From this article you will learn: what is indirect cardiac massage, why, to whom and who can do it. Is it possible to harm a person by performing this procedure, and how to make it really help.
Indirect cardiac massage is an emergency resuscitation measure aimed at replacing and restoring stopped cardiac activity.
This procedure is the most important for saving the life of a person whose heart has stopped and is in a state of clinical death. Therefore, every person must be able to do cardiac massage. Even if you are not a specialist, but you at least know approximately how this procedure should take place, do not be afraid to do it.
You will not harm the patient if you do something not quite right, and if you do nothing, it will lead to his death. The main thing is to make sure that there are really no heartbeats. Otherwise, even a perfectly performed massage will cause harm.
When is resuscitation necessary?
The onset of clinical death of the patient is accompanied by the absence of pulse, breathing and pupillary reaction to light. Unless caused by serious injury or other life-threatening illnesses, the condition is reversible. The optimal time for resuscitation is no more than five minutes after death. If assistance is provided later, there is a risk of developing severe complications from the central nervous system and other internal organs.
Assistance to a person who develops clinical death should be provided in accordance with a specially developed resuscitation program. The main tasks here include restoration of blood circulation, respiration of brain cells and functions of the central nervous system. Possessing knowledge of the basics of SRL and practical skills in this area gives a real chance of saving a person’s life.
Indications for use
When a patient develops clinical death, it is necessary to use a basic set of actions, which in many cases helps bring the patient back to life. To do this, it is important to know the symptoms of this condition. All signs of death are divided into primary and secondary. In the first case, we are talking about the following manifestations in humans:
- absence of pulse in the area of large vessels (asystole);
- unconsciousness (coma);
- lack of constriction of the pupils in bright light (mydriasis);
- lack of breathing in the victim (apnea).
Apnea is confirmed by complete immobility of the chest. To understand that there really is no breathing, you should lean towards the patient and listen. Another option is to hold a mirror to his mouth. If there is weak breathing, it will fog up.
To verify asystole, you need to find the carotid artery. In other places, it is quite difficult to feel the pulse, since in unconscious patients the systolic pressure often drops to 60 mmHg. Art. To palpate the carotid artery, place your middle and index fingers in the middle of the neck, then move them left or right to the cavity. Here the pulse is clearly felt. If it is absent, we are talking about the onset of clinical death.
The reaction of others when a person’s heart stops must be immediate.
To determine mydriasis, you need to open the victim's eyelid. If the pupil does not constrict when exposed to light, this indicates an acute lack of blood and oxygen supply to the brain tissue.
Among the secondary signs, paleness of the skin, loss of muscle tone, and complete absence of reflexes should be noted. If the above-described manifestations are detected in the patient, cardiopulmonary resuscitation should be started immediately.
When is resuscitation contraindicated?
Primary resuscitation of patients according to the new standard is carried out with the aim of saving the patient’s life. Further professional assistance is provided in a hospital setting by qualified specialists. If the death occurs as a result of a long-term course of various pathologies in a person that cannot be treated, the feasibility and effectiveness of life-saving measures are called into question. Such diseases include cancer, severe heart failure and other conditions incompatible with life.
In addition, there is no chance of saving a life if the following symptoms develop:
- body cooling;
- formation of cadaveric spots;
- cloudiness and dryness of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- the appearance of the cat's eye phenomenon;
- muscle hardening.
These signs indicate the onset of biological death that cannot be resuscitated.
If there are signs of biological death, resuscitation is not carried out
Important! It is advisable to carry out resuscitation actions only in the event of clinical death that is not caused by serious degenerative processes in the patient.
Indications: who really needs this procedure
The most important thing in cardiac massage is to determine whether a person needs it or not. There is only one indication – complete cardiac arrest. This means that even if an unconscious patient has severe rhythm disturbances, but at least some cardiac activity is preserved, it is better to refrain from the procedure. Compressing the contracting heart can cause it to stop.
The exception is cases of severe ventricular fibrillation, in which they seem to tremble (about 200 times per minute), but do not perform a single full contraction, as well as weakness of the sinus node and atrioventricular block, in which the heartbeat is less than 25 beats per minute. If such patients are not helped, the condition will inevitably worsen and cardiac arrest will occur. Therefore, they can also be given indirect massage if there is no other way to help.
