Reasons for the increase
This condition occurs only in the presence of certain diseases.
Excess levels of total protein can be absolute or relative. In the first case, this is due to a change in the volume of circulating blood, and in the second - with thickening of the plasma. An increase in total protein levels is called hyperproteinemia
The absolute reasons for exceeding the norm of total protein are:
- Malignant tumors that have their own metabolism and actively synthesize proteins.
- Infectious diseases of acute form or occurring in a severe stage. At the same time, they are accompanied by the spread of purulent lesions and blood poisoning.
- Autoimmune diseases. These include lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. Such pathologies manifest themselves in the form of the body producing antibodies to its own immune cells.
- Parasitic infections. Increased protein in the blood is observed in the presence of roundworms in the intestines.
- Inflammatory diseases of a chronic type, characterized by constant destruction of body tissues.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Relative causes of increased protein levels contribute to a decrease in the concentration of water in the vessels, resulting in dehydration of the body. A similar condition is observed in the following pathologies:
- Intestinal infections, which are accompanied by frequent and loose stools. Such diseases include cholera, dysentery and others. With these diseases, elevated protein levels in the blood are established.
- Intestinal obstruction. Pathology occurs against the background of difficulty in the absorption of liquid from the digestive tract.
- Poisoning with food or drugs, which is accompanied by frequent vomiting and diarrhea. The result is dehydration.
- Intense bleeding. Against the background of their occurrence, there is a large loss of fluid, which causes an increase in total protein.
- Long-term use of corticosteroid drugs. They provoke an increase in the amount of vitamin A.
It is impossible to determine the cause of high total protein in the body based on the results of a laboratory blood test. For this, the patient is prescribed a number of other studies. Also, when making a diagnosis, the doctor relies on the patient’s existing symptoms and medical history.
Total protein in the blood during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the female body undergoes certain changes. They are expressed not only externally. In the early stages, only internal changes in the level of certain substances in the body, including total protein, are observed.
But during pregnancy, this indicator decreases slightly as blood volume increases. In cases where the indicator is significantly exceeded and is more than the norm, the reason for such deviations should be found out.
The reasons for the increase in protein in the blood of a pregnant woman may be:
- Infectious diseases of an acute nature.
- The presence of malignant formations, when the protein begins to be synthesized in larger quantities than required.
- Autoimmune diseases such as chronic hepatitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, reactive arthritis and others.
- Lack of fluid in the body due to diarrhea, vomiting or intestinal obstruction.
Timely identification of the causes of this condition will eliminate the development of complications and a number of fetal pathologies.
- Total protein in the blood is low - what does this mean, causes and treatment
Interpretation of results
Norms vary depending on the gender and age of patients. Significant changes in indicators are observed in many physiological conditions (for example, during pregnancy). Minor deviations may be one of the first signs of various diseases, or may not indicate the presence of pathology. When interpreting the results, the doctor takes into account a large number of factors (history, presence of complaints, etc.). If necessary, additional examination is prescribed.
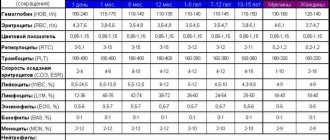
For adult patients, reference values are 64-83 g/l. In children, the norm is determined in accordance with their age. When assessing results, it is necessary to take into account the patient's level of physical activity. The test is not intended for self-diagnosis. Only a doctor can correctly interpret its results.
What is C-reactive protein
h22,0,0,0,0—>
In the results of blood biochemistry, among the protein indicators, you can find a separate type of protein - C-reactive protein (abbreviated as CRP or CRP). This substance belongs to the acute phase proteins or dominant proteins, which are produced at an accelerated rate during damage to body tissues and the development of inflammatory reactions. The protein mobilizes the immune system to fight foreign antigens and activates defense mechanisms. Today it is considered to be a marker of inflammation in the body, much more sensitive than ESR. When a pathological process develops in tissues, the concentration of C-reactive protein quickly increases tenfold.
p, blockquote8,0,0,0,0—>
Why are proteins needed?
Proteins perform many functions in the human body. First of all, it is a building material - those bricks on which the foundation of all organs and tissues is laid. They create the framework of cells - their cytoskeleton, participate in the formation of organelles of movement - and by the way, thanks to the latter, leukocytes are able to leave the systemic bloodstream in the direction of the source of inflammation. It is the connective tissue collagen that largely gives structure not only to the skin, but, say, to blood vessels. In turn, keratin is part of nails and hair.
Protein molecules carry out signal transmission, mediating intercellular interactions, transport hormones, fatty acids, and form complexes with a variety of biologically active substances. Those of them that do not circulate in the serum, but are built into the plasma membrane - a selective barrier at the border of the intra- and extracellular environments - are an important factor in the regulation of water-salt balance: by forming ion channels, they facilitate the entry of potassium, sodium and some others into the cytoplasm charged particles.
