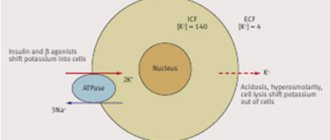
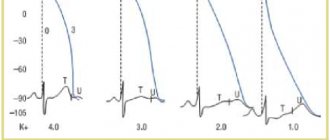
The problem should not be ignored, because the substance in question is considered a very important electrolyte present in muscle cells, working together with sodium. It is potassium that ensures proper muscle contraction, and its lack can lead to frequent cramps, decreased strength potential, and tissue dehydration. Potassium preparations are presented in quite a large number to choose from, so special attention should be paid to determining the most suitable remedy. Here you need to take into account the composition, quantity and mass fraction of components in order to achieve maximum effect. Potassium can be presented in the form of an independent preparation, or also be part of various preparations necessary for rehydration.
Composition of potassium preparations
The main active ingredient of the drugs is potassium salts. But it is important to pay attention to the form in which they are contained here. The amount of pure potassium will depend on this. Its 1 gram is contained in: • 2 grams of potassium chloride; • 3.3 grams of potassium citrate; • 6 grams of potassium gluconate; • 4.4 grams of potassium orotate. Potassium can be contained in preparations as an independent active ingredient and in combination with other components that are no less important for the body. Which composition option to choose should be decided together with the appropriate specialist - a nutritionist. This is the only way to achieve the desired result.
Properties of drugs
Potassium preparations have numerous properties that are valuable for the body of an ordinary person and an athlete. They are as follows: • stabilization of heart function, reduction of myocardial excitability and conductivity; • strengthening blood vessels and increasing their permeability; • stabilization of blood pressure in vessels; • increasing the elasticity of bone tissue; • increased muscle contractility; • stimulation of enzyme functionality; • normalization of the processes of transmission of nerve impulses; • restoration of proper kidney function; • maintaining healthy skin; • normalization of water balance in the body; • effective cleansing of the body from accumulated toxins; • ensuring proper oxygen supply to the brain and all organs and body systems; • neutralization of the negative effects of sodium on the body when it is in excess; • increasing the body's endurance, facilitating easier perception of intense physical activity; • improved appetite; • normalization of liver function; • reducing the period of recovery of the body after various diseases. Another important point: potassium has a very useful assistant, such as sodium. Together, these components have the following effect: sodium retains fluid in the body, potassium pumps it into muscle cells. Due to this, a beautiful muscle relief is formed and active muscle growth is stimulated. That is why potassium supplements are widely used among professional athletes. They are used no less frequently than carbohydrates and proteins, which are also very popular and are available in the form of numerous sports supplements. Due to its numerous beneficial properties, potassium preparations have become widespread and are also often used in complex therapy of various pathologies. But it is important to take the medications correctly in order to achieve maximum effect and eliminate the development of side effects.
Medicines containing calcium and potassium
Home Medical Encyclopedia Medicines Medicines that primarily affect tissue metabolic processes
ASPARCAM (Asparcamum)
Pharmachologic effect. Eliminates electrolyte imbalance (impaired ionic composition) in the body, promotes the penetration of potassium and magnesium ions into the intracellular space. It is close in composition and action to panangin.
Indications for use. Heart failure, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, arrhythmia (heart rhythm disturbance), hypokalemia (low potassium level in the blood).
Method of administration and dose. 1-2 tablets 3 times a day after meals for 3-4 weeks. The course of treatment can be repeated.
Side effect. Patients suffering from anacid gastritis (inflammation of the stomach, accompanied by a lack of hydrochloric acid secretion) or cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) may experience discomfort or a burning sensation in the epigastric region.
Contraindications. Acute and chronic kidney failure, hyperkalemia (increased potassium content in the blood), impaired atrioventricular conduction (impaired passage of excitation through the conduction system of the heart).
Release form. Tablets in a package of 50 pieces. A mixture of potassium aspartate and magnesium aspartate, 0.175 g each.
Storage conditions. In a place protected from light.
