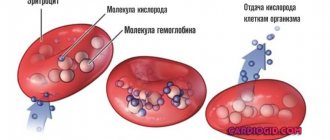
One of the important indicators included in the clinical blood test is the hematocrit number (Ht). This parameter allows you to estimate the volume of red cells in a child’s blood. Red blood cells perform an important function in the body - they supply tissues with oxygen and nutrients. This is possible due to the ability of hemoglobin, located in red cells, to bind to oxygen molecules in the lungs, transport them to the organs and give them to the cells, and then transfer carbon dioxide to the lungs. If the hematocrit is low or high, pathology may be developing in the body. Using this parameter, the doctor will be able not only to suspect the disease, but also to determine the degree of its severity.
How is the analysis carried out?
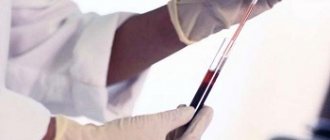
The hematocrit number is calculated during a general blood test. To do this, the blood is placed in a special tube called a hematocrit and centrifuged for one and a half hours. As a result, heavier formed elements, most of which are red blood cells, settle to the bottom of the tube, and plasma remains at the top.
Using the applied divisions, you can determine what volume the red cells occupy in relation to the plasma. In modern laboratories, the hematocrit number is calculated using hematological analyzers, which provide more accurate results. Despite the fact that the Ht indicator gives a quantitative, but not qualitative assessment of red blood cells, this analysis is considered quite informative. It is most often expressed as a percentage, sometimes it is written as a fraction - liter/liter.
Deviations from the norm
Deviation, both upward and downward, may indicate pathology, but may also have physiological reasons.
If Ht is increased in children, then the blood becomes thicker and more viscous due to an increase in the number of formed elements relative to the volume of the liquid part. This condition is dangerous because there is a risk of blood clots. If the norm is exceeded by 10-12% in a child under one year old, as a rule, this is due to physiology and should not cause concern. It’s another matter if a high level is observed in a child older than one year.
With a low hematocrit in children, the volume of red blood cells that supply oxygen and nutrients to the organs does not reach normal. In this regard, the acid-base balance in the child’s body is disturbed, and the cells experience oxygen starvation. As a result, your health worsens, namely weakness, rapid fatigue, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and pale skin.
This is how blood hematocrit is determined
Reasons for decline in women
{banner_banstat10}
In the fairer sex, the development of a pathological process is possible as a result of exposure to natural factors.
Pregnancy
As practice shows, a decrease in hematocrit is a completely normal phenomenon in the second and third trimesters of gestation.
Natural processes occur, which, in fact, act as a kind of catalyst for a drop in the number of red blood cells.
No action needs to be taken. Provided that the woman does not have the diseases described above.
Menstrual cycle
Approximately in the middle of the cycle, hematocrit values begin to fluctuate downward. This is also normal.
No special treatment is needed. Everything will return to normal after the cycle is completed.
Menopausal process
The reason for a decrease in hematocrit in a woman after 45-50 years is the attenuation of reproductive function with a gradual drop in hormone concentrations.
Occurs in all women and is called menopause. There is no reason to worry, this is also a temporary phenomenon.
Causes of high Ht
The hematocrit may be increased in the analysis if the child did not drink before donating blood, as well as in case of dehydration due to vomiting or an increase in body temperature. Increased Ht may be associated with pathological processes in which the concentration of red cells in the child’s blood increases. Among them:
- congenital and acquired renal diseases: neoplasms, polycystic disease, hydronephrosis;
- pathologies of the respiratory system;
- injuries and burns;
- heart disease;
- leukemia;
- peritonitis;
- erythremia;
- intestinal obstruction;
- oxygen starvation without symptoms;
- taking certain medications for a long time (mainly glucocorticosteroids).
Causes of low Ht
The hematocrit is considered to be reduced if it has dropped to 25%. A low level of this indicator in a blood test in children is a reason for additional examination to determine the cause. In most cases, the decrease is due to the following pathologies:
- slow formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow;
- increased rate of breakdown of red cells;
- hyperproteinemia, or increased levels of protein in the blood;
- overhydration, or thin blood;
- anemia;
- large volume of blood;
- acute bleeding.
Most often, in children, the hematocrit is reduced due to anemia. In this case, you need to see a doctor who will help you create the right diet and, if necessary, prescribe medications to increase Ht levels. You need to include more foods rich in iron in your food: apples, meat, liver, eggs, nuts. Doctors recommend using hematogen, which can be bought at any pharmacy.
Reasons for decreased hematocrit in adults
A decrease in the concentration of formed cells is possible due to a variety of provocateurs. To be more specific.
Cirrhosis
A disorder in which there is gradual or sudden destruction of liver cells. Hepatocytes.
