By the frequency, rhythm and strength of oscillatory blood beats, one can judge a person’s physical health as a whole, record dangerous cardiac disorders, and determine the effectiveness of sports training. Changes in heart rate are symptoms of many life-threatening conditions and diseases, so it is important to know physiological norms. They are different for people of different ages.
Why is the pulse called arterial?
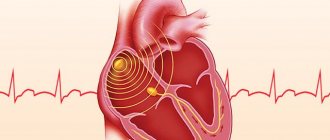
The arterial bed receives the entire volume of blood that is pushed out by the heart chamber at the time of contraction. The periods of systole - an increase in pressure as blood comes out - are accompanied by rhythmic beats. The subsequent stages of relaxation of the myocardium for new filling with blood - diastole, make it possible to determine the frequency and strength of these impulses. The oscillations made by the arterial walls are called the pulse. Damage to these vessels, especially large ones, is the most dangerous, as they are accompanied by massive rapid bleeding.
The stronger the pulse beats, the greater the blood flow through the arteries, the more active the oxygen supply to internal organs and overall metabolism. The main “impact” force is provided by the walls of the left ventricle of the myocardium. The following pulse characteristics are important:
- frequency;
- rhythm;
- speed;
- voltage.
Violation of one or more points indicates acute or chronic pathology. Changes in pulse intervals, for example, are a sign of cardiac arrhythmia. An increase or decrease in speed indicates hypertension or a hypotonic state.
Causes of arrhythmia and methods of prevention
Disturbances in normal heart rhythm in adults occur for the following reasons:
- age-related changes;
- bad habits;
- stressful situations, psycho-emotional stress;
- lack of physical activity or its excess.
To maintain cardiovascular health, it is important to lead an overall healthy lifestyle. Experts say walking at an average speed is the most beneficial for the heart. Unlike running and other intense exercises, you can do walking for a long time without feeling very tired. While walking, there is no significant increase in heart rate, so this exercise is suitable even for people with heart disease.
How to measure your pulse correctly
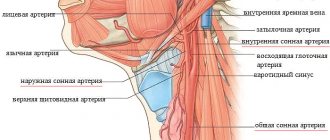
Wave-like fluctuations in the blood are clearly noticeable when touching certain parts of the body. Those under the skin of which large arterial vessels are located. To measure the frequency and assess the rhythm of the pulse, you should apply your fingers: fixing them at one point quite tightly, but without strong pressure. Areas to check for pulsation:
- carotid artery: a point on the front surface of the neck, on the right, under the jaw;
- radial artery: on the inside of the wrist of the left or right hand;
- temporal artery: on the side of the left or right temples;
- brachial artery: on the inner surface of the elbow;
- popliteal: in the area of the popliteal folds of the legs;
- femoral: at the junction of the pelvis and lower limbs.
The measurement accuracy is the same for all methods. The most popular methods remain recording the pulse on the wrist or neck. To calculate its frequency, it is important to use a stopwatch or electronic timer. Applicable time interval: 1 minute. It is necessary to measure at rest, preferably before eating: for example, after waking up or during a period of rest.
The rhythm and force of the beats cannot be assessed without the use of special instruments. But with the manual method, sudden changes in the nature of the pulsation are noticeable. Normally, it is measured, at equal intervals, without acceleration or fading. If the blood impulses are poorly palpable, too weak or uneven, this is an unfavorable sign. You should undergo a detailed diagnosis.
Slow and fast heartbeat
The heart muscle can contract at an increased (tachycardia) or decreased (bradycardia) rhythm. If the pulse does not correspond to the norm, there is no need to immediately sound the alarm: the reason may be not only in pathology, but also in the physiology of the female or male body. Thus, some increase in heart rate is observed when women reach menopause, or when estrogen levels decrease; slowing of the pulse - when taking certain medications.
Various physical and mental stress affect the heart rate, even the difficult digestion process after a heavy holiday dinner and the use of energy drinks. Typically, physiological causes of abnormal heart rate are temporary. After 45 minutes, the pulse readings can return to normal.
Record your heart rate readings on both hands - this will allow you to get more accurate data when measuring this indicator manually.
Clinical practice shows that the pulse often increases when the nervous system is damaged, cardiac pathology, or hormonal system disorders. It is possible that with high readings a tumor or some kind of infection develops in the body.
The pulse slows down if the body experiences intoxication, peptic ulcer disease, or increased intracranial pressure, myocardial infarction develops. Perhaps this signals a lack of thyroid hormones, organic damage to the heart, or poor oxygen supply to tissues.