HYDROXYAPATITE (Hydroxyapatite)
Pharmachologic effect. The drug is the basis of the inorganic matrix of bone tissue. It is characterized by biocompatibility with human tissues and does not cause a rejection reaction. Stimulates osteogenesis
(formation of bone tissue), after filling the bone cavities, it does not resolve or harden, but is replaced by full-fledged bone tissue.
Indications for use. As a component of dental filling pastes, for filling root canals in the treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis (inflammatory diseases of the teeth), treatment of periodontitis (inflammation of the bone tissue surrounding the tooth root), when replacing bone defects with allografts (donor bone), for replacing bone defects after extraction cysts, resection (removal) of the apex of the tooth root, filling of various intraosseous cavities, etc.
Method of administration and dose. The drug in powder form is mixed on glass with sterile saline solution, ethylene glycol or an oil solution of retinol acetate to a paste consistency in compliance with the rules of asepsis (a set of measures aimed at preventing bacterial contamination of the powder). To fill root canals, the paste is prepared with eugenol; if eugenol is incompatible with filling materials, it is prepared with saline solution. For better radiopacity, add 50% zinc oxide. Further actions after applying the paste do not differ from the generally accepted ones. To prevent complications, the paste is removed beyond the apex of the tooth root.
The drug in the form of granules is used to fill bone pockets with a depth of 5 to 1 mm in case of periodontitis. To do this, the bone pocket prepared during the flap operation is tightly filled with granules to the level of the preserved bone of the alveolar process, the wound is sutured, and postoperative management is traditional. Filling of bone cavities with granules after sequestrectomy (removal of dead bone tissue), resection of the apex of the tooth root, etc. is carried out as when using other materials.
In surgery, during bone grafting, to enhance the osseointegrative properties of the graft (the ability of the transplanted bone tissue to mix with its own bone tissue), to prevent its rapid resorption and to reduce the inflammatory reaction, the drug is used to fill the places of incomplete adhesion and unevenness between the grafts and the receiving bone bed.
The drug in the form of powder or granules (sterile) in the intended volume is moistened with sterile saline to the consistency of a thick paste and the areas of loose fit between the grafts and along the graft are filled with a trowel. The wound is sutured layer by layer. Postoperative management of the patient is traditional.
Sterilization of the drug can be carried out an unlimited number of times in a drying cabinet at a temperature of + 150'C for 10-15 minutes.
Contraindications. Individual intolerance.
Release form. Powder or granules.
Storage conditions. In a dry place.
FOAMING POTASSIUM (Kalium)
Pharmachologic effect. A potassium preparation used to replenish potassium deficiency in cases of hypokalemia (low potassium levels in the blood) of various origins. Potassium is involved in maintaining intracellular osmotic pressure; in the process of conducting nerve impulses and transmitting them to innervated organs; contraction of skeletal muscles; processes of glucogenesis (glucose formation) and glycolysis (glucose breakdown without oxygen consumption) in the liver; synthesis of proteins and phospholipids.
Indications for use. Hypokalemia of various origins: lack of potassium due to insufficient intake into the body, for example, with decreased appetite, monotonous diet; loss of potassium in various diseases: diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, vomiting, diarrhea, surgical fistula (a surgically created channel connecting body cavities or hollow organs with the external environment or with each other) of the small intestine and/or bile ducts, acute pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas glands), nephropathies (kidney diseases), chronic heart failure, myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, hyperaldosteronism (edema, fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, increased blood pressure associated with increased aldosterone levels); loss of potassium caused by drug therapy (diuretics, glucocorticosteroids, uncontrolled use of laxatives).
Method of administration and dose. The dosage regimen is set individually depending on the degree of hypokalemia. The daily dose is from 1 to 4 sachets. Open the sachet and dissolve its contents in 100 ml of water. Take after foaming stops.
Side effect. In rare cases, allergic reactions.
Contraindications. Severe hypovolemia (decrease in circulating blood volume), burn disease, “crash” syndrome (poisoning of the body by metabolic products of compressed or crushed tissues due to injury), diabetic ketoacidosis (acidification due to excess levels of ketone bodies in the blood associated with increased sugar levels in the blood). blood), severe renal dysfunction, pancreatic necrosis (death of pancreatic tissue). Caution should be exercised when prescribing the drug to patients with impaired renal function. The simultaneous use of other potassium preparations and potassium-sparing diuretics is not recommended.