Occurs with increased, prolonged consumption of alcohol. Much less frequently, the disorder occurs in patients with infectious hepatitis. Toxic lesions of the largest gland. These are classic prerequisites for the development of a pathological process.
The symptoms are typical, although not always noticeable to patients in the initial stages:
- Painful sensation in the right side of the abdomen, under the ribs. It acts as an alarm signal, the first symptom of a pathological process.
- Formation of spider veins and spider veins on the skin.
- Indigestion. Like a prolonged feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating. Other options are possible.
- Increased formation of intestinal gas. Even without connection with a specific diet.
- Feeling of fullness in the abdomen. Which is not usually associated with cirrhosis.
- Also bleeding. Especially at advanced, sub- and decompensated stages of the pathological process. The typical clinical picture is accompanied by severe organ dysfunction. The synthesis of coagulation factors is disrupted. This is why heavy bleeding begins.
Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a hepatologist. If there is no such specialist on staff, a gastroenterologist works. Loading doses of hepatoprotectors are prescribed. These drugs are designed to slow down the progression of cirrhosis. Mitigate its consequences.
If possible, transplantation is performed. Transplantation of the largest gland in the body. But in advanced stages this is not advisable, since bleeding begins.
A reduced hematocrit appears later, at advanced stages of cirrhosis. This is the result of bleeding, a drop in the physical volume of red blood cells. Red Taurus.
Heart diseases
Of very different nature. The most common place is coronary artery disease, heart attack, angina pectoris. Coronary insufficiency of all forms.
The disorder is accompanied by a reflex decrease in the intensity of bone marrow function. This is the result of ischemic events. Insufficient oxygen transport.
As time passes, the situation only gets worse. After all, the concentration of red blood cells decreases. Consequently, gas exchange and tissue respiration weaken and the hematocrit decreases quite quickly, this can be seen from the test results.
Symptoms depend on the specific pathological process. As a rule, there is heaviness and pain in the chest, breathing problems, weakness and poor tolerance to physical activity. There are many options.
Symptoms of the pre-infarction state, including delayed ones, are described here.
Treatment is carried out under constant supervision of a cardiologist. If the cause of the pathological process is an anatomical disorder or defect, consultation with a cardiac surgeon is indicated. Treatment is appropriate.
In the first cases, protectors are prescribed. Like Mildronate, Riboxin, to support the muscle organ.
In others, surgery is indicated to restore the anatomical integrity of tissues or to replace valves or altered structures.
Anemia
Name of the group of pathological processes. The most common forms of the disorder develop:
- Iron deficiency. As the name suggests, the body does not have enough ferrocontaining components and substances.
- Megaloblastic. When there is little folic acid and/or vitamin B12.
- Hemolytic. Develops against the background of spontaneous destruction of red blood cells. As a rule, it is genetically determined.
There are other varieties: sickle cell, aplastic.
They are all united in the same process. The concentration of red blood cells decreases. Cells die faster than usual, or immature structures are released into the blood, hct in the blood test will be lowered. This is not a normal situation.
Symptoms depend on the specific form of the disorder. The following manifestations are typical for all anemia:
- Exercise intolerance.
- Breathing disorders.
- Weakening of cardiac activity. Or it intensifies, but there is no sense in it. As a rule, it manifests itself as arrhythmias.
Other signs are also possible.
Therapy is the task of a hematologist. It is necessary to quickly detect the primary factor, forms of anemia and carry out complete treatment. Various techniques are used for this.
The iron deficiency type is eliminated with ferrocontaining drugs. Megaloblastic is corrected with vitamins B9 and B12 in shock dosages.
And so on. The question remains up to the experts.
Bleeding
Massive, as a rule. In this case, the hematocrit is reduced to a minimum. This is the result of the physical release of large numbers of red blood cells. Especially if the connective tissue is thick.
Symptoms are characteristic of traumatic or other blood loss:
- Headache.
- Weakness.
- Impaired consciousness. The patient may fall into stupor, coma and die.
- Breathing disorders.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Hallucinatory syndrome.
- Feeling of excruciating thirst.
- Inability to get up.
The development of a pathological process is possible as a result of injuries or damage to internal organs.
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a traumatologist or specialized surgeon. The point is to stop the bleeding as quickly as possible.
Hemostasis is carried out surgically. The goal is to close the wound and restore the anatomical integrity of the tissue.
As a rule, this is not enough. To return the patient to normal, transfusions of blood, donor plasma, and red blood cells are indicated.
The hematocrit comes to its senses gradually. This is not a momentary process.
Inflammatory chronic disorders
It does not matter whether it is infectious or autoimmune in nature. Options may vary.
The hematocrit is lowered because mild but persistent inflammation requires a large amount of the body's resources to maintain the lesion in an isolated state. All formed cells suffer, including red blood cells, which die prematurely, carrying large amounts of oxygen.
