Step-by-step instruction
How to measure blood pressure correctly with a mechanical tonometer:
- Take a sitting position (a sofa or armchair is suitable for this).
- Lean your back on the back of the chair, and place your feet on the floor (it is not recommended to cross them, tuck them in, throw them on top of each other, etc.).
- The left hand is freed from clothing and placed on a table or any other flat surface. The main thing is that it is not in a canopy.
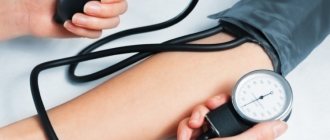
- Open the cuff, insert your hand into it and secure it slightly above (2-3 cm) the elbow bend.
- Place part of the stethoscope in the form of a small metal disk on the inside of your elbow. It is important that the pulsating artery is clearly felt in this place.
- If you are performing this procedure for the first time and do not yet fully understand how to correctly measure pressure with a mechanical tonometer, then first feel the pulse with your fingers. For the future, you will know exactly where to place the metal part of the stethoscope.
- Then insert the hearing aid stethoscope into your ears.
- Make sure the air release wheel on the bulb is tightly closed.
- Place the rubber bulb of the tonometer in your hand and begin manually supplying air. The arrow on the dial will begin to move. After it reaches the 200-220 mm mark. rt. Art., stop squeezing the bulb and slowly begin to spin the wheel. The air should come out slowly, about 4 mmHg. Art. per second.
- As the air descends, you should hear a pulse. The number where the needle will be on the first beat is your systolic pressure (i.e., top). The pulse will be heard for some time. The value at which the needle will be at the last beat is your diastolic blood pressure (i.e., lower).
- Measure blood pressure on the other arm. Consider higher values as reliable. In the future, measure the pressure on the arm where it is higher.
- Both results obtained must be written down or remembered.
In general, this process will take you a few minutes. This procedure must be carried out daily, recording the data obtained. Thus, you can determine the average values of your upper and lower pressure.
Technique for measuring blood pressure with a mechanical tonometer
Technique for measuring blood pressure with a mechanical tonometer
Note! Hypertension - why are blood pressure pills harmful? Dr. Bubnovsky about two safe and simple steps to life without hypertension Read more »
To measure your blood pressure, you need to perform a series of sequential steps:
- Sit at the table, placing the hand being examined on its surface, palm up.
- Wrap the cuff loosely around your shoulder with the hoses facing down. Secure it with Velcro.
- If the device comes with a phonendoscope, then insert its ends into your ears, and attach the head with the membrane to the place of the strongest pulsation, usually located on the inside of the elbow joint. If there is no phonendoscope, blood strokes will have to be determined visually, guided by the sensations in the hand.
- Screw the valve on the bulb all the way and use your free hand to inflate the cuff with air until you feel numbness in your shoulder and the pulsation stops. At the same time, watch the pressure gauge needle: it should reach a value of 20–30 mm Hg. Art. higher than your normal blood pressure.
- Slowly open the bulb valve. At this point, you will hear a series of beats (about 8-10 in total) corresponding to your heartbeat. Remember to look at the meter dial: the needle will quickly move in the opposite direction, towards zero. You should see what mark it will be at when you hear the first and strongest impulse of blood - this is the value of systolic, or upper, blood pressure.
- The pulse beats will gradually subside. The last audible beat of the series corresponds to the lower (diastolic) pressure. For example, if you heard the first beat of blood when the needle was at 140, and the last one was at 90, then your blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg. Art.
- When finishing the measurement, open the bulb valve completely and release all the air from the cuff.
Having certain experience and skill, using a hand-held tonometer for measuring pressure with a phonendoscope, you can measure these indicators on the leg, if necessary. The point of most audible vascular pulsation is located on the outside of the dorsum of the foot.
RULES AND FEATURES OF MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE IN CHILDREN
Unfortunately, arterial hypertension can occur not only in adults, but also in children. In order to detect it in a timely manner and take appropriate measures, children need to have their blood pressure (BP) measured at certain intervals. Regulatory information on this issue can be found here: https://minzdrav.gov.by/upload/dispanserizatsiya/instruktsiya/000127_245033_postan96.pdf.
Annual blood pressure measurements in children are carried out from the age of 3. Obtaining accurate blood pressure readings in children under 3 years of age is often difficult. However, if technically possible, it is better to measure the baby’s blood pressure level.
It should be remembered that in healthy children, increased blood pressure may occur. However, such phenomena are usually rare, short-lived and are not accompanied by complaints of feeling unwell. Many factors influence blood pressure readings:
- mood;
- nutrition;
- health status;
- physical exercise.
Means for measuring blood pressure
Devices (tonometers) for measuring blood pressure are different:
- mechanical - consist of a cuff, a bulb (for pumping air), flexible tubes, a pressure gauge (a device with a scale and units for measuring pressure), a stethoscope (a tube for listening to the pulse);
- semi-automatic - consist of a cuff, a bulb and an electronic display;
- automatic - consist of a cuff and an electronic display.
