Patients of different genders and ages will have different symptoms and consequences of the disease. For example, signs of stroke in older women may be nonspecific (unlike symptoms in men). That is why it is important to monitor your own condition and the condition of loved ones at risk more carefully.
Types of stroke
Clinicians distinguish two types of stroke: hemorrhagic and ischemic. The ischemic type accounts for more than 80% of all cases of the disease. It occurs due to narrowing or blockage of blood arteries, which impedes the flow of oxygen to the brain. Typically, this type of stroke occurs after age 60.
Hemorrhagic occurs when blood vessels rupture as a result of high blood pressure and bleeding in the brain. In this case, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable and the survival rate is quite low.
It is also worth highlighting transient ischemic attack (ministroke). An acute transient circulatory disorder lasts from 5 to 10 minutes, but if this is not given due importance, the consequences can be quite serious.
Periods of stroke
Among the huge number of neurological diseases, stroke is the most important problem. Hemorrhage in the brain leads to disruption of intracranial circulation, neuronal necrosis and disruption of vital body functions.
In ischemic stroke, a number of processes are observed that together lead to the death of neurons. Cell destruction occurs against the background of cerebral edema. At the same time, the brain increases in volume and intracranial pressure increases.
Due to cell swelling, displacement of the temporal lobe is observed, as well as infringement of the midbrain.
Compression of the medulla oblongata may also occur due to wedging of the cerebellar tonsils into the foramen magnum. This process quite often leads to death. Therefore, early hospitalization of the patient is extremely important.
When the first signs of an ischemic stroke appear, medical assistance should be provided within the first three hours, otherwise the prognosis is disappointing.
There are several periods of ischemic stroke:
- acute;
- spicy;
- early recovery period of stroke;
- late recovery;
- stage of residual effects.
The most acute period
In the first three hours, it is possible to restore blood flow and eliminate or reduce neuronal death through the use of thrombolytics. It is also possible to administer drugs into the stroke area itself, which helps prevent the development of complications.
Then doctors take measures to restore pressure, carry out rehydration, dehydration and oxygen therapy.
During the most acute period of a stroke (from 4 to 5 hours after the attack), the patient should be under the close supervision of a doctor in a hospital setting.
Acute period
The period up to 14 days after the attack is considered acute. The patient continues to undergo treatment in a specialized department of the hospital. He is undergoing drug therapy aimed at:
- reduction of cerebral edema;
- maintaining normal blood viscosity and coagulability;
- maintaining normal functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- relapse prevention;
- maintaining normal blood pressure.
Early recovery period
The early recovery period is considered to be the period from 2 to 6 months after a stroke. At this stage, complex treatment is carried out:
- the patient takes medications according to an individual treatment regimen;
- in case of speech impairment, a speech therapist works with the patient;
- various manipulations are prescribed to restore sensitivity of the limbs and other parts of the body (massages, baths, acupuncture and others);
- physical therapy – the method helps strengthen ligaments and muscles.
Late recovery period
The late recovery period is the time six months after the stroke. At this stage, the results of treatment and rehabilitation measures taken during the early recovery period are already visible.
The patient's finger sensitivity is restored and motor skills improve. It is extremely important not to stop the complex of procedures. Rehabilitation after a stroke is a long and labor-intensive process.
Period of residual effects
The time from one to two years after a stroke is considered the residual period. At this stage, it is important to follow all doctor’s instructions and take measures to prevent a recurrent stroke.
Rehabilitation specialists and neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital create a treatment and rehabilitation program individually for each patient, which allows achieving high results in recovery after a stroke.
Expert opinion
Author: Vladimir Vladimirovich Zakharov
Neurologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Memory Disorders
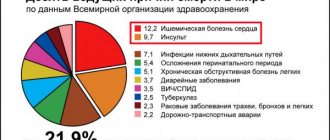
According to statistics provided by WHO, stroke ranks third in prevalence among all neurological diseases. Doctors note an annual increase in incidence. In Russia, 400 thousand new cases of stroke are registered every year. More than 30% of them are fatal. Acute cerebrovascular accident is not a disease characteristic of older people. The disease can be diagnosed in 5-year-old children. A distinctive feature of old age is considered to be a greater number of factors predisposing to the development of stroke.
