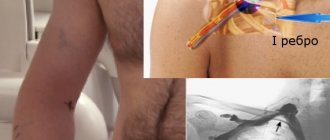
X-ray image of a patient with osteochondrosis.
Cervical osteochondrosis is often accompanied by signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia. These are paroxysmal or constant rapid heartbeat, increased sweating, dizziness, and fainting. The intensity of the symptoms of VSD and the nature of the course of cervical osteochondrosis are interrelated. During relapses of degenerative-dystrophic pathology, the severity of functional disorders increases significantly.
The relationship between VSD and cervical osteochondrosis
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is not an independent disease, but a set of symptoms that accompany the course of any systemic pathology. This term refers to a disorder in the regulation of homeostasis by the autonomic nervous system, expressed in changes in blood pressure, heart rate, heat transfer, and the functioning of internal organs.
VSD also occurs with cervical osteochondrosis against the background of compaction and flattening of the intervertebral discs, instability of the vertebral bodies, weakening of the muscles and ligamentous-tendon apparatus. There is a gradual involvement in the destructive process of vascular and nerve trunks localized in the area of damaged vertebral structures.
Sleep disturbances are a common sign of osteochondrosis.
The spinal roots are irritated and injured when they are pinched:
- bone growth (osteophyte);
- displaced disk;
- muscle spasm;
- inflammatory edema.
Irritation of sensitive nerve endings leads to spasm of the arteries, insufficient blood supply to the brain with oxygen and nutrients. Neuronal ischemia provokes a disruption in the production of hormones - biologically active substances that regulate the functioning of the peripheral nervous system. This becomes the reason for the disruption of its work and the appearance of symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Vascular dystonia and salt deposition: cause and effect
With VSD and cervical osteochondrosis, the painful symptoms are similar. To choose an effective treatment, it is necessary to correctly determine the root cause of the disease.
- It is possible that the main diagnosis of a sick person is vegetative and vascular disorders. At the same time, he leads a sedentary lifestyle (at school, work and at home). In this situation, already at school age the child develops osteochondrosis (usually in the cervical spine). In this case, it is necessary to treat two diseases separately. Prescribe medications that regulate the activity of the nervous system, vitamins to nourish nerve tissue, as well as physical therapy, active movements (to accelerate blood flow and dissolve salt deposits). In some cases, when the destruction processes are advanced, chondroprotectors are prescribed (to restore cartilage tissue). Manual therapy is also indicated.
- If the patient’s main diagnosis is osteochondrosis of the neck, then symptoms of VSD can develop against the background of impaired cerebral blood supply and improper transmission of nerve impulses. In this case, there is no need to treat vascular dystonia with traditional neuroprotectors. Treatment of the underlying disease – osteochondrosis of the neck – is necessary. Moreover, as the condition of the cervical vertebrae improves, the painful symptoms will go away on their own.
Now let’s take a closer look at how VSD and salt deposition are similar, and how to differentiate them (distinguish them from each other).
Reasons for appearance
One of the main reasons for the development of cervical osteochondrosis is the natural aging of the body, accompanied by a slowdown in recovery processes. Systemic diseases, for example, gout, deforming osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, can provoke the destruction of intervertebral discs. Osteochondrosis develops against the background of a sedentary lifestyle, excessive physical activity, endocrine and metabolic disorders, congenital or acquired skeletal abnormalities. And the prerequisites for the appearance of characteristic symptoms of VSD are the following factors:
- frequent stressful situations;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- drinking alcohol, coffee;
- deficiency of microelements, water- and fat-soluble vitamins in food;
- sudden change in weather;
- respiratory, gastrointestinal infections;
- injuries.
Excessive mental stress leads to VSD.
The likelihood of functional disorders increases in people with certain personality and character traits. As a rule, they tend to experience ordinary everyday conflicts acutely. Such people initially have increased anxiety and suspiciousness.
