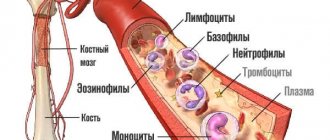
Formed blood cells are represented by a wide group of cytological structures. According to the generally accepted classification, white blood cells are divided into granulocytes and agranulocytes.
Granulocytes are represented by three types of cells:
- Basophils. They are fat structures. The largest of all the others.
- Eosinophils. Significantly less. Capable of phagocytosis. They mainly fight parasitic infestations.
- Neutrophils. These are the most numerous cells. They make up up to 70% of the total mass of immune structures, and are divided into band and segmented.
If granulocytes enter the battle first and are responsible for the initial response of the defense system, agranulocytes start later. They are represented by monocytes and lymphocytes.
If neutrophils are low, this is a clear sign of inflammatory processes, disorders of the bone marrow, allergic reactions and other diseases. Which ones exactly need to be clarified separately.
The condition is called neutropenia and has its own ICD-10 code - D72. Accompanied by a group of symptoms, mainly caused by the primary pathological process.
What do you need to know about this violation?
Development mechanism
In total, four main pathogenetic factors can be named. They start the disorder.
Inflammatory processes
The fact is that neutrophils are the very first to enter the “battle”. These are the most numerous cells, therefore any deviations in the quantitative composition are noticeable immediately.
As soon as a foreign agent enters the body, the body begins to produce granulocytes in large quantities. Those that already exist die, which causes increased activity of the immune system.
But if the pathological process continues for too long, the structures become depleted. They can no longer work as before. Outside help needed. The concentration of neutrophils decreases, which is quite logical.
This state of affairs persists for some time after the end of the illness.
Bone marrow disorders
Various deviations lead to the pathology in question. Mainly associated with inhibition of red matter. Cells are either not produced at all, or there are many of them.
There is another option, when the disorder is accompanied by immature cytological structures.
Formally, the quantity is normal. But the cells do not have time to form and are not registered according to the test results.
Irradiation
The effects of radiation on the body. Accompanied by suppression of bone marrow function. The body is not able to resist such influence. Moreover, the red substance is extremely sensitive to iosinizing radiation.
Recovery is carried out in a hospital setting. It is important that the patient receives help in the first hours after the onset of the pathological process. Otherwise, critical disorders of the immune system cannot be avoided.
Attention:
Irreversible deviations are possible that will make the patient disabled.
Use of certain medications
Capable of inhibiting the production and maturation of neutrophils. For example, some antibiotics, immunosuppressants (Methotrexate and similar).
Also, glucocorticoids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs provoke a decrease in neutrophils in the blood. Whether the drug has such a side effect or not, you need to look in the annotation for the medication.
There are many mechanisms and all are caused by pathological processes. Deviations that are provoked by natural phenomena are extremely rare.
Decoding the norms for neutrophil lymphocyte indicators
The state of the human immune system when deciphering the analysis is determined by the percentage of young and mature cells. The normal indicators do not depend on gender; for women and men the percentage of neutrophils will be the same. But at the same time, the patient’s age is taken into account.
Band cells are always elevated in infants and make up from 3 to 12% of the total number of leukocytes, but by the month of life the balance between young and mature cells returns to normal.
In children under 3 years of age, immunity has not yet been formed, so the percentage of segmented cells may fluctuate, which is also considered normal within acceptable values.
The following are the norms for neutrophil levels in a child, adolescent and adult.
| Person's age | Band cells | Segmented cells |
| Newborn | 3-12% | 46-70% |
| Infant up to 2 weeks of life | 1-5% | 30-50% |
| Infant from 2 weeks to a year of life | 1-5% | 16-46% |
| 1-2 years | 1-5% | 28-48% |
| 3-5 years | 1-4% | 32-55% |
| 6-7 years | 1-4% | 37-58% |
| 8-9 years | 1-4% | 41-60% |
| 10-11 years | 1-4% | 43-60% |
| 12-15 years | 1-4% | 45-60% |
| from 16 years old and adults | 1-3% | 45-70% |
Before conducting a general analysis, you need to warn your doctor or stop taking certain medications that distort the level of neutrophil granulocytes. These include: sulfa drugs, diuretics, corticosteroids, penicillin drugs and analgesics.
