Formed blood cells can be classified into three large groups. Each type of structure performs its own vital functions:
- Platelets. Acts as a kind of stopper. As soon as a blood vessel is damaged, the cells immediately rush to the site of the injury, stick together and create a barrier. Thus, dangerous complications are prevented.
- Red blood cells. Red blood cells. They perform the task of providing tissues with oxygen and removing carbon dioxide. Without these structures, normal breathing at the micro level is impossible.
- Leukocytes. White blood cells. Protectors of the body. Very different in character.
Among the latter, we can distinguish the most numerous group of cytological units. These are the so-called neutrophils. They make up about 70% of the total mass of leukocytes.
The vast majority (70%) of these cells are segmented neutrophils; these are mature structures that perform their inherent functions of destroying pathogenic microorganisms and absorbing viruses.
A decrease in cell count is called neutropenia. This is a dangerous condition, but not in itself. And since it is provoked by certain diseases. Let's try to figure out why the cell level drops.
Structure
Leukocytes are divided according to their structure into granulocytes, which have pinpoint granules in the plasma, and agranulocytes, without additional inclusions. Unlike red blood cells and platelets, these cells are endowed with a nucleus and are able to exit blood vessels and move towards inflamed tissues.
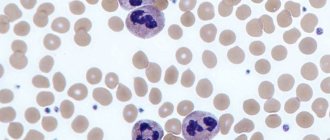
There are two neutrophils in the center, their nuclei are divided into parts (segments)
Granulocytes differ in relation to staining using the Romanowsky method for basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils.
The group of neutrophils is also not homogeneous: according to the shape of the nucleus, they are divided into segmented (the nucleus is divided into parts by constrictions) and rod-nuclear (the nucleus has the shape of an elongated ball).
In the normal blood composition of an adult, the level of segmented neutrophils is 47–75%, and band neutrophils are only 1–6%. “Rods” are considered the precursors of nuclear division; their small number is normally explained by the rapid process of transformation into a segmental, more mature form.
If you are interested in the norms of this indicator in children and the reasons for their deviation, we recommend reading this article.
Normal in blood
Neutrophils are the most numerous cells of all types of leukocytes: their share is from 50% to 70% of all white blood cells.
If you look at the test form, you can see their different designations due to the fact that when counting, neutrophils are divided into band (not fully mature) and segmented (fully mature). The norm of segmented leukocytes in the blood of women is the same as that of men, and is 1500 – 8000 units/mm3. The determination of low segmented neutrophils in the blood of a child differs from the norm in an adult. The lower norm for children aged 2 weeks to 1 year is 1000 units/mm3. But after a year, this norm becomes like that of an adult.
It should be noted that the count of leukocytes strongly depends on the type of equipment (ie hematology automatic analyzers) on which the count is carried out. Therefore, segmented neutrophils, the norm of which is measured on different equipment and in different laboratories, should always be compared only with those values that are printed on tests in the laboratory.
Functions of neutrophils
The doctrine of immunity is constantly evolving and becoming more complex. The role of each type of leukocyte cell is clarified. Some are “scouts”, others retain the memory of the attack by a foreign agent and “train” young cells.
Segmented cells, together with lymphocytes, are responsible for the direct organization of the “attack” and participate in the “fight” with pathological organisms both in the blood and in tissues.
Beginning of the attack: the neutrophil draws in an unclear object
What is important is their ability not only to “swim” along the bloodstream, but also to release their own “legs” and move towards the lesion with amoeba-like movements (flowing from one part to another).
The neutrophil, approaching the source of infection, envelops the bacteria and destroys them. In this case, it dies itself, releasing a substance into the blood that attracts help from other cells to the focus. Millions of leukocytes die in a purulent wound. Dead cells are found in the discharge.
Neutrophils have a special preference for bacteria, but they practically do not touch viruses. Therefore, in a blood test for any acute bacterial infection, an increased number of segmented cells is detected.
By the number and percentage of neutrophils, viral and bacterial infections can be distinguished. Any deviations from the norm indicate important disorders in the immune system.
