A test that evaluates the rate of separation of blood into plasma and red blood cells. The rate of separation is mainly determined by the degree of their aggregation, i.e., the ability to stick together.
Synonyms Russian
Erythrocyte sedimentation reaction, ROE, ESR.
English synonyms
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, Sed rate, Sedimentation rate, Westergren sedimentation rate.
Research method
Capillary photometry method.
Units
Mm/h (millimeters per hour).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous, capillary blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate alcohol from your diet for 24 hours before the test.
- Do not eat for 2-3 hours before the test (you can drink clean still water).
- Stop taking medications 24 hours before the test (in consultation with your doctor).
- Avoid physical and emotional stress for 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
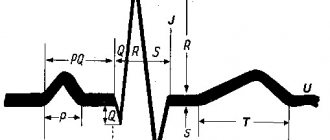
Determination of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is an indirect method for identifying inflammatory, autoimmune or oncological diseases. It is performed on a sample of venous or capillary blood, to which a substance has been added that allows it not to clot (anticoagulant). When analyzing ESR using the Panchenkov method, blood is placed in a thin glass or plastic tube and monitored for an hour. At this time, erythrocytes (red blood cells), as having a large specific gravity, settle, leaving a column of transparent plasma above them. The ESR is calculated based on the distance from the upper boundary of the plasma to the red blood cells. Normally, red blood cells settle slowly, leaving very little pure plasma. For this method, a Panchenkov apparatus is used, consisting of a tripod and capillary pipettes with a 100 mm scale.
For capillary photometry (automatic analyzers ROLLER, TEST1), the kinetic “stopped jet” method is used. At the beginning of the ESR analysis, programmed mixing of the sample occurs in order to disaggregate the red blood cells. Ineffective disaggregation or the presence of microclots can affect the final result, since the analyzer actually measures the kinetics of red blood cell aggregation. In this case, the measurement occurs in the range from 2 to 120 mm/h. The results of measuring ESR by this method have a high correlation with the Westergren method, which is the reference method for determining ESR in the blood, and have identical reference values.
The results obtained using the capillary photometry method in the region of normal values coincide with the results obtained when determining ESR using the Panchenkov method. However, the capillary photometry method is more sensitive to an increase in ESR, and the results in the zone of increased values are higher than the results obtained by the Panchenkov method.
An increase in the level of pathological proteins found in the liquid part of the blood, as well as some other proteins (the so-called acute-phase proteins that appear during inflammation) contributes to the “gluing” of red blood cells. Because of this, they settle faster and the ESR increases. It turns out that any acute or chronic inflammation can lead to an increase in ESR in the blood.
The fewer red blood cells, the faster they settle, which is why women have a higher ESR than men. The ESR rate varies depending on gender and age.
What is the research used for?
- For the diagnosis of diseases associated with acute or chronic inflammation, including infections, cancer and autoimmune diseases. Determining ESR is sensitive, but one of the least specific laboratory tests, since an increase in ESR in the blood itself does not allow determining the source of inflammation, in addition, it can occur not only due to inflammation. That is why analysis of ESR is usually used in combination with other studies.
When is the study scheduled?
- When conducting diagnostics and monitoring: inflammatory diseases,
- infectious diseases,
- oncological diseases,
- autoimmune diseases.
What do the results mean?
Reference values (ESR norm - table)
| Floor | Age | Reference values |
| up to 15 years | 2 - 20 mm/h | |
| Male | from 15 to 50 years | 2 – 15 mm/h |
| over 50 years old | 2 - 20 mm/h | |
| Female | up to 50 years | 2 - 20 mm/h |
| over 50 years old | 2 – 30 mm/h |
The results of this test must be interpreted in light of clinical data, medical history, and other tests.
Reasons for increased ESR in the blood
- Infectious diseases (usually bacterial causes). ESR can increase in both acute and chronic infectious diseases.
- Inflammatory diseases.
- Connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic scleroderma, vasculitis).
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis).
- Oncological diseases: Myeloma. As a rule, it is accompanied by a very high level of ESR in the blood, because with it pathological proteins are synthesized in large quantities, which cause the formation of erythrocyte “coin columns”.
- Hodgkin's disease is a malignant disease of the lymph nodes. The ESR indicator is usually used not to make a diagnosis, but to monitor the course and effectiveness of treatment of an already diagnosed disease.
- Cancer of various localizations, especially hemoblastosis. It is believed that an extremely high level of ESR in the blood indicates the spread of the tumor beyond the primary site (i.e., metastases).
- Myocardial infarction. When it occurs, damage to the heart muscle occurs, which causes a systemic inflammatory response and, accordingly, an increase in ESR. After a heart attack, the ESR peaks about a week later.