At the Yusupov Hospital, diagnosis of cerebrovascular accidents is carried out using modern medical equipment. CT and MRI make it possible to assess the size of the pathological lesion, its location, and the type of stroke. Treatment is developed individually for each patient. The drugs used meet quality and safety standards. If necessary, surgical intervention is performed. During the rehabilitation period, each patient is prescribed a course of physiotherapy and a complex of physical therapy. Experienced massage therapists work the muscles, helping to restore lost functions.
Signs of a stroke
Most often, cerebrovascular accident occurs suddenly. Symptoms include:
- Increased blood pressure.
- Strong headache.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of balance.
- Noise in ears.
- Visual impairment (loss of fields).
- Numbness of the facial muscles and limbs.
- Articulation impairment.
In addition, older women may have atypical symptoms: hiccups, fever, attacks of fear.
A stroke can develop from several hours to days. You can understand that changes in blood circulation are occurring by the occurrence of tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), attacks of fear, decreased attention, and loss of orientation.
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to seek emergency medical help. Taking timely measures will help stop cell death and avoid serious complications.
Main symptoms
The following symptoms are typical for women:
- severe headaches (characteristic of migraines);
- decreased intensity of facial expression activity;
- failure of nerve conduction in the facial muscles;
- disturbance of speech and motor activity of the limb on one side;
- visual impairment;
- dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus;
- gag reflex and uncontrollable muscle contractions;
- self-perception disorder;
- sagging corner of the mouth;
- feeling of mental unsettlement.
Stroke in older women
According to statistical studies, stroke occurs in 1.5-2% of the population every year, while timely medical care is provided only in 50% of cases. It is for this reason that this pathology often causes disability and death.
As a rule, women are susceptible to stroke after 60 years of age, while in men this risk occurs much earlier - after 40 years of age. This is largely due to hormonal disorders that occur in the body of women during menopause. Smoking, alcohol, long-term use of hormonal drugs, and blood clotting disorders also contribute to the development of stroke in women.
Women suffer the pathology more severely than men and only a small percentage of patients return to a normal lifestyle. The reason for this is untimely provision of medical care.
Patterns of development of the pre-stroke state
Primary signs of a pre-stroke condition in elderly women may be nonspecific. May appear:
- frequent headaches;
- nausea;
- malfunction of the sense organs.
Similar symptoms can appear with the progression of many diseases, including hypertensive crisis, a drop in sugar levels, and others.
However, despite the nonspecificity of the symptoms, it is still possible to recognize a pre-stroke condition. There are several factors that allow you to determine pathology at an early stage:
- The pre-stroke state was preceded by a long period. It is clear that transient ischemia cannot develop suddenly over a few days or hours. There is always an initial stage from which signs are taken into account. This stage usually takes 14-21 days, but in some patients it can last longer.
- The general condition worsens. In women, pre-stroke is much more severe than in men and often ends in necrosis.
- The manifestations are more pronounced. This factor is directly related to the previous one.
- The likelihood of an emergency occurring is much higher. Most often it is characterized by tissue death.
How to recognize a stroke
You can determine the development of a stroke by doing the following:
- Try to quickly repeat the phrase.
- Smile widely (if a stroke develops, the immobility of part of the face will be noticeable).
- Raise your arms up (if cerebral circulation is impaired, this will not be possible).
- Ask the person to show their tongue (in the case of a stroke, its tip will be deviated towards the brain lesion).
If the patient cannot pass this test, you must immediately call an ambulance, and during this time provide first aid:
- Lay the patient down, raising his head above body level.
- Provide air flow (open a window, balcony).
- Free yourself from tight clothing (unfasten your bra, belt, belt, tie, etc.).
- When vomiting, turn your head to the side.
- Measure blood pressure, pulse, record all readings.
When signs of a stroke appear, it is important to behave calmly and reassure the person, since excessive emotionality contributes to increased blood pressure.