Release form. Dry substance for preparing an effervescent drink in bags of 10 pieces. 1 sachet contains 1.18 g of potassium in the form of potassium citrate and potassium carbonate.
Storage conditions. In a dry place.
Kalinor
Pharmachologic effect. The drug replenishes the deficiency (lack) of potassium and prevents the development of hypo. kalemia (low potassium levels in the blood) in the body.
Indications for use. Severe hypokalemia (low potassium content in the blood - 3.2 mmol/l), especially with simultaneously observed metabolic acidosis (acidification due to metabolic disorders). Neuromuscular disorders or cardiac arrhythmias caused by hypokalemia, therapy with cardiac glycosides. Prevention of hypokalemia during ketoacidosis (acidification due to excess ketone bodies in the blood).
Method of administration and dose. Take 1-3 effervescent tablets per day. The dose depends on the potassium deficiency being replaced, with 50-100 mmol per day generally being sufficient. You should not take more than 100-150 mmol per day. A single dose should not exceed 40 mmol of potassium, which corresponds to one tablet. Dissolve the effervescent tablet in a glass of water (100-200 ml) and drink in small sips for 10-15 minutes while eating. The daily dose - 2 or more tablets - should be evenly distributed. Continuous use of the drug is recommended for the entire period as long as hypokalemia persists.
Side effect. Nausea, vomiting, belching, heartburn, flatulence (accumulation of gases in the intestines), stomach pain, diarrhea. Allergic reactions in the form of itching of the skin, swelling of the face.
Contraindications. Diseases that are often accompanied by hyperkalemia (increased potassium levels in the blood): dehydration, decreased kidney excretory function, Addison's disease (insufficient adrenal function), Hamstorp syndrome (a form of paralysis associated with increased potassium levels in the blood).
Release form. Pills. One effervescent tablet contains: 2.17 g of potassium citrate monohydrate, 2 g of potassium acid carbonate, 2.057 g of citric acid.
Storage conditions. In a dry place, protected from light.
POTASSIUM-MAGNESIUM-ASPARAGINATE (Kalii-Magnesii-asparaginat)
Pharmachologic effect. An infusion solution that replenishes potassium and magnesium deficiency.
Indications for use. Heart failure, myocardial infarction, intoxication (poisoning) with cardiac glycosides, heart rhythm disturbances; hypokalemia (lowering the level of potassium in the blood) during therapy with saluretics (diuretics that enhance the excretion of sodium and chlorine - see page 296), laxatives, steroid hormones, chronic vomiting, prolonged diarrhea, etc.
Method of administration and dose. Intravenously, 1-2 infusions per day of 500 ml at a rate of 20-25 drops per minute. During the week before cardiac surgery and during the week after surgery, 500 ml is infused daily.
Side effect. Symptoms of hyperkalemia (increased potassium in the blood) and hypermagnesemia (increased magnesium in the blood) - with an increased infusion rate.
Contraindications. Severe renal dysfunction, hyperkalemia, hypermagnesemia, atrioventricular block (impaired conduction of excitation through the conduction system of the heart), myasthenia gravis (muscle weakness), fructose and sorbitol intolerance, fructose-1,6-biphosphatase deficiency, methyl alcohol poisoning.
Release form. Solution in 500 ml bottles. 1 liter of solution contains DL-aspartic acid 15.16 g, potassium hydroxide 3.9 g, magnesium oxide 1.116 g and xylitol 16.7 g. Calorie content About kcal/l (461.4 kJ/l). The total nitrogen content is 1.56 g/l.
Storage conditions. In a cool place, protected from light.
POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (KaSH chloridum)
Synonyms: Potassium chloride, Potassium chloride, Potassium hydrochloride.
Pharmachologic effect. Potassium is a major intracellular ion that plays an important role in regulating body functions.
Indications for use. Heart rhythm disturbances (atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal tachycardia), intoxication (poisoning) after administration of cardiac glycosides and diuretics (diuretics - see page 296), lack of potassium in the body, including during treatment with corticosteroids, etc.
