Are you experiencing back pain and numbness in your limbs? These are the first signs of osteochondrosis. Insufficient mobility in lifestyle, sedentary work, stress on the neck and spine lead to cartilage wearing out, losing moisture, resulting in micro-tears.
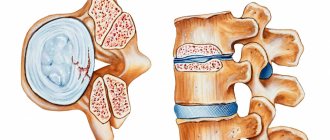
With cervical osteochondrosis, degenerative changes occur in the intervertebral discs. Not only the discs are damaged, but also the vertebrae and joints in the cervical region. If the disease is not treated for a long time, the patient’s general well-being worsens: constant headaches, the appearance of a vertebral hernia, deterioration of cerebral circulation, as a result of which cognitive functions decrease.
Reasons for the development of osteochondrosis
An incorrect sitting position, in which the neck is pulled forward, leads to the development of cervical disease. In this case, excessive pressure occurs on the intervertebral discs, which leads to changes in the nuclei pulposus and compression of blood vessels. This is the position a person takes at a workplace in front of a computer. Therefore, office workers are most often exposed to the development of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
In addition, the reasons for the development of pathology may be:
- improper load distribution when carrying bags;
- excessively soft sleeping place (the spine bends in an unnatural shape);
- genetic predisposition;
- lack of vitamins and microelements in the diet;
- endocrine system disorders;
- curvature of the spine and poor posture during active growth of the body;
- cervical vertebrae injuries;
- presence of bad habits.
Gymnastics for osteochondrosis for hypertensive patients
For osteochondrosis and other diseases of the spine, it is necessary to regularly engage in physical therapy. There are several techniques developed to restore normal neck function. These include a set of exercises by Norbekov and the Bubnovsky (or Shishonin) method.
Exercises for osteochondrosis and hypertension are aimed at restoring normal blood circulation in the affected area, as well as increasing neck mobility, normalizing metabolic processes, improving muscle elasticity, and reducing tissue swelling. They also reduce the risk of osteophytes.
The techniques are suitable for self-study at home. Along with physical exercise, it is necessary to adjust your diet, visit a massage therapist regularly, and find time for long walks or swimming.
Before starting classes, you should consult with your doctor to protect yourself from possible consequences associated with the characteristics of the underlying disease.
Stages of the disease
Determining whether your pain symptoms are signs of the development of cervical osteochondrosis and what stage of development of the disease can only be determined by an experienced doctor after examination and palpation. In total, cervical osteochondrosis goes through four stages of development:
- The nucleus pulposus, the central part of the intervertebral disc, undergoes moderate dehydration during the first stage. As a result, the supporting and shock-absorbing functions of the intervertebral discs are gradually lost. During the first stage, you will experience pain with sudden movements, hypothermia, and staying in one position for a long time.
- The second stage of development is characterized by the appearance of congestion and spasms, which compress capillaries and blood vessels, preventing normal blood circulation. As a result, the frame of the intervertebral disc becomes thinner, forming a protrusion (bulging forward or backward). Under the influence of excessive load, osteophytes are formed on the cervical vertebrae - bone growths. Pain sensations are localized in one place; with sudden turns and tilts of the head, dislocations of the cervical vertebrae can occur.
- Extrusions are formed as a result of thinning of the intervertebral discs. The edge of the nucleus pulposus breaks the fibrous ring and extends beyond the edges of the vertebral body. Muscles and nerve endings are compressed. Pain is felt in the neck, back and limbs.
- At the fourth stage of the disease, the intervertebral discs are displaced and central and lateral hernias form. In addition, scars form on the discs, which leads to immobility of the affected joint. The patient experiences persistent back pain that radiates to other parts of the body, a constant feeling of fatigue, and asymmetry of parts of the body occurs.
VBSN
Periodic disturbances in blood supply can also lead to vertebrobasilar vascular insufficiency. VBSD is a reversible process of brain dysfunction. It develops both against the background of osteochondrosis and hypertension. Patients with VBSD experience the following symptoms:
- Nausea and vomiting,
- A sharp deterioration in vision,
- Disorders of consciousness of various types,
- Sudden memory loss,
- Difficulty breathing and swallowing,
- Impaired movement coordination
- Severe dizziness.
