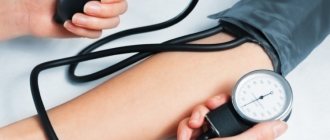
If you have hypertension, it is very important to learn how to independently determine your blood pressure. This will help keep the disease under control and promptly seek help for a hypertensive crisis. The main method of self-monitoring for hypertension is regular monitoring of changes in blood pressure (BP).
Let's talk about how blood pressure is measured. Are you sure you know how to do this correctly? After all, before starting a measurement, some preparation is needed so that the results are always correct.
How to choose and determine the most accurate blood pressure monitor? A person with hypertension should always have it on hand.
What equipment do I need to measure my blood pressure?
To measure blood pressure at home, you can use dial and digital tonometers. A dial tonometer has a scale with divisions, as well as an arrow, with the help of which the pressure is determined. There is a cuff and a pressure bulb. The cuff is placed on the surface of the shoulder and a pressure above the expected systolic pressure is created in it using a rubber pressure bulb. The tightness of the cuff is assessed as follows: a finger should pass between the cuff and the surface of the shoulder. A digital tonometer can have either a manual or an automatic bulb. The measurement results of such a tonometer are displayed on a small screen. Choose which type of blood pressure monitor best suits your needs.
What are the pros and cons of a dial tonometer?
One of the advantages of such a tonometer is that it can be easily moved from one place to another. In addition, a stethoscope is already built into the cuff, which means you do not have to additionally purchase a separate stethoscope. The dial tonometer does not require very careful treatment. He may also have a special device with which you can put the cuff on your arm even with one hand. And on top of that, a dial tonometer is cheaper than a digital one.
But the dial tonometer also has some disadvantages. First, it is a complex device that can easily break, resulting in inaccurate measurements. This device is quite difficult to use unless it has a special device - a metal ring - that makes it easier to put on the cuff. The rubber bulb used to apply pressure to the cuff may be difficult to inflate. In addition, such a tonometer is not suitable for people with impaired hearing, since when using it it is necessary to listen to sounds through a stethoscope.
What are the pros and cons of a digital blood pressure monitor?
A digital blood pressure monitor is automatic, which is why it is a more popular device for measuring blood pressure. The measurement results are easy to read as they are displayed on the screen. Some electronic tonometers have a built-in printer with which you can print the results of the measurements.
A digital tonometer is easier to use than a dial one. With such a tonometer, the stethoscope and the measuring device itself are connected into a single device, and the measurement results are easy to read. There is also an indicator indicating an error. After the measurement, the air is automatically released from the cuff. The cuff can be inflated either automatically or manually, depending on the model. This tonometer is suitable for people who are hard of hearing, since when using it there is no need to listen to sounds through a stethoscope.
The disadvantage of a digital tonometer is that the accuracy of the measurements varies with different body movements and arrhythmias. In addition, this tonometer requires batteries. Some models are made in such a way that they can be used to measure pressure exclusively on the left hand. This makes them difficult to use for some people. In addition, digital blood pressure monitors are expensive.
Can I use a finger/wrist monitor?
Studies have shown that finger/wrist blood pressure monitors measure blood pressure very inaccurately. They are very sensitive to posture and body temperature, and, in addition, they are much more expensive than other types of tonometers.
Professional devices measuring eye pressure
Measuring intraocular pressure is a mandatory step in any ophthalmological examination. To accurately determine this indicator, an eye tonometer is used. The principle of operation of any of its varieties is based on measuring the level of deformation of the eyeball under the influence of a strictly dosed external factor.
Using this device, the doctor quickly, accurately and painlessly performs the studies necessary to make a diagnosis. The use of a tonometer does not create any discomfort even in patients with increased sensitivity of the cornea.
How to choose the right tonometer
Details you need to pay attention to when purchasing a tonometer:
- It is very important to choose the correct cuff size. Ask your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist what size cuff you need based on your arm size. Your blood pressure readings may be incorrect if your cuff size does not match your arm size.
- The numbers (measurement results) should be easy to read on the display. You should be able to see them clearly.
- If you are using a stethoscope, you should be able to hear sounds through it.
- Price is also an important factor. Since now the prices of different models of tonometers vary greatly, you have the opportunity to take a closer look at their prices and quality, and, by comparing all this, make the right choice. The most expensive models and the accuracy of their measurements may not be better than cheaper ones.
How can I make sure that my blood pressure monitor is accurate and that I am using it correctly?
Once you buy a blood pressure monitor, take it to your doctor to check how accurate the measurements are. You should check your blood pressure monitor once a year. Careful use and storage are also necessary. Make sure that the screw valve on the bulb is closed at the time of purchase, and keep it (the bulb) away from fire and hot objects. Check the pear periodically for cracks and holes.
Ask your doctor or nurse to teach you how to use the blood pressure monitor correctly. Using a blood pressure monitor correctly will help you and your doctor achieve good results and monitor your blood pressure regularly.
