Are you experiencing back pain and numbness in your limbs? These are the first signs of osteochondrosis. Insufficient mobility in lifestyle, sedentary work, stress on the neck and spine lead to cartilage wearing out, losing moisture, resulting in micro-tears.
With cervical osteochondrosis, degenerative changes occur in the intervertebral discs. Not only the discs are damaged, but also the vertebrae and joints in the cervical region. If the disease is not treated for a long time, the patient’s general well-being worsens: constant headaches, the appearance of a vertebral hernia, deterioration of cerebral circulation, as a result of which cognitive functions decrease.
Reasons for the development of osteochondrosis
An incorrect sitting position, in which the neck is pulled forward, leads to the development of cervical disease. In this case, excessive pressure occurs on the intervertebral discs, which leads to changes in the nuclei pulposus and compression of blood vessels. This is the position a person takes at a workplace in front of a computer. Therefore, office workers are most often exposed to the development of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
In addition, the reasons for the development of pathology may be:
- improper load distribution when carrying bags;
- excessively soft sleeping place (the spine bends in an unnatural shape);
- genetic predisposition;
- lack of vitamins and microelements in the diet;
- endocrine system disorders;
- curvature of the spine and poor posture during active growth of the body;
- cervical vertebrae injuries;
- presence of bad habits.
Possible complications
With osteochondrosis, the development of ventricular types of heart rhythm disturbances, which include tachycardia, is usually observed. Its atrial paroxysmal form is rarely diagnosed. The pathogenesis is based on organic damage to the heart muscle in combination with osteochondrosis. If left untreated, vertebral artery syndrome develops, which causes cerebral circulation disorders in the vertebrobasilar region. And this leads to a decrease in the functional activity of the cardiovascular system.
Stages of the disease
Determining whether your pain symptoms are signs of the development of cervical osteochondrosis and what stage of development of the disease can only be determined by an experienced doctor after examination and palpation. In total, cervical osteochondrosis goes through four stages of development:
- The nucleus pulposus, the central part of the intervertebral disc, undergoes moderate dehydration during the first stage. As a result, the supporting and shock-absorbing functions of the intervertebral discs are gradually lost. During the first stage, you will experience pain with sudden movements, hypothermia, and staying in one position for a long time.
- The second stage of development is characterized by the appearance of congestion and spasms, which compress capillaries and blood vessels, preventing normal blood circulation. As a result, the frame of the intervertebral disc becomes thinner, forming a protrusion (bulging forward or backward). Under the influence of excessive load, osteophytes are formed on the cervical vertebrae - bone growths. Pain sensations are localized in one place; with sudden turns and tilts of the head, dislocations of the cervical vertebrae can occur.
- Extrusions are formed as a result of thinning of the intervertebral discs. The edge of the nucleus pulposus breaks the fibrous ring and extends beyond the edges of the vertebral body. Muscles and nerve endings are compressed. Pain is felt in the neck, back and limbs.
- At the fourth stage of the disease, the intervertebral discs are displaced and central and lateral hernias form. In addition, scars form on the discs, which leads to immobility of the affected joint. The patient experiences persistent back pain that radiates to other parts of the body, a constant feeling of fatigue, and asymmetry of parts of the body occurs.
How to cure panic attacks without medications?
To get rid of anxiety attacks, it is necessary to cure the disease itself, which provoked them. It is not recommended to resort to medications to treat instability of the cervical vertebrae. There are a number of remedies that can alleviate the condition without the use of drugs. This includes manual therapy, massage, therapeutic exercises, etc. To cure cervical osteochondrosis and forget about panic attacks forever, you must remember that the best therapy for this disease is movement.
With properly selected exercises, you can restore nutrition to the vertebrae, disc, and peripheral circulation. It is also recommended to wear a special corset if you have to travel long distances and sit in one place. Through gymnastics and periodic “unloading” of the spine, osteochondrosis can be cured and a natural muscle corset can be created to maintain the neck in the correct position. And then the arteries and veins will not be compressed, and blood circulation in the head will always be sufficient.
We must not forget that panic attacks leave a negative “mark” on the human psyche. Even after complete physical recovery, it is necessary to restore the nervous system in order to gradually return to a normal lifestyle. To treat mental illness, specialists resort to the following types of therapy:
- Cognitive-behavioural. Allows you to understand the nature of symptoms, teaches you to cope with them without the use of medications.