The automatic blood pressure monitor requires maintenance and recalibration. The measurements obtained with this device are usually higher than those obtained with a mechanical tonometer. Measuring blood pressure with a mechanical tonometer requires certain skills. Today, measuring blood pressure using a mechanical tonometer is the “gold standard”.
The image is for illustrative purposes only.
- It is preferable to measure blood pressure in the first half of the day, if necessary, every 3 hours.
- Before measuring blood pressure, you should avoid physical activity, eating and taking medications, and you should also empty your bladder.
- Immediately before measuring blood pressure, the child should sit quietly for about 5 minutes.
- The measurement is carried out on the right hand, which should lie relaxed on the table with the palm facing up.
- At the time of measuring blood pressure, it is necessary that the child is in a comfortable sitting position with support on the back of a chair.
- Legs cannot be crossed; they must be supported.
- During the entire procedure, you should not talk or change body positions.
- Blood pressure should be measured three times with an interval of 2-3 minutes, the average value of all measurements is taken into account.
- For children under 2 years of age, blood pressure is measured while lying on their back.
- Choosing the right cuff is important for accurate measurements. The cuff should cover 2/3 of the length of the shoulder. A cuff that is too wide will underestimate blood pressure, while a cuff that is too narrow will overestimate it.
Recommended cuff sizes for children:
| Purpose of the cuff | Cuff width, cm | Cuff length, cm | Shoulder circumference, cm |
| Newborns | 4 | 8 | 10 |
| Infants | 6 | 12 | 15 |
| Children | 9 | 18 | 22 |
| Large children, teenagers | 10 | 24 | 26 |
Full information can be found here
Method of measuring blood pressure in children
- The cuff is placed on the bare shoulder, one finger should pass between it and the shoulder, and its lower edge should be placed 2-3 cm above the elbow.
- Rubber tubes are placed on the inner surface of the shoulder.
- The head of the phonendoscope is placed in the center of the cubital fossa.
- You should close the valve of the bulb, and then use it to begin pumping air into the cuff.
- Next, you need to open the valve and slowly release the air.
- The first tone heard will correspond to the systolic pressure, and the disappearance of the sounds will correspond to the diastolic pressure.
If an automatic tonometer is used to measure blood pressure, it must be calibrated and in good condition. Before use, be sure to read the instructions. All of the above criteria for preparing for blood pressure measurement, positioning the child and selecting a cuff must also be met.
Next, you need to press the “start” button, the tonometer will automatically begin pumping air into the cuff. When the measurement is completed, the blood pressure and heart rate results will be displayed on the screen.
Blood pressure indicators in children depend on the gender, age and height of the child. Special tables and medical calculators are used, which present blood pressure norms for a child with certain indicators of physical development.
Source: https://scardio.ru/content/images/recommendation/diagnostika_lechenie_i_profilaktika_ag_u_detey_i_podrostkov.pdf
Approximate formulas for assessing blood pressure indicators:
| Age | Systolic blood pressure, mm. Hg Art. | Diastolic blood pressure, mm. Hg Art. |
| Up to a year | 60 mm. Hg Art. | 1/2-2/3 systolic blood pressure |
| Over a year old | 90+2 x age in years | 60+ age in years |
Source: https://medvvolske.ru/docs/2018_04_11/sH42r878E5e9i7kA298S6rB6Q.pdf
If, when measuring blood pressure at home, you notice a stable increase or decrease in blood pressure in a child, you should not give him medications yourself. In this case, you need to contact a pediatrician to examine and examine the baby. In some cases, the doctor may recommend a special examination - 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM), which allows you to study in detail the characteristics of the child’s cardiovascular work.
Do not ignore your child’s complaints of weakness, headache, rapid heartbeat, loss of consciousness, or nosebleeds. Start by taking your blood pressure.
The health of the child is the main value of every parent.
Literary sources:
- Propaedeutics of childhood diseases: textbook / M. V. Chichko [et al.]; edited by M. V. Chichko and A. M. Chichko. – Minsk: Misanta, 2021. – 912 p.
- Arterial hypertension in children: clinical recommendations // Association of Pediatric Cardiologists of Russia; Union of Pediatricians of Russia. – 2016. – 71 p. – Access mode: https://scardio.ru/content/images/recommendation/diagnostika_lechenie_i_profilaktika_ag_u_detey_i_podrostkov.pdf. – Access date: 03/01/2021.
The material was prepared by clinical resident of the Department of Pediatrics of BelMAPO A.M. Kudina, Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department of Pediatrics of BelMAPO A.P. Ruban.
Diagnostic technique
You need to relax and be silent
How to correctly measure blood pressure with a mechanical tonometer? An inflatable cuff with a balloon is fixed on the shoulder at the site of pulsation of the brachial artery. The lower edge of the cuff should not reach the elbow (2 cm from it).
