They pricked the baby’s finger, took blood, and the next day, after standing in a long line, you took the test. Is it time to take another turn to show the test to the doctor? Let's take a look there ourselves and try to figure out what all these Latin words and mysterious numbers mean.
Whatever happens, doctors prescribe the same thing - a general blood test. Kidneys hurt - a general blood test, chest pain - the same thing, the temperature has risen - again a general blood test, and then we'll see. At least we are adults, but what if a child is sick? Why should he prick his fingers in vain - he’s crying!
In addition, doctors, having looked deeply into this analysis, always prescribe the same thing - antibiotics. Thirty years ago they prescribed oletethrin, ten years ago - smallpox, now augmentin and suprax are in fashion. I’ll tell you a secret: smallpox, suprax and augmentin, although different in chemical composition, work exactly the same, and even against the same bacteria.
Let's decipher the blood test together.
Why might neutrophils be low?
Low blood levels are characteristic of some diseases and conditions:
- infections of viral origin (chickenpox, hepatitis, influenza);
- inflammatory processes;
- radiation sickness;
- taking certain medications (usually cytostatics or immunosuppressants in the treatment of autoimmune diseases or malignant tumors, as well as antimicrobials - penicillin, cephalosporin, sulfonamide);
- chemotherapy for cancer;
- agranulocytosis;
- anemia (aplastic and hypoplastic);
- exposure to radiation.
Preparation and conduct of analyzes
The leukocyte test is highly sensitive and requires careful preparation. To avoid getting false results, parents must follow the rules.
2-3 days before donating blood, you should pay attention to the child’s nutrition. The diet should not contain food:
- fat;
- high protein.
There should be a calm environment at home. Strong emotions and tears should not be allowed. It is especially important to ensure that the child does not cry, since strong emotions lead to increased production of white blood cells.
Strenuous physical activity on the eve of the analysis distorts the results of the analysis. It is worth reducing physical activity 2 days before your visit to the laboratory.
The test is taken on an empty stomach in the morning. At least 8 hours must pass from the last meal to blood sampling.
You are allowed to drink water before the test, but you cannot take medications without the approval of your pediatrician. In the queue in front of the office, it is advisable to keep the child occupied so that he does not run up the stairs, cry, or worry.
Why do lymphocytes increase?
Lymphocytes are considered the main immune cells. They produce antibodies against foreign microorganisms and form humoral immunity. They make up about 25-40% of all leukocytes. Their increase in the blood occurs in the following cases:
- for viral diseases;
- for tuberculosis;
- for acute and chronic lymphocytic leukemia;
- with lymphosarcoma;
- with hyperthyroidism.
An increased level of these cells is said if their absolute number exceeds 3.6x109 per liter. Neutrophils in the blood in such pathologies may be reduced.
Monocytes are killers in the body
Monocytes make up 10% of white blood cells and perform the main “destructive” function of the immune system. Also called tissue macrophages. They are formed in the bone marrow within 5 days and immediately go out to “hunt” without leaving a reserve. They quickly penetrate tissues and destroy foreign proteins. A large number of monocytes are found in the liver, spleen and lungs. They exist for about 60 days and process foreign proteins into antigens, which are subsequently dealt with by immune cells.
An increase in monocytes in the blood, or monocytosis, indicates that there are chronic infections in the body. They can also talk about infections that are located in the cells themselves: viruses, chlamydia and mycoplasma.
Causes of increased lymphocytes and decreased neutrophils
The leukocyte formula has a more important diagnostic value, since most often changes occur in it, while the total number of leukocytes does not change. Thus, during viral infections, the absolute level of leukocytes in the blood remains within normal limits or is slightly increased, while in the leukogram, lymphocytes are increased and neutrophils are decreased. As mentioned above, this occurs mainly with viral infections, malignant tumor diseases, exposure to radiation, and after taking certain medications. Such changes in the leukogram indicate that the body is fighting the disease.