First aid for stroke
It is impossible to determine the nature of a stroke in the first hours, therefore it is necessary to normalize vital functions (breathing, blood circulation) and ensure the prevention of possible complications (pneumonia, thromboembolism, bedsores).
The first step is to call an ambulance. It is advisable to reassure the patient and measure blood pressure. If there is vomiting, place the patient on his side and place his hand under his head. Do not bend your neck, because blood flow cannot be impaired. The airways need to be clear. In case of severe respiratory distress, mechanical ventilation must be started.
If breathing is impaired, it is necessary to free the patient from tight clothing. Free the oral cavity from foreign objects, mucus, and vomit. If the patient is indoors, access to fresh air is necessary. If a person is conscious, it is advisable to cheer him up and calm him down.
If you lose consciousness, you need to make sure that the person is not injured or bruised.
There is no need to take medications so as not to worsen the patient’s condition.
If it is not possible to call an ambulance, then you must transport the victim to the hospital yourself.
Prognosis and possible complications
Stroke in old age often has severe complications and consequences. The most favorable prognosis is partial restoration of functions affected by damage to parts of the brain.
Most often, older people who have suffered from this disease have problems with disorientation, speech and coordination of movements. However, this is only possible if medical care was provided in a timely manner.
If medical assistance is not provided within 2-3 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, then the person is susceptible to complications such as:
- Paralysis, paresis.
- Serious speech defects (up to its complete absence).
- Strabismus and other vision pathologies.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Poor circulation of the inner ear, often hearing loss.
- Parkinson's disease.
In most cases, people who have had a stroke are unable to lead a normal life and require constant care.
The relationship between brain regions and the clinical picture of stroke
If the right lobe is affected, this is expressed by paralysis of the left limbs or loss of sensitivity in them.
The patient has a pronounced depressive state and a decrease in the desire for recovery. If the hippocampus area is affected, then the patient cannot grasp objects with his hand, loses the ability to navigate in space, cannot remember what happened yesterday, but memories of a longer period are preserved.
The hippocampus is responsible for emotions, short-term and long-term, spatial memory necessary for orientation in space.
If the left lobe is affected, then paralysis, decreased or loss of sensitivity in the right half of the body is characteristic, the patient does not perceive speech and speaks inarticulately.
If the cerebellum is affected, there is a lack of coordination, the patient feels nausea and dizziness. When the stem structures are damaged, the patient may experience double vision, the act of swallowing is disrupted, and involuntary movements occur.
Rehabilitation
Elderly people who have suffered a stroke must undergo a long course of rehabilitation. This period is very important, since rehabilitation will help minimize the consequences of circulatory disorders and significantly improve your overall condition.
The list of actions to restore the patient includes both physical and psychological assistance. A person must feel important and supported; only in this case will he be able to overcome the psychological discomfort associated with the partial loss of cognitive functions.
Even if the patient’s motor function is normal, it is necessary to purchase an orthopedic mattress. When a disruption in activity does occur and a person has limited physical capabilities, it is necessary to regularly change his position (to avoid bedsores).
Often, a person who has suffered a stroke is prescribed medications to normalize blood circulation. They must be taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the attending physician. If signs of apathy or aggression appear, the help of a psychologist, and in some cases a psychiatrist, is necessary.
Statistics on stroke in old age
Stroke is the second most common cause of premature death. According to WHO, 5–6 million people worldwide have a stroke every year, and 450 thousand in the Russian Federation. It occurs in people regardless of gender and age, but most often affects the elderly. After reaching 60 years of age, the likelihood of occurrence increases sharply and doubles after every 10 years. 75% of the total number of recorded cases of stroke occur in patients 65 years of age and older.
According to statistics, stroke affects men 11.25 times more often than women. Women are susceptible to stroke at a later age, which is why women's mortality from the pathology exceeds men's. A genetic predisposition has also been proven if the parents had a stroke. This is explained by the inheritance of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism disorders, hypertension.
The spinal type is the least common - 1% of the total number of cases.
Prevention
The following preventive measures will help prevent a stroke:
- Annual medical examination (cholesterol control, blood glucose levels).
