Purpose of determining prothrombin time
The process is controlled by the protein prothrombin circulating in the plasma. Normal synthesis of this substance is possible only in the absence of vitamin K deficiency in the body.
In healthy men and women, prothrombin in the bloodstream is stable; an active surge in the concentration of the substance occurs only after contact with deformed tissues. The indicator is determined during a blood test. In practice it matters:
- PTI – prothrombin index: the ratio of normal prothrombin time to the test blood sample;
- INR (international normalized ratio) is a decoding of test results from any laboratory in the world based on any diagnostic methods.
Prothrombin time is determined to:
- determination of blood viscosity while taking antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants (Aspirin, Warfarin, Clopidogrel);
- research into the effectiveness and adequacy of treatment;
- assessing a woman’s health status when planning pregnancy;
- identifying the causes of liver dysfunction;
- diagnosis of vascular pathologies to prevent stroke, heart attack, early diagnosis of aneurysm;
- determination of vitamin K levels;
- prevention of thrombosis;
- hemophilia control;
- control of disseminated vascular coagulation syndrome;
- detection of anemia in chronic form;
- monitoring dysfunction of homeostasis.
The analysis is carried out by taking blood from a vein or finger and examining the material on an automatic analyzer. Despite its simplicity, this is an informative technique. It is suitable for accurate diagnosis.
Content
- Indications for the purpose of analysis
- Increased thrombin time
- Changes in indicator during pregnancy
Thrombin time is an indicator that allows us to evaluate the final stage of the blood clotting process (coagulation), namely, the formation of fibrin from fibrinogen. That is, thrombin time is the time during which fibrinogen is converted into fibrin in citrated plasma after the addition of calcium and thrombin. In this case, the rate of formation of a fibrin clot mainly depends on the amount and usefulness of fibrinogen, as well as the presence of anticoagulants in the blood. Thrombin time is used to assess blood anticoagulant activity and identify dysfibrinogenemia.
Valid values
In domestic medicine, the prothrombin time method in seconds is used:
- children - from 14 to 18 seconds;
- adult men and women – from 10 to 15.
In practice, different laboratories use different reagents and therefore obtain different ranges of standards. To standardize the process, the result is assessed within the framework of the INR. In healthy men and women, the normal prothrombin time is the same:
- for a newborn, an interval of 14 to 18 seconds is considered normal;
- for children under six years of age – from 13 to 18;
- for adults – from 15 to 20.
If the analysis is carried out in a technical laboratory, then the optimal value for children is from 70 to 100%, for adults - from 95 to 105%.
The normal prothrombin time in pregnant women depends on the trimester:
- in the first and third trimester – from 0.8 to 1.3;
- in the second – from 0.8 to 1.1.
When using blood thinners, levels can increase to 3.5 units in the INR.
Indications for the purpose of analysis
- determination of fibrinogen deficiency or deficiency;
- monitoring the results of therapy with heparin, thrombolytic or fibrinolytic drugs;
- assessment of the patient’s condition with DIC syndrome;
- liver pathology;
- detection of the presence of fibrinogen/fibrin degradation products in the blood;
- in the presence of two spontaneous cases of pregnancy termination before 22 weeks.
Thrombin time depends on the level of fibrinogen in the blood: a decrease in the level of fibrinogen increases thrombin time and for this reason, the analysis of thrombin time is usually combined with the analysis of fibrinogen, as well as other coagulogram indicators. Thrombin time - the norm is 15-18 seconds. However, in various diseases, the thrombin time indicator goes beyond the normal range - the thrombin time is increased or decreased)
Increasing the indicator
If the prothrombin time exceeds the norm, this indicates that blood clotting is too slow. It is liquid due to many reasons:
- liver dysfunction as a result of hepatitis, cirrhosis, when hepatocytes are gradually replaced by connective tissue, the synthesis of coagulation factors fades;
- taking medications: anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Warfarin);
- lack of vitamin K - impaired prothrombin synthesis;
- disturbances in the synthesis of fibrinogen and other clotting factors;
- hereditary pathologies;
- blood transfusions;
- hormonal imbalance;
- diabetes mellitus;
- tumor growth.
Thrombin time is normal
To measure thrombin time, the following reference values are accepted:
- 10.3 – 16.6 seconds.
