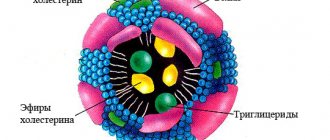
Cholesterol is an organic compound found in cell membranes. Necessary for cell construction, synthesis of sex hormones, bile acids, and nutrient metabolism. It plays an important role in the human body, but sometimes causes significant harm.
There are two types of cholesterol in the blood: “good” (HDL) and “bad” (LDL). An increase in the concentration of the latter becomes the main cause of the formation of plaques in blood vessels, resulting in an increased risk of stroke and heart attack. High cholesterol levels are dangerous to health, so they need to be reduced. The most effective methods will be discussed in the article.
What causes cholesterol to rise?
Up to 80% of total cholesterol is synthesized by the human body from fats and only 20% comes to us with food. Moreover, this organic substance is contained exclusively in products of animal origin.
Until recently, it was the abuse of animal fats that was considered the main cause of high cholesterol, but as it turns out, this is not an entirely correct assumption. There are no high or low density lipoproteins in food; they become so during processing in our body. Therefore, metabolic disorders, endocrine diseases, diseases of the liver, intestines and adrenal glands are the main causes of high cholesterol.
At risk of increased LDL and early development of atherosclerosis are:
- patients with diabetes mellitus, obesity;
- people with endocrine diseases, for example, hypothyroidism, deficiency of sex hormones;
- women over 50 years of age, as well as men over 35 years of age;
- people with bad habits;
- patients with diseases of the kidneys, liver, pancreas;
- patients with a hereditary predisposition;
- women who have been taking hormonal medications for a long time.
People at risk should definitely undergo a blood cholesterol test. Because they are susceptible to heart and vascular diseases.
The risk of high blood cholesterol increases with predisposing factors. These include a sedentary lifestyle, bad habits, overeating, an abundance of unhealthy and fatty foods, deficiency of vitamin D, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the diet.
High cholesterol in women is more often due to excess weight or low estrogen levels. Typically, this problem occurs during menopause. High cholesterol in men occurs at a younger age, after 35 years. The reason for this is bad habits and poor nutrition.
Results
HDL and LDL are the most important participants in cholesterol metabolism, the amount of which in the blood must meet certain standards. Low-density lipoproteins supply the body's cells with cholesterol, which is produced by the liver. High-density lipoproteins cleanse blood vessels of excess fat, preventing the development of atherosclerosis.
Dyslipidemia, otherwise an imbalance of LDL and HDL, accompanies a number of chronic diseases or is a consequence of unhealthy eating behavior, bad habits, and physical inactivity. You can check your fat metabolism levels by donating blood for a special test - a lipid profile.
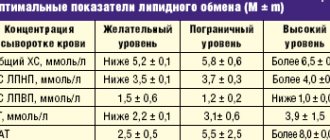
Normal cholesterol levels
On average, a healthy person contains about 2 g of cholesterol per 1 kg of body weight. If we talk about laboratory standards, then this is 3.6-7.8 mmol/l. However, when deciphering the results, it is important to understand what kind of cholesterol we are talking about. There are the following varieties:
- HDL – high-density lipoproteins, “good” cholesterol, which utilizes excess “bad” cholesterol;
- LDL - low-density lipoproteins, the main carriers of cholesterol in the blood, have a second name - “bad” cholesterol;
- VLDL are very low density lipoproteins that transport endogenous lipids.
A high level of the last two types is a predisposing factor for the development of atherosclerosis.
What cholesterol is considered high? Any (general, “good” or “bad”), if its concentration is above 5 mmol/l. If previously there were no limits for HDL, now scientists have come to the conclusion that its optimal level for men is 1.9 mmol/l, for women – 2.4 mmol/l. It is important that its concentration does not fall below 1.5 mmol/l, as this will cause an increase in LDL cholesterol.
If the level of “bad” cholesterol is within 5-6 mmol/l, then it is moderately elevated. If it reaches 7 mmol/l or more, it is life-threatening.
Studies have confirmed that extremely high cholesterol in men increases the risk of premature death by 106%. For women, this figure will be 68%. But the situation is no better in the case of extremely low HDL levels. An excessive decrease in “good” cholesterol also adversely affects health and increases the likelihood of early mortality.
What are HDL and LDL in cholesterol metabolism?
Cholesterol refers to fat-containing alcohols. The substance is concentrated in cell membranes and serves to protect cells. The body needs cholesterol as a participant in the most important processes that support life:
- hormonal synthesis (steroid and sex hormones);
- production of bile acids;
- absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, D);
- maintaining pregnancy;
- interaction between the spinal cord and brain.
