Detailed description of the study
Alkaline phosphatases (ALP) are a group of enzymes that catalyze the reaction of the removal of phosphates from various molecules, usually proteins. The name of enzymes is due to the fact that they exhibit maximum biochemical activity in an alkaline environment.
Alkaline phosphatase is a collective term: in the body the enzyme is presented in the form of several fractions. The largest amount of alkaline phosphatase is found in the liver, the walls of the bile ducts and bones, and to a lesser extent in the intestinal mucosa, kidneys and placenta - an organ formed during pregnancy to connect mother and fetus. Normally, 80% of the ALP level in the blood consists of the liver and bone fractions of the enzyme.
As an enzyme, alkaline phosphatases catalyze reactions in the formation of components of cell membranes (phospholipids), carbohydrates, ATP molecules (the main source of energy in the body) and other nucleotides, as well as bone tissue structures.
Under physiological conditions, serum alkaline phosphatase levels may vary with age. In young children and adolescents, enzyme concentrations may increase as a result of bone growth and development. Adult men may have lower ALP values than women.
Also, a physiological increase in the enzyme can be observed in pregnant women, especially during the third trimester. This is due to the active production of alkaline phosphatase by the placenta. In the presence of clinical symptoms - most often itching and less often yellowing of the skin - an increase in alkaline phosphatase may indicate cholestasis in pregnancy. In this case, you need to consult your doctor as soon as possible.
Excessive levels of alkaline phosphatase in the blood can occur in pathologies of the bone and urinary systems. However, most often the indicator increases in diseases of the liver and biliary tract.
Bile is a biological fluid that is formed in the liver. Its main functions include:
- Emulsification and absorption of fats in the wall of the small intestine;
- Removal of bilirubin and cholesterol from the body.
Liver cells secrete bile, which first enters the cavity of the duodenum (small) intestine through intrahepatic and then through extrahepatic ducts. Part of the bile is stored in a special organ located on the lower surface of the liver - the gallbladder.
When the outflow of bile is disrupted, stagnation occurs (cholestasis). The causes of this pathological condition can be different - stone getting into the ducts, compression of them by a tumor, etc. Clinically, cholestasis can occur in the form of skin itching, less often jaundice (yellowness of the sclera, skin and/or mucous membranes, darkening of urine and discoloration of feces) - for due to the large amount of bilirubin entering the blood from the liver.
It has been established that with cholestasis the level of alkaline phosphatase in the serum begins to increase sharply. This is a response of the liver in response to a violation of the outflow of bile. Moreover, if the obstacle is at the level of the extrahepatic ducts, the increase in alkaline phosphatase in the blood is more pronounced.
This study is advisable to carry out when diagnosing the following diseases:
- Obstructive jaundice due to cholelithiasis, neoplasms of the liver, bile ducts, pancreas;
- Liver inflammation, cirrhosis due to infectious, autoimmune and other pathologies;
- Malignant bone tumors and bone metastases.
Indications for the study
The test results give the doctor the opportunity to assess hepatobiliary function, identify biliary tract obstructions, cholecystitis, cirrhosis, liver oncology, hepatitis. It is necessary to undergo an examination if symptoms such as vomiting, pain in the right hypochondrium, or jaundice appear.
From the musculoskeletal system, indications for a blood test for alkaline phosphatase are the following pathologies:
- osteomalacia (softening of bones);
- rickets (lack of calcium and vitamin D, which leads to weakening of bone tissue);
- Paget's disease (skeletal pathology in which abnormal restructuring of the bone structure occurs).
The test is also used in conjunction with other studies to diagnose pathologies due to vitamin D deficiency, examine patients with malignant neoplasms, and abnormal bone growth.
Lipase
Another digestive enzyme, the “homeland” of which is the pancreas.
It participates in the breakdown of fats, “biting off” long fatty acids from triglycerides. Just like amylase, it is part of pancreatic juice and increases in the blood during pancreatic diseases. However, it is more specific because it remains within the normal range for ectopic pregnancy, acute appendicitis, infectious mumps and liver diseases. Also, its activity in acute pancreatitis may increase earlier than amylase activity, and this is associated with greater diagnostic value. Norm:
13-60 units/ml.
Increased:
acute pancreatitis, malignant neoplasms of the pancreas, cholestasis, metabolic diseases (gout, obesity, diabetes), taking certain medications (indomethacin, barbiturate sleeping pills, heparin, narcotic painkillers).
Decreased:
hereditary lipid pathologies (triglyceridemia), unhealthy diet with a lot of fat, removed pancreas, tumors of any location except the pancreas.
Tags:
- Blood
To leave a comment you must be an authorized user
Interpretation of results
Reference values for the concentration of this enzyme are 240-270 U/l. An increase in indicators during pregnancy usually does not indicate pathology and is explained by physiological processes in the woman’s body. Enzyme deficiency is rare. Its excess can indicate a number of diseases (rickets, mononucleosis, some types of oncology, bacterial infection, etc.). The diagnosis is established taking into account the clinical picture, the results of other laboratory and instrumental studies. Sometimes the amount of enzyme increases in healthy people. Only a doctor can correctly interpret the test results; it is unacceptable to use it for self-diagnosis.
