Pain under the shoulder blade
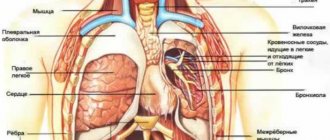
- a fairly typical localization of back pain, although it is much less common than, for example, lower back pain. The scapula is a flat bone, approximately triangular in shape, adjacent to the back of the chest in the area from the 2nd to the 8th rib. The shoulder blades tend to protrude slightly, forming the relief of the back, so we all know where they are and describe pain in relation to the shoulder blade if we feel it in the upper back to the right or left of the spine.
Pain in the shoulder blade area can be caused by various reasons. A simple indication of what hurts under the shoulder blade is not enough to determine what caused the pain, which means you cannot self-medicate without visiting a doctor and establishing the nature of the disease. At the same time, pain under the shoulder blade can be caused by very serious diseases, so if you experience severe or recurring pain under the shoulder blade, you should definitely consult a doctor. Don't expect the problem to go away on its own.
If you have pain under the shoulder blade, you need to pay attention to other symptoms, this will help the doctor make a diagnosis.
Causes of pain between the shoulder blades
In some cases, the patient complains that he has pain between the shoulder blades. Such localization is typical, first of all, for diseases of the thoracic spine - osteochondrosis, scoliosis, kyphosis, spondyloarthrosis, intervertebral hernia, protrusion of the intervertebral disc. Also, pain between the shoulder blades can be observed with coronary heart disease, intercostal neuralgia, and gastrointestinal diseases.
The causes of pain that cause pain under the right or under the left shoulder blade are different.
Heart and blood vessels
Back pain below the left shoulder blade is often the result of problems in the cardiovascular system.
Substernal pain in the central part or to the left, with extension to the upper part of the body, signals myocardial infarction. At the same time, a strong burning sensation may be observed under the left shoulder blade from the back. It is impossible to clearly characterize the pain syndrome. It can be aching, or it can manifest itself in an acute form.
Lack of blood supply to the myocardium causes an attack of angina, characterized by pressing or squeezing retrosternal pain, often radiating to the left shoulder blade, arm, and lower jaw. At the same time, blood pressure may increase, sweating and pallor may appear.
Angina attacks usually occur in stressful situations or from increased physical activity. They are treated with nitroglycerin. When the duration of pain exceeds 20 minutes or medications do not provide relief, the presence of myocardial infarction can be assumed.
High blood pressure or atherosclerotic lesions lead to aneurysm (enlargement) or dissection of the aorta (incomplete rupture or tear of the endothelium with subsequent spread of blood between the layers of the vessel wall).
Small aneurysms do not manifest themselves in any way. As they increase, a person begins to feel a dull pain in the back. A dissecting aneurysm is characterized by a pronounced clinical picture. When a tear occurs, the pain sensation is sharp and short-lived. It affects the chest and back, leading to a reflex decrease in blood pressure and fainting. After a certain period of time, a person feels a burning pain in the chest, arms, neck, under the left shoulder blade. The syndrome cannot be eliminated using available medications. In this condition, death is very possible, so urgent medical attention is necessary.
Pain below the left shoulder blade is caused by:
- ischemia – lack of blood supply to the heart;
- pericarditis – inflammatory processes in the pericardium;
- endocarditis - an inflammatory disease of the inner lining of the heart;
- myocarditis – inflammation of the heart muscle.
Disturbances in the autonomic nervous system cause vegetative-vascular dystonia. The disease is characterized by numerous manifestations, including pain under the left shoulder blade, similar to heart pain. In addition, the person suffers from irritability, memory impairment, increased sweating, etc.
Causes of pain under the left shoulder blade
Pain under the left shoulder blade can be due to the following reasons:
- incorrect position while sleeping. In this case, a person wakes up with pain under the left shoulder blade and in the left shoulder. This pain usually goes away quite quickly;
- stomach ulcer. Peptic ulcer is a fairly common cause of pain under the left shoulder blade. In this case, the pain, as a rule, is aching in nature, gradually increasing, accompanied by gagging, heartburn and belching. After vomiting there is usually relief. As a rule, with a peptic ulcer, the onset of pain is associated with food intake;
- stress, panic and other psychological reasons. Psychogenic pain is described as congestion, compression, heaviness; may be accompanied by fever or a tingling sensation. Sometimes dizziness or a feeling of a lump in the throat is added. In this case, the pain is localized in the chest, and radiates under the left shoulder blade (people say “gives away”). The pain can spread wider, involving the shoulder blade itself, the neck, turning into a headache;
- heart diseases such as myocarditis, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction. A heart problem is very likely if there is pain both under the left shoulder blade and behind the sternum;
- osteochondrosis. With osteochondrosis, pain often occurs in the morning, that is, a person wakes up with pain. Patients in this case often say that the pain under the shoulder blade radiates to the arm or head;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- inflammatory lung diseases, in particular pneumonia.