The disease can result in a stroke or dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine manifest themselves differently depending on the stage of development of the pathology. In the early stages it can occur with virtually no symptoms. Pain in the neck and back can only appear if you stay in one position for a long time, sharply bend or turn.
At later stages of development, a crunching sound is heard in the spine, back pain radiates to other limbs, and numbness occurs in parts of the body. When osteophytes and extrusions form, the following occurs:
- headaches in the back of the head and parietal part;
- speech disorders and numbness of the tongue;
- decreased sensitivity of the skin of the neck;
- breathing disorders;
- changes in blood pressure;
- heartbeat disturbances;
- noise and congestion in the ears;
- fainting.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in women are much more pronounced than in men. This is due to the fact that women have a predisposition to vascular diseases and a more fragile structure of the bone segments of the spine. Signs of the disease begin to appear when intervertebral discs change. This leads to disruption of normal blood circulation and causes severe headaches, dizziness, and neuroses. An exacerbation of the disease in women often occurs during menopause, when the body is subject to hormonal changes.
The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men are similar to those in women; erectile dysfunction can be observed separately.
Headache with cervical osteochondrosis is caused by poor circulation in the brain and spinal cord. When the vertebrae become misaligned, they compress the arteries and the oxygen content in the blood decreases. Unfortunately, such pain may not go away even after taking strong painkillers. Therefore, it is important to approach solving the problem comprehensively. Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis may be accompanied by darkening of the eyes and the appearance of tinnitus. This happens because spasming muscles cause a reduction in oxygen supply to the brain.
A lump in the throat with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as well as burning, difficulty breathing and muscle spasms are a common occurrence. The disease provokes compression of the nerve fibers of the cervical spine to the head and neck. Disturbances in nerve impulses cause sore throat.
Due to spasms of blood vessels and irritation of nerve endings, jumps in blood pressure occur. Increased lower pressure in osteochondrosis indicates that the blood supply to certain areas of the brain is impaired, since the vertebral artery is compressed by the intervertebral discs. As a result, oxygen starvation occurs and blood pressure rises.
Prevention
The main rule of preventive measures is that they must be comprehensive and observed on an ongoing basis. This is the only way they will bring the expected results. Prevention is indicated for people who are at risk.
- Watch your posture. The ideal body position is that the head and back are on the same line. Always make sure that your shoulders are straightened, your stomach is pulled in, and your chest is raised. The gait also plays a role - it should be springy and smooth. Never give yourself any slack; at the initial stage, it is important to discipline yourself; in the future, correct posture will become a habit.
- A properly organized workplace. When working, the shoulders should be relaxed; constant tension in the lumbar girdle has a direct impact on the cervical spine. The basic requirements are a chair with a comfortable back and armrests, a monitor at eye level, a keyboard below the elbows (the angle between the shoulder and forearm is about 120 degrees). While working, make it a habit to take a break every 40-50 minutes and perform basic stretching exercises.
- Correctly adjust the car seat. Many motorists are faced with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine due to the fact that they adjust the driver’s seat not according to the rules, but in a way that is comfortable for them. Correct body position in a chair - the entire spine touches the back, not just the shoulders. It is advisable to purchase special lumbar pillows that will help support the body in the desired position. When driving for a long time, it is important to go out into the streets after 1.5-2 hours and warm up.
- Watch your diet. Problems with the cervical spine are often associated with the fact that the patient eats incorrectly. Dangerous foods that increase the risk of osteochondrosis include: white bread, baked goods, sweets, dishes high in salt and sugar, fried and fatty foods. The main danger is refined sugar - the substance helps wash calcium out of the body. Include legumes and nuts, foods high in protein, seasonal vegetables and fruits in your daily diet. Low-fat fermented milk products - kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, natural yoghurts - will also have a positive effect. If you have a problem with excess weight, visit a nutritionist.