Factors influencing the result
Sometimes the results may be distorted. There are a number of reasons for this:
- Age (in newborns, thrombin time is normally prolonged);
- Violations of the rules for preparing for a coagulogram;
- Violations of the algorithm for blood collection, its transportation and storage;
- Incompetence of laboratory workers;
- Taking interfering drugs;
- Transfusion of frozen plasma shortly before the test (hides quantitative and structural fibrinogen abnormalities);
- Menstruation (reduces clotting rates);
- Acute febrile syndrome in a patient during venous blood sampling;
- Recent injuries, wounds, burns, surgery.
Preparing and conducting analysis
No special preparation is required for the test. To increase the reliability and accuracy of the testing, a couple of days before the upcoming manipulation you need to give up green tea, soy, liver, cabbage of any kind, leafy vegetables, beans, and alcohol.
Blood sampling for analysis is carried out in a laboratory in compliance with all rules of asepsis and antisepsis, on an empty stomach. The sequence is as follows:
- during intravenous sampling, a tourniquet is applied to the forearm to reduce the speed of blood flow and provide convenient access to the vein;
- the injection site is treated with an antiseptic;
- After drawing blood, the tourniquet is removed and the injection site is disinfected.
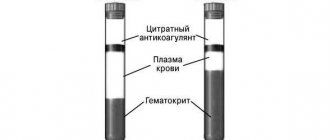
A blood sample taken from a finger or vein is submitted for testing: the required amount of blood is added to a test tube with sodium citrate so that the blood does not clot. To completely neutralize the effect of the clotting factor, the test sample is centrifuged by adding thromboplastin and calcium chloride. The time of clot formation is recorded - prothrombin time.
Today you can carry out such testing at home using a special analyzer. This is necessary for patients who are being treated with Warfarin against the background of thromboembolism, pre-infarction, when certain fluctuations in PTI or prothrombin time save a person’s life. The analyzer has a simple device and does not require special skills to operate.
Hemostatic system: thrombin time
A blood thrombin time test is an assessment of the end stage of the natural clotting process. In laboratory conditions, thrombin time refers to the time it takes for fibrinogen to be converted to fibrin in citrated plasma (blood is drawn into a tube with sodium citrate, hence the name) after the addition of calcium and thrombin.
The rate of blood clot formation is determined by the amount and efficiency of fibrinogen and the presence/absence of direct anticoagulants in the blood.
Indirect anticoagulants do not have any effect on the results of the study.
Indications for the purpose of analysis
A thrombin time study is performed to assess the anticoagulant function of the blood and to confirm dysfibrinogenemia.
The analysis is prescribed:
- to identify fibrinogen deficiency and/or defectiveness;
- to monitor the effectiveness of heparin, thrombolytic (streptokinase, urokinase) and fibrinolytic (fibrinolysin) agents;
- to monitor the patient’s condition with thrombohemorrhagic syndrome;
- with pathological changes in the liver;
- for determination of fibrinogen and/or fibrin breakdown products in plasma;
- in confirmed cases of spontaneous abortion (up to 22 weeks).
Preparing for diagnosis
The study will make it possible to evaluate blood clotting. If you are taking medications that affect blood coagulation, you should notify your doctor about this, since you will have to temporarily stop taking them in order for the test results to be as reliable as possible. There is no need to follow a diet or limit the consumption of any foods; it is enough to take a blood test in the morning on an empty stomach.
Research norm and interpretation of analysis results
Thrombin time is determined by the fibrinogen content in the blood. Thus, a decrease in fibrinogen concentration prolongs thrombin time, which is why these studies are often combined. However, you can get a complete picture of blood clotting only by doing a complete blood test, that is, a coagulogram . The norm is considered to be blood coagulation with the formation of a blood clot in 15-18 seconds . Under certain conditions, this value may vary: be lower than normal or higher.
An elevated thrombin time indicates reduced blood clotting.
This is possible with:
- long-term use of fibrinolytics or heparin treatment;
- disturbances in liver function and/or pathology of protein absorption, which leads to a decrease in fibrinogen content to less than 0.5 g/l;
- excess natural coagulants;
- blood pathologies;
- at the 2nd stage of thrombohemorrhagic syndrome (impaired blood coagulation in severe injuries, burns, shock);
- dysfibrinogenemia (defects in the molecular structure of fibrinogen), which can be hereditary or acquired (most often in liver pathologies);
- paraproteinemia (appearance in the plasma of abnormally structured and defective proteins from the group of immunoglobulins in myeloma).