- Relaxation. Teaches various breathing techniques that allow you to quickly get rid of anxiety.
- Supportive. Allows a person to get rid of interpersonal problems that provoked anxiety.
- Group. Offers to get rid of internal pressures and conflicts.
- Family. Psychotherapeutic sessions involve not only the patient, but also his family.
Which treatment is wrong?
Many psychotherapists prescribe medications for people suffering from unexplained anxiety - sedatives, antidepressants, etc. But if you consider that the problem does not arise on its own, it has a clear cause, then such treatment can be very detrimental to health. Such therapy is aimed only at suppressing the nervous system, which is why a person loses his personality and character. And with prolonged use of drugs, he may even become mentally disabled, acquire real mental illnesses that he did not have before. In addition, he becomes dependent on pills, because panic attacks do not go away and continue to plague him. Such treatment is fundamentally wrong, as it causes dependence on medications and a number of other negative reactions of the body, but does not solve the problem itself.
With such a disorder, there is a danger of self-soothing with other stimulants, such as alcohol. The person thus tries to drown out the feeling of anxiety and resorts to various means just to give himself relief. But you shouldn't do this. In this state, it is not recommended to drink drinks containing alcohol at all, as they aggravate the situation and increase the feeling of anxiety. There are often cases when, after treating physiological and psychological problems, it was also necessary to get rid of alcohol addiction.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine manifest themselves differently depending on the stage of development of the pathology. In the early stages it can occur with virtually no symptoms. Pain in the neck and back can only appear if you stay in one position for a long time, sharply bend or turn.
At later stages of development, a crunching sound is heard in the spine, back pain radiates to other limbs, and numbness occurs in parts of the body. When osteophytes and extrusions form, the following occurs:
- headaches in the back of the head and parietal part;
- speech disorders and numbness of the tongue;
- decreased sensitivity of the skin of the neck;
- breathing disorders;
- changes in blood pressure;
- heartbeat disturbances;
- noise and congestion in the ears;
- fainting.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in women are much more pronounced than in men. This is due to the fact that women have a predisposition to vascular diseases and a more fragile structure of the bone segments of the spine. Signs of the disease begin to appear when intervertebral discs change. This leads to disruption of normal blood circulation and causes severe headaches, dizziness, and neuroses. An exacerbation of the disease in women often occurs during menopause, when the body is subject to hormonal changes.
The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men are similar to those in women; erectile dysfunction can be observed separately.
Headache with cervical osteochondrosis is caused by poor circulation in the brain and spinal cord. When the vertebrae become misaligned, they compress the arteries and the oxygen content in the blood decreases. Unfortunately, such pain may not go away even after taking strong painkillers. Therefore, it is important to approach solving the problem comprehensively. Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis may be accompanied by darkening of the eyes and the appearance of tinnitus. This happens because spasming muscles cause a reduction in oxygen supply to the brain.
A lump in the throat with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as well as burning, difficulty breathing and muscle spasms are a common occurrence. The disease provokes compression of the nerve fibers of the cervical spine to the head and neck. Disturbances in nerve impulses cause sore throat.
Due to spasms of blood vessels and irritation of nerve endings, jumps in blood pressure occur. Increased lower pressure in osteochondrosis indicates that the blood supply to certain areas of the brain is impaired, since the vertebral artery is compressed by the intervertebral discs. As a result, oxygen starvation occurs and blood pressure rises.
What to treat first
Tachycardia in osteochondrosis is a concomitant clinical manifestation that disappears after adequate treatment of the underlying disease. When the lumbar pathology worsens, “lumbago” occurs, and when the cervical disease recurs, the person suffers from dizziness and surges in blood pressure. Thoracic osteochondrosis, in addition to tachycardia, is clinically manifested by severe pain in the heart, reminiscent of an angina attack. Therefore, the patient’s well-being can only be improved by simultaneous treatment of pathologies.
Dizziness is one of the signs of osteochondrosis.
How is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine diagnosed?