The main clinical forms of neurotic conditions (general neuroses):
Neurasthenia (so-called exhaustion neurosis)
It is characterized by a combination of increasing irritability and excitability with increased fatigue and rapid exhaustion.
Hysteria
A pathological form of a person’s reaction to a situation that is unbearable or unacceptable for some reason. Such patients are distinguished by particular suggestibility and self-hypnosis with a clear tendency to “flight into illness”; noticeable demonstrativeness (with wringing of hands, lamentations, etc.; theatrical behavior in search of sympathy and attention from others. The clinical picture of hysteria can imitate almost any somatic or neurological disease. However, it should be borne in mind that serious organic diseases can also be hidden under the mask of hysteria central nervous system (up to a brain tumor) Therefore, seeing a doctor if you have the above signs of the disease is a prerequisite.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder
Obsessive thoughts, memories, doubts, fears, actions and desires against a background of low mood with a feeling of inferiority and hopelessness.
Most often it develops against the background of neurological and somatic diseases.
Clinical picture
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations. Their large number is due to the disorder of all basic vegetative functions - breathing, blood supply, sweating, urination, digestion, peristalsis. In most cases, symptoms of VSD occur with cervical osteochondrosis of grade 2, 3, when changes in the vertebrae and discs have become irreversible. Often, complications of the disease—protrusions, hernial protrusions, discogenic myelopathy—lead to functional disorders.
Cardiac symptoms
Most often, VSD is clinically manifested by tachycardia - an arrhythmia characterized by a heart rate of more than 90 beats per minute. There are sensations of interruptions in the functioning of the heart, its freezing, vascular pulsation not only in the back of the neck, but also in the legs and arms.
One of the leading symptoms of VSD is pain in the cardiac region. It can be acute, but more often it is dull, aching, pressing. Diadynamic functional disorders are also noted. Blood pressure increases or decreases, blood and lymph circulation is disrupted.
Pain in the heart area.
Respiratory system
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is characterized by respiratory symptoms that occur against the background of dysregulation of the respiratory system. Tachypnea (rapid breathing), sensations of lack of air, heaviness, congestion in the chest, and severe shortness of breath, which resembles an attack of bronchial asthma, are observed. A patient with cervical osteochondrosis has difficulty in fully inhaling and exhaling.
Nervous system
The psychoneurological symptoms of VSD are so pronounced that they often lead to panic attacks - sudden attacks of unmotivated fear, increased anxiety, and restlessness. In severe cases, patients are diagnosed with depression. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is manifested by lethargy, weakness, and rapid fatigue with minor exertion.
Patients become irritable, tearful, and mental and physical performance decreases against the background of psycho-emotional instability. Gradually, they develop weather dependence, often experience headaches, and experience a disorder in the change of phases of sleep - it becomes superficial and restless.
Panic attacks, irritability, tearfulness are symptoms of pathology.
Other symptoms
A disorder of the autonomic system makes undesirable adjustments to the functioning of almost all human life systems. Symptoms of VSD rarely appear in isolation. More often they are combined with each other, which significantly worsens the patient’s well-being and complicates diagnosis.
| Autonomic disorders | Characteristic signs |
| Thermoregulation disorders | Body temperature is labile - it rises during the day to 38 °C, and then decreases to 35 °C. The patient feels chilly, and then suffers from fever and excessive sweating. Thermoregulatory disturbances may occur from time to time or become permanent |
| Digestive and peristaltic disorders | They manifest themselves as dyspeptic, dyspeptic disorders - attacks of nausea and vomiting, belching, pain in the epigastric region, increased gas formation. Constipation or diarrhea is common |
| Genitourinary disorders | Sexual desire persists against the background of anorgasmia. In the absence of any pathologies of the urinary tract, the urge to empty the bladder becomes more frequent and urination becomes painful |
Types and types of panic attacks
Panic attacks are divided into the following types depending on the nature of their manifestation:
- Vegetative. They have pronounced symptoms - chills, trembling of the limbs, rapid heartbeat, heavy sweating, pain and dizziness in the head, etc.