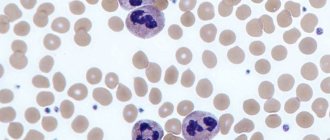
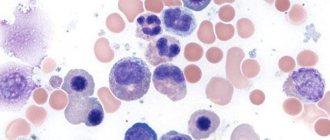
This is what lymphocytosis looks like in the blood under a microscope
A decrease in granulocytes with increased lymphocytes can be observed if a person has recently suffered from acute respiratory viral infection or influenza. As a rule, blood counts do not return to normal immediately, but some time after recovery. Thus, neutropenia against the background of lymphocytosis indicates that the infection is subsiding and recovery is occurring.
It should be said that increased lymphocytes and decreased neutrophils are a normal condition for children. The fact is that the norms for adults are different. Thus, the number of neutrophils in children is less than in adults, and in different years of life ranges from 30 to 60%, in adults this figure is 45-72%. On the contrary, there are more lymphocytes in children than in adults - 40-65%.
What do granulocytes say?
Part of the leukocytes are granulocytes, which get their name due to the presence of granules. There are three types of cells: neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. The types of granulocytes differ from each other due to the color of the granules and the structure of the nucleus.
The granules store immune substances that are important for protecting the body. Thanks to them, cells participate in inflammatory processes. The job of granulocytes is to absorb proteins and chemicals. Granulocytes also digest them.
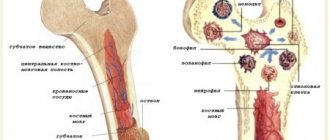
The cells mature in the bone marrow, where the resulting quantity is stored for another 3-4 days. Mature cells enter the blood, where they circulate for 6 hours. After the end of the cycle, granulocytes enter the tissues, where they perform their functions.
The largest number of leukocytes are neutrophils, of which there are always about 1010 in the blood. If a bacterial infection enters the body, neutrophilia begins - an increased amount of neutrophils in the blood. The number of cells that appear depends on the number of harmful bacteria.
The duration of stay of neutrophils in the body is only 4 days, which is why still immature cells (band cells, metamyelocytes, and others) enter the body. This phenomenon is called a “shift of the leukocyte formula to the left.” With neutropenia (reduced number of neutrocytes), the body is less protected from infections.
About 5% of leukocytes are eosinophils, the number of which depends on adrenal hormones. In the morning there are the largest number of them. They are stored in the layer under the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. A quantity above the norm indicates that the following processes are occurring in the body:
- Infestation with parasites;
- Allergy;
- Autoimmune processes.
Medical offers to sign up for diagnostics and tests. In our laboratory it is possible to take all types of tests in Tula. Tel. for recording.
The smallest number (less than 1%) are basophils. They play a role in the release of histamine during allergic reactions. It is these cells that are responsible for itching, redness, irritation and bronchial spasms.
Depending on the location of basophils in the body, the following reactions differ:
- Bronchial asthma;
- Rashes
- Hives;
- Quincke's edema (swelling of the larynx).
Interpretation of analyzes
When deciphering a blood test, all indicators are assessed together. When diagnosing, special attention is paid to the leukocyte formula, which reflects the ratio of all types of white blood cells. In diseases, the content of some leukocytes may change due to an increase or decrease in others. Using the leukocyte formula, one can judge the development of complications, how the pathological process proceeds, and also predict the outcome of the disease.
According to leukogram data, it is possible to distinguish a viral disease from an infectious one. With a viral infection, the total number of all leukocytes does not change or is slightly increased, but there are changes in the leukocyte formula: lymphocytes are increased, neutrophils are decreased. At the same time, ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) increases slightly, with the exception of acute pronounced processes of viral origin. As for bacterial damage, the level of leukocytes increases due to the growth of granulocytes, the relative content of lymphocytes decreases. ESR during bacterial infections reaches very high values.
Complete blood count and inflammation: when are antibiotics indicated?
A general blood test is undoubtedly the most popular of all existing tests. And for good reason, because its capabilities, among other things, make it possible to detect not only the presence and degree of inflammation, but also to determine its “origin” in relation to the pathogen. This means that the choice in favor of antibacterial or antiviral therapy can be made in the very first days of inflammation, which will not only speed up recovery, but will also significantly reduce the risk of serious complications.