How to increase neutrophils
It is impossible to buy a medicine that can increase neutrophil levels. However, it is still possible to influence their content in the blood. For example, if a decrease in phagocyte cells occurred while taking sulfonamide antibiotics, it makes sense to review the course of therapy with your doctor and replace the drugs.
In some cases, the production of neutrophils is affected by a pronounced imbalance of nutrients in the body. The most commonly reported levels of vitamin B9, known as folic acid, and B12 are significantly reduced. Therefore, often, if there is a lack of neutrophils, they additionally take an analysis for vitamin deficiency and prescribe a course of group B. 10-14 days after restoring the balance of nutrients in the body, an increase in the number of neutrophils is observed, which is fixed within acceptable values.
If segmented neutrophils are increased
The growth of cells of the neutrophil species is called neutrophilosis. The level of segmented neutrophils exceeds 75%.
Both segmented and rod cells increase.
Sometimes earlier forms appear in a blood test - myelocytes, but segmented ones do not change. In the leukocyte formula, this looks like a shift to the left (according to the location of cells in the list of leukocyte forms). At the same time, granularity is detected in neutrophils.
The causes of neutrophilia can be:
- infection with acute bacterial, fungal infection, spirochetes;
- exacerbation of the inflammatory process in rheumatism, pancreatitis, polyarthritis;
- the presence of a dead area in the body, for example, in acute myocardial infarction;
- recent vaccination;
- severe alcohol intoxication;
- disintegrating tumor;
- damage to the kidney tissue, especially with diabetic nephropathy;
- treatment with steroid hormones, heparin.
Vaccination of the adult population is carried out according to epidemic indications
A shift to the right is detected when a high level of segmented forms predominates over younger rod forms. It's possible:
- after acute blood loss;
- as a reaction to blood transfusion;
- for some types of anemia.
The cause of a temporary increase in neutrophils may be:
- condition before menstruation in women;
- long-term stress associated with increased workload;
- physical stress.
Pregnancy causes a general increase in white blood cells by 20%. This is the protection of the mother and fetus from unwanted influences. During pregnancy, the absolute number of segmented neutrophils is increased (more than 6 x 109/l), and their relative level in the formula remains unchanged.
To determine the severity of the disease, neutrophilia is divided into forms:
- moderate - the number of cells is not higher than 10 x 109/l;
- pronounced - absolute content from 10 to 20 x 109/l;
- severe - cell count above 20 x 109/l.
Neutrophils - what kind of cells are they?
Neutrophils are a group of white blood cells that fight the spread of infection in the body. They are formed by bone marrow cells and are sent through the body tissues to the site of infection. Having detected foreign cells, neutrophils capture and engulf them. This process is called phagocytosis.
The lack of neutrophils has a scientific name - neutropenia. This is a condition in which blood cells break down too quickly, without having time to build a reliable defense. In some situations, we have to talk about disorders of the hematopoietic system, when the bone marrow does not produce enough protective cells or about the fact of a pronounced decrease in immunity.
To determine the number of neutrophils, two types of measurements are used:
- true;
- relative.
When determining the true number of cells, their content in the analyzed volume of blood is taken into account. When identifying a relative indicator, the total number of leukocytes is taken into account and the percentage that neutrophils make up of the total number is calculated.
Neutrophils are very mobile blood cells; they have access to areas and tissues where the main leukocytes do not penetrate. All neutrophils, depending on their maturity, are divided into band and segmented. The second group is mature cells, their number increases significantly when an inflammatory process occurs. They are the main phagocytes filling the bloodstream, but when infection develops, they quickly migrate to the site of inflammation, overcoming the walls of blood vessels.
If segmented neutrophils are reduced
Segmented neutrophils are low in a condition called neutropenia. Detection of a level in the leukocyte formula below normal (47% or less) requires counting the absolute number of cells.
The usual norm is from 1500 to 7000 cells per mm3 of blood plasma (1.5 - 7.0 x 103 cells/mm3). The decline occurs:
- for diseases of the blood and hematopoietic organs;
- the use of chemotherapy in the treatment of patients with cancer;
- treatment with antiviral drugs;
- long-term exposure to viral infection;
- severe allergic reactions;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- as a result of genetic mutations.