Blood chemistry. Decoding the main indicators
5. Total protein. Total protein in the blood is the total amount of all protein fractions in the blood. The normal level of total protein in the blood in adults ranges from 65 to 85 g/l.
Total protein consists of albumin, fibrinogen and four globulin fractions (alpha1, alpha2, beta and gamma globulins). The level of protein in plasma allows you to assess the condition of organs such as the liver, kidneys, pancreas, identify disturbances in carbohydrate, lipid or protein metabolism, determine micronutrient deficiency, etc.
Urea and creatinine will tell you about the function of the kidneys: 6. Urea. Creatinine. They are indicators of kidney function. A urea test is usually ordered in combination with a blood creatinine test. To assess kidney function in a range of conditions (in conjunction with a creatinine test). For the diagnosis of kidney disease and for checking the condition of patients with chronic or acute renal failure.
Generally, 2.2 - 7.3 mmol/L is considered normal urea level and any value higher or lower means that there is some abnormality in the body and it is necessary to pay attention and find out the reason for the change in urea level.
Creatinine is a chemical waste product created when muscles function. Its increase is affected by the consumption of large amounts of protein or liver pathology.
Creatinine levels may also temporarily increase with intense exercise or with the use of certain medications such as sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, or chemotherapy drugs (such as sports supplements). Other causes include conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure or thyroid disease.
7. Iron. It's also worth checking regularly. Iron is one of the most important microelements in the body. It is part of the hemoglobin of red blood cells and thus participates in the transfer of oxygen. The normal level of iron in the blood is one at which the body can fully function. If hemoglobin is low, this is a reason to consult a doctor and conduct the necessary research. Typical reasons for low iron levels include:
- improper diet;
- heavy blood loss;
- impaired absorption of iron;
- increased need for microelements.
8. C-reactive protein (CRP) is an informative indicator of the current inflammatory process in the body. This protein is synthesized by the liver and is one of the markers of the acute phase of inflammation.
The level of CRP in the blood may increase within several hours after the onset of an infectious disease, injury, or in the first hours after surgery. CRP quickly responds to changes in the dynamics of the disease and quickly returns to normal upon recovery.
9. Uric acid. Normally – up to 428 µmol/l. Uric acid is a waste product from the metabolism of nucleic acids and purines in the body. The latter are formed mainly in the process of natural cell death. Uric acid enters the body from meat products (liver, red meat, legumes, fish) and from liquids (beer, wine) and is formed in the body. A uric acid test is necessary to determine the cause of gout. When the content of this compound in the body exceeds the norm, its salts begin to be deposited in the joints, causing acute arthritis and the formation of nodules called tophi. In addition, this acid promotes the formation of kidney stones.
During the Middle Ages, gout was often called the “disease of kings.” This is explained by constant large meals without any measure, as well as the tendency to illness in men over forty years of age. The kidneys of those who abused food and wine could not cope with the huge concentration of uric acid. Ordinary people ate a limited diet, and could not afford so much meat and alcohol, which contain the most purines, so they got sick less often.
The material was prepared with the direct participation of N.V. Degtyareva, a doctor of laboratory diagnostics of the highest category at the Botkin Hospital.
Thank you for your assistance and information!
General information
ALP is present in many tissues. An increase in its concentration in the blood occurs with significant damage to a particular tissue. The presence of a small amount of enzyme in the bloodstream is explained by the process of cell renewal and does not indicate the presence of a disease. A significant increase in indicators is characteristic of cholestasis (stagnation of bile, which is caused by an obstacle to its outflow, for example, stones). Large amounts of the enzyme are often found in bone tissue. It is present in cells that are involved in bone turnover and growth. Therefore, ALP is significantly increased in patients with fractures and in children.
Alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase is a group of enzymes found in almost all tissues of the body, with a predominant localization in the liver, bones and placenta.
Research method
Kinetic colorimetric method.
Units
U/L (unit per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous, capillary blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood.
General information about the study
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme that is found in the cells of the liver and biliary tract and is a catalyst for certain biochemical reactions in these cells (it does not work in the bloodstream). When these cells are destroyed, their contents enter the bloodstream. Normally, some cells are renewed, so a certain alkaline phosphatase activity is detected in the blood. If many cells die, it can increase very significantly.
Alkaline phosphatase activity increases greatly when there is an obstruction to the flow of bile, such as stones in the bile ducts.
In bones, alkaline phosphatase is formed in special cells - osteoblasts, which play an important role in the formation and renewal of bone tissue. The higher the activity of osteoblasts, the higher the activity of alkaline phosphatase in the blood, so in children and people who have suffered bone fractures, alkaline phosphatase activity is at a high level.
Alkaline phosphatase is also found in intestinal and placental cells.
What is the research used for?
This test is usually prescribed to detect liver or bone diseases. In addition, alkaline phosphatase is elevated in diseases affecting the bile ducts, so this test helps confirm blockage of the bile duct due to stones in the bile ducts or pancreatic tumors.