Understanding medical terms.
- Blood pressure is the force with which blood presses on blood vessels.
- Hypertension is an increase in maximum blood pressure above 130 mmHg. Art.
- The brachial artery is a blood vessel that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. You measure the blood pressure in this artery.
- Systolic pressure is the maximum pressure observed during systole, the moment when blood from the heart is ejected into the aorta.
- Diastolic pressure is the minimum pressure observed during diastole, when the heart “rests”.
- Normal values exist for both systolic and diastolic pressures. Normal blood pressure is 120/80, where the first number is the systolic pressure and the second is the diastolic pressure.
What do I need to do before taking my blood pressure?
- Relax and rest for 3-5 minutes before measuring your blood pressure. Do not speak.
- Find a comfortable position with something to support your back.
- Place your hands on the table so that they are at heart level and sit quietly.
- Wrap a properly sized cuff around the top of your bare arm. The cuff should completely encircle your arm, but your finger should fit comfortably between it and the surface of your shoulder.
- Make sure the bottom edge of the cuff is 1 inch (2.5 cm) above your elbow.
How to use a dial tonometer?
- Wrap the cuff around your arm.
- Insert the stethoscope tubes into your ears.
- Position the head of the stethoscope so that it is on the inside of your arm above the elbow.
- By quickly pumping the bulb, create a pressure in the cuff of 30-40 mmHg. Art. exceeding the systolic pressure value obtained at the previous measurement. You definitely need to download quickly. If you pump the bulb slowly, the result will be inaccurate.
- Gradually slightly opening the screw valve on the bulb (at a speed of approximately 2-3 mm/sec), release air from the cuff, thereby reducing the pressure in it. If you release the air too quickly, the pressure cannot be determined.
- The pressure in the cuff gradually decreases. At a certain pressure, a clear sound appears - a vascular tone. Using a tonometer, the pressure in the cuff is noted at the moment the tone appears and is taken as systolic.
- As the pressure in the cuff decreases further, the sound becomes louder, and then either sharply muffles or disappears. The pressure that the tonometer needle shows at this moment is taken as diastolic.
- Record your measurements. Example: 120/80, where the first number is the systolic pressure value, and the second is the diastolic pressure.
- If you want to repeat the measurement, wait 2-3 minutes until all the air is completely deflated from the cuff.
Ophthalmotonus - why is it so important?
A change in ophthalmotonus should be considered an alarming symptom that indicates pathological processes in the functioning of the visual organs.
Increased intraocular pressure is a consequence of disturbances in the outflow of fluid that is located under the membrane of the eye. Circulation becomes impossible due to the presence of plugs in the tubules that drain fluid. Moisture gradually accumulates, which leads to increased pressure on the shell.
High pressure inside the eye causes pressure on the fundus vessels. As a result, the retina is injured and the photosensitive elements die. Compression of the optic nerve is also observed, which threatens to disrupt the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to cells. If this happens over a long period of time, the tissues of the organ atrophy, vision gradually decreases and, as a result, disappears completely.
Reduced ophthalmotonus also indicates the development of pathological processes. Low pressure leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to the organ, due to which the tissues atrophy and the eyes gradually cease to see.
Changes in ophthalmotonus may result from problems in the functioning of certain organs and systems. Thus, high intraocular pressure is often observed in people with heart and vascular diseases, and low intraocular pressure may be a concomitant sign of liver failure or the initial stages of retinal detachment.
How to use a digital blood pressure monitor?
- Wrap the cuff around your arm. Turn on the device.
- In automatic models of digital tonometers, the pressure in the cuff will be created automatically when a button is pressed. Semi-automatic models have a rubber pressure bulb for this purpose. As soon as the required pressure is created in the cuff, the automatic mechanism will begin to gradually reduce it.
- Look at the display to see the result of your measurements. The device will show you your systolic and diastolic pressure values on the screen. Record your measurements. Example: 120/80, where the first number is the systolic pressure value, and the second is the diastolic pressure.
- Press the special button to deflate all the air from the cuff.
- If you want to repeat the measurements, wait 2-3 minutes until all the air is completely pumped out of the bulb.
This article was prepared using information provided by the American Academy of Family Physicians.
Translation from English by Irina Korobkova
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Measuring IOP at home
Patients with glaucoma in extreme stages are advised to monitor eye pressure throughout the day. To perform such measurements, special portable instruments are used. One of them is the ICare device. It helps determine the degree of ophthalmotonus by applying special replaceable sensors to the cornea of the eye.
Among the advantages of this technique are:
- minimal error in the obtained data;
- efficiency of the procedure;
- no negative consequences for the cornea;
- patient comfort during the examination;
- eliminating the risk of infection.
Since the device has a memory function and stores the results of the last 10 measurements, this increases the convenience of monitoring changes.