Symptoms of pathological processes depend on the disorder. It is impossible to say anything specific without knowing the localization.
The correction takes place under the supervision of specialists of various profiles. Infectious disease specialists, rheumatologists and other doctors. This is determined by the condition and probable diagnosis. The goal is to eliminate the primary violation.
For this purpose, antibiotics are prescribed if we are talking about a septic process. Or immunosuppressants, glucocorticoids. When the disorder is of autoimmune origin.
Low hematocrit values persist for some time after the underlying disease has been eliminated. This is a completely acceptable phenomenon.
It will return to normal within a few weeks. All this time, the patient's condition is monitored.
Internal organ injuries
This provision was partially discussed earlier. We are talking about damage to tissues and structures of the body with the flow of large amounts of blood.
It should be noted that even a minimal release of liquid connective tissue affects the body in the same way. Only to a much lesser extent, the indicators are not declining so quickly.
The treatment is identical. Surgical correction is prescribed and the wound is sutured. Next, hemostatic drugs are used.
Reference:
It is important to say that the damage can be iatrogenic. Provoked by the actions of doctors. This also happens.
Kidney failure
Develops slowly. In some cases, it is acute in nature, then it develops in a matter of days and even hours. Accompanied by a group of obvious symptoms.
- Decreased urine volume. As a rule, oliguria develops. This is a condition in which the amount of the substance drops to 500 ml per day or even less. At the initial stage of the pathological process, the condition may be exactly the opposite.
- Pain in the lumbar region. On one side or in the projection of both organs at once.
- Urinary disorders. Urine retention is possible. Although this is a relatively rare occurrence.
- Irregularities in blood pressure. So-called malignant hypertension develops when blood pressure levels are unstable. Or only growth is possible, without falling. Which is even more dangerous, since there is a high risk of stroke or heart attack. Emergency conditions.
Low hematocrit in the case of renal failure is due to the release of blood in the urine. This is quite possible and probable.
Treatment is under the supervision of a nephrologist. Or a urologist, if there is no specialized specialist who follows a narrow direction.
Diuretics are prescribed. In case of critical disorders, hemodialysis cannot be avoided. A kidney transplant is possible. If appropriate.
Lymphomas
Mostly Hodgkin's. A type of malignant tumor with a specific structure. They grow, as the name of neoplasia suggests, from lymphatic tissue.
The pathological process is accompanied by a pronounced drop in the number of red blood cells with intact plasma volumes, which causes a violation of the hematocrit concentration.
Of course, this cannot be called a specific sign, but a significant decrease in the hematocrit level should raise possible suspicions.
Lymphoma is accompanied by a group of typical symptoms.
Present:
- Body pain. Aching bones.
- Unbearable skin itching.
- Increase in temperature for no apparent reason. Up to 39-40 degrees Celsius. At the same time, the indicators are not stable, so serious jumps are possible.
- Weakness, drowsiness. Violation of the general condition of the body.
In the area of formation of the main tumors, the relief of the body changes. Large altered areas may form. Hypertrophied due to the growth of neoplasia.
Treatment is surgical. The neoplasms themselves are removed. The lymph nodes. Radiation is also carried out and courses of chemotherapy are prescribed. Depends on the condition of the individual patient.
Some cancers
Oncological conditions are not limited to lymphomas. The fact is that the pathological process can occur in another location, of a completely different type.
The essence remains approximately identical. The fact is that the disorder causes bleeding. Especially when the neoplasia is large and begins to disintegrate.
The more massive the bleeding, the worse the situation with the hematocrit: it drops below normal rapidly, and this will happen until the underlying pathological process is corrected.
Symptoms depend on the exact location of the disorder. Cancer gives different signs. All types are characterized by pain. Sometimes very intense and even unbearable. There are definitely disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Recovery is carried out by oncology specialists. This is not a quick process.
The gold standard of treatment includes three techniques:
- The actual operation. It is necessary to excise the tumor and remove it as radically as possible. In some cases, it is necessary to capture part of relatively healthy tissue in order to achieve maximum effect.
- Chemotherapy. It involves the introduction of special drugs that slow down the synthesis of fast cells. Nails, hair, immune structures and, of course, the cancerous tissues themselves.
- Radiation treatment. The use of radiation for targeted destruction of cellular structures.
Poisoning with drugs and poisons
{banner_banstat9}
Mainly cytostatics. Just the same ones that are used for chemotherapy.
Damage from other poisons is also possible. For example, substances of toadstool or salts of heavy metals.
In all cases of poisoning, the hematocrit in an adult is reduced due to impaired synthesis of red blood cells and the rapid death of these cells. Inpatient care is needed as soon as possible.
Treatment is carried out urgently. Specific antidotes are prescribed. Detoxification therapy course.