Neutropenia can be temporary, manifesting itself in low numbers in the first 3 to 4 days when suffering from influenza or adenoviral infections. A reduced level of segmented neutrophils is found in 95% of patients undergoing treatment with the well-known antiviral drugs Interferon and Ribavirin.
It is important to promptly identify severe neutropenia and diagnose its cause.
- A decrease in granular neutrophils to 500–1000 cells per 1 mm3 is considered moderate.
- If the number of cells is below 500, then the form of the disease is severe, it is accompanied by a breakdown of all protective reactions.
“Over the counter” does not mean safety, quite the contrary.
Clinically, it manifests itself as pneumonia, severe ulcerative stomatitis, inflammatory diseases of the ears, and a septic condition as a complication of a common infection.
Various scientists have identified 20 to 30% of the adult population who have persistent neutropenia without other blood changes. These people do not have any symptoms of disease. This is usually reflected in the outpatient card. Patients should be aware of their peculiarities and warn the doctor.
Another normal variant is cyclic neutropenia. It is found in human blood repeatedly with intervals from several weeks to two months. At the same time, the level of monocytes and eosinophils increases. Changes return to normal on their own.
Leukocyte formula
A general blood test shows not only the number of neutrophils, but also the ratio of mature forms - segmented and immature - band. The leukogram reflects information in sequence from left to right: first indicate the number of band granulocytes, then segmented granulocytes. Therefore, an increase in the number of young forms of leukocytes is called a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left, and an increase in mature forms is called a shift to the right.
An increase in the number of band-nuclear, immature neutrophils indicates the mobilization of the body's defenses. With severe infection, extreme stress of the immune system, metamyelocytes and promyelocytes appear in the blood. In healthy people, they are found in the bone marrow and are not found in the blood. Their appearance is a signal of alarm and the need for medical attention.
A shift in the leukocyte formula to the left is a consequence of the following pathological conditions:
- acute inflammation;
- purulent infections;
- large blood loss;
- exogenous poisoning.
A shift in the leukocyte formula to the right is an increase in mature segmented neutrophils. Evidence of inhibition of leukopoiesis is the formation of young forms of leukocytes, a decrease in the reproductive function of the bone marrow.
Occurs due to:
- severe diseases of internal organs that last a long time with severe intoxication;
- renal, liver failure;
- aplastic anemia;
- malignant tumors;
- radiation sickness;
- chemotherapy of oncological diseases.
A shift in the leukocyte formula to the left or right appears in the early stages of diseases. An alarming signal is the tension of the body’s defenses in the fight against severe pathology. Its early diagnosis is an important condition for effective, timely treatment.
Leukocyte formula
How to maintain normal neutrophil levels
To have normal levels of segmented neutrophils, you should take care to support your immunity and not waste it. Particular importance should be given to a woman’s environment during pregnancy.
- Vitamins from fruits and vegetables have a positive effect; food should be moderately high in calories and varied.
- According to indications, you should get vaccinated against influenza and other diseases, without waiting for the beginning of the period of increased incidence.
- To the usual hygiene rules of washing hands with soap, you should add rinsing your nose with clean water. Cleansing the mucous membrane and villi improves their protective function.
Hardening procedures can relieve the body of many problems.
Results
Segmented neutrophils are mature neutrophils (a type of leukocyte) responsible for eliminating infections, primarily the activity of pathogenic bacteria. With bacterial infection, the number of segmented cells increases.
In clinical practice, this is an indicator of an acute infectious process. Sluggish chronic diseases of bacterial etiology and viral diseases are not accompanied by an increase in the values of segmented cells. Chronic neutrophilia may indicate the development of oncological processes.
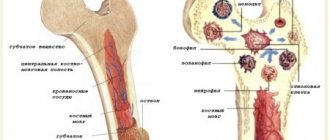
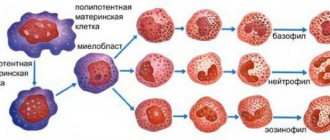
Education mechanism
After the initial myeloblast cell has developed, the neutrophil gradually matures into a band cell.
It then penetrates the blood plasma. After a period of time, the core of the element changes.
It is divided into segmented shares. This is how mature neutrophils appear.
Full-fledged cells, ready for protection, penetrate the capillary walls in 2-5 hours.