The rationale for the feasibility of this procedure is described in the table:
| When to massage | When not to do it |
Manifestations of clinical death:
| 1. Signs of biological death:
|
| 2. Presence of cardiac activity - there is a pulse in the carotid artery of the neck. |
Clinical death is the stage of dying after the cessation of cardiac activity lasting 3–4 minutes. After this time, irreversible processes occur in the organs (primarily in the brain) - biological death occurs. Therefore, the only time when you need to do cardiac massage is the period of clinical death. Even if you don't know when your heart stopped and you're not sure if there's a heartbeat, look for other signs of cardiac arrest.
Algorithm of actions
According to new standards of resuscitation, assistance to a person should consist of the following stages:
- Determining symptoms, calling an ambulance.
- Performing indirect cardiac massage.
- Artificial respiration.
- Defebrillation.
- Application of intensive care methods.
- Drug treatment of asystole and other conditions.
The algorithm of actions is carried out in accordance with the recommendations of the American Heart Association. For convenience, each of the stages of assistance is designated by letters - A, B, C, D, E. Let's consider each of them in more detail:
- Airway (A) – restoration of airway patency. The procedure is performed using tracheal intubation. The purpose of the event is to eliminate a life-threatening violation;
- Breathing (B) – artificial maintenance of a person’s respiratory function. Here the mouth-to-mouth technique is used. To prevent infection, it is recommended to use an Ambu bag;
- Circulation (C) – performing indirect massage of the heart muscle to ensure restoration of blood circulation throughout the body;
- Disability (D) – determination of neuralgic status, assessment of the victim’s vital functions;
- Exposure (E) – assessment of the patient’s external signs, relief of life-threatening conditions.
Help should be provided in compliance with all recommendations
The CPR standards described above are designed for physicians. People who provide first aid need to have knowledge and skills in carrying out the first three points.
Rules for ensuring the safety of the patient and resuscitator before the ambulance arrives. To increase the effectiveness of resuscitation actions and the safety of all participants in the process during the provision of assistance, the following recommendations should be adhered to:
- During CPR, the victim and the person performing resuscitation must be in a safe environment. People often need help after an accident on the road or in factories. All actions are carried out away from the road or dangerous equipment;
- when performing resuscitation, you need to call passers-by or neighbors, since the presence of several people will facilitate and speed up the procedure;
- If you can’t feel the pulse, you can’t focus on it. It is necessary to evaluate the patient's other vital functions (breathing, pupil reaction to light);
- the pupils stop responding to light only a few minutes after the heart stops. This nuance should be taken into account without wasting precious time.
Help must be provided in a safe environment
The sooner help is provided to the patient, the greater the chance of saving his life, preventing the death of brain cells, and, therefore, avoiding serious complications.
Technique for performing resuscitation measures
Without medical education and special skills in performing resuscitation actions, only three assistance techniques can be used. These include precordial stroke, indirect massage of the heart muscle, and artificial respiration. In the ambulance and in the hospital, doctors have access to such types of resuscitation as fibrillation and direct cardiac massage. In combination with these procedures, the necessary medications are used.
Precordial beat
This method is a substitute for the cardiac fibrillation procedure. It is advisable to perform it within the first few seconds after cardiac arrest. In this case, the actions of the resuscitator should be as follows:
- If the situation allows, place the patient on his back; the surface should be flat. If the pulse cannot be felt in the area of the carotid artery, the technique should be started immediately.
- Two fingers are placed in the chest area, in the area of the xiphoid process. The blow is delivered with a hand bent into a fist, slightly above this area.
- If there is no further pulse, the person providing assistance should begin chest compressions.
Precordial beat helps start the heart
Important! Precordial shock is not used to resuscitate patients under 8 years of age. This can only make the situation worse due to injury.
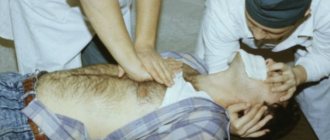
Chest compression
Another name for this resuscitation technique is indirect cardiac muscle massage. To perform the procedure correctly and effectively, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- The victim must lie on a stable surface. This will help prevent the body from shifting during the massage;
- it does not matter which side the resuscitator will be on during the session. Here attention should only be paid to the correct placement of the hands. They should be in the lower part of the sternum;
- the hands are joined with a lock or placed one on top of the other in the area 3–4 cm above the xiphoid process. Pressure is applied only with the palms, there is no need to work with fingers;
- chest compression is performed using the resuscitator’s body weight. Since each person has his own body weight, during the session you need to make sure that the chest is not pressed through more than 5–6 cm. If the pressure is stronger, you can injure the victim.
