Causes of pain
The head in the forehead area can hurt without damage to the internal organs. The cause may be mental fatigue. For knowledge workers, tension accumulates in the center of the forehead. At the end of the working day, a pressing feeling arises. A light massage of a point in the center of the forehead, and then upward, to the sides, will help to remove it.
Head pain in the forehead area may occur due to poisoning by toxic fumes. Such sensations often haunt employees of household chemicals and building materials stores. Low-quality products have a strong odor and emit fumes that cause pain, dizziness, and nausea. People who are sensitive to this should change their job or profession, and wear a respirator before leaving.
Severe headaches are sometimes caused by cerebral vasospasm. This condition manifests itself against the background of smoking, alcohol abuse, and sometimes due to changes in climate zones. Pain can also be triggered by physical or emotional stress.
Read also: Sweating head
Why does my head hurt after sleep?
A morning headache brings discomfort throughout the day. Night sleep is the time when, after a hard day, our body restores strength. But from time to time awakening is overshadowed by unpleasant sensations.
The reason for such an uncomfortable awakening may be:
- Uncomfortable sleeping position.
- Incorrectly chosen pillow or mattress. Ignoring this moment leads to morning pain throughout the body, including the head.
- When the condition of blood vessels deteriorates, blood pressure is disturbed, which affects the quality of our sleep. Then feeling unwell becomes frequent.
- Head injuries can also contribute to headaches in the morning. It can occur a week or a month after the injury.
- Sinusitis makes breathing difficult, which causes a headache when waking up.
- Cervical osteochondrosis is a displacement of the spine in the cervical region. With this disease, the supply of oxygen to the brain is disrupted.
Possible diseases
In some cases, the head hurts in the forehead and there is pressure due to pathologies of the internal organs. Associated diseases:
- infections: acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections (cause a rise in temperature and intoxication, which is why the head hurts and puts pressure on the forehead);
- ENT diseases: sinusitis, ethmoiditis, frontal sinusitis (a characteristic symptom is severe nasal congestion);
- inflammation of the membranes of the brain: encephalitis, meningitis (accompanied by fever);
- pathologies of the nervous system: migraine (pain intensifies due to sounds, bright light, and recedes in silence and darkness), neuralgia (sharp, severe pain);
- injuries: concussions, skull fractures, bruises of the soft tissues of the head;
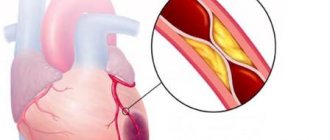
- diseases of the cardiovascular system: changes in intracranial pressure, hypertension, atherosclerosis, neurocirculatory dystonia;
- endocrine disorders: pathologies of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands;
- ophthalmological diseases: changes in intraocular pressure, uveitis, inflammation of the optic nerve, myopia;
- oncological pathologies: brain tumor, neoplasms in the sinuses or pituitary gland.
Headaches in the forehead area can occur against the background of a large number of diseases. A comprehensive examination of the body will allow you to identify and eliminate the provoking factor.
Hypertension - causes and mechanism of development
Hypertension is a chronic disease in which there is a frequent increase in blood pressure. If normally it is 120/80 mm. rt. Art., then at 140/90 mm. rt. Art. The initial stage of the disease has already been diagnosed. In some patients, only the systolic (upper) pressure increases, but the lower (diastolic) pressure may also increase along with it. The diagnosis is made based on the results of measuring blood pressure in different physiological states: during rest and after exercise.
Blood pressure increases due to dysregulation, vascular spasms and other factors. In most patients, hypertension is primary - it manifests itself as an independent disease, and a hereditary predisposition can also be observed. In other cases, the disease is caused by long-term use of certain groups of drugs, including hormonal drugs, kidney disease and metabolic disorders. Thus, secondary (symptomatic) hypertension is diagnosed, which also often causes headaches and high blood pressure.
Doctors identify risk factors that can provoke attacks of hypertension, as well as aggravate the course of the disease in the early stages. These include:
- overweight – up to 85% of patients diagnosed with chronic hypertension suffer from obesity;
- smoking - this bad habit reduces the ability of blood vessels to respond to changes in blood pressure, and also provokes ischemia (oxygen starvation) of the myocardium;
- insufficient physical activity, sedentary lifestyle, working behind a monitor;
- stressful situations that activate the sympathetic nervous system and lead to a persistent increase in blood pressure;
- patient's age.
According to statistics, in young people hypertension is secondary and is associated with a person’s lifestyle. High blood pressure and headaches are often triggered by bad habits, stress and poor diet. At the age of 40 years and older, sclerotization of the arteries is diagnosed - a decrease in their strength and elasticity as a result of the growth of connective tissue. This process is irreversible, but can be reversed by taking medications, adequate exercise and a therapeutic diet.
Diagnostics
People come to a therapist and neurologist with headaches. Additionally, patients are asked to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist to assess the condition of the fundus. Further testing to determine the cause of headaches includes:
- complete blood count to rule out infections;
- EEG - determines the electrical activity of the brain, detects epileptic activity, migraine;
- ECG - checking the state of the cardiovascular system;
- analysis of thyroid hormone levels;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- X-ray of the cranial sinuses - to determine ENT diseases.