Method of administration and dose. Orally in the form of a 10% solution, 15-20 ml 3-4 times a day (if necessary, the single dose is increased to 60-120 ml), intravenously drip up to 2.5 g in 500 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution or in 5% glucose solution .
Side effect. Paresthesia (feeling of numbness in the limbs), in rare cases a paradoxical reaction
(increased number of extrasystoles / heart rhythm disturbances /), when taken orally, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
Contraindications. Impaired renal excretory function, complete heart block; Caution is necessary in case of disturbances of atrioventricular conduction (conduction of excitation through the conduction system of the heart).
Release form. Powder.
Storage conditions. In a well-closed container.
Potassium chloride is also included in the drug Adelphan-Ezidrex K.
CALCIUM + ASCORBIC ACID
Synonyms: Calcium-C 1000 Sandoz, Calcium S, Lekovit S-Sa.
Pharmachologic effect. A drug that replenishes the lack of vitamin C and calcium mineral in the body. Ascorbic acid (Vit. C) increases the body's resistance to infections, is necessary for the formation of collagen and reparative (restorative) processes in tissues, normalizes vascular permeability, plays an important role in the biological processes of oxidation and reduction, as well as in cellular respiration. Calcium is an essential mineral element necessary to maintain the balance of electrons in the body and the adequate functioning of numerous regulatory mechanisms (muscle excitability and contractility, blood clot formation, bone mineralization, etc.).
Indications for use. Increased need for calcium and vitamin C (period of intensive growth in childhood and adolescence, during pregnancy and lactation, during physical and psychological stress). Calcium and vitamin C deficiency; maintenance therapy for infectious diseases (influenza, acute respiratory / respiratory system / viral infections, etc.) and during the period of convalescence (recovery). Elderly age.
Method of administration and dose. Adults and children over 7 years of age are prescribed 1-5 tablets per day. Children from 3 to 7 years old - 2-2 tablets per day.
In children under 3 years of age, the drug is used only as prescribed by a doctor. With long-term use of the drug, especially with a high calcium content, it is necessary to monitor the level of calcium and potassium in the blood and calcium in the urine.
Side effect. Rarely - nausea, flatulence (accumulation of gases in the intestines), diarrhea (diarrhea); shortness of breath, feeling of heat. When taking large doses - headache, fatigue, indigestion, thirst, polyuria (profuse urination).
Contraindications. Hypercalcemia (increased calcium levels in the blood), nephrolithiasis (renal stone disease), nephrocalcinosis (a disease accompanied by the accumulation of insoluble calcium salts in the kidney tissue), severe renal dysfunction.
Release form. Effervescent tablets containing 0.26 g of ionized calcium and 1 g of ascorbic acid. Effervescent tablets containing calcium lactate and ascorbic acid 500 mg each, calcium carbonate 165.6 mg each, in a package of 12 pieces. Effervescent tablets containing 0.6 g of calcium carbonate (=0.24 g of ionized calcium) and 0.5 g of ascorbic acid.
Storage conditions. In a dry, cool place.
CALCIUM GLUCONATE (Calcii gluconas)
Synonyms: Calcium gluconic.
Pharmachologic effect. Close to calcium chloride, but less irritating.
Indications for use. Used in the same cases as calcium chloride.
Method of administration and dose. Orally before meals, 1-3 g 2-3 times a day; children from 0.5 g to 2-3 g 2-3 times a day. Intramuscularly and intravenously (slowly) inject 5-10 ml of a 10% solution daily or after 1-2 days; for children only intravenously, depending on age, from 1 to 5 ml of a 10% solution every 2-3 days.
Side effect. With parenteral (bypassing the digestive tract) administration, in rare cases, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, slow pulse.
Contraindications. Hypercalcemia (increased calcium levels in the blood), atherosclerosis, tendency to thrombosis (formation of a blood clot in a vessel).
Release form. Powder; tablets of 0.5 g in a package of 10 pieces; ampoules of 10 ml of 10% solution in a package of 10 pieces.
Storage conditions. In a well-closed container.
Calcium gluconate is also included in the preparation algipor.
