About cryoablation surgery
Cryoablation is one of the most effective, safe and simple ways to treat heart rhythm disorders.
It is used to isolate the mouth of the pulmonary veins (the source of pathological pulsation that leads to atrial fibrillation) and stop the transmission and spread of unwanted electrical impulses throughout the atria. It is performed without incisions using local anesthesia, through controlled destruction of arrhythmogenic areas using freezing. In the cardiology center of the Federal Scientific Research Center FMBA, a fairly young, but successful type of operation has been carried out since 2021. Holter monitoring is carried out in two ways:
- Spot – replaces radio frequency; instead of high-frequency current, liquid nitrogen is supplied and spot freezes the damaged areas;
- Balloon - a catheter with a balloon at the end is inserted into the femoral artery, reaching the pulmonary veins, the balloon is inflated, completely filling the place where the vein flows into the atrium, and cauterizes the pathological area with cold.
“Freeze” heart defects: cryoablation at the Republican Clinical Hospital of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Tatarstan
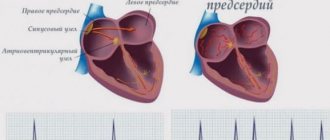
“Atrial fibrillation” is a term used throughout the world and is included in the International Classification of Diseases. Atrial fibrillation is common among Russian doctors. “Uh, flicker” - you can hear from the lips of arrhythmologists. But no matter what this type of arrhythmia is called, its insidiousness has been known since ancient times. And the most important thing that experts highlight is that the situation is dangerous due to its complications: thrombosis, stroke, heart failure, which often result in disability and sometimes death.
Can atrial fibrillation be corrected with medication? – the question in our newspaper for 2010 No. 44 was addressed to the chief cardiologist of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Tatarstan, Professor Albert Sarvarovich Galyavich.
“It is atrial fibrillation that requires careful attention. Firstly, it is necessary to carry out a competent diagnosis using an ECG, then establish the cause of the rhythm disturbance - as a rule, a detailed examination of the heart is carried out, and then choose a tactic for managing a patient with atrial fibrillation. It is possible to achieve a rhythmic pulse using medications. Heart rate slowers are used to “keep” the heart rate between 60 and 80 beats per minute.
There are drugs such as beta blockers that slow down the heart rate, which do not lose their relevance, and drugs that have been used by cardiologists for many years. One way or another, the choice of a particular drug is determined by the doctor, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient, what concomitant diseases are present, and so on,” answered the chief cardiologist of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Tatarstan.
Is it possible to rid a person suffering from atrial fibrillation forever from this disease by solving the problem surgically? This is another question, which Kazan surgeons can currently answer in the affirmative. For the first time in the republic, operations were performed to treat complex heart rhythm disorders using modern technology - cryoablation. Surgical interventions were performed under the guidance of a specialist from the Federal Center for Cardiovascular Surgery in Tyumen, Grigory Vladimirovich Kolunin.
What is the essence of the technique, and what are the plans of Kazan arrhythmologists to introduce cryoablation into practice - about this in an interview with the head of the department of x-ray surgical methods of diagnosis and treatment of the Republican Clinical Hospital of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Tatarstan Sergei Aleksandrovich Eremin.
— The cryoablation method is a targeted effect of cold on certain areas of the heart that are sources of arrhythmia. Cryoablation uses liquid nitrogen, the temperature of which ranges from -40º to -80º C. This method is used to treat one of the most common types of arrhythmia - atrial fibrillation. “Frozen” areas responsible for the formation of an arrhythmia focus, accordingly, cease to participate in this process.
— How are these foci of atrial fibrillation determined?
— During an electrophysiological study, the final stage of which is cryoablation.
— How relevant is the problem of atrial fibrillation?
— Atrial fibrillation is a disease in which the atria contract chaotically, as a result of which the heart loses the ability to make coordinated contractions. As a result, most people with atrial fibrillation have an increased risk of developing blood clots, which, due to their mobility, can contribute to the development of a stroke. The transition of the paroxysmal form of atrial fibrillation to a permanent form can contribute to the development or progression of chronic heart failure. That is why it is necessary to pay increased attention to both the treatment and prevention of heart rhythm disturbances.
— What are the advantages of this technique over previously used radiofrequency ablation? Is it possible to compare them?
— The indications are different for each patient. In cases where surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation is necessary, we also use radiofrequency ablation, and now cryoablation. Cryoablation is, one might say, the last word in medical practice. The technique has been used in the world quite recently. This type of surgical intervention is even newer for Russia. If 4 years ago only experimental cryoablation operations were carried out abroad, now the trend is widely spreading here. If we compare the methods, cryoablation is less risky for the health of patients, since it almost completely eliminates the possibility of damage to the conduction pathways of the heart. The likelihood of blood clots also decreases. But in terms of the final result and time of implementation, both radioablation and cryoablation are comparable.