Only a specialist can answer the question why your pulse is too fast or too rare. In any case, consult a doctor immediately if your pulse is abnormal:
- dyspnea
- my head is spinning
- fainting or presyncope
- heart pain
- vision problems
When playing sports, it is important to regularly measure your pulse.
What heart rate is considered normal?
The current general standard for beats per minute readings for healthy people is 60–80. These are numbers for determining your resting heart rate. As a rule, they correspond to the heart rate. Many doctors find it necessary to expand this range by adding 10 units to the extreme values. That is, define as the norm indicators from 50 to 90 beats per minute. This scatter is explained by physiological differences between people and the characteristics of the heart and blood vessels in different age groups. In addition, normal heart rate depends on lifestyle. For athletes and simply physically active people, it is slightly higher than for habitually calm people. Women's indicators also differ upward.
The pulse rate invariably increases during physical activity, acute stress, and nervous tension. This is a normal reaction of the body. When activity and exposure to external factors decrease, the heart gradually normalizes contractions. For healthy people, the period of return to normal heart rate is no more than 10 minutes. In the presence of pathologies, especially endocrine or cardiovascular ones, increased pulsation persists longer. Unreasonable disturbances in a state of rest should cause severe anxiety. The periodic appearance of bradycardia, tachycardia and other disorders may be the primary sign of ischemia, hypoxia, intoxication and other dangerous conditions.
In pregnant women, the pulse rate is closer to the upper limit: 80–90 beats. This is explained by the pressure of the growing uterus on the diaphragm and changes in hormonal levels. Overweight people also experience increased heart rate. And obesity often provokes the development of tachycardia due to the high load of body weight on the blood vessels and heart.
Children have different heart rates than adults. In infants, it reaches 140 beats per minute, gradually decreasing as the body develops. By the age of 6, the heart of preschoolers beats with a force of 100 beats, and by approximately 16 years it reaches the level of adults.
General heart rate norms by age:
- first month of life: 110–140;
- up to 1 year: 100–130;
- up to 2 years: 95–120;
- in children 3–8 years old: 93–110;
- from 9 to 12 years: 65–100;
- from 13 to 16 years: 60–95;
- from 17 to 20 years: 60–90;
- from 21 to 40 years: 60–90;
- from 40 years old: 60–85.
The given indicators are reliable for a state of rest. In women and men, the average heart rate differs slightly. They are more influenced by the individual characteristics and lifestyle of people.
Rhythm
Normally, the intervals between heartbeats should be the same. This pulse is called rhythmic. Normally, a person should not feel the heartbeat at rest. If you can feel your heart beating, the person may have an arrhythmia.
It is manifested by the loss or appearance of extra beats, an increase or decrease in the intervals between them. With arrhythmia, the heart seems to freeze or, conversely, begins to beat too quickly. Arrhythmia can be determined using an ECG.
The most commonly diagnosed are extrasystolic arrhythmia (extrasystole) and atrial fibrillation.
Extrasystolic arrhythmia is the appearance of extra heart contractions. Patients complain of a feeling of cardiac arrest, weakness, and dizziness. This phenomenon is typical for a number of diseases. These include cardiac malformations, VSD, and ischemia. Extrasystoles may indicate the presence of pathologies of internal organs and occur due to abuse of tobacco products. Isolated occurrences of extra heartbeats occur in healthy people, but regular extrasystoles are a reason to consult a doctor. Atrial fibrillation or atrial fibrillation is characterized by a pulse deficit. With this pathology, the heart rate does not coincide with the pulse. Atrial fibrillation is caused by chaotic twitching of the atria. Because of this, the ventricles of the heart cannot contract synchronously and at the same rhythm.
Atrial fibrillation can be episodic, long-term or chronic. If the pathology occurs sporadically, it may go away on its own. People with long-term (more than a week) and chronic atrial fibrillation require drug therapy - taking beta1-blockers. Also, a special procedure is used to restore the heart rhythm - ablation or ablative destruction. It involves applying electric current to the pathological area.
For severe arrhythmia that cannot be treated, the patient is advised to undergo surgery to install a pacemaker or portable defibrillator.
What is maximum heart rate?
Maximum heart rate is the highest heart rate during physical activity. You can calculate your estimated maximum heart rate using the formula: 220 - your age = maximum heart rate.
Photo: istockphoto.com
For example, for a 40-year-old person the rate will be 180 beats per minute. This is the simplest, but also the least accurate method of calculation: it does not take into account gender, the presence of diseases and other characteristics. There are more complex formulas, but the most reliable method is to undergo a medical test using special equipment.