Stages of violation
The disease or, more precisely, the pathological condition is accompanied by a decrease in the content of neutrophils. How pronounced a change occurs depends on the primary cause.
As for the stages or severity of the disorder, there are three of them.
Lightweight
Or the very first one. The concentration of granulocytes drops to the level of 1-1.5*109 /l. There are no symptoms yet. The patient does not even suspect that there are any health problems. Minor disorders and changes in well-being are possible.
Neutrophil norms by age in both sexes are described in detail here.
Moderate
The cell concentration drops to 0.5-1*109 /l. Much more noticeable in terms of symptoms. The patient suffers from frequent colds. It is necessary to strengthen the immune system and treat the primary pathological process.
Heavy
It is accompanied by either a complete absence of neutrophils or a significantly reduced number of formed cells. Urgent treatment in a hospital is required. Measures are being taken to strengthen the immune system.
Typically, the disorder develops as a result of immunodeficiency. Viral or otherwise. Possibly with severe radiation sickness.
Attention:
The condition poses a real threat to the health and life of the patient.
Stages are a laboratory indicator. It is examined as part of a general blood test. In case of disorders or disorders that were detected earlier, additional examinations are prescribed.
Neutrophil function and indications for their determination
The leukocyte formula gives a general idea of human immunity and includes a harmonious ratio of five leukocytes: monocytes, eosinophils, lymphocytes, neutrophils and basophils. Violation of the norm of these indicators in a general blood test helps to recognize pathologies, including malignant neoplasms.
Indications for a general blood test, in particular to determine the quantitative ratio of the neutrophil fraction, are the following diseases:
- upper respiratory tract diseases (sore throat and pneumonia);
- pathologies of parenchymal organs (pancreatitis and cholecystitis);
- sepsis, gangrene and extensive burns of the skin;
- heart attack;
- tuberculosis;
- hypoplastic and aplastic anemia;
- blood loss;
- appendicitis and peritonitis;
- chemical poisoning;
- rheumatic attacks.
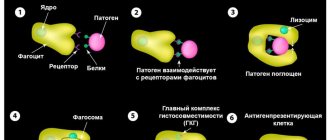
In general, leukocytes perform a protective function for the body: they create a barrier to pathogenic microflora (infections, viruses and bacteria), and are also designed to absorb pathogenic bacteria, the products of their vital activity and decay.
The leukocyte protective barrier involves the complex functioning of individual factions, each of which strictly performs its own functions. Thus, the task of neutrophils is to absorb pathogenic microorganisms and break them down in their own body. Having completed its “mission,” the neutrophil lymphocyte dies, forming exudate and attracting other leukocyte cells. At the same time, the neutrophil secretes antibacterial substances and enzymes.
The mechanism is simple: if there is a focus of inflammation in the body, a segmented (adult) neutrophil from the blood is directed to the pathogenic focus, so its quantitative ratio with other leukocytes in the blood stream may temporarily decrease. A sharp decrease in cell levels in some cases occurs due to intensive therapeutic methods such as radiation or chemical therapy.
Reasons for decreased neutrophils
There are quite a lot of factors in the development of the pathological process. They follow from the mechanisms described above.
Burdened heredity
Severe genetic disorders. Mainly represented by different types of Kostman syndrome.
This is a disorder in which there are no full-fledged forms of neutrophils in the bloodstream. In the early stages of maturation everything is fine. But incapacitated types of cytological structures emerge from the bone marrow.
Low neutrophils pose a catastrophic danger, and severe symptoms of the pathological process pose a threat to the patient’s life.
Among the manifestations of the violation:
- Frequent infections. Formation of boils on the skin.
- Development of phlegmon. Septic lesions of subcutaneous fat.
- Necrosis of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and genital organs. Also the digestive tract.
All disorders pose a huge threat, since the development of sepsis and the death of the patient are possible.
Changes begin from the very first days of a person’s life. Therefore, it is impossible not to notice the pathological process.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital. At least at the first stage. It is necessary to prescribe a special drug. This is a special hormone, G-CSF. It is able to stimulate the maturation of neutrophils.