CALCIUM LACTATE (Calcii lactas)
Synonyms: Calcium lactic acid.
Pharmachologic effect. The drug compensates for the deficiency of calcium ions.
Indications for use. Calcium lactate is used orally in the same cases as calcium chloride and calcium gluconate (see pp. 495, 496).
Compared to chloride, calcium lactate is better tolerated because it does not irritate the mucous membrane. Compared to calcium gluconate, it is more effective when administered orally, as it contains a higher percentage of calcium.
Method of administration and dose. Take calcium lactate orally at 0.5-1.0 g per dose in powders, tablets or in a 5-10% aqueous solution (dissolved in hot water) 2-3 times a day.
Side effect. Not noted.
Contraindications. Not identified.
Release form. Tablets of 0.5 g in a package of 10 pieces.
Storage conditions. In a well-closed container.
CALCIUM CHLORIDE (Calcii chloridum)
Synonyms: Calcium chloride, Crystalline calcium chloride.
Pharmachologic effect. Calcium plays an important role in the functioning of the body. Calcium ions are necessary for the process of transmission of nerve impulses, contraction of skeletal and smooth muscles, activity of the heart muscle, formation of bone tissue, blood clotting, as well as for the normal functioning of other organs and systems.
A reduced calcium content in the blood plasma is observed in a number of pathological conditions. Severe hypocalcemia (low calcium levels in the blood) leads to the development of tetany (convulsions).
Correction of hypocalcemia is carried out with the help of calcium supplements, as well as hormonal drugs (see potassium tonin - p. 543, parathyroidin - p. 545), ergokaliferol, etc.
Indications for use. In case of insufficient function of the parathyroid glands, accompanied by tetany or spasmophilia (a disease in children associated with a decrease in the content of calcium ions in the blood and alkalinization of the blood). With increased release of calcium from the body, which can occur during prolonged immobilization of patients. For allergic diseases (serum sickness, urticaria, angioedema, hay fever, etc.) and allergic complications associated with taking medications. The mechanism of the antiallergic effect is unclear; however, it should be noted that intravenous administration of calcium salts causes excitation of the sympathetic nervous system and increased secretion of adrenaline by the adrenal glands. As a means of reducing vascular permeability in hemorrhagic vasculitis (hemorrhage due to inflammation of the walls of blood vessels), radiation sickness, inflammatory and exudative processes (release of protein-rich fluid from small vessels of tissue) - pneumonia (pneumonia), pleurisy (inflammation of the membrane covering lungs and lining the wall of the chest cavity), adnexitis (inflammation of the uterine appendages), endometritis (inflammation of the inner surface of the uterus), etc. For skin diseases (itching, eczema, psoriasis, etc.). For parenchymal hepatitis (inflammation of liver tissue), toxic liver damage (damage to the liver by harmful substances), nephritis (inflammation of the kidney), eclampsia (severe form of late toxicosis of pregnancy), hyperkalemic form of paroxysmal myoplegia (paroxysmal / periodically occurring / paralysis occurring with an increase in the content of potassium in the blood).
Also used as a hemostatic agent for pulmonary, gastrointestinal, nasal, and uterine bleeding; in surgical practice, it is sometimes administered before surgery to increase blood clotting. However, there is no sufficiently reliable data on the hemostatic (hemostatic) effect of calcium salts introduced into the body from the outside; Calcium ions are necessary for blood clotting, but the amount of calcium normally contained in blood plasma exceeds the amount required to convert prothrombin into thrombin (one of the blood clotting factors).
It is also used as an antidote for poisoning with magnesium salts (see magnesium sulfate - page 197), oxalic acid and its soluble salts, as well as soluble salts of fluoric acid (when interacting with calcium chloride, non-dissociating / non-disintegrating / and non-toxic calcium oxalate and fluoride are formed ).
The drug is also used in combination with other methods and means to stimulate labor.
When taken orally (8-10 g) it has a diuretic (diuretic) effect; According to the mechanism of action, it belongs to acid-forming diuretics (diuretics - see ammonium chloride).