A shortened thrombin time indicates an increased risk of blood clots; in addition, it may indicate the development of diseases that are accompanied by an increase in the concentration of fibrinogen in the blood (stage 1 of thrombohemorrhagic syndrome).
Only a doctor can accurately interpret test results and prescribe appropriate treatment!
Diagnostic significance of determining thrombin time
A laboratory blood test, which allows one to study the time required for the formation of a blood clot and changes in the amount of soluble plasma protein fibrinogen (coagulation factor FI, which is secreted by hepatocytes), is used in diagnosing thrombosis, liver diseases and pathologies associated with spontaneous abortion in the early stages.
Thrombin is a key enzyme that ensures the regulation of the functional activity of the coagulation system - the stability of a blood clot, which is important for stopping bleeding, depends on it. Changes in the plasma level of this enzyme reflect disturbances in hemocoagulation processes, in which many components take part. The formation of a blood clot goes through several stages:
- Cleavage of subunits A and B (fibrin peptides) from fibrinogen and connection of the remaining protein strands with each other.
- Formation of plasma-soluble complexes.
- Activation by thrombin (an enzyme that triggers fibrin polymerization) of coagulation factor FXIII and plasma transglutaminase and the conversion of fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin (a form that is practically indestructible), stabilizing the blood clot.
Very often, at the final stage, various changes in the structure of fibrinogen molecules and disruption of its functions are observed. These phenomena indicate dysfibrinogenemia - congenital or acquired hemorrhagic syndromes, which are characterized by prolongation of thrombin time and increased aggregation of blood platelets (platelets). There are no changes:
- activated partial thromboplastin time (the period during which a blood clot forms);
- concentrations of fibrinogen and D-dimer (fibrin breakdown product);
- the number of thrombus particles - soluble fibrinogen-monomer complexes.
In most cases, the occurrence of dysfibrinogenemia is caused by the presence of liver diseases (cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma, liver failure), characterized by multiple coagulation disorders, fibrinolysis (post-traumatic coagulopathy manifestations of DIC syndrome) or inheritance of a defective gene encoding the synthesis and function of fibrinogen. The following pathologies are distinguished: afibrinogenemia (complete absence of protein in the plasma) and hypofibrinogenemia (the minimum amount required for blood clotting).
A person may not even be aware of the presence of hemostasis pathology for a long time. Dysfibrinogenemia is detected accidentally, most often during preparation for surgery. The main clinical sign of fibrinogen deficiency is excessive bleeding or a tendency to increased blood clot formation - patients experience:
- poor healing of wound surfaces;
- bleeding that is very difficult to stop;
- massive spontaneous hematomas;
- hyper-menorrhea;
- petechial rash.
A blood test to determine thrombin time is also necessary when establishing the causes of pregnancy pathology and conducting anticoagulant therapy.
Method of performing the study
Thrombin time is studied using the side light scattering detection method. Its principle is to create in laboratory conditions the final stage of the coagulation process - the reaction of thrombin binding to platelets when exposed to:
- a special water-soluble mixture of thromboplastin and calcium chloride reagents, which allows you to convert the complex inactive plasma protein prothrombin into the active enzyme thrombin;
- tissue enzymes;
- tissue and coagulation factors – FV, FVIII, FXI, FXIII.
Its final result, depending on the presence of coagulation inhibitors in the test sample, is the conversion of soluble fibrinogen into stable fibrin.
Important Notes
You should know that newborn infants have a longer thrombin time than adults.
The results of the study may be distorted if:
- Transfusion (transfusion) of fresh frozen plasma - in this case, a change in the amount of fibrinogen and a violation of its structure is very difficult to differentiate.
- The use of Warfarin and unfractionated heparin - such measures provoke an extension of thrombin time.
To accurately interpret the final test data, it is necessary to take into account clinical symptoms and the results of other laboratory tests characterizing the state of the blood coagulation system.
What affects the accuracy of the result?
In some cases, the analysis result is inaccurate. The following can increase blood clotting time: alcohol, overeating, fatty foods, legumes, vegetables. Medicines reduce PTI: antibiotics, anticoagulants, anabolics, heparin, diuretics, laxatives.
The time period can be shortened by: eating foods rich in vitamin K (cabbage in all varieties, primarily spinach, beef liver), dehydration of various origins, antihistamines, contraceptives, caffeine-containing substances.
