chronic diseases of the pulmonary system, hyperthyroidism and necrosis of renal tissue. Lipid levels also drop in people who have suffered severe injuries or burns.
Lipids
Triglycerides and cholesterol are members of the fat family (also called lipids) but have different functions. Cholesterol is a fat-like substance that is used by the body to produce hormones, vitamin D, and is part of the membrane surrounding cells. Cholesterol is similar to wax and has no odor. The liver produces it from animal products.
Cholesterol and triglycerides in their pure forms cannot mix with the blood. As a result, the liver sends them bundled with proteins called lipoproteins. Lipoproteins move cholesterol and triglycerides throughout the body through the bloodstream ().
There are three types of lipoproteins. These are low-density lipoproteins (LDL), very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL). LDL, also called LDL cholesterol, is considered the “bad” kind of lipoprotein because it contributes to the buildup of plaque in the arteries. HDL cholesterol is considered "good" cholesterol because it removes LDL from the arteries ().
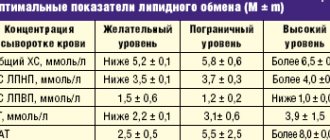
Triglycerides are normal in women (table by age)
We bring to your attention a table: the norms of triglycerides (TAG / TG) in the blood of women (by age) / in girls and young women (i.e. in small children or adolescents). Units of measurement: mmol/l and mg/dl.
- Blood cholesterol levels - table by age. Cholesterol in the blood - norms for women, men and children
| AGE | (mmol/L) | (MG/DL) |
| up to 10 years | 0.41 – 1.25 | 36.3 – 110.6 |
| 10-15 | 0.42 – 1.49 | 37.2 – 131.9 |
| 15-20 | 0.41 – 1.54 | 36.3 – 136.3 |
| 20-25 | 0.42 – 1.49 | 37.2 – 131.9 |
| 25-30 | 0.43 – 1.64 | 38.0 – 145.1 |
| 30-35 | 0.45 – 1.71 | 39.8 – 151.3 |
| 35-40 | 0.46 – 2.00 | 40.7 – 177.0 |
| 40-45 | 0.52 – 2.17 | 46.0 – 192.0 |
| 45-50 | 0.53 – 2.43 | 46.9 – 215.0 |
| 50-55 | 0.60 – 2.64 | 53.1 – 233.6 |
| 55-60 | 0.63 – 2.97 | 55.7 – 262.8 |
| 60-65 | 0.64 – 2.71 | 56.6 – 239.8 |
| 65-70 years | 0.69 – 2.72 | 61.0 – 240.7 |
How to take the test correctly
To determine triglycerides, blood is taken from a vein. Before the analysis, preparation is prescribed:
- 3-5 days in advance, it is necessary to agree with the doctor on the possibility of using medications: diuretics, hormonals (including contraceptives), hypoglycemic drugs based on metformin, anti-cholesterol drugs;
- within 24 hours, give up alcohol, overeating, severe dietary restrictions, physical and emotional overload;
- 12 hours in advance you cannot eat, drink juices, sweet drinks, or smoke.
If the timing of meals is disrupted (the patient had breakfast in the morning or drank tea with sugar), then triglycerides can increase 6-8 times compared to the norm. It is also very important to take into account daily fluctuations in blood lipids. It is necessary to donate blood in the morning and to accurately confirm the results at least twice.
Expert opinion Alena ArikoExpert in the field of cardiology Over the course of a month, there may be changes in the concentration of blood fats within 25-45%, down or up. This is called biological variation and reduces the diagnostic value of a single test.
Effective ways to lower triglycerides
A high level of TG in the blood is not a reason to panic. If you start treatment in time, the situation can be corrected. There are several main ways:
- nutrition adjustments;
- playing sports;
- taking medications.
Sometimes one component is enough. Most often, diet and exercise are used together. If these methods do not give the desired effect, medications are added.
Proper nutrition
By changing your attitude towards food, you can improve your body’s health and reduce the risk of developing most diseases. To do this, you need to focus on the right products. Be sure to include fish and other seafood in your menu. They are enriched with healthy proteins and amino acids. Salmon, shellfish, crabs, and oysters are suitable.
According to research from the University of Oregon, daily consumption of such foods reduces TG levels in the blood by 50%.
It will be useful to enrich your diet with dried beans and garlic.
To achieve lasting results, you will have to exclude the following:
- sweets (sugar, cakes, pastries, baked goods);
- fatty meat, lard;
- semi-finished products (sausages, frankfurters, sausages);
- sweet juices, soda;
- alcoholic drinks.
Products to avoid - gallery
Alcohol
Carbonated drinks Sweets and flour products Convenience foods Fatty meats
Physical activity
Physical activity reduces fat mass and normalizes TG levels. Take every opportunity - walk a few stops, take the stairs instead of the elevator, do exercises while watching TV. Ride a bike, go for a run. The main thing in the approach is regularity.
- Increased blood triglycerides in women and men
Taking medications
Sometimes it is not possible to avoid taking pharmacological drugs. This is especially true for patients in the older age group and people with a high degree of obesity. The following means are used:
- Fish fat. Contains fatty acids (Omega-3) in sufficient quantities. Effectively normalizes TG levels.
- A nicotinic acid. Reduces the production of dense lipoproteins by the liver.
- Fibrates. Organic compounds that attract and remove fat molecules.
- Satins. More used to lower cholesterol levels. The process of reducing triglyceride concentrations is also affected.