| Author of the article: | |
| Sleptsov Ilya Valerievich, Doctor of Medical Sciences, endocrinologist surgeon, professor of the Department of Faculty Surgery of St. Petersburg State University, deputy director for medical affairs of the St. Petersburg Multidisciplinary Center of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, member of the European Thyroidological Association, European Association of Endocrine Surgeons | |
| If you have been diagnosed with medullary thyroid cancer that requires surgical or chemotherapy treatment, or an increase in blood calcitonin levels, you can contact Ilya Valerievich Sleptsov by phone +7 921 9517088 to receive recommendations for diagnosis and treatment |
general characteristics
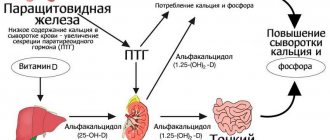
Peptide hormone. Produced by parafollicular C cells of the thyroid gland. Its physiological function as a parathyroid hormone antagonist is to inhibit bone osteoclast activity and reduce serum calcium levels. It may increase with benign lung diseases and during pregnancy. Gradually decreases with age. Typically, an increase in serum levels of both basal and stimulated levels of calcitonin during a provocative test with intravenous calcium administration serves as the main diagnostic criterion for medullary thyroid carcinoma, even in the absence of radioisotope diagnostic data, and correlates with the stage of the disease and the size of the tumor. An unfavorable prognostic criterion for medullary carcinoma after surgery is considered to be an increase in calcitonin levels > 150 pg/ml and a reduction in the time for a twofold increase in calcitonin levels from 2 years to 6 months.
What is calcitonin
Calcitonin is a thyroid hormone, it is produced by C-cells located around the follicles (vesicles with the main hormones - thyroxine, triiodothyronine).
The role of calcitonin:
- takes part in the regulation of phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the body;
- stimulates the work of bone-building cells (osteoblasts) and inhibits destructive cells (osteoclasts);
- slows down the destruction of bone tissue;
- prevents a decrease in bone mineral density (osteoporosis).
The formation of calcitonin depends on the calcium content in the blood; the more calcium, the more hormone is produced. Thyroid tumors produce a lot of calcitonin, so it is considered as a tumor marker.
C-cells belong to the diffuse endocrine system, that is, they are not only in the thyroid gland, therefore increased formation of calcitonin also occurs in cancer of the blood, stomach, lungs, mammary, gonads, tumors of the pancreas and adrenal glands (pheochromocytoma).
Preparatory stage
In order for the result to be true, you will have to carefully prepare. Despite the fact that the basis for the study is not the blood itself, but plasma after its separation from other particles, this does not exclude the need to adhere to several rules.
From a medical point of view, preparation involves drawing blood using standard methods and then freezing it for successful transportation to the laboratory. If storage or transportation conditions were violated, this will significantly affect the overall reliability of the information. The list of tips on how to prepare includes several important points:
- do not eat food eight hours before the expected examination;
- avoid any physical activity on the eve of the procedure;
- avoid stressful situations.
There are a number of factors influencing the results of the study:
- taking calcium supplements;
- circadian rhythms (calcitonin concentration increases towards noon);
- exercise stress.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Due to the individual physiological characteristics of the body, as well as insufficient skills of the laboratory assistant, the patient may experience bruises at the puncture site after the manipulation. But this is quite a common phenomenon, as is the burning sensation during blood sampling along with pressure on the vessel. All inconveniences go away on their own after a couple of days.
References
- Osteoporosis. Clinical recommendations. — Russian Association of Endocrinologists, 2021. — 107 p.
- Felsenfeld, A., Levine, B. Calcitonin, the forgotten hormone: does it deserve to be forgotten. - Clin Kidney J., 2015. - Vol 8(2). — P. 108-187.
- Danila, R., Livadariu, R., Branisteanu, D. CALCITONIN REVISITED IN 2021. - ActaEndocrinol (Buchar), 2021. - Vol. 15(4). — P. 544-548.