- Anemia. A decrease in the number of red blood cells can lead to an increase in their sedimentation rate.
- Burns, injuries.
- Amyloidosis is a disease associated with the accumulation of pathological protein in tissues.
Reasons for decreased ESR in the blood
- Diseases accompanied by changes in the shape of red blood cells, such as sickle cell anemia or hereditary spherocytosis (they make it difficult for red blood cells to settle).
- Polycythemia (increased number of red blood cells) and conditions that lead to it, such as, for example, chronic heart failure or lung diseases.
What can influence the result?
- ESR in women usually increases during pregnancy and menstruation.
- Oral contraceptives, theophylline, and vitamin A may increase ESR.
- Taking corticosteroids and administering albumin can reduce ESR in the blood.
Monitoring the indicator during pregnancy
For the expectant mother and child, the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction is of fundamental importance, since it is the first to indicate the risk of fetal hypoxia. This is due to the fact that red blood cells contain hemoglobin, the main carrier of oxygen in the body. It is this that gives red blood cells their scarlet tint. These cells live no more than 4 months, after this period they are utilized by the liver and spleen. Constant monitoring of ESR can tell a lot, but the main thing is to warn about the inflammatory process, which is especially important during pregnancy.
The main factor influencing the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is, of course, plasma with its protein component. Conception physiologically provokes an increase in plasma protein content, and the level of protein concentration and the number of red blood cells changes by trimester. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly monitor ESR during pregnancy. In order to do this, you just need to donate blood for analysis, following a number of rules:
- Blood is donated in the morning (the last meal is the night before).
- Blood is taken from a finger when the patient is completely calm.
- Before taking the test, all physical procedures, physical activity and medication are excluded.
The result of ESR is influenced by the qualifications of the laboratory technician, the sterility of the instruments, and the determination method. In any case, each antenatal clinic has its own subjective errors when carrying out the reaction, so the interpretation of the analysis is always carried out taking into account objective reference values.
- ESR in rheumatoid arthritis - Orthopedist.info
Tests in the second trimester
In addition to mandatory monthly visits to the gynecologist, the following tests are taken:
- Repeated ultrasound - screening + 3 triple test (determination of β - hCG, AFP and free estriol fraction);
- General blood analysis;
- General urine test at each appearance;
- Blood test for toxoplasmosis;
- Blood test for glucose;
In addition to the above tests, the doctor will prescribe a gynecological examination, which will give an idea of the size of the uterus and determine the presence of tumors. For chronic diseases, additional studies are prescribed. Also, starting from the second trimester, the doctor will be required to listen to the fetal heartbeat, using a special device - an obstetric stethoscope.
What signs indicate an increased ESR?
If an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate is caused by infectious diseases, then a woman may notice such unpleasant symptoms as:
- Headache.
- Increased body temperature.
- Feeling chilly.
- Decreased appetite.
- Excessive weakness, fatigue.
- Increased heart rate.
- Pallor of the skin.
If you notice such symptoms, you should definitely consult your doctor. He will prescribe the necessary tests and then make an accurate diagnosis.
Tests in the third trimester
- General blood analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- General urine test at each appearance;
- Repeated vaginal flora smear;
- Repeated tests for HIV infection, hepatitis B and C;
- Wasserman reaction;
- Last screening ultrasound;
- Additional tests as recommended by doctors.
In addition to these tests, a cardiotocogram is prescribed - an instrumental diagnostic method designed to determine the fetal heart rate and also record its movements.
What does ESR mean?
When performing laboratory tests on a blood sample from a pregnant woman, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate must be measured. These red blood cells are involved in the process of transporting oxygen and necessary substances to the internal organs. They consist mostly of hemoglobin. It is he who colors them red.
- ESR in diabetes mellitus: normal and high levels in the blood in type 2 disease
ESR is determined after adding an anticoagulant to the blood. Under the influence of this substance, red blood cells begin to settle . The number of blood cells that manage to sink to the bottom of the test tube in 60 minutes is shown by the ESR.
This parameter alone cannot be used to judge the presence of diseases in the body. But its change may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process.
What does ESR depend on?
If you take a flask, pour blood into it and then add an anti-clotting agent inside, the liquid will separate over time. Pure plasma will remain on top, and at the bottom there will be sediment, mainly consisting of red blood cells. This occurs under the influence of gravity due to the difference in weight.
The normal ESR level for an adult woman is in the range from 2 to 15 mm/h, for a man - from 2 to 12 mm/h. In a newborn child, regardless of gender, this figure is around 1-2 mm/h.