- Daily physical activity. Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis at home with the help of physical exercise is an excellent preventative against spinal diseases. It is important to do the exercises at an easy pace, without exceeding the permissible load. If you don’t have time for a full set of exercises, make it a rule to take daily walks.
- Massage. Correct techniques restore muscle tone, relieve tension, and trigger metabolic and regenerative processes in the body. It is not necessary to visit specialists; proper massage of the cervical spine can be performed independently.
- Proper sleep. During the day, the intervertebral discs experience increased stress; complete relaxation and rest can only be achieved during night sleep. To prevent osteochondrosis, it is important to organize the right place to sleep and monitor the time (at least 8 hours).
How is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine diagnosed?
Diagnosis of pathology begins with consultation with a specialist. At the first manifestations of osteochondrosis, consult a rheumatologist, neurologist, surgeon or orthopedic traumatologist. The doctor will ask about the symptoms and the frequency of their occurrence; you need to provide the specialist with a complete medical history and the results of earlier studies (if any). The specialist will conduct a visual examination and palpation, and refer you for tests. During the examination, the doctor pays special attention to neck mobility, muscle tone, skin sensitivity and identifies the most painful areas.
To identify the condition of muscles, ligaments, blood vessels, and to detect inflammatory processes or tumors, an informative and safe diagnostic method is prescribed - MRI of the cervical spine. During an MRI of osteochondrosis, the patient lies on a special sliding table with his back. Rollers are placed on the patient's head to relieve muscle tension, and the limbs are secured with belts. Any slight movement during the procedure can affect the quality of the result. Next, the table moves into the tomograph area. The procedure does not cause pain. The tomograph makes a lot of noise during scanning, so you can use headphones to avoid discomfort.
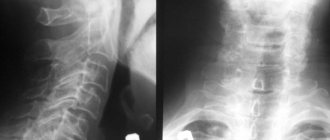
If MRI is contraindicated, there are other diagnostic methods such as computed tomography and radiography. X-ray is suitable only for primary diagnosis and does not provide a layer-by-layer image of the affected tissue. However, this study is the simplest and most economical, allowing you to examine the patient’s body in several projections. Due to the strong radiation exposure to the body, radiography cannot be performed frequently.
During a computed tomography scan, a scan is performed using one or more beams of ionizing rays. They pass through the human body and are recorded by detectors. The detectors move along the patient's body in opposite directions and record up to 6 million signals. The image displays tissues of different densities with precise definition of the boundaries of organs and the affected areas in the form of a section. The procedure allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image.
Possible complications
High blood pressure in combination with osteochondrosis can lead to serious complications for the body. The consequences in the absence of funds and timely treatment are disastrous:
- Inability to lead a normal lifestyle due to concomitant symptoms of pathological changes and pain;
- increased risk of heart attack or bleeding;
- decreased mental performance, memory;
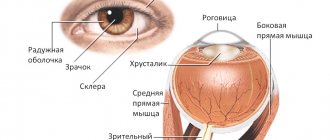
- deterioration and abnormal vision.
With a complex course of the disease, the patient can not only become disabled, but also significantly increase the risk of death.
Types of exercises
For hypertensive patients, two types of exercises have been developed aimed at normalizing blood pressure:
- Isotonic,
- Isometric.
Isotonic exercises also have another name - cardio exercises. They consist of tensing the main muscle groups of the arms and legs. This leads to burning calories, strengthening muscle tissue and improving posture. Exercising requires a lot of oxygen, which puts more strain on the heart. The result is a decrease in blood pressure.
Isometric or strength exercises aim to build muscle mass in the body. Most often, such exercises are performed in the gym under the supervision of a personal trainer. Doctors approach their prescription with caution: an increase in body weight often provokes an increase in blood pressure. Another disadvantage is that hypertensive patients are not recommended to lift weights, and the isometric set of exercises is designed taking into account the use of heavy sports equipment.
