A microstroke is microdamage and disruption of the brain as a result of lack of oxygen; the first bell before a stroke. It does not cause significant harm, but is an indicator of various disorders. At the same time, doctors generally do not call such a disease as a microstroke; now they are increasingly inclined to think that this is the same stroke (only in a mild form) or a transient cerebrovascular accident. But, no matter what we call this disease, the fact is a fact: it exists, affects people and has its consequences.
Differences between a minor stroke and an ischemic one
In fact, in terms of symptoms, these two diseases are quite similar (even to diagnose a microstroke at home, the patient needs, for example, to try to raise both arms; the same exercise is used for stroke). They are distinguished only by their duration (a ministroke comes and goes quickly) and the consequences for the body (a minor stroke can go away on its own, without medical intervention). But the diagnostic and treatment methods are the same, because usually a microstroke foreshadows the onset of an ischemic one.
Make an appointment
Possible manifestations: numbness and immobilization of one half of the face, unsteadiness of gait, severe headache, dizziness. Symptoms can be isolated or combined. With microstrokes, the symptoms disappear within 24 hours.
Self-help if you suspect a microstroke - how to help yourself if no one is around?
If alarming phenomena that are similar in symptoms to a microstroke have made themselves felt, and the patient is alone at home, he should take the following measures:
- Call one of your friends or relatives and ask them to come urgently.
- Call an ambulance , describing your complaints to the dispatcher.
- Open the windows in the apartment to ensure oxygen enters the room.
- Free the chest from constricting clothing , remove the belt (if any).
- Take a lying position , placing a pillow under your shoulders and head. You can place a basin near the bed in case of vomiting.
- A bandage or handkerchief soaked in cold water and applied to the forehead can alleviate the general condition.
- Until the ambulance arrives, any movement should be minimized . You also need to try to relax and tune in to positive thoughts.
Myths about microstroke
Many of us have heard the name “ministroke,” but not everyone knows what it is and why this condition is dangerous.
To begin with, we note that, at the same time, it is necessary to distinguish between this condition and a stroke, and not.
Why?
- A disease that doesn't exist? Experts do not separately identify such a disease as microstroke. In the medical lexicon, this is called transient cerebrovascular accident (TCI);
- "Micro" disease? The prefix “micro” in the word is only misleading: it does not mean at all that there is no need to be afraid of this condition or that there is no need to take urgent measures to eliminate it; rather, on the contrary, it emphasizes the “kinship” with stroke with only one difference - in symptoms. The symptoms of a minor stroke are not as severe as those of a cerebral hemorrhage, and they go away much faster.
- Is it possible to recover? After a mini-stroke, the body can often recover without the help of a doctor, but it is still worth getting examined: even if the symptoms have already disappeared, the specialist should know that they were there. Thus, it is more likely that relapses and strokes will be prevented.
The “micro” in the word does not make this disease insignificant, it only hints that the disease is reversible (unlike a full-blown stroke). Therefore, diagnosis and treatment should be approached with full responsibility. So what myths about microstroke are just myths and should not be believed?
- Minor stroke is a rare disease. Unfortunately, it is not. Every year it affects tens of thousands of people, and many of them, without proper treatment, lead to disability.
- Only old people can get sick. Unfortunately no. This disease increasingly affects people aged 20-30 years. True, a young body usually fights the consequences better than an older person’s body, but that’s another story.
- What can happen cannot be avoided: a stroke cannot be prevented. This is also a myth. There are certain preventive measures that can help avoid encountering this unpleasant disease.
- A microstroke cannot be recognized: the symptoms are too mild. In part, this is not a myth; the symptoms are really mild. But if you have the signs described above, the time-tested exercise “raise both arms up” is suitable - one part fails during a microstroke, so the patient can only raise one arm.
- Micro-stroke, stroke and heart attack are the same thing. If we mentioned the differences between the first two diseases above, then the third differs from both of them in location. A heart attack is located in the heart, while a (micro)stroke is located in the brain.
Diagnosis of microstroke at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using modern medical equipment. European CT and MRI installations make it possible to accurately determine the location of the lesion and its extent. An individual treatment and rehabilitation program is developed for each patient. The recovery period takes place under the supervision of experienced neurologists, massage therapists, exercise therapy instructors and physiotherapists. A personal approach can reduce the time of hospital stay and reduce the risk of recurrent microstroke.
