Vascular genesis of the brain is a pathological condition that includes a whole complex of diseases associated with impaired blood supply to the brain. Pathological changes in the vessels are accompanied by neurosis-like symptoms, but at the initial stage the clinical picture may be limited to only a headache. If the pathology is not detected in a timely manner, obstructed blood circulation in the cerebral arteries can provoke the development of severe complications. Therefore, at the first signs of a vascular disorder, patients should consult a specialist to further determine the cause of the disease.
Characteristics of the pathology
When identifying vascular pathology, most patients are interested in what it is?
The concept of “vascular genesis” is not an independent disease; the term is intended to designate pathological changes in the cerebral circulatory system.
The pathology may be associated with circulatory disorders both in microvessels and central cerebral veins and arteries
Depending on the nature of the brain damage, the following disorders are distinguished:
- General or organic disorders (characterized by the appearance of constant headaches, accompanied by nausea and vomiting).
- Focal changes (the formation of a pathological focus is accompanied by a disorder of certain functions).
Nutrition of the brain is provided by several main vessels; disruption of their blood circulation leads to the development of various vascular diseases.
Prolonged vascular obstruction leads to improper functioning of the circulatory system, which leads to stroke
Cerebrovascular disease includes several main types of pathology:
- Transient cerebrovascular accident. Local and general damage to the organ is observed. There is a disorder of motor function, as well as a decrease in the sensitivity of certain parts of the body. The pathological process has a reversible course with restoration of damaged body functions.
- Blocking the lumen of the arteries. Narrowing of the lumen of the arteries leads to malnutrition, which is revealed by functional disorders of the brain. As a result, ischemia occurs in individual areas of the organ.
- Cerebral artery aneurysm. When it ruptures, hemorrhage occurs, which becomes the cause of a hemorrhagic type of genesis.
- Ischemic stroke. It can act as an independent pathology when the brain undergoes organic changes.
Relapse Prevention
After a patient undergoes a course of medication or after surgery, he should follow a certain set of rehabilitation and restorative measures, which together will contribute to a speedy recovery, normalization of the vascular system and brain function.
Thus, the main procedures that are most often prescribed by a doctor for the rehabilitation of a patient include physiotherapeutic procedures, a set of therapeutic exercises, therapeutic exercises and physical education.
The doctor also selects individually effective methods to combat excess weight and metabolic failures that provoke the formation of blood clots and plaques in the vessels, and also prescribes drugs to restore the functioning of the heart, vascular network, and brain.
It is equally important for the patient to adhere to a certain daily routine - a minimum of stress and physical activity, emotional stress, in the case of diagnosing transient disorders - bed rest is required until the negative symptoms in the form of nausea, vomiting and dizziness disappear.
Causes of pathology
The main causes of insufficient blood circulation are hypertension and atherosclerotic vascular damage. Thus, arterial hypertension contributes to the thickening of the vascular wall and narrowing of its lumen, and therefore the blood flow slows down. In some cases, complete stenosis occurs when the circulatory process stops. Against the background of these destructive changes, the genesis of cerebral vessels is formed.
Atherosclerosis develops as a result of a violation of fat metabolism, when the bloodstream contains an increased level of cholesterol, which is subsequently deposited on the walls of blood vessels. Cholesterol formations interfere with normal blood circulation, clogging the lumen of the blood arteries. When lipid formations disintegrate, they spread throughout the circulatory system, becoming the cause of thrombosis.
Osteochondrosis can provoke pinching near the vertebral arteries and thus lead to a disorder of brain nutrition
The main causes of vascular origin are the following pathological conditions:
- arterial hypertension;
- systemic diseases;
- cerebral artery aneurysm;
- interruptions in cardiac activity;
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- diabetes;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- anemia of various origins.
Increased risk factors for cerebrovascular accidents include:
- persistent increase in blood pressure;
- high concentration of glucose in the body;
- metabolic disorder;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- previous head injuries;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- excess body weight.
Chronic fatigue syndrome can cause a cerebrovascular accident, which causes a disruption in the endocrine and nervous system.
Questions and answers
What are the ways to prevent vascular dementia?
To prevent the formation of vascular dementia, it is useful to take vitamins and substances with antioxidant properties. These include vitamin E, C, and all types of polyunsaturated fatty acids. It is necessary to monitor sufficient levels of B12 and folic acid, and exclude foods high in cholesterol from the menu.