- Regular blood pressure monitoring.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- Sleep at least 7 hours.
- Daily walking.
- Proper nutrition (the diet should include a lot of protein, vegetables, fruits).
- Active lifestyle (exercise, yoga, swimming).
Stroke is a disease that leads to disability. To avoid it, you need to be careful about your health and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Consequences of stroke for elderly patients
The older the patient is at the time of admission to the hospital, the more severe the pathology will be and the lower the chances of recovery. The following may reduce the likelihood of full recovery after a stroke:
- It is not always possible to dissolve blood clots in blood vessels with medications in elderly patients. Pensioners usually have a large number of contraindications to the insertion of catheters and surgical intervention, so the risk of death increases.
- The younger age of the patient guarantees the restoration of lost functions thanks to an alternative blood supply. Age-related changes in vascular channels (including atherosclerosis) significantly reduce the likelihood of complete recovery in elderly patients.
- Age often goes hand in hand with a variety of third-party chronic diseases. They usually affect the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, heart muscle, respiratory organs, etc. And since a stroke is a huge stress for the body, the progression of all existing chronic pathologies is inevitable. This significantly influences medical prognoses.
- Stroke goes hand in hand with infectious complications. Since one of the consequences of a stroke is paralysis, due to which the patient is forced to constantly lie motionless in bed, the formation of bedsores and congestion is inevitable. Large areas affected by purulent lesions are the best way for infections to enter the body.
Stroke is especially dangerous for older women, because the likelihood of a second attack following the first is extremely high. Usually the consequence of such an illness is loss of consciousness or coma. So you should be especially careful about your health in retirement age, because full recovery of the body after a stroke is almost impossible in the presence of third-party chronic pathologies or predisposition.
Risk factors
- Severe arterial hypertension. This also includes persistently high blood pressure. Pathologies are observed in 70% of elderly people. Over the course of a year, 3–4 hypertensive crises occur, which after 80 years of age often provoke a stroke.
- Atrial fibrillation (another name is atrial fibrillation). It is a heart rhythm disorder that causes uneven blood flow and blood clots in the heart. When blood clots enter the brain, they cause a stroke.
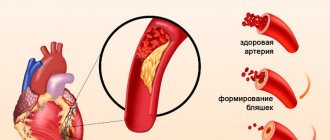
- Increased blood cholesterol levels. In older people, lipid metabolism is disrupted, as a result of which excess cholesterol begins to settle on the walls of blood vessels. Over time, blood flow becomes more difficult and, in severe cases, stops completely.
- Obesity in combination with the metabolic syndrome characteristic of the elderly (metabolic disorders, production of vital hormones and other processes). Increases the load on the heart.
- Myocardial infarction. Heart failure in people over 85 years of age. They are signs of the development of atherosclerotic processes that affect all vessels, including cerebral ones.
- Floor. There is a predisposition in females up to 80 years of age, and in males after 82 years of age.
- Alcoholism and smoking. They worsen the condition of the cardiovascular system and provoke obesity.
- Uncontrolled use of medications that affect blood circulation and the functioning of the heart muscle. For example, taking estrogen-containing contraceptives by women who smoke and have hypertension increases the risk of stroke.
- Diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle with little physical activity. Provokes slow blood circulation and obesity.
- Constant stress, increased mental stress, nervous exhaustion. Contraindicated for older people who have already had a stroke before.
Important! The presence of two or more factors in an elderly person increases the risk of a fatal stroke.
Also at risk are older people who have:
- congenital defects in the structure of the myocardium and valve apparatus;
- chronic diseases that provoke an increase in blood pressure, but are not pathologies;
- acquired defects of the cardiac folds, leading to disruption of blood flow;
- narrowing of the paired artery;
- damage to the cranial bones and soft tissues of the head;
- IHD;
- inflammatory process in the arterial vessels of the legs;
- holding your breath during sleep;
- inflammatory process of an autoimmune nature of the walls of blood vessels;
- muscle and joint diseases affecting the cardiovascular system.
The causes of a spinal stroke can be:
- injuries, surgeries and other physical impacts;
- atherosclerotic pathological processes;
- embolism.