One of the most important functions performed by this class of organic compounds is undoubtedly catalytic. All enzymes are protein in nature - and this mediates strict conditions (including a certain temperature and pH), deviations from which in the slightest direction lead to a kind of transport collapse at the molecular and cellular levels. So, say, many remember from school biology lessons: an excessive increase in temperature is fraught with denaturation of protein molecules - in essence, their destruction. Here, as a rule, the analogy with fried eggs is clear: just think what “metamorphoses” happen to a chicken egg as soon as it hits a hot frying pan.
In addition, a large number of hormones are also represented by polypeptides and proteins - this allows us to highlight the regulatory effect as a separate item: both local and at the level of the entire organism (take, for example, thyroid hormones, the influence of which begins with cellular metabolism and ends with entire organ systems ).
Reasons for the increase
h24,0,0,0,0—>
A condition in which the concentration of proteins in the blood increases is called hyperproteinemia. It can be absolute, if the change in the amount of proteins is not associated with disturbances in blood volume, or relative, if the shift in concentration is due to blood thickening and fluid loss.
p, blockquote16,0,0,0,0—>
Factors that provoke protein levels are the same for adults and children. There are no specific reasons for patients of different age categories. Absolute hyperproteinemia in most cases is associated with the destruction of body tissue and metabolic disorders. It can be caused by:
p, blockquote17,0,0,0,0—>
- diseases of a malignant nature (sarcoidosis, lymphogranulomatosis, tumors of internal organs);
- autopathologies (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, autoimmune hepatitis);
- chronic inflammatory processes (protein indicator reflects the dynamics of development);
- severe infections (leptospirosis, syphilis, tuberculosis, malaria, sepsis, purulent-necrotic processes);
- blood diseases (leukemia, iron deficiency anemia).
Relative hyperproteinemia is much more common than absolute hyperproteinemia. It is short-lived and more often associated with transient conditions. The concentration of proteins can increase against the background of a decrease in blood volume, with significant losses of its liquid part, namely:
- Total protein in the blood: norms and causes of deviations
p, blockquote18,0,0,0,0—>
- loss of water due to diarrhea and vomiting due to intestinal infections (salmonellosis, dysentery, cholera, rotavirus);
- impaired fluid absorption due to obstruction and inflammatory diseases;
- acute intoxication;
- burns of more than a fifth of the body area;
- hemorrhages (overt massive or prolonged hidden);
- taking glucocorticoid drugs, some NSAIDs, antibiotics, vitamin A;
- after surgical operations;
- for significant injuries.
In addition, an increase in protein concentration is not due to pathological reasons. These include dietary habits, loss of fluid by the body in hot conditions, when drinking a small amount of water, after physical exertion or severe stress.
p, blockquote19,0,0,0,0—>
When C-reactive protein (CRP) increases
h31,0,0,0,0—>
CRP reacts with lightning speed to any inflammatory and necrotic changes in the body. By the degree of increase in protein, you can determine how serious the violations are. The indicator increases when:
Useful information: Nitrites in urine - causes, treatment. What to do with nitrituria and is the condition dangerousp, blockquote20,1,0,0,0—>
- transition of chronic diseases to the acute phase;
- activation of inflammatory changes;
- development of allergic reactions;
- acute infectious diseases (bacterial or viral);
- burns, frostbite;
- injuries;
- the formation of foci of purulent tissue melting.
C-reactive protein can indicate the formation of a cancerous tumor in the body. The indicator changes at the earliest stages, when other blood characteristics are still within normal limits and there are no symptoms.
p, blockquote21,0,0,0,0—>
What is hypoalbuminemia?
Albumin structure
Hypoalbuminemia (HA) is a condition in which the main blood plasma protein albumin is reduced. HA develops unnoticed and can lead to serious consequences, so it is important to identify the pathology as early as possible.
- Protein tests: from the variety of studies to the specifics of analyzing total protein in blood serum
Albumin is a simple protein consisting of 585 amino acid residues. The oncotic pressure of the plasma depends on its concentration, that is, the protein is involved in regulating the passage of fluid through the capillary wall. With HA, due to a lack of albumin, fluid accumulates in the intercellular space, which is manifested by edema.
The albumin molecule contains many reactive sites, thanks to which the protein easily binds and transports substances necessary for the body: fatty acids, calcium, magnesium, chlorine, bile acids, bilirubin, vitamins, hormones, and medications. In case of GA, the usual intake of medications can lead to intoxication, since albumin does not effectively perform its function of delivering them to the detoxification organs. Albumin is a central participant in the body's detoxification system. It is able to bind to heavy metal ions and toxic waste products, promoting their elimination. With GA there is a sharp increase in the toxicity index.
Albumin synthesis occurs in the liver, producing about 12 g of protein daily. With increasing needs of the body, for example, with a decrease in osmotic pressure, the process of albumin formation accelerates. But as a result of various diseases, liver hepatocytes are not able to produce enough protein molecules or the rate of albumin breakdown exceeds the rate of its synthesis.