You must first free your hand from clothing. Initially, a palpation method of examining blood pressure is performed. Air is quickly inflated into the cuff to a level of 70 mmHg. Art. on the pressure gauge, then gradually increase the air pressure in the balloon by 10 mm until the pulse on the radial artery completely disappears. Then the air is gradually released until a pulse appears.
This method helps prevent overinflation of the cuff in the presence of the phenomenon of auscultation failure.
After the palpation method of recording pressure, the auscultatory method is carried out. To take measurements you will need the same thing and a phonendoscope.
The phonendoscope should be placed at the level of the ulnar fossa (a little higher and closer to the middle). Gradually pump air into the balloon so that the pressure in the cuff exceeds the pressure at which the pulse in the artery disappears by 20-30 mmHg. Then they open the valve a little and monitor the Korotkoff sounds and their changes.
- How to use a glucometer - instructions for use, rules of use, types and times for measurement
Algorithm for studying blood pressure in peripheral arteries
1. Preparation for the procedure:
1) Introduce yourself to the patient, explain the purpose and course of the procedure.
2) Treat hands hygienically and dry.
3) Give the patient a comfortable position, sit or lay him down.
2. Performing the procedure:
1) Expose the patient's hand, placing it palm up, at the level of the heart.
2) Place the blood pressure cuff on the patient’s shoulder. Two fingers should be placed between the cuff and the surface of the shoulder (for children and adults with small arms - one finger), and its lower edge should be located 2.5 cm above the ulnar fossa.
3) Gradually inject air with the tonometer bulb until the pulse disappears (the disappearance of the pulse is recorded by the researcher by palpation). This pressure level, recorded on the tonometer scale, corresponds to systolic pressure.
4) Deflate the air from the tonometer cuff and prepare the device for re-inflation.
5) Place the stethophonendoscope membrane at the lower edge of the cuff above the projection of the brachial artery in the area of the ulnar cavity, lightly pressing it against the skin, but without making any effort.
6) After fixing the membrane, quickly inflate the cuff to a level exceeding the obtained result by 30 mmHg.
7) Maintaining the position of the stethoscope, begin to deflate the air from the cuff at a speed of 2-3 mm Hg. in a second. When the pressure is more than 200 mmHg. it is allowed to increase this indicator to 4-5 mm Hg. in a second.
 Remember the appearance of the first tone on the scale on the tonometer - this is the systolic pressure, the value of which should coincide with the estimated pressure obtained by palpation.
Remember the appearance of the first tone on the scale on the tonometer - this is the systolic pressure, the value of which should coincide with the estimated pressure obtained by palpation.
9) Mark on the scale on the tonometer the cessation of the loud last tone - this is diastolic pressure. To control the complete disappearance of sounds, continue auscultation until the pressure in the cuff decreases by 15-20 mm Hg. relative to the last tone.
3. End of the procedure
1) Inform the patient the result of blood pressure measurement.
2) Treat the phonendoscope membrane with an antiseptic or disinfectant.
3) Treat hands hygienically and dry.
4) Record the results in the appropriate medical records. If there is a change in the patient's blood pressure, inform the doctor.
Pulse research algorithm.
I. Preparation for the procedure.
1. Introduce yourself to the patient, explain the process and purpose of the pulse examination procedure. Obtain patient consent for the procedure.
2. Treat hands hygienically and dry.
3. Offer the patient or give him a comfortable position.
II. Execution of the procedure.
1. Place the first finger of the hand on the back side above the patient’s hand, and the second, third and fourth fingers along the radial artery, starting from the base of the patient’s first finger.
2. Lightly press the artery to the radial hand and feel its pulsation.
3. Take a watch with a stopwatch.
4. Count pulse waves in the artery for 1 minute.
5. Determine the intervals between pulse waves (pulse rhythm)
6. Determine pulse filling (volume of arterial blood forming a pulse wave).
7. Compress the radial artery and evaluate the pulse tension.
III. End of the procedure.
1. Register the pulse rate in the temperature sheet graphically, and in the observation sheet digitally.
2. Inform the patient about the results of the study.
3. Wash and dry your hands.
4. Treat your hands with an antiseptic.
Hand-held device
A manual tonometer for measuring pressure is an air-filled cuff with Velcro, connected by hoses to a rubber pump - a bulb and a meter (manometer). The cuff is wrapped around the patient's shoulder and fastened. The bulb is equipped with a screw-on valve. By compressing it several times, air is pumped into the cuff.
The most common breakdown of a mechanical tonometer is a violation of the seal of the bulb: the bulb bursts, or an invisible crack appears on it over time, which requires replacement of this part of the device.
In addition, some devices come with a phonendoscope for listening to blood impulses in the arteries. These blood pressure monitors are certainly more convenient.