Method of administration and dose. Calcium chloride is prescribed orally, intravenously by drip (slowly), intravenously by stream (very slowly!), and also administered by electrophoresis (percutaneous administration of medicinal substances through an electric current).
Taken orally after meals in the form of a 5-10% solution 2-3 times a day. Adults are prescribed 10-15 ml per dose (dessert or tablespoon of solution); children - 5-10 ml (teaspoon or dessert spoon).
6 drops per minute are injected into a vein, diluting before administration with 5-10 ml of a 10% solution in 100-200 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution. 5 ml of a 10% solution is injected intravenously slowly (over 3-5 minutes).
For the treatment of allergic diseases, the combined use of calcium chloride and antihistamines is recommended.
Side effect. When taking calcium chloride orally, pain in the epigastric region and heartburn are possible; when administered into a vein - bradycardia (decreased heart rate); Rapid injection may cause fibrillation
ventricles of the heart (chaotic contractions of the heart muscle). With intravenous administration of calcium chloride, a feeling of heat appears first in the mouth, and then throughout the body. This feature of the drug was previously used to determine the speed of blood flow; The time between the moment of its introduction into the vein and the appearance of a feeling of heat was determined.
Contraindications. Calcium chloride solutions cannot be administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly, as they cause severe irritation and necrosis (death) of tissue.
Calcium chloride is contraindicated in cases of a tendency to thrombosis (blockage of a vessel with a blood clot), advanced atherosclerosis, or increased calcium levels in the blood.
Release form. Powder in small, well-sealed glass jars with a stopper filled with paraffin; 10% solution in ampoules of 5 and 10 ml; 5% and 10% solutions for oral administration.
Storage conditions. Powder - in a dry place.
Calcium chloride is also included in the preparations: hemostatic sponge with Ambien, antiseptic sponge with kanamycin.
PANANGIN
Pharmachologic effect. A preparation containing potassium aspartate and magnesium aspartate. It is assumed that aspartate is a carrier of potassium and magnesium ions and promotes their penetration into the intracellular space. Entering cells, aspartate is included in metabolic processes (metabolism). Magnesium ions contribute to the therapeutic effect of the drug.
Indications for use. Used for cardiac arrhythmias (heart rhythm disturbances), caused mainly by electrolyte disturbances (disturbances in ionic composition), primarily hypokalemia (decreased potassium levels in the blood). The drug is indicated for rhythm disturbances associated with intoxication (poisoning) with digitalis preparations, for paroxysms of atrial fibrillation (atrial rhythm disturbance), recently appeared ventricular extrasystole (disturbance of the ventricular rhythm of the heart).
Panangin is used in the treatment of coronary insufficiency (discrepancy between the heart's need for
oxygen and its delivery). There is evidence of a decrease under the influence of the drug in hypoxic (caused by insufficient supply of oxygen to the tissue or impaired absorption of it) disorders of myocardial metabolism (metabolism of the heart muscle) associated with the deterioration of coronary / cardiac / blood circulation and hypokalemia (decrease in the level of potassium in the blood) caused by the use of saluretic drugs (diuretics that enhance the excretion of sodium and chlorine).
Method of administration and dose. Usually prescribed orally, 1-2 tablets 3 times a day, and in more severe cases (with coronary circulation disorders, intolerance to digitalis drugs, etc.) - 3 tablets 3 times a day. After 2-3 weeks. reduce the dose to 1 tablet 2-3 times a day. In relatively mild cases, 1 tablet is prescribed immediately, 2-3 times a day. Take after meals. To relieve (relieve) attacks of arrhythmias, a panangin solution is administered intravenously, for which the contents of 1 ampoule (10 ml) are diluted in 20-30 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution and injected slowly into a vein or the contents of 1-2 ampoules are diluted in 250 -500 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution and injected into a vein by drip. If necessary, you can add a solution of strophanthin or other cardiac glycosides (see pages 135, 130).
Side effect. When using the drug, nausea and dizziness are possible (when administered into a vein). For patients complaining of dizziness, reduce the dose.
Contraindications. The drug is contraindicated in acute and chronic kidney failure and hyperkalemia (increased potassium levels in the blood). In case of rhythm disturbances in combination with atrioventricular block (impaired conduction of excitation through the conduction system of the heart), it is not recommended to prescribe the drug.