As a rule, patients take it systematically throughout their lives. From time to time, planned inpatient treatment is carried out.
On the other hand, a bone marrow transplant is a good option. But this measure is not always effective. It all depends on the nature of the pathological process and indications.
Inflammatory conditions
Mainly of infectious origin. Reduced neutrophils in the blood are found against the background of rubella, measles, scarlet fever, ARVI, and previous influenza. There are many more options than mentioned.
Theoretically, even a minor pathological process can lead to neutropenia. The only question is individual characteristics.
The reason is pretty obvious. The body sends immune cells to the site of injury. Structures are dying and need others to replace them. The body actively synthesizes new neutrophils to ensure the full functioning of the defense forces.
At a certain point, the body's capabilities are exhausted. Consequently, the changes become clearly visible.
The longer the inflammation lasts, the lower the content of neutrophils in the blood. It is necessary to treat disorders as early as possible.
Therapy is carried out with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Also broad-spectrum antibiotics.
It is necessary to sanitize the main source of damage. Infectious focus. This is the key to successful recovery. The problem is solved under the supervision of a competent therapist and/or specialized specialist.
Radiation sickness
Complex pathological process. Due to the negative impact of radiation on the patient’s body. The fact is that the factor damages cells.
Charged particles penetrate tissue and easily remove electrons from the atoms of the substance that make up the cytological structures.
Accordingly, a change in the condition of the tissue occurs. They become damaged and can no longer work as expected.
Radiation sickness is accompanied by a lot of symptoms, but as a rule, they have a delayed development. That is, they are formed after exposure to a damaging factor. Up to a day or even more.
Among the manifestations:
- Hair loss. Up to complete baldness.
- Burns. They are localized in the place of greatest influence of ionizing radiation.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Disturbances in the functional activity of tissues. For example, paresis and paralysis appear.
The bone marrow is extremely sensitive to the effects of radiation, which causes a rapid drop in the concentration of neutrophils, even to a critical level. And then the body is not able to recover on its own.
Where a person is at risk of encountering dangerous doses of radiation:
- On submarines.
- At nuclear power plants.
- When undergoing radiation therapy (cancer treatment).
A systematic effect of small doses in environmentally unfavorable areas is also possible: Bryansk, Ivanovo regions in Russia, Kyiv in Ukraine. Gomel in Belarus.
Therapy of the pathological process is carried out strictly in a hospital. The task is to remove radioactive isotopes from the body. Return the body to its normal state and maintain it.
The number of neutrophils is restored on its own. Some time later. With minor damage, the prognosis is favorable.
Parasitic infestations
Worms. Contrary to possible belief, foreign organisms penetrate not only into the intestines. Some species can enter the eyes, liver, brain, and lungs through the bloodstream. The only question is how actively the immune system works.
Although eosinophils play the main role in the fight against worms, neutrophils do not stand aside. Toxins that are produced during the life of helminths inhibit the functioning of the bone marrow and the content of neutrophils in the blood decreases.
Symptoms depend on the type of parasite. Typically manifests itself in several ways:
- From the dermis - profuse rashes, itching, pain.
- From the point of view of the central nervous system - drowsiness.
- Manifestations of general intoxication of the body also develop. Body temperature rises, headache. The patient is in a weak, weak state.
Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a parasitologist. Recovery requires taking special anthelmintic drugs. Which ones exactly depends on the location of the pathological focus.
On the other hand, if access is difficult, surgical correction is prescribed. The forecasts are generally favorable.
Immunodeficiency
Not necessarily the virus of the same name. AIDS. Although HIV also plays a big role - neutrophils drop to almost zero.
Pathological changes are possible against the background of autoimmune and septic, infectious inflammation. It is necessary to carefully approach the issue of diagnosis.
As a rule, the disorder is not accompanied by any special symptoms. A person often gets sick and becomes covered in boils.
Disorders of the anatomical integrity of the mucous membranes of the body are possible.
Up to a certain point, the pathological process is classified as idiopathic. That is, the exact cause is impossible to identify. Treatment depends on the specific pathological process.