Breathing exercises are gentle and effective. It has no contraindications, but with its help you can increase the flow of oxygen to the lungs, improve the flow of lymph and establish normal metabolism. It does not help cope with osteochondrosis, but it saturates the brain with oxygen, which reduces the symptoms of the underlying disease to a minimum, improves overall well-being and elevates mood.
First aid
If your health suddenly deteriorates due to low or high blood pressure, you must call an ambulance. Then you need to remove constrictive clothing or unfasten buttons, take a reclining position, and cover your legs with a warm blanket. As a rule, in such a state a person becomes restless, anxiety, fear appear, and panic attacks are possible. You should take 10-15 drops of motherwort or valerian tincture. Nifedipine, Captopril or Moxonidine can be used to lower blood pressure. Strong, sweet tea, tinctures of Eleutherococcus, and ginseng will help increase blood pressure.
Seven simple exercises
You can perform gymnastics both standing and sitting. The main thing is to keep your back straight, align your shoulders and bring your shoulder blades together.
Start by tilting your head. Perform them smoothly and slowly until you feel muscle tension. Fix the position with maximum muscle tension for 7-10 seconds. Repeat in each direction 5 times. Next, they begin turning left and right. When turning the head, the chin is pulled forward. Repeat in each direction 5 times, maintaining the position of maximum muscle tension for about 10-12 seconds. After working out the lateral muscles, they begin to work with the front and rear ones, and to do this they make smooth bends back and forth. Perform to the maximum possible tension in the muscles, but do not allow pain to appear. Fix your head in the lower and upper positions for 10-15 seconds. Repeat on both sides 10 times.
Then they begin to describe a circle with the chin. During movement, it is kept parallel to the floor. The diameter of the circle gradually increases. Describe 5 circles to the left and the same number to the right. The next exercise is to tilt your head back and turn left and right. You need to try to see the floor. Avoid pain in the cervical muscles. Repeat 10 times. After this, they begin to make circular movements with their heads. The head should be pulled up and to the sides as much as possible. The chin describes a circle, but in a vertical plane. The back remains straight, the shoulders are motionless. It is enough to make only 10 rotations.
The gymnastics is completed with an exercise for the shoulders. They rise up, reaching as close as possible to the earlobes. Fix the position for 9-12 seconds, relax. Take two or three deep breaths, repeat again. A total of 5 approaches are done at equal rest intervals.
The advantage of this complex: accessibility and ease. The exercises do not require physical training and have no contraindications.
They are suitable for both children and the elderly. They take no more than 10 minutes, which means they can be performed even in the office during your lunch break. Gymnastics relieves fatigue and tightness in muscle tissue, improves blood circulation and mobility of cervical discs.
Medical facts about the physiological connection
The fact that osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine and pressure are interconnected is evidenced by the results of studies:
- Inflammatory processes in the intervertebral discs almost always disrupt the conduction of nerve impulses and exacerbate hypertension. Often crises that occur during exacerbation of neurological pathology are difficult to control with conventional medications. The patient may experience relief without the use of antihypertensive drugs after reducing pain in the spine.
- If frequent pinching of the processes occurs, then causeless strong fluctuations in blood pressure from high to very low numbers are possible. Sometimes the diagnosis of VSD is erroneously made.
- With timely treatment of osteochondrosis, spontaneous cure of hypertension is possible. In advanced forms of spinal disease, this is impossible - dystrophic changes in cells occur in the blood vessels and heart due to impaired blood supply.
As you can see, there is a connection between hypertension and vertebral diseases. And if, during a diagnostic examination for high blood pressure, pathologies of the intervertebral discs are revealed, this conclusion should not be ignored. After all, if you treat the spine in a timely manner, you can maintain the health of the heart and blood vessels.
Denial of responsibility
The information in the articles is for general information purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. This article is not a substitute for medical advice from a doctor (neurologist, therapist). Please consult your doctor first to know the exact cause of your health problem.
I will be very grateful if you click on one of the buttons and share this material with your friends