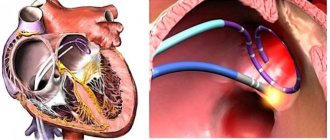
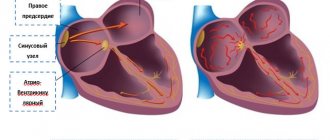
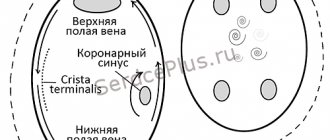
Cryoablation has two modifications - catheter, which, figuratively speaking, replaces radiofrequency, and cryoballoon, used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation - the most complex type of arrhythmia. The advantages of balloon cryoablation are that the ostia of the pulmonary veins are isolated more effectively and reliably. The pulmonary veins are a recognized source of pathological pulsation that leads to atrial fibrillation.
Four pulmonary veins flow into the left atrium, and the technique is attractive in that we isolate each of these four veins in turn with a special balloon and cool the balloon to -40 ºC with liquefied gas, damaging the mouth of the vein. The operation is carried out “in one go”; there is no need to repeatedly do point cauterizations, as with radiofrequency ablation. We immediately obtain isolation of the entire vein, which we then confirm with an electrophysiological study. This is a fairly good chance of a cure for such a disease as atrial fibrillation.
— What role does functional diagnostics play in cryoablation?
— Functional diagnostics is a service that refers patients to us, gives a preliminary and often final diagnosis, and determines indications for surgery.
— What are the prospects for the development of this technique?
— We will expand the indications for cryoablation – this most concerns patients with atrial fibrillation. Today, there are few such operated patients - the operation is expensive and complicated, but let's hope that the capabilities of our republic to carry out this type of surgical intervention will increase.
Ekaterina Lobanova
The cryoablation method is a targeted effect of cold on certain areas of the heart that are sources of arrhythmia. During cryoablation, liquid nitrogen is used, the temperature of which ranges from -40º to -80º C.
Cryoablation is less risky for the health of patients, since it almost completely eliminates the possibility of damage to the conduction pathways of the heart. The likelihood of blood clots also decreases.
Key benefits of cryotherapy
efficiency - during the operation, the pathological focus that provokes rapid heartbeat is completely blocked, the heart rhythm is restored
duration – the operation takes 1-1.5 hours
safety - due to the speed of the procedure, the time of radiation exposure to the patient is reduced, and the likelihood of blood clots is reduced. The risk of postoperative complications is minimal
simplicity of execution - the operation does not require dissection of the chest, it is performed using a single puncture of the femoral artery
About the technique of radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is performed using combined (intravenous and local anesthesia). After anesthesia, a catheter is inserted into the patient’s heart through one of the vessels. Then endocardial electrodes are installed, intended for permanent cardiac pacing and temporary stimulation of the right ventricle separately. In the next step of the procedure, the doctor places an ablation electrode in the anterior septal region of the right atrium. Then, during RFA, multiple rearrangements of the electrodes are performed, which is necessary to diagnose the functioning of the His bundle. With the help of high-frequency exposure using temperatures in the range of 40-60 ° C, the focus is destroyed, which produces pathological electrical impulses that provoke tachycardia in the patient. During the operation, an artificial AV block is created, which requires maintaining a normal heart rhythm through temporary stimulation of the right ventricle. To solve this problem, the endocardial electrodes mentioned above are used. After making sure that the achieved effect is stable, the doctor moves on to the final stage of RFA. At this stage, if necessary, a permanent pacemaker is implanted into the patient. The entire procedure takes from 15 to 6 hours and is carried out under the control of X-ray television and electrophysiological equipment.
Indications for balloon cryoablation
The indication for the operation is atrial fibrillation.
Like any minimally invasive operation, cryoablation has contraindications:
- life-threatening condition of the patient;
- the presence of blood clots in the atrium;
- thrombosis of the left atrial appendage;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- acute stroke;
- infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes in the body;
- diseases of the kidneys, liver, respiratory organs;
- an allergic reaction to the contrast used during surgery.
Preparing for surgery
To determine whether there are contraindications to the operation and to ensure a successful outcome of ablation, the patient must undergo a series of studies. They can be divided into two parts:
- clinical and laboratory tests:
- clinical blood test;
biochemical blood test: total protein, creatinine, urea, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, glucose, pancreatic amylase;
- general urine analysis;
- expanded coagulogram;
- ADP platelet aggregation;
- determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- markers of infections: HIV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis;
- Pro-BNP, CRP, troponin.