References
- Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of rare blood clotting disorders: hereditary deficiency of factors X, II, VII, 2021.
- Volkova, P.O., Zolotavina M.L., Didenko S.N. and others. Dependence of polymorphism of blood coagulation genes and blood group and rhesus affiliations in women. — Scientific almanac, 2021. — No. 1-2(15). — P.455-458.
- Sturov, V.G., Plyushkin, V.A., Anmut, S.Ya. and others. The final stage of blood coagulation: modern clinical and laboratory diagnosis of dysfibrinogenemia syndrome. - Thrombosis, hemostasis and rheology, 2008. - No. 2 (34). — P.8-15.
- Undas, A. Determination of fibrinogen and thrombin time (TT). — Methods in molecular biology, 2021.
Therapeutic measures
If the study reveals a decrease in prothrombin time compared to normal
, the patient is prescribed direct-acting anticoagulants (Heparin) or indirect (Warfarin), a special diet is recommended: fatty fish (halibut, herring, mackerel), oatmeal with olive or flaxseed oil, cranberries, figs, blueberries, plums, ginger. Drinks include green tea and cocoa.
When the PTI indicator is higher than normal
, you need to take coagulants or synthetic blood clotting accelerators (Vikasol). Dietary nutrition involves excluding from the diet fatty foods, buckwheat, greens, legumes, red currants, chokeberries, blackberries, wheat baked goods, and smoked meats.
Reduces blood viscosity by drinking clean drinking water in accordance with the age and weight drinking ration (40 ml per 1 kg of weight).
Prothrombin time is an indicator of coagulation, which literally saves a person’s life if determined in a timely manner.
Complexes with this research
Extended coagulogram Extended study of the functional state of hemostasis 4,150 ₽ Composition
Planning pregnancy. Clinical indicators 6,630 ₽ Composition
Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure 23,020 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Female infertility RUB 16,210
- Coagulogram RUB 2,020
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 9,620 RUR
- Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 16,690 RUR
- Miscarriage RUB 40,070
Reasons for the decline
Taking into account the observed shifts, the formal prothrombin index is normally determined by the limit of up to 150%. This also includes some errors during the examination and individual characteristics of the body. Anything less clearly indicates problems.
PTI in the blood decreases as a result of the influence of pathological factors:
- Congenital anomalies in which insufficient fibrin protein is produced. This substance is involved in the binding and aggregation of platelets, its activation is provided by coagulation factors. With pathologies of this kind, the prothromboin index decreases. Depending on the nature of the process and the body’s ability to compensate for the violation.
- Congenital diseases, all forms of coagulopathies.
- Liver disorders. Which are not associated with the destruction of its tissues. These are mainly functional disorders. They are difficult to diagnose using routine tests such as ultrasound. Scintigration is required, laboratory tests may be performed.
- Often, a decrease in the prothrombin index is detected in the process of taking drugs to influence the rheological properties of the blood. Be it Aspirin and its analogues based on acetylsalicylic acid or modern medications for thinning. Especially often, abnormal results are obtained after finishing taking thrombolytics, which have an even more aggressive effect on fluid connective tissue.
- DIC syndrome.
- Other drugs also have a negative effect on the blood. For example, laxatives due to the active removal of fluid from the patient’s body.
It is not recommended to use nicotinic acid for a long time, as well as drugs to suppress the patient’s immune system. Methotrexate is especially aggressive.
Hormonal drugs and anabolic medications manifest themselves in the same way. If problems are detected, the course of therapy should be reconsidered.
If the deviations are purely laboratory in nature and do not manifest themselves objectively, moreover, there is no such tendency, it is possible to continue treatment.
A low prothrombin index indicates excessive blood thinning and prolonged clotting; spontaneous bleeding of varying degrees of intensity is possible.
Norms during pregnancy
During gestation, the maximum upper limits are slightly higher, which is due to the need to more actively “displace” blood through the vessels in order to get rid of fetal waste products.
Typically, the prothrombin index in such patients is considered according to Quick. Normally, it ranges from 75 to 142%, and in pregnant women the level is defined as 98-152%. Plus or minus. Depending on the case.
Deviations should be considered as a potential disorder; only by proving the opposite can one calm down. Otherwise, there are no differences.
During the entire gestation period, the prothrombin index is approximately identical and does not change within significant limits.