- Toledo, S., Lourenço, D., Santos, M. et al. Hypercalcitoninemia is not pathognomonic of medullary thyroid carcinoma. - Clinics (Sao Paulo), 2009. - Vol. 64(7). — P. 699-706.
When should you check your calcitonin levels?
Clinical recommendations for testing are the presence of nodules in the thyroid gland. According to statistics, out of 300 patients with nodules, only one is diagnosed with medullary carcinoma.
If there is confirmed cancer in the thyroid gland, a calcitonin test should be taken every 3-6 months.
It is also recommended to get tested if you have the following problems:
- Signs of osteoporosis are skeletal deformation, multiple fractures, bone pain. The analysis will assess calcium metabolism disorders.
- Hypoparathyroidism - if the level of parathyroid hormone decreases, the concentration of calcium also decreases, therefore, phosphates in the blood increase.
- Suspicion of multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome - in this case, the analysis will help to exclude or confirm the presence of tumors of several glands and genetic autosomal dominant syndrome.
It is also recommended to check the concentration of calcitonin if there are symptoms of hidden pathological processes:
- constant fatigue and weakness;
- apathetic state;
- enlarged lymph nodes and growth of nodes in the thyroid gland;
- lethargy;
- weight loss for no reason;
- dryness and pallor of the skin;
- hair loss and brittle nails;
- loss of performance;
- memory impairment;
- discomfort in the thyroid gland.
An endocrinologist may prescribe a calcitonin test to a patient:
- if the development of neoplasms is suspected;
- impaired absorption of phosphorus and calcium;
- the size of nodules in the thyroid gland is more than 1 cm;
- osteoporosis;
- to assess the condition of the kidneys, stomach and mammary glands;
- monitoring the dynamics after tumor removal;
- prophylaxis in patients who are predisposed to medullary tumors.
Endocrinologists recommend taking a calcitonin test on a regular basis in conjunction with an annual preventive examination. The cost of the study is low, so including it on the list of required ones will not be difficult.
Calcitonin is normal
When testing blood for calcitonin and assessing the results of this analysis, it should be remembered that there is no lower limit of normal for this hormone
. If its level in the blood is zero, this is also normal. It is important that it does not rise above those limits that are designated as the upper limit of normal for this particular analyzer and this particular set of reagents.
It doesn’t make much sense to indicate any specific norm for calcitonin here, since laboratories now use very diverse models of analyzers - this leads to the fact that the concept of norm in this case should not even be discussed. When you take a calcitonin test in a high-quality modern laboratory, the norm will be indicated on the same form - this rule is followed very strictly by good laboratories.
How to prepare for analysis
To test for calcitonin, venous blood is needed.
Rules for preparing for the study:
- We recommend donating blood between 8 and 11 am;
- blood must be donated on an empty stomach, after an 8-12 hour overnight fast;
- on the eve of the study - a light dinner with limited intake of fatty foods;
- on the day of the test, you can drink still water and it is better to avoid coffee and tea;
- 24 hours before the test, exclude alcoholic beverages;
- 1 hour before the test it is better to refrain from smoking;
- 24 hours before the study, exclude the use of medications (in consultation with the attending physician);
- 24 hours before the test, eliminate emotional and physical stress;
- You should not donate blood after radiography, ultrasound, massage, endoscopic and physiotherapeutic procedures;
- It is recommended to rest for 10-20 minutes before donating blood.
The dangers of high and low calcitonin
Elevated calcitonin indicates diseases:
- medullary thyroid cancer and other tumor diseases;
- renal failure;
- megaloblastic anemia due to vitamin B-12 deficiency;
- increased function of the parathyroid glands;
- alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver;
- inflammation of the thyroid gland.
Low calcitonin is normal; its decrease while taking prescribed medications or after surgery indicates the effectiveness of therapy.