- Instrumental studies:
- chest x-ray;
ECG;
- EchoCG;
- EGDS;
- Ultrasound scanning of brachiocephalic arteries;
- Ultrasound scanning of the arteries of the lower extremities;
- Ultrasound scanning of the veins of the lower extremities;
- FVD;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- TEE;
- coronary angiography;
Depending on the presence of concomitant diseases, additional studies, tests and consultation with specialized specialists (neurologist, endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, etc.) may be prescribed.
After the studies, the patient needs to prepare for surgery:
- a few days before cryoblation, the doctor stops taking medications;
- on the day before surgery, breakfast, lunch and light dinner are allowed;
- 12 hours before the test you cannot eat anything, you must stop taking liquids 8 hours before;
- at night the patient is given a cleansing enema;
- in the morning on the day of surgery, the patient takes a shower and performs hygiene procedures (it is necessary to shave the hair at the site of the catheter insertion - usually in the groin area);
- Before the operation, the patient is examined by a surgeon and an anesthesiologist. A mild sedative is administered to help relax and calm anxiety.
The Cardiology Center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency offers patients planned hospitalization to conduct all necessary studies and prepare for ablation. Our multidisciplinary center is equipped with its own laboratory and modern equipment. Therefore, you can take tests and undergo all studies in our clinic. We guarantee the accuracy of the results and the speed of their delivery.
Carrying out cryoablation
Cryoablation to isolate the pulmonary veins is performed in the radiology department.
During the operation the following manipulations are performed:
- the arrhythmologist surgeon makes a puncture in the groin area, inserts a diagnostic catheter through the femoral artery and leads it to the heart;
- reaching the right atrium, the doctor makes a puncture (puncture) of the interatrial septum. This allows access to the left atrium;
- a contrast agent is injected, using a diagnostic catheter, the doctor will determine the pathological focus and see the necessary place for ablation on the screen of the X-ray machine;
- after the diagnostic catheter, a cryoballoon is inserted, reaching the left atrium, the balloon is inflated;
- the doctor brings the balloon to the mouth of the pulmonary vein and closes the passage, thereby stopping the blood flow between the atrium and the vein;
- once closure is confirmed, the physician injects a refrigerant into the cryaballoon;
- The criaballoon, evaporating, takes heat from the damaged heart tissue. At this point, the tissue becomes scarred and can no longer generate and distribute electrical impulses that were the cause of heart rhythm disturbances;
- the balloon is deflated and the catheters are removed. A tight antiseptic bandage is applied to the puncture site;
- The patient is transported from the operating room to the intensive care unit.
Cryoablation is a modern method of treating arrhythmias, which appeared in medical practice quite recently, but has already proven itself to be effective and safe. Our arrhythmologist surgeons perform this operation every day and see how effective and safe it is. If you have concerns or doubts, you can always call us and consult with a specialist.
Radiofrequency ablation of the heart
The invention and active introduction into widespread practice of minimally invasive interventions with maximum effect is the main path of development of modern medicine. Radiofrequency catheter ablation refers to precisely such operations.
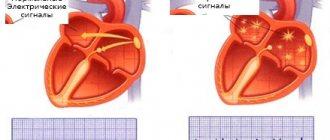
RFA is a technique for treating cardiac arrhythmias by physically destroying the focus of pathological excitation or areas of abnormal impulse conduction.
This operation made it possible to abandon complex open-heart surgery in the treatment of many types of arrhythmias, including those resistant to drug therapy.
Indications for surgery
Radiofrequency catheter ablation of the heart is the option of choice in the treatment of arrhythmias in young patients, as it allows in a relatively short time not only to improve the patient’s well-being and quality of life, but also to reduce the risks of sudden cardiac death and disability.
Pathologies for which doctors strongly recommend RFA of the heart:
- Atrial fibrillation with ventricular tachysystole.
- Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
- Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia.
- Arrhythmic disorders associated with cardiomyopathies.
- The presence of additional pathways, subject to a family history of sudden death.
- Intolerance or serious side effects when taking traditional antiarrhythmics.
- Tachyarrhythmias resistant to drug therapy.
If absolutely necessary, RFA can be performed even on children without congenital heart defects, starting from an early age. In this case, the indications for RFA surgery will be the development of tachycardia-dependent cardiopathy with a decrease in the pumping function of the heart and the lack of the desired effect after the use of all groups of antiarrhythmic drugs.