Leukocyte squads
For the “uninitiated” people, a general blood test with a leukocyte formula (1.0.D2.202) most often looks like “Chinese”. To find a “sentence” about the nature of inflammation, which, at first glance, seems completely impossible. Whereas in fact, for a primary clarification of the nature of the infection, a “cursory” assessment of the number of various representatives of leukocytes is often sufficient.
1. Neutrophils
The “instant response group” in the fight against bacteria are neutrophils, the relative (%, in relation to other types of leukocytes) increase in which in a general blood test is a reliable marker of any bacterial inflammation and, accordingly, justification in favor of the antibacterial nature of treatment.
Whereas an absolute increase in the number of neutrophils (cells per liter of blood) often accompanies fairly severe forms of infections.
These representatives of leukocytes are the very first to migrate from the blood to the site of inflammation, where they literally “eat” and “digest” the enemy with the help of “poisonous” granules.
True, after such a “snack”, the neutrophils themselves become unviable and die. And the clinical reflection of this process is the formation of pus at the site of inflammation.
2. Lymphocytes
Simultaneously with the increase in neutrophils, in the blood of a “bacterial” patient there is a relative (%) decrease in the main virus fighters – lymphocytes, which is a reflection of the normal redistribution of “immune assets” for the current tasks of protection. And the process itself is called “relative lymphopenia”.
3. Monocytes
As “liquidators of the consequences” of inflammation, monocytes are “pulled” from the blood into the focus. Which are already “in place” transformed into larger ones - macrophages, and effectively cleanse the “space” of destroyed cells and bacteria.
The maximum increase in monocytes in a general blood test is usually observed only at the very end of inflammation, as a marker of the completion of the process and the beginning of the recovery period.
And, among other things, monocytes are universal “soldiers” and are involved in both bacterial and viral (especially herpetic origin), as well as autoimmune and some other mechanisms of inflammation. Therefore, their increase to one degree or another is characteristic of almost all types of inflammatory process.
Normal indicators
Leukocytes provide an immune barrier against infection, inflammation, and the growth of a malignant tumor. Immune functions are carried out by the most numerous populations of white blood cells:
- neutrophils (NEU);
- lymphocytes (LYM).
The concentration of leukocytes is measured as a percentage. The indicators reflect the amount of total leukocytes that accounts for each cell group.
Important information: What does reduced hematocrit mean during pregnancy in the 1st-3rd trimester
The leukocyte norm in children differs from the norm in adults. The newborn has elevated white blood cells due to a high concentration of neutrophils. Their LYM levels, compared to the norm in adults, are reduced.
After 7 days, the parameters of the LYM and NEU cells in the newborn are equalized. This balance is called leukocyte crossover. From 7 days to 5 years, the LYM value should normally be greater than neutrophils.
This distinguishes the leukocyte proportions in children and adults. Parents, not knowing this feature, often get scared and begin to worry.
At 5-6 years, the LYM analysis and the number of NEUs again become approximately the same, as was observed at 7 days in newborns. This phenomenon is called second leukocyte crossover and reflects normal immune development.
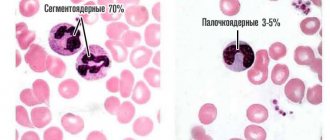
Neutrophils
Neutrophilic white blood cells increase during inflammation caused by bacterial infections. There are 2 groups of neutrophils present in the blood:
- immature rod forms (NEUp);
- mature segmented forms (NEUc).
An informative indicator is the number of segmented NEUc cells.
Normal NEUc in children depending on age (in%):
- 1-2 — 28-48;
- 2-3 — 32-55;
- 3-6 — 32-55;
- 6-9 — 38-58;
- 9-12 — 43-60.
Lymphocytes
The group is responsible for the production of antibodies to foreign proteins. A significant increase in these blood elements is observed in viral diseases.
Normal lymphocyte counts in children depending on age (in%):
- 1-2 — 37-60;
- 2-3 — 33-55;
- 3-6 — 33-55;
- 6-9 — 30-50;
- 9-12 — 30-46.