- Phobic. Anxiety arises in a specific place or in a specific situation.
- Hyperventilation. This type is characterized by symptoms such as shortness of breath without physical exertion and painful sensations in the muscles.
- Conversion. The person loses his voice, and pain occurs in the left side of his chest. He may lose consciousness or be on the verge of it. At the same time, he is tormented by thoughts of death.
- Affective. The patient's mood changes, depression and inexplicable melancholy occur. Physically, you feel tired and exhausted.
- Senestopathic. “Goosebumps” are felt throughout the body, tingling and numbness occur in the limbs.
- Depersonalization-derealization. A person feels disconnected from reality and the world around him. Or it seems to him that everything around him is not happening for real.
Types of panic disorders depending on the situation:
- Spontaneous. Anxiety arises “out of the blue”, without any obvious reason.
- Situational. Panic is felt during a specific situation. This may be a premonition of a quarrel, conflict, before taking an exam, in the event of real dangers, threats to life and health.
- Conditional-situational. Symptoms appear due to the influence of any “activators” on the body. This includes taking hormonal pills, drinking alcohol, using drugs, drinking strong tea or coffee.
Diagnostics
It is very difficult to identify VSD due to the large number and variety of symptoms. Therefore, its diagnosis consists of differentiating pathologies with a similar clinical picture. Patients must be referred for consultation to a neurologist, cardiologist, or endocrinologist. Characteristic signs of cervical osteochondrosis are detected using x-ray examination.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine on x-ray.
Family history is of no small importance when making a diagnosis. The development of VSD in a patient with parasympathicotonia is suggested by the presence of bronchial asthma, ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, and neurodermatitis in close relatives. If sympathicotonia is suspected, indirect confirmation of the diagnosis is the identification of hypertension, coronary heart disease, hyperthyroidism, and diabetes mellitus in family members.
When conducting diagnostics, the initial autonomic tone and indicators of autonomic reactivity are assessed. To do this, patients' complaints are analyzed, the results of an electrocardiogram and electroencephalography of the brain are studied.
How it manifests itself: symptoms of a panic attack during VSD
The first symptoms of a panic attack during VSD appear in the form of an increase in feelings of anxiety, fear, and obsessive thoughts. Then adrenaline is released into the human blood. A vascular crisis begins - the muscle wall spasms, the lumen of capillaries, arterioles and arteries narrows. The brain does not receive enough oxygen, glucose and other nutrients. As a result, a full-fledged clinical picture of a panic attack with VSD develops:
- increased heart rate up to 110 – 130 beats per minute;
- breathing becomes shallow and frequent;
- there is a feeling of suffocation and lack of air;
- blood pressure levels increase;
- fear of death appears;
- the muscles of the body, upper and lower extremities weaken and cannot be controlled;
- cold sweat appears.
How a panic attack manifests itself during VSD depends on the type of crisis, the trigger that provoked it and the general health of the patient. With a weakened immune system, in a state of convalescence after a protracted illness, a panic attack is less pronounced and much easier to tolerate.
What to do when you have a panic attack
During an attack, it is not informative to measure blood pressure or heart rate, since during a panic attack they are far from normal. You should lie down and take a comfortable body position. Doctors recommend smiling despite fear. There is a connection between the facial muscles and the brain, so your health will soon improve.
It is recommended to use deep breathing techniques. You need to hold the air for a couple of seconds, and then exhale smoothly, slowly. You also need to squeeze the “anatomical snuff box” for one minute. This is the name of the hole that forms at the base of the thumb of the left hand when it is raised.
"Anatomical snuff box".