Cholesterol is divided into two types: exogenous, entering the body with animal fats (butter, meat, milk, etc.); endogenous, produced by liver cells (hepatocytes) inside the body.
Reference: The share of exogenous cholesterol is 20% of the total amount.
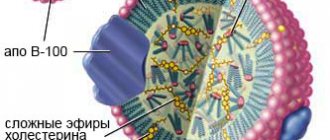
Cholesterol, like fat, cannot move through the bloodstream on its own. Once in the blood, its molecules combine with apoprotein proteins and other lipids (triglycerides, phospholipids), forming courier lipoproteins of different densities. The less protein there is in lipoproteins, the lower their density.
20% of cholesterol enters the body with food, and 80% is produced by liver cells
Triglycerides (TG or TG) are formed from fatty foods and are stored in fatty tissues. Essentially, this is the body's lipid reserves, used to replenish energy. Phospholipids are a special type of fat that is not synthesized by the body; they consist of fatty acids, polyhydric alcohols and phosphoric acid and are necessary for the construction of cell membranes.
Types of lipoproteins
Five main types of lipoproteins are involved in cholesterol metabolism.
Accepted classification of lipoproteins and main functions
| Full title | Function | Abbreviation | The average size | |
| Latin | Russian | |||
| low density lipoproteins | transport endogenous cholesterol from the liver to peripheral tissues and cells of the body | LDL | LDL | 18-26 nm |
| very low density lipoproteins | VLDL | VLDL | 30-80 nm | |
| lipoproteins of average (otherwise, intermediate) density | BOB | 25-35 nm | ||
| high density lipoproteins | collects excess LDL and VLDL and delivers them to the liver for excretion | HDL | HDL | 8-11 nm |
| chylomicrons | transport exogenous cholesterol from the intestines to the liver and body tissues | HM | 75-1200 nm | |
LDL and VLDL are positioned as “bad” cholesterol. When moving through arteries and capillaries, they “cling” to microdamages in the intima (the inner layer of the vascular wall) and settle.
A cholesterol stain forms inside the vessel, on the basis of which a cholesterol plaque is subsequently formed, which becomes the cause of atherosclerosis. HDL is called “good” cholesterol because it escorts low-density and very low-density lipoproteins out of blood vessels, preventing them from sticking to the intima.
Components of lipoproteins in percentage
The table shows that chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins contain the most fat (triglycerides).
Complications from high cholesterol
High cholesterol is dangerous because it increases the likelihood of developing the following diseases:
- atherosclerosis – accompanied by the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, decreased elasticity of vessel walls, and narrowing of the arteries;
- coronary heart disease – accompanied by narrowing of the coronary artery, which causes myocardial hypoxia and disrupts its functioning;
- hypertension - manifests itself as high blood pressure, against the background of which stroke, heart attack, heart failure and other serious complications are likely;
- stroke - an acute disorder of cerebral circulation as a result of blockage or rupture of a cerebral vessel;
- heart attack – death of a section of the heart muscle due to loss of blood supply.
Most of these diseases are known to be fatal.
High cholesterol at a young age causes early disability and mortality. Due to the increased concentration of LDL, the walls of blood vessels become less elastic, atherosclerotic plaques are deposited on them, which impede blood flow. As a result, blood clots form, which cause heart attack and stroke.
Signs of High Cholesterol:
- heart pain, angina attacks;
- heaviness, pain in the legs even after minor physical exertion;
- the appearance of blood clots with mild bleeding;
- yellow spots on the skin, mainly in the eye area, wen.
More severe symptoms of high cholesterol in men and women appear when LDL levels are at critical levels. This may be a pre-stroke or pre-infarction condition.
The earlier high cholesterol and its causes are identified, the more effective the treatment.
Standard tables
Among women:
| Age (years) | Normal LDL level (mmol per liter) |
| 20-25 | 1.48-4 |
| 25-30 | 1.8-4.2 |
| 31-35 | 1.88-4.03 |
| 31-35 | 1.9-4.5 |
| 41-45 | 1.9-4.5 |
| 46-50 | 2.0-4.8 |
| After 50 | 2.2-5.2 |
For men:
| Age | Substance concentration (mmol/liter) |
| 20-25 | 1.7-3.8 |
| 25-30 | 1.8-4.2 |
| 31-35 | 2.0-4.8 |
| 36-40 | 1.9-4.4 |
| 41-45 | 2.2-4.8 |
| 46-50 | 2.5-5.2 |
| Over 50 | 2.8-5.25 |
In children:
| Age | Norm (mmol/l) |
| 0-5 | 1.3-2.5 |
| 5-10 | 1.63-3.35 |
| 10-15 | 1.6-3.45 |
| 16-20 | 1.61-3.53 |
In children, significant deviations from the norm are possible. Also, for women, the indicators will be slightly lower than in the table.