It is worth noting that for a number of arrhythmic disorders, radiofrequency ablation of the heart is recommended even if the patient does not want to take antiarrhythmic drugs for life or does not tolerate them well.
8
24/7
Purpose of the operation
The goals pursued when performing RFA of the heart are always aimed at eliminating the cause of arrhythmogenesis - a pathological conduction pathway or an abnormally active area of the myocardium. To do this, during cardiac ablation, a targeted destruction of a malfunctioning section of the cardiac conduction system is performed, which can have two different effects, each of which is optimal for its own group of heart pathologies. Thus, in the treatment of atrial tachycardia with anomalies of AV conduction, the method of choice is complete or partial radiofrequency ablation of the atrioventricular junction. At the same time, in the case of ventricular tachycardia or the presence of bypass paths, RFA will be aimed at destroying the most pathological area of the heart.
Radiofrequency catheter ablation of the heart allows you to avoid a number of negative consequences of living with arrhythmia, such as:
- high risk of early and sudden death from arrhythmia;
- ischemic stroke;
- myocardial infarction;
- expansion of the cavities of the heart with subsequent development of heart failure;
- long-term use of a large number of medications;
- progressive decrease in working capacity;
- high risk of death for the mother during pregnancy (for some types of arrhythmias this is an indication for abortion).
Types of RFA
Since the principle of catheter ablation is to destroy a small area, all types of this procedure differ in the physical factor causing destruction:
- radiofrequency ablation;
- electroablation;
- Ultrasonic destruction;
- laser cardiac ablation;
- cryodestruction.
However, the effectiveness, controllability of destruction and implementation features for these methods are not the same. Nowadays, RFA is most often used, since it is this technique that has produced the largest number of positive results. Whereas, for example, most cardiac surgeons are moving away from ablation with direct electric current in favor of RFA of the heart and other techniques.
Preparation for surgery, necessary tests and examinations
Before the operation, when communicating with the cardiac surgeon who will perform radiofrequency ablation of the heart, it is necessary to clearly state the list of medications taken by the patient and their dosages. It is also important to provide your doctor with information about the presence of an implanted pacemaker, allergic reactions or intolerance to medications, if any.
The list of mandatory diagnostic procedures before cardiac ablation includes the following:
- General clinical blood test.
- Biochemical studies of venous blood: bilirubin and liver enzymes, glucose, creatinine and urea with GFR calculation, total protein, etc.
- Coagulogram.
- General urine analysis.
- Electrocardiography.
- Holter (24-hour) ECG monitoring.
- Echocardiographic study.
Also, in the presence of concomitant pathology, in addition to routine methods, additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be required. For example, patients with coronary artery disease may be prescribed a lipid profile, and patients with diabetes mellitus may be prescribed a study of the level of glycated hemoglobin. It is important to consider that many patients with arrhythmias receive anticoagulant therapy, so an INR study may be added to the above.
It is recommended not to take food or water the day before RFA (at least 12 hours).
Method of operation
When performing radiofrequency ablation, general anesthesia is not required, so the patient is only anesthetized at the insertion site of the catheter electrode and is also prescribed sedatives. Already in the operating room, stable venous access is provided: it will be needed for the administration of contrast agents, antiarrhythmics or other drugs that may be needed during RFA of the heart.
The main instruments of the team of electrophysiologists and cardiac surgeons are flexible catheter electrodes. They are introduced through a large vessel, preferably through the femoral artery. Other options for introducing electrodes, for example, through the subclavian vein or other vessels, are not excluded. Radiofrequency ablation is performed under fluoroscopy guidance, so the patient does not have to worry that cardiac surgeons are operating blindly.
Typically, RFA surgery is performed in two stages:
- Performing an electrophysiological study.
- Actually radiofrequency ablation.
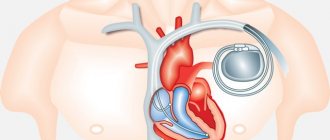
In the case when pathology (for example, atrial fibrillation) requires destruction of the atrioventricular connection, then another stage is added - implantation of a pacemaker, since with such ablation of the heart the conduction of impulses from the tissues of the atria to the myocardium of the ventricles completely stops.
An electrophysiological study is the compilation of a kind of map of the heart, which will reflect the areas where pathological conduction or formation of electrical impulses occurs. This procedure is performed by introducing a specific contrast and electrical stimulation of areas of the heart. During this procedure, disturbances in the rhythm of the heart are usually induced, but in an operating room these arrhythmias do not pose a threat to the patient.