This list contains the most common causes; the full list of causes of pain under the left shoulder blade is much longer.
The mechanism of development of pain
How does it happen that the heart hurts, but it stings under the shoulder blade, and most often with the left one? I think the answer to this question interests many readers. To understand the origin of this phenomenon, it is necessary to delve a little into the doctrine of the processes of intrauterine development of the fetus. At the time when our heart takes on its final form, the formation of the neck, back and girdle of the upper extremities, which includes not only the arms themselves, but also the shoulder blades, is completed - all these formations receive nerve fibers from nearby segments of the spinal cord. Therefore, the pain impulse can “jump” from one floor to another. This phenomenon was called irradiation.
This leads to the conclusion: there is no need to go to extremes and attribute a heart attack to yourself before a full medical examination.
Causes of pain under the right shoulder blade
The most common causes of pain under the right shoulder blade are:
- problems of the biliary system. Acute pain under the right shoulder blade can be observed with acute cholecystitis or cholelithiasis. The usual localization of pain in this case is in the right hypochondrium. The pain may radiate to the scapula or right shoulder. Associated symptoms are a bitter taste in the mouth, heartburn, nausea, vomiting;
- kidney diseases – nephritis, pyelonephritis. In this case, pain under the right shoulder blade is usually accompanied by pain in the lumbar region;
- liver diseases. The liver is located in close proximity to the right shoulder blade, and liver problems often lead to pain in this area;
- coronary heart disease (angina pectoris, myocardial infarction);
- osteochondrosis.
Also, pain under the right shoulder blade can be caused by other reasons, among which there are very dangerous diseases - aortic aneurysm, appendicitis and some others.
Expert advice
Many people with back pain that develops against the background of osteochondrosis begin to warm the affected area with heating pads, apply alcohol compresses, go to the bathhouse or rub themselves with gels with an irritating effect based on capsoicin. This cannot be done, since the nerve is pinched, inflamed and swollen. Such treatment only worsens the situation. To quickly get rid of unpleasant sensations, take NSAIDs, limit yourself in physical activity and use local anesthetic drugs.
Causes of pain between the shoulder blades
In some cases, the patient complains that he has pain between the shoulder blades. Such localization is typical, first of all, for diseases of the thoracic spine - osteochondrosis, scoliosis, kyphosis, spondyloarthrosis, intervertebral hernia, protrusion of the intervertebral disc. Also, pain between the shoulder blades can be observed with coronary heart disease, intercostal neuralgia, and gastrointestinal diseases.
How to prevent shoulder pain
To prevent pain from occurring, the following conditions must be observed:
- lead an active lifestyle, move more, engage in feasible sports;
- Avoid prolonged periods with your arms raised above your head, as well as movements associated with unilateral load on the shoulder joint; At risk are weightlifters, tennis players, and miners; If a representative of one of these groups feels persistent pain in the shoulder, perhaps he should change his occupation or at least reduce his exposure to harmful factors as much as possible.
When you need a doctor for pain under the shoulder blade
If the pain under the shoulder blade appeared for the first time and quickly passed, then it was probably associated with an accidental cause - for example, the body was in an uncomfortable position for a long time. If the pain persists, intensifies or causes discomfort (in case of severe pain), you should definitely consult a doctor.
In some cases, emergency medical attention is required. Call an ambulance if:
- pain under the shoulder blade is associated with injury. Especially in the presence of bleeding and signs of bone fracture;
- along with pain, deformation, swelling, edema or redness in this area is observed;
- pain is accompanied by increased heartbeat, difficulty breathing (shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air);
- the pain is accompanied by dizziness and faintness.
Shoulder Pain Treatment
Treatment of shoulder pain should be carried out strictly individually, taking into account examination data and the established diagnosis. It is performed by an orthopedist-traumatologist or rheumatologist. In case of very severe pain, pain therapy is carried out by an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. A specialist will always find something to treat even very severe shoulder pain.