How to treat high cholesterol
To reduce LDL levels, it is important to address the cause of high cholesterol and any predisposing factors. First, you should do a lipid profile. The examination shows how serious the increase is . High cholesterol is treated by a general practitioner or cardiologist. There is also a more specialized specialist - a lipidologist.
To reduce high cholesterol levels in the body, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Follow a diet. Namely, reduce the consumption of animal fats, “fast” carbohydrates, and foods with trans fats. Nutritional correction reduces LDL levels by 10-15%.
- To refuse from bad habits. Moreover, not only active smoking, but also passive smoking is detrimental to health.
- To live an active lifestyle. It is useful to walk in the fresh air and set aside time for physical exercise. Exercise for at least 30-60 minutes. in a day.
- Control your weight. Fat deposits in the abdominal area are especially dangerous.
- Control blood sugar levels. This recommendation applies to patients with diabetes, as well as people who are predisposed to this disease.
- Cure endocrine diseases, normalize hormonal levels.
Sometimes statins are needed to treat high cholesterol. They produce an immediate effect, but scientists are increasingly talking about their shortcomings. Drugs in this group do not have a selective effect, they reduce everything - both “bad” and “good” cholesterol, and also negatively affect the functioning of the liver. However, their harm is less than the complications of critically high LDL levels.
Preparing to donate blood for a lipid profile
Preliminary preparation for analysis is necessary to obtain accurate results. 2-3 days before the prescribed procedure, it is recommended to refuse foods rich in animal fats and alcoholic beverages (including weak alcohol), and stop taking any medications other than those necessary for medical reasons.
The day before the procedure:
- reduce physical activity;
- limit sugar intake.
Blood sampling is performed strictly on an empty stomach. The fasting regime should be at least 8 hours.
Products that need to be limited
I would like to say right away that it is impossible to recover with diet alone. Treatment for high cholesterol is complex. However, some dietary restrictions are simply necessary.
If your LDL level is high, limit your consumption of the following foods:
- meat - beef, veal, lamb, pork;
- bird – duck, goose;
- lard, animal by-products;
- sausages, smoked meats;
- canned food;
- high fat dairy products;
- seafood - caviar, shrimp, oysters;
- margarine, mayonnaise;
- chicken yolk;
- coffee;
- sugar, flour products;
- fast food, convenience foods, chips, crackers and other unhealthy foods;
- salt (it prevents the breakdown of fats).
The consumption of fried foods is also limited, but it is impossible to completely remove all animal fats from the diet. If the body feels a lack of cholesterol coming from outside, it will increase its synthesis. When planning a diet, it is important to consult a nutritionist.
Pathological reasons for the increase
There are other causes of elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels. Mostly related to diseases.
Diabetes
A chronic, serious disease in which the level of glucose in the body increases. Usually associated with a condition of the pancreas. When little insulin is produced. On the other hand, a situation is possible in which the tissues are simply insensitive to this substance.
Both options are equally dangerous. The disease is accompanied by critical metabolic disorders. And that's the minimum. Low-density lipoproteins in diabetes constantly increase, so therapy is carried out systematically. For many years.
For immediate treatment, statins are prescribed, as well as fibrates as needed. As well as nicotinic acid.
But this is not enough. Insulin is used to stop attacks. In addition, a strict diet is indicated. Avoid sweets and sugar from your diet, and don’t get carried away with starch.
Herbal products are required. It is necessary to reduce body weight. The issue is resolved under the supervision of a competent endocrinologist.
Liver pathologies
Diseases in which an organ stops working as it should. Be it hepatitis, inflammation or cirrhosis (that is, death of the tissues of the largest gland).
Since the liver is primarily responsible for fat metabolism, all functions begin to be disrupted, including lipid processing.
What is the therapy? It is necessary to prescribe hepatoprotectors. Karsin, Essentiale, Phosphogliv. These are special means that prevent organ destruction.
The main diagnosis is being corrected. For example, hepatitis. Drugs are used. Next, the patient’s condition is monitored over time. Check how the prescribed course works.
Treatment is the prerogative of the hepatologist. If there is no such doctor within reach, a consultation with a gastroenterologist is indicated.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder. Accompanied by impaired bile production. This substance is involved in the processing of fats.