Can dementia be cured?
Vascular dementia cannot be completely cured. But with the right approach to therapy, it is possible to increase the patient’s life and activity.
What are the complications of dementia?
Complications are observed in severe stages of this disease and in the absence of complex therapy. A person completely loses social adaptation and ability to work, and injuries may occur due to ataxia. The main diseases that lead to brain pathology are getting worse - diabetes, hypertension, atherosclerosis.
Classification of violations
Brain nutritional disorders are divided into types:
- Binswanger's disease. The condition is accompanied by pathological changes in the white matter, where local vascular genesis occurs. The damage mostly affects neurons. The main symptom of the disease is a daily drop in blood pressure, as a result of which patients’ thinking processes deteriorate and memory decreases.
- Micro stroke. Insufficient supply of nutrients leads to deformation of microvessels. Low capillary permeability contributes to necrosis of nerve cells of the white and gray matter.
- Deformation of the main arteries. Thrombosis of the cerebral veins, as well as their bending, lead to insufficient blood circulation.
Traditional treatment
- To inhibit the processes of sclerosis of blood vessels and neurons:
400 gr. mix crushed leaves of 5-year-old aloe with 650 mg of honey and 650 g. red Cahors. Let it brew in a dark place for at least 5 days. Take 1 teaspoon 3 times before meals. The course of treatment is 2-4 weeks.
- To dilate blood vessels in the brain:
2 tbsp. Mix dill seeds and a glass of crushed valerian root with 1.5-2 glasses of honey, pour 1 liter of boiling water. Let it brew for a day. Before meals, take a tablespoon of the mixture for 4-6 weeks .
150-250 gr. Pour boiling water over hawthorn fruits. Let it brew for 30 minutes. Take the infusion 1 tbsp. half an hour before meals. The course of treatment is up to 1.5 months .
The first signs of vascular insufficiency
As a rule, the initial symptoms of vascular insufficiency of the brain appear after prolonged emotional and physical stress or prolonged exposure to a poorly ventilated room.
As the initial stage progresses, moments of increased excitability of the nervous system are observed
The first symptoms in patients are:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- heaviness and noise in the head;
- sleep disorder;
- increased fatigue.
At this stage, there are no significant neurological symptoms. The appearance of the first signs of cerebrovascular disease serves as the basis for a comprehensive diagnosis in order to exclude atherosclerosis, neurosis and dystonia.
Stages
There are several stages that indicate the development of a disease associated with insufficient nutrition of the brain.
The dynamics may be different, as it is influenced by several factors, such as heredity, lifestyle, environmental conditions, and so on. At the first stage of the disease, people often have headaches, irritability, forgetfulness and sleep disturbances. In the second stage, memory deteriorates more severely; a person can sleep during the day, but at night sleep is disturbed. Obsessive thoughts also appear, the patient begins to think about the same problem. The gait becomes unsteady. Uncoordinated movements appear. Performance decreases. At the last stage of the disease, dementia sets in, the person stops recognizing relatives and finding his way around on the street.
Mental disorders
Mental disorders may have a vascular origin as a result of pathological changes in the circulatory system of the brain.
Therapeutic measures to eliminate mental symptoms will not bring the desired effect, since these disorders are a concomitant pathology.
Vascular diseases are manifested by increasing weakness as a result of insufficient supply of nutrients and oxygen to brain tissues
Pseudoneurasthenic syndrome is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Sleep disorder. Deterioration of venous outflow causes frequent headaches, as well as dizziness with a sudden change of position. At the same time, the process of falling asleep becomes difficult, and sleep is short. On average it is 4 hours. Chronic fatigue leads to a sharp deterioration in general condition.
- Increased sensitivity to irritating factors. Intolerance to loud sounds and bright light appears due to insufficient oxygen supply to the brain tissues.
- Frontal lobe eating disorder is manifested by functional changes in the processes of thinking, memory and planning. The patient lacks focus and consistency in activities.
Subsequently, the progression of pathologies of vascular origin leads to a change in a person’s personal qualities, and the most pronounced character traits appear. The asthenic syndrome, which is characterized by suspiciousness, increased anxiety, and uncertainty, is intensifying. As a rule, changes in personal qualities are associated with the localization of vascular changes in the brain.
Treatment of pathologies of vascular origin, in contrast to true mental disorders, responds well to conservative therapy.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of gliotic foci of vascular origin is determined by the localization of the replaced tissue. The modified tissue does not cause gross disturbances, however, in the presence of large-scale foci, gliosis “reduces” the general background of life, worsening its quality.