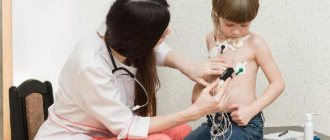
Diagnostics
A correct diagnosis is the path to prescribing adequate treatment and relieving the patient of pain. In diagnosis, examination and clinical examination of the patient by the attending physician using special assessment tests is of particular importance. They allow you to preliminarily determine which structures were damaged. The location of the damage is determined in more detail using functional tests.
Clinical data are confirmed by laboratory and instrumental studies that reveal inflammatory reactions, the presence or absence of infectious, autoallergic processes, the degree of destruction of articular and periarticular tissues. In identifying tendonitis and capsulitis, the main instrumental diagnostic methods are ultrasound and MRI.
How to treat shoulder pain
Treatment for shoulder pain begins with limiting the load on the affected limb. The patient is allowed movements that he can perform painlessly. Immobilization of the limb (scarf bandage) is carried out in short courses if the severity of the pain syndrome is very great. Prolonged immobilization contributes to the consolidation of hand dysfunction. Today, for partial gentle immobilization, taping is often used - fixing muscles with adhesive tapes in a certain position to prevent injury. This significantly improves the quality of conservative therapy.
After acute pain in the shoulder has been eliminated, treatment is continued by prescribing courses of physical therapy (physical therapy) and massage. At any stage of the disease, conservative therapy includes physiotherapy and reflexology courses. In case of severe pain, this is electrophoresis with novocaine, then warming procedures, mud and baths.
At the same time, drug therapy is prescribed. We remove pain by prescribing drugs from the NSAID group in tablets, injections, ointments (the drug with the best analgesic properties is Ketorol). For very severe shoulder pain, treatment includes narcotic painkillers (Tramadol) and glucocorticosteroids (GCS - Betamethosone). Sometimes folk remedies are also used.
To restore cartilage, chondroprotectors (Dona, Artra, Structum) are prescribed. Drugs in this group also help restore damaged periarticular tissues - tendons and ligaments, since they have the same origin as cartilage cells.
Surgical assistance will be required for some types of fractures, dislocations, ruptures of tendons and ligaments. If joint function is completely lost, if conservative treatment does not help, the destroyed joint must be removed and replaced with an artificial one (endoprosthesis surgery).
To prevent pain from reoccurring, a complex of rehabilitation measures is carried out using exercise therapy, massage, reflexology courses, and sanatorium-resort treatment.
What injections to give for shoulder pain
Injections are prescribed for severe pain that is not relieved by pills and external means:
- Analgin (Baralgin)
- one ampoule contains 1 ml of solution or 500 mg of active substance - a single dose for an adult; may have a toxic effect on hematopoiesis, so use it with caution; - Ketorolac (Ketorol)
– in one ampoule 30 mg of active ingredient – a single dose for an adult; contraindications: peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, increased bleeding.
Blockades are widely used - injections of painkiller solutions into the most painful points.
The Moscow Paramita clinic uses the most modern methods of diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of all diseases that cause shoulder pain syndrome.
If necessary, if the disease threatens the patient’s life, after examination by a doctor, he is urgently sent to the hospital. But we treat most pain syndromes on an outpatient basis. Detailed information about treatment can be found on our website.
Injections for shoulder pain
Pain under the shoulder blade: which doctor should I contact?
If you complain of pain under the shoulder blade, it is recommended to consult a general practitioner (general practitioner or family doctor). It is the general practitioner who must determine which specialists should be examined.
If the pain under the shoulder blade is associated with eating, accompanied by heartburn, belching, or a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, you will probably need to consult a gastroenterologist.
If there is reason to believe that the pain is related to the spine, for example, if the pain intensifies with movement of the torso or shoulder, then you will be referred to a neurologist, vertebroneurologist or chiropractor.
You must be prepared that you may need to consult a cardiologist or urologist.
Musculoskeletal system
Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system are provoked by various injuries:
Why does my upper back hurt?
- fractures and cracks caused by impacts, falls, road accidents, etc. The aching pain intensifies when a person makes movements. Also, the damaged area swells, a bruise appears, and mobility decreases;
- dislocations, which are observed in rare cases and occur when there is a strong pull on the arm or a blow to the shoulder blade. In this case, the bone rotates, shifts, and takes on an abnormal position. Its lower edge is compressed between the ribs.
