During a consultation with a cardiologist or surgeon, the patient may be diagnosed with an enlarged jugular vein in the neck; the causes of this phenomenon vary. Depending on the predisposing factors, a treatment regimen is prescribed.
The function of the jugular veins is to be responsible for the process of blood flow from the brain to the neck. Thanks to these blood veins, unpurified blood flows to the heart muscle so that the filtration process can take place.
Jugular veins are divided into several types:
- Internal. It is located at the base of the skull, and its end is in the region of the subclavian fossa. At this site, the vein pours unpurified blood into the brachiocephalic vessel.
- The external one begins under the auricle, goes down to the sternum and collarbone, enters the internal jugular vein, as well as the subclavian vein. This vessel has valves and processes.
- The anterior one originates from the outer part of the mylohyoid muscle and flows near the midline of the neck. This vein enters the subclavian and external, thereby forming an anastomosis.
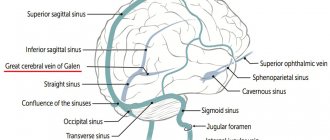
Types and location
The venous vein consists of 3 independent venous channels. Accordingly, their anatomy is separate.
The veins of the head and neck, which are responsible for the correct outflow of blood from the brain cavity, are divided into 3 types. These are the anterior, external and internal jugular veins.
Internal
It has a relatively wide trunk, compared to the other 2. In the process of pushing out blood, it easily expands and contracts, thanks to its thin walls and diameter of 20 mm. The outflow of blood in a certain amount occurs with the help of valves.
As the lumen expands, the superior bulb of the jugular vein is formed. This occurs at the moment when the IJV enters from the hole.
Typical anatomy diagram:
- start – area of the jugular foramen;
- localization - the skull, or rather its base;
- further - its path goes down, the place of localization is in the posterior muscle, the place of attachment is the collarbone and sternum;
- the place of intersection with the posterior muscle is the area of its lower and posterior parts;
- after that the path is laid along the trajectory of the carotid artery;
- a little lower it comes forward and is located in front of the carotid artery;
- then, together with the carotid artery and the vagus nerve, they are directed through the site of expansion;
- as a result, a powerful bundle of arteries is created, which includes the carotid artery and all jugular veins.
Blood enters the IJV from the tributaries of the skull, the location of which is the cranium and outside it.
Comes from vessels: brain, eye, auditory. Also suppliers are the dura mater of the brain, or rather its sinuses.
Outdoor
Location: neck tissue. Blood is directed from the face, head and outer part of the cervical region. Perfectly visible visually when coughing, screaming or stress.
Construction scheme:
- origin - lower angle of the jaw;
- further down the muscle that attaches the sternum and clavicle;
- crosses the outer part of the muscle. The place of intersection is the area of the rear and lower part.
It has only 2 valves located in the initial and middle parts of the neck.
Front
The main task is to carry out drainage from the chin area. Location: neck, middle line.
Anatomical features:
- passes along the muscle of the tongue and jaw (along the front), downwards;
- Then, on both sides, the veins connect with each other, and a venous arch is formed.
Sometimes the arc of collected together as\nals forms a middle one.
External jugular vein
The structure and location of the external jugular vein (abbreviated EJV) makes it easy to visualize it, especially if a person talks passionately and loudly for a long time, sings or screams. It is smaller in diameter than the outer one, which makes its anatomical structure more typical of the venous network: the muscle layer in it is less developed, but there are more valves for directing blood flow, and there are no bulbs at the base.
The external jugular vein has many lateral tributaries that fill it with blood along its entire length. This is what distinguishes it from the IJV, which is filled with venous blood only from one end. The posterior auricular, occipital, suprascapular and transverse branches, as well as the third anterior UR, flow into the MN. The main function of the external jugular vein is to drain blood from the lower jaw and chin, neck and surface of the skull.
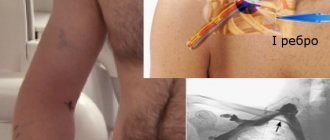
It is the NJV that is used to install a catheter when it is necessary to administer long-term intravenous drug solutions.