An alkaline phosphatase test, as well as a gamma-glutamyl transferase test, is carried out in order to diagnose diseases affecting the biliary tract: primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Any condition that involves bone growth or increased bone cell activity increases alkaline phosphatase activity. Repeated administration of alkaline phosphatase is used to monitor the activity of diseases in which it is elevated or to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
What do the results mean?
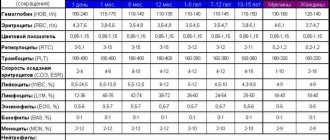
| Age, gender | Reference values |
| 17-19 years old, female | 45 - 87 U/l |
| 17-19 years old, male | 55 - 149 U/l |
| > 19 years old, female | 35 - 105 U/l |
| > 19 years old, male | 40 – 130 U/l |
If the values obtained as a result of other tests, such as bilirubin test, ALT, AST, are also elevated, then the increase in alkaline phosphatase activity in the blood may be due to liver damage.
If calcium and phosphorus levels are altered, the most likely cause of elevated alkaline phosphatase is bone pathology.
An increase in alkaline phosphatase activity almost always means damage or involvement in the pathological process of the liver, biliary tract or bones.
Reasons for increased alkaline phosphatase activity
1. Damage to the liver and bile ducts.
2. Bone damage.
3. Other reasons.
- Hyperparathyroidism.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Ulcerative colitis, intestinal perforation.
Reasons for decreased alkaline phosphatase activity
- Severe anemia.
- Massive blood transfusions.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Lack of magnesium and zinc.
- Hypophosphatasia.
- A pronounced decrease in alkaline phosphatase in pregnant women is a sign of placental insufficiency.
What can influence the result?
- During pregnancy, alkaline phosphatase activity is normally increased, as it is contained in the placenta.
- A temporary increase in alkaline phosphatase activity is observed after fractures.
- In children and young people, alkaline phosphatase activity is higher than in adults, which is how their bones grow.
- Aspirin, paracetamol, allopurinol, antibiotics and a number of other drugs can increase the activity of alkaline phosphatase.
- Taking oral contraceptives sometimes leads to a decrease in alkaline phosphatase activity.
Important Notes
Alkaline phosphatase activity sometimes increases in healthy individuals; this does not necessarily indicate any pathology. To correctly interpret changes in alkaline phosphatase activity, a comprehensive assessment of the results of other tests, as well as other medical data, is needed.
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK)
An enzyme that provides energy to muscles, mainly striated muscles (skeletal and cardiac).
It is located inside muscle cells and is responsible for the transfer of phosphoric acid residue to creatine and the resulting activation of energy metabolism. We have already mentioned many times above that intracellular enzymes, increasing in the blood, indicate that destruction of a specific tissue is occurring somewhere. In the case of CC, this tissue is muscle. This is the earliest and most specific marker of myocardial infarction; its activation can be detected within two hours after the occurrence of a focus of necrosis in the heart muscle. Norm:
up to 190 units/l for men, up to 167 units/l for women.
Increased:
myocardial infarction, myocarditis, myocardial dystrophy, heart failure, tachycardia, hypothyroidism, malignant tumors and some diseases of the central nervous system (schizophrenia, psychoses, epilespy, head injury).
It can also increase after operations and diagnostic manipulations on the heart, after physical activity. Decrease:
sedentary lifestyle, severe decrease in muscle mass, cachexia (exhaustion).
3.How the analysis is carried out and the risks of analysis
How is a blood alkaline phosphatase test performed?
A blood alkaline phosphatase test is performed after drawing blood from a vein. Blood sampling from a vein is carried out according to a standard procedure.
Risks of Alkaline Phosphatase Blood Tests
If you are donating blood for an alkaline phosphatase blood test, then possible risks may only be associated with taking blood from a vein. In particular, the appearance of bruises at the site of blood sampling and inflammation of the vein (phlebitis). Warm compresses several times a day will relieve phlebitis. If you are taking blood thinning medications, you may bleed at the puncture site.
How to return alkaline phosphatase to normal?
The level of alkaline phosphatase in the blood will return to normal on its own as soon as you eliminate the cause of the deviation. Those. It is necessary to influence not the ALP itself, but the factors that led to its increase or decrease.
Minor abnormalities should not be a cause for concern because enzyme levels fluctuate throughout the day and vary from person to person.
If a patient has an acute deficiency of vitamins and minerals, he should enrich his diet with the following foods:
- fresh fruits and vegetables, especially citrus fruits and dark leafy greens
- red meat and fatty fish
- unrefined vegetable oil (olive, sesame, camelina, flaxseed, corn, etc.)
- whole grain cereals
- natural probiotics (yogurt, kefir, kimchi and sauerkraut)
If there are liver problems, you should eat according to the recommendations of the classic therapeutic diet Table No. 5. The patient will also need to normalize their weight and increase physical activity. Drug support traditionally includes ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), a drug for the hepatobiliary system with a high degree of evidence. It protects liver cells from damage, reduces the load on the organ, allowing it to recover faster. In case of serious pathologies (cirrhosis, cancer, viral hepatitis), antiviral therapy and surgical intervention may be required.
A patient with a gallbladder is first monitored dynamically. If the situation worsens, despite the use of UDCA, cholecystectomy is prescribed - removal of the bladder.