Blood test for calcitonin
Blood calcitonin is now determined by various laboratories using equipment of various classes to study the level of this indicator. The most modern analyzers, which give the calcitonin analysis maximum accuracy, are 3rd generation immunochemiluminescent analyzers. Widespread and cheap to operate and handle, 2nd generation enzyme immunoassay analyzers provide a significant error in determining the level of calcitonin in the blood, which can lead to incorrect actions both at the stage of examining the patient and at the stage of his treatment. That is why, if during a blood test, calcitonin is the main indicator you are interested in, ask the laboratory what method is used to perform the analysis.
The laboratory of the North-Western Endocrinology Center performs a blood test for calcitonin using an automatic 3rd generation immunochemiluminescent analyzer Liaison XL manufactured by DiaSorin (Italy)
– one of the world's largest manufacturers of equipment for studying blood hormone levels. The accuracy of calcitonin testing using the high-tech 3rd generation method is so high that it often eliminates the errors of tests performed by other laboratories using less modern methods. Very often, patients who have elevated blood calcitonin turn to the North-Western Endocrinology Center - and often a simple double-check of the results using precision equipment makes it possible to find out that in fact the hormone is within normal limits.
| Automatic immunochemiluminescent analyzer 3rd generation DiaSorin Liaison XL (Italy) | 3rd generation chemiluminescent immunoassay analyzer for determining blood calcitonin levels with maximum accuracy |
Why is calcitonin so interesting to endocrinologists and endocrinologist surgeons? The fact is that from the C-cells that produce this hormone, a very dangerous malignant tumor of the thyroid gland grows, which is called medullary cancer or C-cell carcinoma. Medullary cancer grows slowly (this is perhaps its only positive quality), but extremely stubbornly - it is not “afraid” of chemotherapy, with the exception of some drugs from the group of kinase inhibitors, and also does not accumulate radioactive iodine at all and does not respond to external beam radiation therapy. Medullary cancer actively metastasizes to the lymph nodes of the neck, mediastinum, and also spreads its metastases through the blood to the lungs, bones, liver, and brain. Early and timely surgery is the main thing that can bring victory over medullary cancer.
Due to the fact that C-cells, which are the basis for the growth of this type of cancer, produce the hormone calcitonin, its concentration in the blood increases sharply. It is this indicator that is used for the early diagnosis of medullary thyroid cancer. Calcitonin is a method that, if used correctly, can save thousands of human lives.
Currently, about 100-150 cases of medullary thyroid cancer are detected annually in Russia. Not long ago, summary data on the diagnosis of medullary cancer in 16 large and densely populated regions of the European part of Russia were published. Overall data showed that about 40 cases of medullary cancer are detected annually in this vast region. You may be surprised, but in 2013 alone, specialists from the Northwestern Endocrinology Center identified and treated 38 patients with medullary thyroid cancer
. It turns out that one center, albeit a large one, detects as many cases of C-cell cancer per year as 16 regions of our country - and the reason for this lies not only in knowledge of the intricacies of diagnosing this tumor, but also in the competent and active use of calcitonin as a tumor marker.
It should be noted that at present, almost all deaths of patients suffering from various forms of thyroid cancer are caused by medullary or anaplastic cancer. And if we still do not have an effective treatment for anaplastic cancer, medullary cancer is completely curable - and a blood test for calcitonin is designed to help with this.
After lengthy debate, in 2012 the European Thyroid Association in its recommendations indicated the need for a single calcitonin test for all patients with thyroid nodules. The test does not need to be done annually - if the first test shows that the hormone level is not elevated, the next test should be performed only if new nodes appear that were not previously recorded.
Large international studies have shown that when calcitonin levels are determined in all patients with thyroid nodules, previously unsuspected medullary cancer is detected in 1 case out of 300
. In this regard, the European endocrine community is inclined to believe that spending 299 times the money on analysis (and insurance companies pay for the examination there, not the patients themselves) is quite reasonable if, as a result, one patient is diagnosed with cancer at an early stage, when it is still can be cured. By the way, the American Thyroid Association has not yet supported this opinion - in the USA it is believed that such spending of money is unwise (we are talking about the economic efficiency of the method, not about its clinical significance and usefulness - no one has any doubts about this).