Even a complete examination does not guarantee that the cause of the pain will be discovered. But it allows you to exclude serious diseases or identify them and select therapy.
Read also: Headaches in the temple area
How to determine the cause of a forehead headache before treatment
Unfortunately, few people immediately turn to a doctor about their problems. Most patients try to relieve pain by taking painkillers. And only a small part of patients consult a specialist. To understand exactly what factor leads to pain, the doctor carefully examines and interviews the patient who seeks help, measures his blood pressure, and sends him for laboratory blood tests. Tries to find out what exactly was the source of pain. If necessary, a person suffering from frontal pain is examined by a highly specialized specialist - a psychoneurologist, traumatologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, psychoneurologist. In some cases, additional diagnostic methods are required.
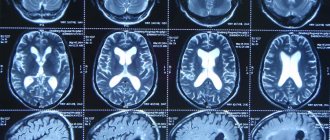
Most often, X-rays are used of the frontal part of the head, sinuses, and eye sockets. A safer and more accurate method is MRI of the head. Usually these measures are enough to find the root of the problem. Next, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Treatment
Headaches cannot be tolerated, so during attacks you should take analgesics. These can be drugs based on paracetamol, ibuprofen, ketorol and others that help a particular patient.
The main treatment for headaches is always aimed at their cause. If there are serious pathologies of internal organs, hormone therapy or chemotherapy, drugs for migraines or epilepsy, and drugs for heart disease are prescribed. Treatment is selected individually, taking into account the results of the examination and the general condition of the patient.
Dear patients!
Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33 Be healthy and happy!
When should you call an ambulance?
If a patient has a headache of moderate or severe intensity, according to medical professionals, it cannot be tolerated and it is better to take action as soon as possible. So, in particular, there are several signals with which you can determine in which cases you should act immediately and call an ambulance.
Doctors - specialists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) spoke about them:
- severe headache on the left, right, center, front or back and resembles blows - this is one of the symptoms of subarachnoid hemorrhage;
- The headache is tolerable, getting worse when lying down and going away on its own within 20-30 minutes when standing. This symptom can be caused by extremely dangerous illnesses: a brain tumor, serious consequences of a traumatic brain injury, problems with the cerebrospinal fluid;
- headache and dizziness are accompanied by loss of consciousness or unusual behavior of a person, as well as a deterioration in his motor activity (inability to get up, stand or walk independently). The cause may be a life-threatening disease that requires urgent treatment in a hospital;
- part of the head hurts or all of it, along with a sharply increased or increasing body temperature, can also be combined with discomfort in the muscles and photophobia. These are characteristic symptoms of meningitis, the positive outcome of treatment of which comes within hours.
On the basis of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) there is a 24-hour emergency department, so if you recognize one of the symptoms listed above, do not hesitate, call specialists immediately. A serious illness that has been promptly and correctly diagnosed is much easier and faster to cure than to deal with the severe consequences of a neglected condition.
Non-hazardous conditions
Cephalgia is often observed during pregnancy, especially in the first half, when hormonal levels are greatly unbalanced, immune defense drops, and emotional reactions become poorly controlled. At this time, women often catch colds, suffer from long-forgotten chronic diseases, feel pressure surges, and are under moral stress. All these factors affect the development of pain in the forehead and temples, which are of a compressive, aching nature. Triggers such as:
- unhealthy eating behavior (hunger, overeating, consumption of alcohol, citrus fruits, sweets);
- physical stimuli (sharp sounds, smells, bright lighting);
- change of climate zone;
- sleep problems, fatigue.
The appearance of pain can also be associated with everyday situations when a person is forced or deliberately in the open sun in hot or, conversely, cold, windy weather. Irradiation to the forehead or temples also occurs due to mechanical impact on the eyes. If a person wears contact lenses, it can cause dry eyes and headaches. The composition of the diet also affects the patient’s sense of well-being. If you exclude harmful components from the diet (caffeine, alcohol, fast food, processed foods, smoked foods), the discomfort in the head may disappear on its own.
What to do if you have a migraine?
- Take a drug that stops the attack as soon as possible. NSAIDs may help in the early stages, but triptans are the best treatment today;
- Lie down comfortably in a dark and cool place, provide access to fresh air;
- If necessary, place a towel moistened with cool water on your forehead;
- Avoid exposure to light and sounds;
- Try to sleep;
- If medications and sleep do not help, and the attack becomes more and more painful, you need to call an ambulance.
What causes migraines?
There are a number of potential triggers that can trigger a migraine:
- Wine, dark chocolate, cheese, honey, coffee;
- Bright or flashing lights are a common migraine trigger;
- The sound is too harsh or loud;
- Menstruation. In women with this type of migraine, attacks occur in the first days of the cycle;
- Too much or too little sleep. For migraine patients, it is important to know your sleep norm and try to stick to it;
- Stress.
But in this matter everything is individual. Migraines can occur suddenly even after waking up and being well rested.