Upon completion of mapping, cardiac surgeons insert an ablation electrode through the same access and begin performing RFA of the heart. A catheter ablation electrode is installed in the projection of the pathological area and its destruction is carried out by the point action of radio frequency waves. If there is a large lesion or several abnormal zones in the tissues of the heart, their destruction can be performed during one operation or RFA will need to be repeated later.
After the RFA procedure, if indicated, a pacemaker can be installed and programmed.
Since the patient is conscious during cardiac ablation, this is sometimes associated with some discomfort. Therefore, if you experience any unpleasant sensations, it is advisable to inform your doctor. At the same time, you should not be afraid of this intervention, because almost all manipulations with the electrodes are painless for the patient.
The amount of time spent performing radiofrequency ablation ranges from 3 to 7 hours.
Description of the postoperative period and rehabilitation
One of the most significant advantages of RFA compared to open heart surgery is its low morbidity and rapid recovery. While a patient after a sternotomy will feel pain in the sternum, wear a special bandage for months, and limit his exercise, a patient after RFA will be able to return to his normal rhythm of life in a couple of weeks, which will no longer be burdened by arrhythmia.
8
24/7
Directly from the operating room, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, where he spends the first day after RFA. Here, constant monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure is carried out. To prevent bleeding from the ablation catheter insertion site, it is recommended to lie down for the first 4-5 hours after surgery.
If there are no complications, the patient will be able to leave the clinic where the cardiac ablation was performed the next day.
Possible complications with RFA
An intervention such as cardiac ablation has a very low risk of serious complications, but does not completely eliminate them. Most often, patients experience a hematoma at the site of electrode insertion, but they usually do not require any specific treatment and go away on their own within a few weeks.
Less common are more serious complications:
- perforation of the walls of blood vessels or tissues of the heart;
- pneumothorax;
- development of complete atrioventricular block.
The risk of death with this operation is usually about 0.2% or less.
RFA results
The effectiveness after RFA surgery will depend on the type of arrhythmia, the anatomical features of the patient’s heart and the presence of concomitant pathology of the internal organs in general and the heart in particular. The percentage of successful RFA ranges from 75% to 95%, for example, in the treatment of supraventricular arrhythmias it is about 96%. The incidence of complications when performing cardiac ablation is no more common than 1.5-2%.
Sometimes, after a successful first RFA operation, new abnormal areas are formed over time, which is associated with the peculiarities of the electrophysiology of the heart of a particular patient; in such clinical situations, repeated ablation may also be required.
In the vast majority of cases, patient reviews of quality of life after RFA are positive. They can engage in activities that were previously denied access due to the risk of arrhythmia. Patients can exercise, women of fertile age can safely carry and even give birth to a child on their own. A significant advantage is that for a number of pathologies after RFA of the heart it is not necessary to continue taking medications continuously.
Cost of the operation
Performing radiofrequency ablation requires high-tech equipment and the presence of qualified specialists, so it is not yet carried out everywhere. Typically, clinics with these resources are located in large cities, and there are even several of them in St. Petersburg and Moscow.
The cost of radiofrequency cardiac ablation is calculated individually for each patient and can vary significantly due to different volumes of intervention, the need for implantation of a stimulator, and the level of the clinic in which the operation is performed. The average price is from 150 thousand rubles.
It should be noted that in the Russian Federation there are quotas for free RFA of the heart.
After operation
After ablation, the patient is under the supervision of our specialists in the postoperative rehabilitation ward. For the first few hours, medical personnel monitor the patient's vital signs, heart rate and pain symptoms. The first day the patient was prescribed bed rest. During this time, the heart will adjust to a new rhythm, and the wound at the site of insertion of the catheter will begin to heal. On the second day, you are allowed to gradually get up and move slowly around the ward. If all indicators are normal, the patient is discharged on the 3rd day. Before discharge, the patient is examined by a doctor, who gives his recommendations and instructions on rehabilitation.
Cryoblation therapy is very effective and can completely relieve the patient of arrhythmia, but the effect of the operation largely depends on the patient himself. During the rehabilitation period (1-3 months), it is necessary to follow all doctor’s instructions and recommendations for recovery:
- avoid heavy physical activity;
- avoid psycho-emotional stress and stress;
- refuse hardening, hot baths, trips to the bathhouse and other activities with possible temperature changes;
- monitor proper nutrition and follow a diet: give preference to boiled dishes rather than fried ones, exclude fatty foods, do not eat fast food, avoid excessive consumption of salt and sugar, add fish, lean meat, fresh vegetables and fruits to the diet;
- give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, overeating);
- Take medication in consultation with your doctor;
- Visit a cardiologist promptly for a routine examination. An ECG must be done a month after surgery, then after 3 and 6 months.