The muscles connecting the scapula and spine are subject to excessive stress, causing stretching and possible rupture.
Pain in the area of the left shoulder blade on the back caused by injury occurs immediately after the injury and only goes away as the patient recovers.
In addition to injuries, pain in the area of the shoulder blade from the back is often caused by diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Pain syndrome under the scapula, which is a consequence of cervical osteochondrosis (dystrophic-degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs of the spine), is spontaneous and can be aching and pulling. Increased pain is observed when a person remains in a sitting position for a long time and during physical exertion. Taking medications does not bring relief.
A pinched, inflamed intercostal nerve causes unbearable pain in the sternum, in the area where it lies. The syndrome intensifies as a person moves, when he coughs, sneezes, inhales deeply, and changes body position. Constant or paroxysmal pain syndrome is sharp, strong, shooting in nature. Sometimes pain manifests itself in the heart area, in the lower back, and affects the neck and arms. It can also affect the shoulder blade.
Manifestations of intercostal neuralgia are similar to symptoms caused by cardiac problems, cholecystitis, angina pectoris, and pleurisy. Only a qualified specialist can make a correct diagnosis
When there is inflammation in the shoulder tendon and capsule of the shoulder joint without damage to the joint and cartilage itself (humeral periarthritis), pain affects the shoulder joint, sometimes the area between the shoulder blades and the bone itself. They are sharp and intensified at night. The disease is accompanied by slight swelling of the shoulder, elevated temperature in the range of 37–37.4ºС, and limited circular movements of the shoulder. The pathology is widespread and is diagnosed as a consequence of injuries, bruises, and increased loads on the shoulder joint.
With inflammation of the cervical muscles (myositis), caused by overstrain or infection, severe pain affects the entire cervical-brachial region, radiating to the scapula, occipital region, and arms.
Muscle pain in the scapula area occurs due to physical strain or impact on the bone.
Pain due to malignant lesions of the bone structure or soft tissues refers to the initial manifestation of the disease. At first, they do not differ in intensity and appear periodically, which makes timely diagnosis difficult. The development of pathological processes leads to an increase in the severity of negative sensations that haunt a person even at rest, mainly at night. Not eliminated by non-narcotic analgesics. Next, the bone becomes deformed, the surrounding tissues swell, the skin over the malignant focus changes, and fractures occur that are not associated with trauma.
In the presence of an inflammatory process in the bone (osteomyelitis) caused by streptococci, staphylococcus, salmonella, E. coli and other infectious agents, the patient is exposed to high fever, chills, and increased heart rate. There are complaints of back pain in the scapula and muscles, which decrease when the abscess is opened.
Please note! Painful manifestations under or above the left shoulder blade and in the bone area are inherent in congenital anomalies. These include aplasia (absence of an organ), hypoplasia (insufficient bone development), pterygoid scapula, and Sprengel's disease. At the same time, a person often suffers from cosmetic defects and limited motor activity.
Intervertebral hernia and protrusion of the discs of the cervical spine lead to compression of the nerve roots by bone formations, which causes pain when moving, especially when tilting the head.
FAQ
In what cases does pain radiate to the shoulder?
With cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, it begins in the neck and extends to the shoulder girdle and arm.
Why might shoulder pain occur during pregnancy?
As a woman's body prepares for childbirth, the ligaments and tendons relax. This happens not only in the pelvic area, through which the fetus passes during childbirth, but throughout the entire body. This includes the shoulder joint becoming slightly unbalanced. With light loads, it may become sore. This is not dangerous.
With adequate conservative therapy, the patient can be relieved of pain, achieving complete recovery or stable remission. In medicine they know how to do this.
Literature:
- Belyaev A.S. Principles of treatment of myofascial pain syndromes / A.S. Belyaev, O.M. Maslova, I.V. Eliseeva // Manual medicine. 1994. No. 7. pp. 24-25.
- Mironov S.P. et al. Shoulder pain syndrome: monograph. Volgograd: VolgMU Publishing House, 2006. 287 p.
- Campbell CC, Koris MJ Etiologies of shoulder pain in cervical spinal cord injury. Clin-Orthot. 1996. 322(2). 140-145.
Sign up for a free initial appointment