Release form. Available in the form of dragees and ampoules. One dragee contains 0.158 g of potassium aspartate (corresponding to 36.2 mg of potassium ion) and 0.14 g of magnesium aspartate (11.8 mg of magnesium ion); one ampoule (10 ml) contains 0.452 potassium aspartate (103.3 mg of potassium ion) and 0.4 g of magnesium aspartate (33.7 mg of magnesium ion).
Storage conditions. In a dry place, protected from light.
| print version | This information is not a guide to self-treatment. A doctor's consultation is required. |
Indications and contraindications for potassium supplements
First of all, you need to figure out who needs potassium salts and when. This will avoid hyperkalemia, which leads to numerous negative consequences. Thus, indications for taking potassium are: • frequent urination, leading to disruption of the water-salt balance; • poisoning accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea; • increased fatigue, which occurs even with minor physical exertion, often manifests itself as weakness in the legs; • disturbance of the frequency and rhythm of heart contractions (arrhythmia); • systematic increase in blood pressure; • frequent convulsions localized in the lower extremities; • constant stress, contributing to the development of nervous tension; • disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory system; • intense physical activity leading to active sweating; • playing sports in a hot room or in the summer; • multi-day competitions and long training sessions; • the need for active and rapid muscle mass building; • long period of recovery after intense physical activity; • to maintain high energy levels in the body. If there are such indications, taking potassium supplements will be quite justified. But first you should definitely consult your doctor. This will allow you to choose the right remedy, as well as determine the optimal dosage, which will make it possible to achieve the desired result and eliminate the likelihood of side effects. Despite the fact that potassium is a substance that plays an important role in the life of the body, taking it in the form of drugs that act as an additional source of macroelements is contraindicated in some cases. The use of potassium salts is strictly not recommended in the following situations: • hyperkalemia, which may be a consequence of renal failure and other disorders. It is manifested by increased sweating, arrhythmic conditions, and frequent urination. Also at this time, stomach colic and increased excitability may occur. In this case, you should undergo an examination and stop taking potassium. The prolonged presence of hyperkalemia becomes fertile ground for the development of diabetes mellitus; • violation of the excretory function of the kidneys associated with the presence of certain diseases in the body. In such a situation, the risk of developing the above-mentioned hyperkalemia increases; • individual intolerance to the components of the drug. It is manifested by symptoms of an allergic reaction, which may include problems with the respiratory system, digestion or skin. If you have an allergy, you should stop taking the drug and consult a doctor. Repeated use of the substance that triggered the allergic reaction can lead to a more dangerous condition. As for side effects, they occur quite rarely. Symptoms usually develop in response to an excess dosage, which provokes an excess of potassium. Side effects include: • nausea, sometimes leading to vomiting; • diarrhea; • heart rhythm disturbances; • confusion; • tingling in the hands and feet; • the appearance of shortness of breath; • increased fatigue; • feeling of weakness in the legs. If such symptoms appear, you should stop taking the drug, visit a doctor and undergo an examination to rule out hyperkalemia. Avoiding such signs is quite simple - you need to adhere to the recommended dosage and duration of potassium intake.
Indications for use
Preparations containing calcium and potassium have a wide range of indications for use.
Calcium preparations are used for conditions that are accompanied by calcium deficiency (hypocalcemia): parathyroid insufficiency, vitamin D deficiency, blood transfusions, changes in acid-base balance (alkalosis), as well as overdose of magnesium preparations.
In addition, calcium preparations are indicated as an adjuvant for allergic diseases, inflammatory processes, radiation sickness, liver and kidney diseases, as well as bleeding.
Calcium preparations in combination with cholecalciferol (vitamin D) are used to prevent and treat osteoporosis (increased bone fragility), especially in elderly patients.
Together with magnesium and aluminum preparations, calcium carbonate is used as an antacid to treat conditions associated with increased stomach acidity: heartburn, gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Potassium preparations are used for conditions that are accompanied by potassium deficiency (hypokalemia): overdose of diuretics (diuretics), cardiac glycosides, glucocorticosteroids; uncontrollable vomiting; severe diarrhea; heart rhythm disturbances (arthymia); myasthenia gravis (muscle weakness).