If there is not enough compound after eating, problems with lipid storage begin. At a minimum, over-deposition occurs. When there is too much fat. This means that the concentration of low-density lipoproteins increases. It is very dangerous.
Treatment is carried out on site. Necessary choleretic drugs. Allohol and others. They help the substance to be evacuated faster through special ducts. This means there will be no stagnation.
Attention:
The drug is not used for cholestasis with inflection and organic disorders of the gallbladder. His anatomical disorders.
Then, if necessary, diet therapy is used. A diet high in protein is prescribed.
Plus, they review the amount of food they eat per day. There should be about 5-6 of them so that each time the portion fits in the palm of your hand. This will reduce the load on an organ that is already out of order.
Insufficient production of thyroid hormones
The so-called hypothyroidism. This small organ, along with the pituitary gland, can be called the “conductor” of the entire endocrine system.
All deviations in the functioning of the thyroid gland immediately lead to an increase in the concentration of low-density lipoproteins, therefore, the amount of cholesterol also increases. Depending on the degree of violation, it is very significant.
Attention:
This is a threatening condition fraught with atherosclerosis.
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of an endocrinologist. Possibly in a hospital if there are life-threatening complications.
Special iodine preparations are prescribed. Also a diet high in this substance.
A huge role is played by correcting the primary cause. Often thyroid diseases are secondary. Caused by other factors. For example, problems in the functioning of the pituitary gland, etc.
Adrenal gland disorders
Diseases in which the concentration of adrenaline, cortisol and other substances is disrupted. They indirectly participate in the normal synthesis of LDL and correction of the concentration of low-density lipoproteins.
As soon as the amount of hormones decreases, problems begin. There can be many reasons: for example, Addison's disease or surgery. Correction is carried out immediately. Under the supervision of an endocrinologist.
Treatment is conservative. Substitute drugs are prescribed. Hormonal agents. If possible, artificial stimulation of the adrenal glands is performed. To achieve restoration of their functions.
The process is not fast. Complete rehabilitation requires at least 2-3 months. Often much more. It all depends on the primary factor.
Atherosclerosis
It is quite difficult to say exactly what is the cause and what is the effect. The essence of the pathological process is the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of the arteries.
The vessels cannot bear such a load. Local and even general pressure increases, the nutrition of body tissues is disrupted.
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of an endocrinologist. Prescribed drugs of the statin group. If the plaque becomes calcified and inorganic salts are deposited, there is no point in such medications. The formation is removed surgically. Through minimally invasive intervention.
If LDL is elevated, this means that normal metabolism is disrupted (slowed down). Usually there are two reasons. The first depends on the patient himself. For example, he doesn't eat well. And the second concerns the pathological process. Primary in relation to atherosclerosis.
The result is always the same. If left untreated, dangerous complications develop. Up to stroke, heart attack, arterial aneurysms.
Increase and decrease in the concentration of high-density lipoproteins
An increase is usually associated with chronic intoxication and alcoholism.
The decrease is most often associated with atherosclerosis, acute bacterial and viral infections, nephrotic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, gastric ulcer, myocardial infarction.
Treatment should be based on a well-formulated, balanced diet. Preference should be given to vegetable fats rather than animal fats. That is, you should not completely limit any fatty foods. On the contrary, it is useful to add vegetable oils to the menu at least several times a week - flaxseed, sea buckthorn, etc., as well as fatty red fish.
Thus, not all types of lipoproteins are “dangerous”, and elevated cholesterol levels do not always indicate pathological processes in the body. The results of a lipid profile are more informative. After 35–40 years, periodic monitoring of lipid parameters is necessary.
Diet for patients
To reduce the elevated LDL index, diet table No. 10 is used.
This anti-cholesterol diet is selected individually, but there are general rules for its use:
- Consume large amounts of plant-based cereal products and vegetable oils;
- Limit the consumption of foods with cholesterol (with animal fat);
- Fermented milk products should be low-fat, and you can also eat cheeses with a low percentage of fat;
- The meat should be of low-fat varieties - chicken, turkey, lean young veal and rabbit;
- Introduce sea fish into your diet, which is rich in Omega-3 and vegetable oils and nuts;
- Use vegetables, greens and fruits in the menu as much as possible;
- Avoid sweets and starchy foods;
- Reduce daily salt intake to 2.0 grams;
- Meals should be at least 6 times a day;
- Dishes should be in small portions;
- Don't forget to drink plenty of clean water.
Drink more clean water