Localization:
Frontal lobes
- Single supratentorial foci of gliosis of vascular origin
Leads to a general decrease in cognitive abilities: the pace of thinking slows down, control over one’s behavior is partially lost. Patients have difficulty learning new information and skills. Causal relationships are more difficult to establish. The patient is slower to think.
With deep lesions of gliosis, complex motor patterns are forgotten: patients forget how to tie shoelaces or how to play a musical instrument. The vocabulary becomes poor: sentences are monotonous, there are few or no synonymous words in speech.
The emotional-volitional sphere is upset. Emotions “dull”: all feelings lose their expression and color. Motivation decreases: the desire to explore the world around us is lost.
Temporal, parietal and occipital region
Hearing, speech and vision are affected. The perception of complex compositions is impaired. The sense of rhythm is disrupted. Visual accuracy deteriorates. The threshold of general sensitivity increases: the senses of tactile touch lose their sharpness. Memory deteriorates.
Single supratentorial foci of gliosis of vascular origin
The presence of foci in the cerebellar structures forms a picture of coordination disorder. Gait is disturbed. It is called “drunk” walking: balance is disturbed, the patient spreads his legs wide apart to maintain balance and not fall.
Limbs are shaking. This happens at rest and during movement. Individual fingers also tremble. Vision is impaired. Nystagmus appears - a synchronous rotation of the eyeballs to one side with a frequency of 60 movements per minute.
Muscle tone is impaired towards weakening. At the same time, tendon reflexes decrease. Muscles decrease in size. The synchronicity of the work of the flexor and extensor muscles is disrupted. Handwriting becomes disordered: the patient’s letters are difficult to read and spell out.
- Vascular genesis of the brain: what is it and how to treat it
The clinical picture of single supratentorial foci of gliosis of vascular origin also affects speech disorder. It loses its smoothness and becomes scanned. For example, a person speaks slowly and in syllables: “mo-lo-ko.” At the same time, the speech rhythm is observed.
Determining the nature of the headache
The nature of the headache depends on the nature of the circulatory disorder in the brain. Thus, a circulatory disorder in the arteries causes focal changes, and in the veins – general changes.
Detection of local violations, in contrast to general ones, is much easier
The type of vascular spasm influences the nature of the pain syndrome. An increase in cerebral vascular tone leads to an increase in pulse blood volume. This is the main cause of pulsating headaches, accompanied by specific tinnitus. As the pulsation amplitude decreases, the headache becomes dull and bursting.
Headache due to venous disorder develops against the background of excessive blood filling of the veins, which complicates its outflow. Patients experience a feeling of heaviness in the head, which can spread to the entire skull. A characteristic sign of this deficiency is increased pain in a horizontal position or during coughing, mainly in the morning.
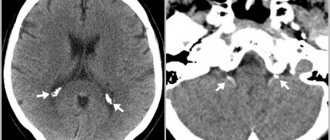
Diagnostic methods
Early brain malnutrition is quite difficult to diagnose, since test results may not reveal any abnormalities.
In parallel with the diagnosis of the brain, 24-hour monitoring of cardiac activity is carried out
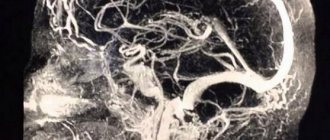
To determine possible vascular pathologies of the brain, a specialist prescribes the following studies:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (analysis of the functional state of the vascular system).
- Ultrasound diagnostics (assessment of the condition of blood vessels is carried out by applying a sensor to the temporal region).
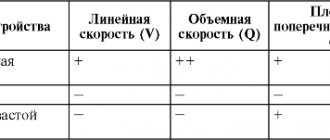
- Dopplerography (allows you to evaluate the speed of blood flow in real time).
- Spectroscopy (assessment of biochemical processes in brain tissue).
- Magnetic resonance angiography (allows us to determine structural changes in the gray matter).
- Electroencephalography (electrical oscillations of brain structures are recorded using rhythmic vibrations).
- Computed tomography (allows you to identify congenital and acquired vascular anomalies).
In case of focal violations, consultation with specialists is necessary. So, if visual acuity decreases, the patient is referred to an ophthalmologist, and if hearing worsens and swallowing is impaired, the patient should visit an otolaryngologist.