Potassium preparations in combination with preparations containing magnesium are used for arrhythmias of various origins.
Instructions for the use of potassium preparations
Potassium tends to accumulate in the body, so it is taken in the form of special preparations in short courses, the duration of which should not exceed 3-4 weeks. As for the doses recommended for a person, they are determined on an individual basis. Everything will depend on the condition of the body, the intensity of life and the indicators of various loads, as well as the dosage of the drug itself. It is usually recommended to take the drug one capsule 1 to 5 times a day. To determine the exact dose, it is worth noting that for an average person, the daily requirement of potassium is 1.5 grams. If we talk about athletes, they need from 2 to 3 grams of the substance. Based on these numbers, the application scheme is calculated. Take potassium supplements with meals, as well as before or after meals. It all depends on the form of release of the product, the version of the active substance. After completing one course, you should take a break of several months. The need for repeated use is discussed individually with a doctor. If potassium is part of vitamin complexes, it is present here in a smaller dosage, respectively, the duration of administration may be longer, or the time interval before the next course will become shorter. But, again, all these points are decided individually.
Sources of potassium and magnesium
It is noteworthy that potassium and magnesium does not make itself known at first. The insidiousness of diseases developing due to a lack of potassium and magnesium lies in the fact that they do not appear overnight, but gradually. This is explained by the fact that both potassium and magnesium have antagonists in the body. These are substances that replace them, but over time either the resource is exhausted or the alternative itself is destructive.
The best way to prevent deficiency would be to actively consume potassium and magnesium naturally - through food. But, unfortunately, the concentration of these microelements in ordinary products is not so high as to cover a person’s daily needs. This partly explains the development of heart disease over time.
So, to prevent potassium and magnesium deficiency, make sure that your daily diet includes the following foods:
- potassium
- potato,
- cabbage,
- carrot,
- raisin,
- dried apricots,
- prunes,
- figs,
- dates,
- bananas,
- nuts,
- Wheat groats,
- oat groats,
- buckwheat grain,
- wheat bran
- seaweed
- sesame
- almond
- Pine nuts
- cocoa
- wheat bran
- dried apricots
- shrimps
- soya beans
The price of potassium preparations and how to buy them
If you want to buy potassium supplements, but don’t know where it’s best to do it, contact our company. We offer a large selection of drugs - dietary supplements, vitamins, mineral complexes, and we guarantee their high quality, which is confirmed by numerous certificates. All drugs have a carefully selected composition, where the active elements are contained in the optimal dose. Before going on sale, products undergo a testing process in laboratory conditions, as a result of which they prove their safety and effectiveness. You can buy potassium preparations from our company in any way convenient for you: • through the website. To do this, just register on the resource, look through the proposed catalog, and determine the appropriate products. After sending it to your cart, all you have to do is fill out a short application, make a payment, and order delivery; • by phone. The purchase process is carried out online with the help of our manager. You will need to answer questions from a company representative, devoting only a few minutes of your personal time to this procedure; • in the shop. Here you can personally familiarize yourself with the range of products, as well as receive detailed advice from our specialist on the topic of choosing the most suitable drug. After payment, you can pick up the goods immediately, receiving it in your hands. In order to make cooperation as convenient and effective as possible, we offer you several payment methods, among which you can choose the most suitable one: • cash upon receipt of the product; • cash on delivery at the delivery service; • non-cash transfer, which is easy to carry out through a terminal or at any bank branch. Delivery is carried out as soon as possible and will be carried out using the method you choose. You will see detailed conditions for the provision of services in the corresponding section of our website, and you can also find out by calling the company manager. The contact telephone number for free calls during business hours is indicated on the website pages. By deciding to buy potassium supplements from us, you are making the right choice and getting the opportunity to make a profitable purchase. We have special offers for wholesale buyers, and retail sales are often carried out with current promotions, which also allows you to save money without compromising the quality of the goods. We work for you, and thank you for your trust!