Symptoms of VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a disease of the human nervous (or, in medical terms, autonomic) system. It is formed due to incorrect transmission of neurological impulses and, as a result, an incorrect reaction of vascular tissue to loads and stress. In this case, either the vessels are constantly in a tense state (this is VSD of the hypertonic type with an increase in pressure), or the walls of the vessels are constantly relaxed (this is VSD of the hypotonic type with a decrease in pressure). As a result, a person develops and experiences:
- Fatigue quickly, low fatigue threshold.
- Periodic fluctuations in blood pressure, its increase or decrease after physical or mental stress, as well as for no apparent reason.
- Headache.
- Sleep disorder.
- Panic attacks, fears, depression.
Important: VSD is a separate disease only in the post-Soviet space. In European countries, vascular dystonia is a syndrome (sign) of other diseases. For example, neurological disorders or osteochondrosis of the neck.
Treatment of pathologies
It is impossible to eliminate the manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia without treatment for cervical osteochondrosis. All its symptoms will weaken or completely disappear at the stage of stable remission of the degenerative disease.
Drug treatment
In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis directly, drugs of various clinical and pharmacological groups are used. These are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, glucocorticosteroids, B vitamins, ointments with a warming and local irritant effect.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for spinal pathologies.
To eliminate functional disorders, patients are prescribed antidepressants, tranquilizers, and sedatives. A course of taking Glycine, Hopatenic and Glutamic acids, balanced complexes of vitamins and microelements can reduce the likelihood of panic attacks.
With pronounced manifestations of functional disorders, beta-blockers, psychostimulants, and antipsychotics are included in the therapeutic regimen.
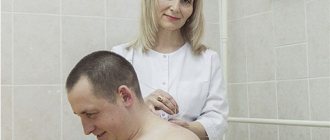
Massage
In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, classic, acupressure, and cupping massage is used. Under mechanical influence, skeletal muscles relax, pinching of the vertebral artery and spinal roots is eliminated. Massage is an effective method not only for the treatment of osteochondrosis, but also for the prevention of its relapses.
Massage of the cervical-collar area.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods used in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis also help get rid of the manifestations of VSD. Patients are prescribed magnetic therapy, laser therapy, UHF therapy, galvanic currents, and shock wave therapy. Neck pain caused by pinched spinal roots is treated well with applications of ozokerite and paraffin. And to normalize the psycho-emotional state and strengthen the body’s defenses, therapy with therapeutic mud and mineral waters is recommended for patients.
Acupuncture for osteochondrosis.
Neck exercises
Therapeutic gymnastics and physical exercise are the most effective way to get rid of all neurological symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, including panic attacks. Most often, a physical therapy doctor includes the following exercises in the complex:
- stand up, spread your feet shoulder-width apart, rotate your head first in one direction, then in the other;
- in a sitting position, place your palm on your chin, try to tilt your head, while offering resistance with your hand;
- Sit up straight, place your palm on your cheek. Tilt your head to the side, resisting with your hand. Repeat the exercise in the opposite direction.
All movements must be performed without jerking, smoothly, slowly, with a small amplitude.
Psychological help
For individual psychological correction, patients are recommended to regularly visit a psychotherapist or psychologist, including group sessions. The doctor explains that you cannot allow yourself to give in to fear, anxiety, and worry. It is necessary to realize that the attack is provoked by another relapse of cervical osteochondrosis, and therefore is not a threat to life.
Traditional methods
Among the folk remedies in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis and VSD, infusions of medicinal herbs with a mild sedative effect are used. To prepare them, pour a teaspoon of dry medicinal raw material with a glass of boiling water. After an hour, filter the infusion and take 100 ml up to 3 times a day. St. John's wort, motherwort, valerian, oregano, mint, lemon balm, and thyme have pronounced sedative activity.
Herbal collection.
Vegetovascular dystonia is one of the most mysterious syndromes
Most doctors do not consider it a serious illness, but rather a collection of various painful manifestations. In fact, vegetative-vascular dystonia can destroy a person’s life, significantly reduce the quality of life and even lead to loss of ability to work.
Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD) is a functional disorder of the nervous system, characterized by a violation of the general condition and well-being, manifested by inorganic malfunctions in the functioning of various organs and systems. In many medical publications you can find other names for this disease, namely: autonomic dysfunction, neurocirculatory dystonia, cardiac neurosis , functional cardiopathy, panic attack, angioneurosis, vasomotor dystonia, etc. Nowadays, the term “autonomic dysfunction” (VD) or “vegetative-vascular dystonia” (VSD) is increasingly used.
Causes of VSD
Among the main causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia syndrome, doctors name factors of hereditary predisposition. For example, most often vegetative-vascular dystonia in children is detected precisely as a consequence of heredity. Increased nervousness and stress already in the first months of pregnancy can have a significant impact not only on the formation of the child’s personality, but also on the higher nervous activity of the brain. Facts show that the emotional instability of a child’s body provokes the development of VSD even in childhood. The teenage years are transitional not only in the process of turning a child into an adult, but also in a neurophysiological one. Conflict situations, emotional stress, chronic diseases, endocrine disorders, lack of movement and other factors are largely provocateurs for the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia in adolescents. In adulthood, hormonal changes in the body play a special role in triggering the mechanisms of VSD. This is why the female half of the world’s population suffers from VSD much more often than the male half. The prenatal period, pregnancy, menopause, all of this, being turning points in a woman’s life, can become the starting point for mobilizing the manifestation of symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is especially unfavorable during pregnancy, when even minor deviations in a woman’s health necessarily affect the condition of the fetus. The same is true for the presence of excess weight, which can provoke manifestations of dystonia. An increase in body weight leads to the development of hypertension, which in turn is an additional burden on the cardiovascular system. The development of vegetative-vascular dystonia in this case affects people of completely different ages and genders.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Sometimes the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia are similar to the manifestation of several diseases at once. These are surges in blood pressure, headaches, dizziness, palpitations and cardiac irregularities, fainting, a feeling of a heat wave, chills, icy hands and feet, increased sweating. A person becomes weather dependent. Patients complain of weakness, fatigue, lethargy, fluctuations in body temperature (can drop to 35 degrees and rise to more than 37). Often indigestion, pain in the abdomen, various pains throughout the body, especially at the time of a deep breath. There are also very specific symptoms: a person cannot ride the subway, stand in line for a long time, sit in a chair at the hairdresser, because he suddenly feels an attack of anxiety or cannot cope with impatience, causeless rage or a sudden feeling of heaviness in his hands and legs. However, the most unpleasant moment in all this is the appearance of a sudden panic attack with severe pain in the heart and under the shoulder blade, accompanied by a feeling of mortal horror.
It is clear that having such symptoms, a person seeks help from doctors. Starting from a therapist and ending with a psychiatrist. But finding the cause of illnesses is not so easy. Only after a thorough examination can doctors make a verdict: “Vegetative-vascular dystonia.” Namely, uncoordinated work of blood vessels at the moment of contraction and relaxation. Thus, there is a disruption in the supply of blood and oxygen to the internal organs, which causes a malfunction in their functioning. Therefore, with vegetative-vascular dystonia, there is no point in treating any one organ; an integrated approach to the entire body as a whole is required. And first of all, treatment will depend on the patient himself.
Current of VSD
In most cases, without provoking factors, the disease is latent (asymptomatic). However, under the influence of unfavorable conditions and overloads, crises often occur. A crisis surge in disease activity is more severe in older people, especially those who suffer from concomitant diseases. In many cases, a crisis is the result of long-accumulated components, and therefore it is not uncommon for a large number of symptoms to manifest simultaneously.
Diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia is significantly difficult by definition. VSD is a complex of various manifestations of various natures. Therefore, it is simply impossible to strictly classify certain symptoms as inherent exclusively to vegetative-vascular dystonia. There are no special devices or special equipment in the arsenal of doctors that would most likely determine the presence of a disorder. Of course, classical methods of examining the most important organs and systems of the body are of great help to the diagnostician, but based only on these results, it is quite difficult to definitively determine the nature of certain symptoms. Often, a complex combination of certain factors, together with the results of multilateral tests, provide grounds for making a diagnosis.