Poisoning
A decrease in the concentration of neutrophils occurs during intoxication with toxic substances. The most dangerous compounds are cadmium and arsenic.
And you don’t have to go far to find them. These chemicals are found in cigarettes and tobacco products.
In case of poisoning, a group of dangerous symptoms develops:
- Disorders of the central nervous system. Headaches, coordination disorders and other pathological changes.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Reduced blood clotting.
Recovery is carried out under the supervision of toxicologists. It is necessary to undergo a full course of cleansing. Diuretics and special saline solutions are prescribed.
The same effect is possible with excessive alcohol consumption.
Detoxification is carried out under the supervision of narcologists. Special preparations are required: Disol, Trisol. It is advisable to carry out the correction in a clinical setting.
Allergies
Autoimmune response to a harmless agent. For example, food products, particles of wool, saliva and others can provoke a pathological process. The patient undergoes therapy under the supervision of an allergist or immunologist.
Symptoms depend on the location of the disorder:
- Skin rash.
- Cough.
- Respiratory dysfunction. Asphyxia is possible with the development of Quincke's edema.
The most dangerous form of allergic reaction provokes anaphylactic shock. This is an emergency. It is necessary to place the patient in intensive care as soon as possible.
The reason for the decrease in neutrophils in allergies is due to the high “consumption” of formed cells: they die, but no beneficial effect is observed. Quite the opposite.
Therapy is carried out using drugs of several groups. In relatively mild cases, antihistamines are prescribed. First or third generations.
The latter are highly effective with few side effects.
If medications are ineffective, glucocorticoids are additionally indicated. Prednisolone and similar. The potency of the drug is determined by the severity of the allergic reaction.
Bone marrow disorders
{banner_banstat9}
Primary pathological processes are quite rare. This group is mainly due to acquired disorders. For example, against the background of long-term treatment with immunosuppressants. Or after exposure to radiation.
Other diseases are predominantly genetic. Hereditary origin.
Symptoms are nonspecific. Depends on the specific pathological process
Treatment of congenital forms is hormonal. As for myeloproliferation, that is, the excessive synthesis of immature cells, it is suppressed by immunosuppressants and glucocorticoids. But in strictly verified volumes.
Use of certain medications
{banner_banstat10}
Antibiotics, hormonal medications and other drugs lead to a decrease in neutrophils.
It is enough to give up the drugs or replace them with other names and the concentration of cells is restored by itself.
This issue cannot be resolved on its own. Only under the supervision of a specialist who prescribed a course of therapy.
How to increase neutrophils in the blood
When a person has a low percentage of neutrophils, it is necessary to eliminate the problem that caused this condition. If this happened due to an infectious disease, then they recover on their own in a short period of time. In other circumstances, the only way to increase neutrophils in the blood of a child or adult is to eliminate the root cause of their decrease. The doctor may prescribe drug therapy, which is relevant for severe neutropenia. If the disease manifests itself moderately, then:
- leukopoiesis stimulants are prescribed;
- The use of Pentoxyl and Methyluracil is considered effective.
Therapy should be carried out after consultation with an immunologist under the supervision of an immunogram. When the body does not respond to treatment and white blood cells are still low, colony-stimulating factor medications are prescribed, for example, Lenograsti, Filgrastim. These same medications are immediately prescribed to patients with agranulocytosis. Such drugs are prescribed only under conditions of inpatient treatment, because this is a potent group of drugs.
Find out what the norm of leukocytes in the blood of women should be.
Additional examinations
Supportive measures are prescribed only by doctors. Among the methods:
- Oral interview with the patient. It is necessary to identify all the symptoms of the pathological process.
- Study of anamnesis.
- General blood and urine analysis. Biochemical methods.
- Allergy tests. Within the framework of which immunological studies are carried out.
- Bone marrow puncture. Quite a risky technique. It is prescribed in extreme cases when there is no other option.
- Immunological tests.
- Chest X-ray.
- Smears from the throat, genitals. From suspected sources of infection.
If neutrophils are low in an adult, this indicates an obvious pathological process: inflammation, poisoning, allergies, disorders of the bone marrow, radiation sickness, or the development of side effects from taking medications.