Diseases and changes
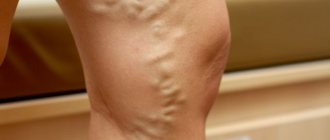
The reasons for the expansion make it known about the dysfunction of the circulatory system. This situation requires an immediate solution. You should know that there are no age restrictions for YV pathologies. They affect both adults and children.
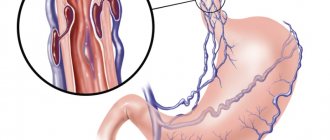
Phlebectasia
A thorough, accurate diagnosis is necessary, the result of which should be the identification of the causes of the pathology, as well as the prescription of comprehensive effective treatment.
Extensions occur:
- in case of stagnation, due to injury to the neck, spine or ribs;
- for osteochondrosis, concussion;
- for ischemia, hypertension, heart failure;
- for endocrine disorders;
- with prolonged sitting at work;
- for malignant and benign tumors.
Phlebectasis can also be caused by stress and nervous tension. With nervous excitement, pressure can increase, resulting in a loss of elasticity of the walls of blood vessels. This can lead to valve dysfunction. Therefore, phlebectasia needs to be detected early.
Circulation can be negatively affected by factors such as: alcohol consumption, smoking, toxins, excessive mental and physical stress.
Thrombosis
It may occur due to the presence of a chronic disease in the body. If they are present, as a rule, blood clots form in the vessels. Once a blood clot has formed, there is a possibility of it breaking off at any time, which entails blocking vital arteries.
Signs of thrombosis:
- sometimes pain occurs in the hand;
- swelling of the face;
- appearance of venous networks on the skin;
- When turning the head, pain occurs in the cervical region and neck.
The result of thrombosis can be rupture of the jugular venous channels, which leads to death.
Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis
Inflammatory changes occurring in the mastoid process or middle ear are called phlebitis. The cause of phlebitis and thrombophlebitis can be:
- bruises, wounds;
- placement of injections and catheters in violation of sterility;
- penetration of medications into the tissues around the vessel. This can often be triggered by calcium chloride when it is injected past an artery;
- infection from the skin.
Phlebitis can be uncomplicated or purulent. The treatment of the 2 pathologies is different.
Aneurysm
A rare pathology is an aneurysm. It can even occur in children at an early age from 2 to 7 years. The pathology has not been fully studied. It is believed that its occurrence occurs from improper development of the base of the venous bed, or rather its connective tissue. It is formed during intrauterine development of the fetus. The anomaly does not manifest itself clinically. It can only be noticed when a child cries or screams.
Symptoms of an aneurysm:
- headache;
- anxiety;
- sleep disturbance;
- fast fatiguability.
Treatment consists of draining venous blood and vascular prosthetics.
Why is the phenomenon dangerous?
It is important to prevent complications, for which you should adjust your lifestyle, especially if there were people with phlebectasis in your family.
It is especially dangerous if the pathology occurs in a child. The disease is diagnosed immediately after birth, sometimes at 3-5 years. This is indicated by tumor-like neoplasms, vasodilatation, and elevated temperature.
Thrombosis becomes a complication. A clot forms inside the vessel. This indicates the presence of chronic diseases in the body. The danger of a blood clot is that it can break off and block the functioning of vital veins.
For those who experience thrombosis, the doctor recommends anticoagulants. Antispasmodics, venotonics, and nicotinic acid are used to relieve inflammation, relax muscles, and make the blood more fluid. The drugs also help in resolving the blood clot. If the therapeutic regimen is successful, there is no need to perform surgery.
To avoid complications, when signs appear, you need to come for a diagnosis and take therapeutic measures. If you do not control the course of the pathological process, consequences arise. For example, the affected area may rupture, causing hemorrhage. The most unfavorable outcome is the death of the patient.
Who is involved in diagnosis and treatment?
If symptoms of the disease occur, you should consult a physician. After consultation, he can refer you to see a phlebologist.
Based on the patient’s complaints, the phlebologist conducts an initial visual examination, the result of which should be the identification of pronounced symptoms of venous disease.