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor must have on hand the results of various studies, the most important of which are: electrocardiography, echography, rheoencephalography, rheovasography, magnetic resonance imaging. Careful examinations and opinions of the following specialists are important: ENT, neurologist, endocrinologist, ophthalmologist and even a psychotherapist. Experience and history of observations of the health status of immediate relatives can also help in determining the causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Classic treatment of VSD
Most often, at the very beginning of the development of VSD, it is not necessary to use potent medications. It is enough to get by only with natural sedatives, such as hawthorn, St. John's wort and valerian. For psychostimulation, natural preparations based on the herbs of zamanika or schisandra are used. Physiotherapeutic measures in the case of vegetative-vascular dystonia are prescribed: exercise therapy, classical massage, acupuncture (reflexotherapy) and water procedures (swimming pool). Doctors also strongly recommend that patients with VSD leave the city as a preventive measure. Changing the stop has a very beneficial effect on both general well-being and neuro-emotional health. Communication with a psychologist can also have a beneficial effect on the emotional state of the patient.
In the drug treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia, the main attention is focused on eliminating concomitant diseases, viral or chronic in nature. It is also important to monitor the functioning of the body’s endocrine system, in particular the thyroid gland. If necessary, complex treatment is carried out with the use of hormonal drugs. In the crisis form of dystonia, drugs that regulate the activity of the heart, sedatives and vitamins (especially B vitamins) are prescribed. Among the stronger drugs, antidepressants, sedatives, drugs to improve blood circulation, etc. are prescribed.
Traditional methods of treating VSD
As soon as a diagnosis of “vegetative-vascular dystonia” is made, you can try time-tested recipes; herbal treatment will gently relieve the disturbing manifestations of the disease.
- Infusion prepared from Oregano herb: 15 g. dry crushed herb, pour 250 ml of boiling water and leave for half an hour, take 2 tbsp. l. a quarter of an hour before meals 3-4 times a day.
- Zamanikha tincture is close in its healing properties to the famous ginseng. It stimulates the central nervous system in hypotonic type of vegetative-vascular dystonia. You can buy a ready-made one or prepare an alcohol tincture yourself: pour 1 glass of zamanikha with vodka and let it brew for at least 1 week. Take 2-3 times a day, 30-40 drops of the drug before meals.
- Valerian tea has a mild sedative effect, which increases the excitability of the cerebral cortex. Its use does not create side effects, so treatment with valerian tea can be carried out for a long time. It's easy to prepare. You need to pour 10-15 grams of boiling water (1 glass) overnight. crushed valerian roots. Then the vessel should be tightly closed. In the morning, decant the infusion and take 30 ml 3 times a day before meals.
- An infusion of motherwort herb has a similar effect. It can be prepared by pouring 15 g. motherwort herb with a glass of water. You need to drink half a glass of this herbal tea 30-60 minutes before meals 3-4 times a day.
- Another useful folk remedy is a mixture of freshly squeezed juices, wine and honey. Prepare 200 ml of carrot, beet, radish and lemon juices; take 200 ml of honey and red wine (preferably Cahors); squeeze the juice of 15 heads of garlic. Mix all ingredients. Take a tablespoon 30 minutes before meals 3 times a day. Continue the course of treatment until the last spoon
Prevention of VSD
Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle are hackneyed phrases, but in the case of vegetative-vascular dystonia, they acquire special significance. Even people with a hereditary predisposition to the disease have every chance of winning over the disease if they counter dystonia with good health and good, restful sleep. Most doctors agree that regular walking (or better yet, jogging) strengthens not only the heart muscle, but also the immune system. Frequent “communication with nature” has a beneficial effect on the body’s regenerative functions, accelerating them and restoring them