What does total protein concentration mean?
h21,0,0,0,0—>
- C-reactive protein is an important indicator in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis
Proteins, or proteins, are constantly present in the blood and are transported throughout the body. Thanks to them:
p, blockquote3,0,0,0,0—>
- coagulation reactions are triggered;
- metabolism occurs and is regulated;
- nutrients and nutrients are transported;
- a stable volume of the bloodstream is maintained;
- immune mechanisms are triggered;
- blood elements are in a suspended state and do not stick together.
The constancy of the protein indicator is the key to homeostasis in the body - stable blood properties and the continuity of metabolic processes in tissues, the connection between all organs and systems. Protein levels can be measured in plasma or serum. The first is the liquid fraction of blood, purified from formed elements. Serum is plasma purified from fibrinogen protein. Because of it, the value of total blood protein increases by 2–4 g/l.
p, blockquote4,0,0,0,0—>
Whey proteins are conventionally divided into 2 types. The first group - albumin - makes up about 55%. These proteins are produced primarily in the liver. They provide transport of pigments, hormones, vitamins, and pharmacologically active substances. Albumins prevent the liquid part of the blood from sweating through the vascular walls into the tissue. If their concentration changes, edema may develop.
p, blockquote5,0,0,0,0—>
The second group is globulins. These substances include enzymes, antibodies, and other substances (about 500 types in total). Thanks to them, nutrients are distributed throughout the body.
p, blockquote6,0,0,0,0—>
p, blockquote7,0,0,0,0—>
Causes of low blood protein
Heart disease may cause hypoalbuminemia
- Impaired albumin formation in liver diseases: cirrhosis, tumors, hepatitis, hepatosis.
- Decreased protein synthesis due to chronic and acute heart failure.
- Impaired protein absorption due to endocrine disorders, inflammatory processes in the intestines, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
- Accelerated breakdown of albumin as a result of infectious infections, extensive injuries and burns, rheumatic pathologies, sepsis.
- Increased protein loss in nephrotic syndrome, characterized by damage to the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys.
- Impaired glomerular filtration of the kidneys as a result of damage to the renal blood vessels in diabetes mellitus.
- Insufficient protein intake during strict diets and fasting.
- In newborns, the cause of HA may be immaturity of liver cells.
- Pregnancy.
Preparing for protein testing
On the eve of the test, you should limit physical activity
Preparation for analysis involves eliminating those factors that may adversely affect its accuracy:
- Drinking enough fluids - blood must be donated on an empty stomach, but it is not recommended to exclude the use of water;
- Elimination of overeating - the day before the analysis, you should refrain from eating large amounts of meat and fish;
- Reducing sports load - it is not recommended to engage in sports 1-2 days before the test.
How to make up for protein deficiency
If protein deficiency was not caused by nutritional factors, then primary attention should be directed to the cause leading to their difficult breakdown and absorption. It is the elimination of this etiological factor that will provide the body with a sufficient amount of proteins - otherwise, everything eaten simply will not be absorbed.
As a rule, the leading role is occupied by hypochlorhydria - a decrease in the secretion of hydrochloric acid by the parietal cells of the stomach. If its cause is a violation of the folate cycle, it is worth starting to work with it, taking a course of active forms of vitamins involved in its mechanisms:
- methylfolate;
- methylcobalamin;
- riboflavin 5-phosphate;
- pyridoxal 5-phosphate.
Provided there is no damage to the gastric mucosa, you can also consider the use of dietary supplements that stimulate the secretion of hydrochloric acid:
- Betaine-pepsin.
- Iodine, chlorine and zinc.
In addition, exposure to stress factors that lead to vasospasm should be reduced or completely eliminated. Increase the tone of the parasympathetic system: as you know, it is the vagus nerve that controls the digestive processes. Take baths with magnesium salts, do relaxing practices like Pilates, yoga, breathing exercises.
Suitable as adaptogens for reducing cortisol levels:
:
- Rhodiola rosea;
- valerian;
- ginseng.
We recommend
“Enzyme deficiency: symptoms and treatment” Read more
Lifestyle changes play a key role in normalizing the condition of the entire body. Move more - let 10,000 steps become not something supernatural for you, but a familiar, everyday norm. Eliminate simple sugars from your diet as much as possible: especially if the cause of impaired secretion of digestive juices lies in the syndrome of excessive fungal or bacterial growth.
Go to bed early: at 11 p.m., the secretion of melatonin, an antioxidant hormone responsible for youth, beauty and actively counteracting the development of oxidative stress, begins. In addition, the release of other, no less important hormones: TSH and somatotropin is also tied to the sleep-wake cycle.
Some tips
- We must remember that you cannot eat the same foods. The diet should be varied.
- Many high protein foods are high in fat, so their consumption should be limited. These are fatty meats, milk, chicken eggs.
- You need to increase the amount of protein food gradually, especially if you are not used to it. Ingesting a large amount of protein at once can be stressful for the body. The digestive system may not accept such food, resulting in poisoning. Therefore, it is best to distribute the total amount of protein foods into five or six meals, but not eat in two or three meals.