How to correctly calculate your heart rate zone and why know it?
What to do if your heart rate is high
High heart rates are called tachycardia. If you suddenly feel suffocation and heaviness in your chest while walking, stop and take a deep breath. If attacks occur frequently and are not associated with increased physical activity, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
In the event of a sudden attack of tachycardia, call an ambulance, and take a comfortable position, try to relax and breathe deeply. Before the doctor arrives, you need to open the windows in the room, unfasten the clothes that are compressing the sternum and put a cold compress on your head.
To prevent heart problems, give up cigarettes and other bad habits in favor of an active lifestyle.
Normal heart rate in adolescence
During adolescence, women's heart rate per minute is lower than that of girls, but still higher than that of an adult. The reason for a high heart rate is hormonal changes due to puberty and the size of internal organs that have not yet reached adult size.
Moreover, in the age range from 10 to 11 years, girls’ hearts can beat faster than boys’ hearts at that age. This is due to the fact that girls experience hormonal changes earlier than boys.
Table No. 3. Normal heart rate for teenagers:
| Teen age | The norm for girls | Norm for boys |
| From 10 to 11 years | 70–130 | 68–108 |
| From 12 to 13 years | 70–130 | 70–124 |
| From 14 to 17 years old | 60–110 | 60–114 |
Pulse and features of its measurement
The pulse is the echo of the contraction of the heart; it can be felt in the form of shocks in the large vessels of the human body, regardless of the person’s age, whether he is a few minutes from birth or 60 years old.
For correct diagnosis of heart rate, the correct measurement is important:
- In children, it is better to measure heart rate in the armpit, by palpation of the carotid arteries and at the temples.
- In adults, measurements are most often taken on the hands and in the hollow of the elbow.
When measuring your pulse, you should adhere to several rules and measure during the calmest periods.
Table No. 1. When to and when not to measure your pulse:
| Favorable moments for measurement | Not favorable moments for measurement |
| At rest, immediately after waking up from sleep | Moments of physical activity |
| State of emotional peace | Emotional tension, excitement - joy, laughter or anger, anger, crying. |
| Before meals, or 1.5 hours after meals | During meals or immediately after meals |
| After visiting a too cold place, for example, a street, or after visiting a very warm place - a bathroom, bathhouse. |
Important: for greater accuracy, measurements can be taken on each “half of the body,” for example, on both arms or both carotid arteries.
The best methods for feeling heartbeats
If a person does not suffer from arrhythmia, then it is enough to count for 30 seconds, and then multiply the result by a factor of 2. An even faster way is to take the measurement for 15 seconds, and then multiply by 4. If there is an arrhythmia, the measurement will have to be taken for a whole minute.
To measure in our time, you can use not only the usual method - palpation of a large vessel, but also modern methods - wearable heart rate trackers, a device for measuring blood pressure.
The photos and videos in this article will show how to correctly measure the heart rate of a little girl and an adult woman.
Normal for women
Walking for ladies is an extremely useful activity. It improves well-being, lifts your mood, and promotes weight loss. Useful for expectant mothers as it provides an additional supply of oxygen.
The normal heart rate when walking in middle-aged women (20-45 years old) is 100 – 125 beats/min. At rest, 60-100 beats/min are considered normal.
Please note that if regular observations show that the values are within the normal range, but are always within the upper limit, this is not a good sign. Especially if other “bells” are observed - pain in the sternum, shortness of breath, dizziness, and other painful sensations. If a woman’s normal pulse rate is regularly exceeded while walking, it is advisable to make an appointment with a therapist who will provide referrals to specialists.
However, high pulse rates do not always signal illness. Often this is just a consequence of a sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise. Start practicing walking without extreme stress. Gradually increase the speed and duration of the session, constantly monitoring your pulse value. As soon as the latter exceeds the norm, slow down, calm down, then continue. Over time, the body will certainly get stronger.
How to calculate the optimal heart rate zone?
Your maximum heart rate helps you determine your optimal heart rate zone for exercise—keeping your heart rate within this range during exercise will help you achieve the best results and reduce the risk of injury. All other things being equal, the optimal heart rate zone for a healthy person is 60-80% of the maximum heart rate. However, in some cases, the doctor may recommend staying within 50%. And if we are talking about high-intensity training, such as HIIT, the optimal zone can move up to 85%.
Photo: istockphoto.com
To check if you're exercising in your optimal heart rate zone, stop and take your heart rate. If it is below optimal, increase the load. For convenience, you can use smart watches or special fitness bracelets: some of them help track not only your heart rate, but also other indicators, such as the number of calories burned.