The hour interval between shocks should not exceed 1–2 seconds. The duration of the pressure itself is less than a second. In addition, it is important to take into account the age characteristics of the patient.
Indirect massage of the heart muscle is carried out with two palms
If we are talking about resuscitation of an infant, pushes are carried out with a finger, not with a palm. Palm compression is performed at an older age of the child. The chest compression procedure is considered effective when a pulse appears in the patient.
Artificial respiration
Before performing artificial ventilation, you should make sure that there are no foreign objects in the mouth that would interfere with normal breathing. For this, the patient is placed on his back, with his head thrown back as far as possible. Under your neck you need to put a rolled up towel or a roller from any available items. After this, the person providing assistance should perform a test breath through the mouth. If the victim’s chest does not rise, you need to examine the mouth and remove foreign objects.
After eliminating obstacles to artificial respiration, the algorithm for performing it is as follows:
- Inhalations are performed through the mouth. At the same time, the resuscitator must cover the nose of the unconscious person. This will ensure that air gets into the lungs.
- When performing the procedure, you need to monitor whether the victim’s sternum rises.
- The amount of air inhaled should be about 1 liter. About 12 breaths should be taken in 60 seconds. There should be a break of at least 5 seconds between them.
If the patient's celiac cavity swells during inspiration, you should be wary. This phenomenon may indicate air entering the stomach.
Artificial respiration ensures life support until doctors arrive
Important! Artificial respiration is most effective when combined with indirect massage of the heart muscle. This type of assistance should be performed by two people.
Direct cardiac massage technique
It is necessary to squeeze the heart carefully with all fingers of the palm at the same time, measuring the strength with the sensations. The thumb should be opposed to the other four. First of all, it is necessary to compress the area of the left ventricle - this will ensure the release of the remaining blood into the systemic circulation. Each press should be within 1-2 seconds. Then a break is made for a few seconds, during which two artificial breaths are taken into the lungs. In the case of artificial ventilation of the lungs, inhalations are carried out using a ventilator and, if there are no special instructions, it should work in the same mode. Before the next cycle of pressing, the hand should move slightly.
The electrocardiogram is recorded only in standard leads - electrodes from the limbs. The first recording can only be made after two resuscitation cycles. And only for a few seconds - usually no more than three. Ideally, the patient should be connected to a pulse oximeter, through which his hemodynamic parameters are displayed on the monitor.
Helping a patient in a hospital setting
After the victim is transported to the hospital, resuscitation continues using techniques such as direct cardiac massage, defibrillation and the use of medications.
Direct cardiac massage
This type of resuscitation care is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting. The technique is carried out like this:
- the doctor dissects the person’s sternum, which provides direct access to the organ;
- A rhythmic heart massage is performed to restore blood flow to the vessels of the whole body.
The effectiveness of massage depends on many factors, among which are the time of death, the professionalism of the doctor, and the reasons that led to cardiac arrest.
Defibrillation
This method involves the use of special equipment - a defibrillator. With its help, doctors apply electric current to the heart. This procedure is effective in severe conditions in patients with disorders such as ventricular fibrillation, supreventricular and ventricular tachycardia. If a complete cardiac arrest occurs, the method is considered inappropriate.
Defibrillation is performed in a hospital using special equipment
Use of medications
When performing resuscitation, the doctor injects the necessary medications into the patient’s vein or trachea. Intramuscular injections have low effectiveness and are used extremely rarely.
The following means are most often used to save human life:
- Adrenaline is most effective in cardiac arrest;
- Sodium Bicarbonate – Used to help patients with hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) and metabolic acidosis.
Depending on the type of disease and the symptoms developed in a person, many other medications are used. Among them it is necessary to highlight anticoagulants, antihypertensive and hypertensive drugs, tranquilizers and others.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, according to new standards, is a series of measures aimed at bringing the victim out of clinical death. The main measures during the provision of assistance include artificial respiration and chest compression. After hospitalization, the decision on the type of resuscitation actions is made by doctors on an emergency basis, depending on the patient’s condition.
Access by direct cardiac massage
In the case of thoracic surgery, no additional incisions are necessary, but access to the organ must be complete. Otherwise, it is necessary to open the chest in the area of 3-5 intercostal spaces with subsequent spreading of the ribs. Even at the cost of their integrity. There is no need to cut the heart sac. This is fraught with both the risk of myocardial damage and loss of time. In the case of abdominal surgery, access to the heart is made through an incision in the diaphragm. In any case, a person’s hand should have freedom to clasp the heart.