In addition, all patients suffering from vascular diseases must be registered with a cardiologist. Jugular vein diseases must be identified in the early stages. Be aware of possible serious consequences.
If at least one symptom of a particular disease appears, you must immediately contact a therapist.
Best answers
Elena Zakamskaya:
The jugular fossa is located on the front of the neck, where in front of the collarbones connect to the sternum, just below the Adam's apple. When we tilt our head forward, the chin rests on the jugular fossa. It is so called because when the animal tilts its head, the yoke rests precisely on this fossa.
*CLIMA* . RE:
Jugular (jugularis) is a term and concept introduced into the French language and into medical vocabulary by the French writer, naturalist and physician Francois Rabelais (Rablais Francois, ca. 1494-1553). It means jugular, cervical: belonging to the throat, the front of the neck (e.g. , jugular fossa above the sternum).
The jugular recess (fossa) (fossa jugularis, BNA, JNA; suprasternal fossa) is a depression in the lower part of the anterior surface of the neck above the jugular notch of the sternum, limited laterally by the sternocleidomastoid muscles. Simply put, the jugular recess is a v-shaped fossa , located at the base of the neck, at the very top of the chest. Often used in needlework when taking measurements.
Alka:
tilt your chin all the way down, you'll rest on it
Contrast enhancement
Intensively homogeneously accumulates contrast.
Fig.707 a-b and Fig.708
A mass formation in the soft tissues of the neck on the left (asterisk in Fig. 707) does not reveal clear contours on a non-contrast study; there is no clarity in the boundaries of the tumor and the type of its growth. Volumetric image reconstructed after intravenous bolus contrast (Fig. 708).
To clarify the boundaries of the formation, the nature of its growth, the topography of its location and relationship to the great vessels, intravenous bolus contrast is used.
Fig.709-711
Volumetric formation in the soft tissues of the left submandibular region, with clearly defined contours (Fig. 709-711). The scan was performed in the arterial phase (Fig. 709), interstitial phase (Fig. 710) and venous phase (Fig. 711). In the arterial phase, the density of arteries exceeds the density of soft tissues and veins (arrow heads in Fig. 709). In the intermediate, interstitial phase, the density parameters of the tissues are leveled out (Fig. 710). In the venous phase, smoothing of the boundaries between the formation and the surrounding soft tissues of the neck is noted (Fig. 711).
Prevention measures
The jugular vessels must be maintained in a healthy condition. Every year you need to undergo routine examinations to identify pathologies in the early stages. Maintaining water balance will also help keep blood vessels toned. Every day it is recommended to drink 1.5 pure still water. Proper nutrition with sufficient vitamins and minerals helps strengthen the walls of the veins.
All medications are carefully studied before use. Some of them may cause allergic reactions. It is recommended to be active. A sedentary lifestyle negatively affects the condition of blood vessels. When infectious diseases appear, treatment should be started immediately. Their development will lead to pathologies of the veins in the cervical region. It is important to follow a daily routine - alternate work with rest and get enough sleep.
Defects in the walls of blood vessels sometimes lead to rupture and death. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the slightest deviation. Only he will be able to determine the type of pathology and type of treatment.
Unconventional description
Why is catheterization of the jugular vein needed and how is it performed?
In addition to the standard medical description of the jugular fossa, one can also consider the non-traditional characteristics of this zone of the human body. For example, in the ancient world, the V-shaped depression was considered a special place where energy could accumulate. Due to the increased sensitivity of the fossa, according to magicians, it was responsible for decision making. The man himself could not do anything: he was controlled by energy centers.
The flowing transparent energy passing through the jugular fossa was “filtered,” allowing the person to make one or another decision. It was believed that this area should not be touched. Therefore, the cavity had to be touched with a special magical object. It was usually a ritual stick made of animal or human bone or wood.
The rituals performed with the jugular cavity were aimed at collecting scattered energy and concentrating it. The main purpose of the rituals was a kind of strengthening of the zone by eliminating indecision and doubt.