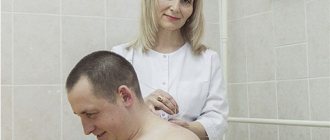
Diagnosis of pathology begins with consultation with a specialist. At the first manifestations of osteochondrosis, consult a rheumatologist, neurologist, surgeon or orthopedic traumatologist. The doctor will ask about the symptoms and the frequency of their occurrence; you need to provide the specialist with a complete medical history and the results of earlier studies (if any). The specialist will conduct a visual examination and palpation, and refer you for tests. During the examination, the doctor pays special attention to neck mobility, muscle tone, skin sensitivity and identifies the most painful areas.
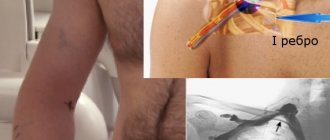
To identify the condition of muscles, ligaments, blood vessels, and to detect inflammatory processes or tumors, an informative and safe diagnostic method is prescribed - MRI of the cervical spine. During an MRI of osteochondrosis, the patient lies on a special sliding table with his back. Rollers are placed on the patient's head to relieve muscle tension, and the limbs are secured with belts. Any slight movement during the procedure can affect the quality of the result. Next, the table moves into the tomograph area. The procedure does not cause pain. The tomograph makes a lot of noise during scanning, so you can use headphones to avoid discomfort.
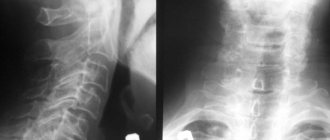
If MRI is contraindicated, there are other diagnostic methods such as computed tomography and radiography. X-ray is suitable only for primary diagnosis and does not provide a layer-by-layer image of the affected tissue. However, this study is the simplest and most economical, allowing you to examine the patient’s body in several projections. Due to the strong radiation exposure to the body, radiography cannot be performed frequently.
During a computed tomography scan, a scan is performed using one or more beams of ionizing rays. They pass through the human body and are recorded by detectors. The detectors move along the patient's body in opposite directions and record up to 6 million signals. The image displays tissues of different densities with precise definition of the boundaries of organs and the affected areas in the form of a section. The procedure allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image.
Which doctor should I contact?
Most patients with complaints of palpitations turn to a cardiologist, and sometimes a therapist. These doctors prescribe all necessary diagnostic tests, including x-rays. Based on its results, a diagnosis is made and the patient is sent for further treatment to a vertebrologist or neurologist.
Osteochondrosis is treated by a vertebrologist.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is used only in the acute phase of osteochondrosis and when other treatment methods are ineffective.
At the height of the disease, painkillers are prescribed, as well as drugs that speed up metabolic processes. Both medications in the form of tablets and injections help.
Groups of medications prescribed:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which also relieve pain. Available in the form of cream, tablets and ampoules for intravenous or subcutaneous administration.
- Vasodilators. During muscle tension and severe pain, vasoconstriction occurs, as a result, blood pressure may increase and oxygen supply to the brain may become difficult. Vasodilators bring vascular tone back to normal.
- Muscle relaxants. This group of drugs is designed to relax and soothe tense muscles. This effect triggers a chain of beneficial changes such as improved blood circulation, regulation of vascular tone and relief from pain. When blood flow is normalized, damaged tissues are restored faster.
- Chondroprotectors and B vitamins. These are drugs that restore cartilage tissue, stopping the destruction process.
- Complex of sedatives. The stress of pain makes the pain worse. Irritability and anxiety trigger the sympathetic nervous system into action, which leads to even greater tone of muscles and blood vessels. Sedatives and sometimes antidepressants can break this vicious circle.
As you can see, the treatment of osteochondrosis needs to be approached comprehensively, having studied all the nuances. It’s best to turn to specialists, thereby protecting yourself from mistakes.
Reflex signs
Symptoms:
- respiratory disorders such as a feeling of lack of air, pain during inhalation and exhalation, difficulty breathing;
- feeling of chills, “goosebumps”;
- feeling of disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, loss of appetite, heartburn, diarrhea or constipation, bloating;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- pain in the chest of a girdling nature, between the shoulder blades, during bending and straightening;
- insomnia, feeling tired with enough sleep, fatigue;
- stiffness of movement in the morning;
- worsening gait;
- irritability;
- decreased libido/potency.
Reflex symptoms are more vague than radicular ones and are often misunderstood by doctors. Therefore, it is very important to find a competent doctor who will take the patient’s complaints seriously and prescribe the correct treatment for thoracic osteochondrosis, especially during an exacerbation.