Kinds
The consequences of a stroke are several types of amnesia. Based on what type of injury the attending physician diagnoses, individual treatment and rehabilitation measures are prescribed.
Types of amnesia:
- Damage to verbal memory;
- Visual glitches;
- Motor skills disorders;
- Damage to emotional-figurative memory.
- Vascular dementia.
Verbal
Verbal memory is the ability to remember, retain and reproduce verbal information.
If the part of the brain responsible for storing information received verbally is damaged, then the patient cannot remember the names of relatives and friends, forgets the names of objects, and loses vocabulary. Communication with others becomes extremely difficult, and the victim has difficulty remembering new information.
Visual memory impairment
A person’s ability to fix, store and use various information that is received in the form of a visual image is called visual memory.
After a stroke, a patient whose area that stores visual information is damaged may not recognize everything around him: his home, family, friends, objects, etc.
Loss of motor skills
Motor skills are a person’s ability to confidently perform complex movements. Patients forget the simplest actions: how to use cutlery, walk, squat, write, grasp objects with their hands, go up and down stairs, etc.
Loss of emotional-figurative memory
Emotional-visual memory is responsible for the ability to record and store feelings and emotions that are associated with any object, person, event or phenomenon. If it is violated, the patient ceases to recognize the images and emotions that are associated with them. He does not remember the taste of dishes that he previously considered favorite, changes his musical tastes, and does not recognize the voices of loved ones and acquaintances.
Vascular dementia
The most complex type of brain disorder, which is difficult to recover, is vascular dementia. The adequacy of a person’s perception of what surrounds him disappears almost completely over time.
A person does not recognize objects that he used to constantly use, does not remember their names and purposes. When communicating with other people, the patient cannot remember their names and where he knows them from. This applies not only to distant acquaintances or strangers, but also to close relatives, friends and colleagues.
However, if you choose the right intensive rehabilitation measures and constantly monitor the patient’s condition, you can slow down the process of dementia and adapt the person to real life.
Causes of microstroke
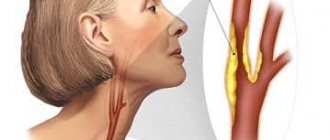
- Atherosclerosis (in this case, the cause of the disease is a plaque in the vessels, which either comes off or sticks to the wall of the vessel: both lead to obstruction of blood through the vessel);
- Thrombosis - separation of a blood clot, disruption of the nutrition of neurons in the lower extremities;
- Vascular spasm, as a result of which blood does not flow to the brain;
- Anemia - a drop in hemoglobin levels, a decrease in oxygen levels in the brain;
- Increased blood viscosity (usually due to chronic diseases, polycythemia, insufficient fluid intake);
- High blood pressure;
- Obesity (there is an increased load on the heart when the body has extra pounds);
- Hereditary brain pathologies;
- Heart attack and other heart diseases that weaken it;
- Previous heart surgery;
- Stress (provokes increased blood pressure);
- Age (despite the fact that this disease is getting younger, more often older people still suffer from it, since their blood vessels are worn out);
- Abrupt climate change (more than 10 degrees).
Medicines
The following groups of medications are used to treat pathology:
- Antihypertensive drugs. Arterial hypertension is the most important risk factor for TIA and stroke, so it is important to keep your blood pressure under control at all times. It should be less than 140/90 mmHg. Art., it is gradually brought to the figures of 130/80 mm Hg. Art. Drugs to lower blood pressure are prescribed the next day after the attack and are selected individually. If the blood pressure is persistently elevated, a combination of several agents is used. Reduce blood pressure below 120 mm Hg. Art. is not recommended, since in this case it is possible to deteriorate blood circulation in the brain and develop a repeated ischemic attack.
- Vascular agents and nootropics are used to restore cerebral circulation and brain functions. These include Cavinton, Cinnarizine, Piracetam. Medicines of animal origin are used - Actovegin, Cortexin. The listed remedies improve blood circulation and eliminate the consequences of a micro-stroke.
- Antiplatelet agents are medications that prevent blood cells from sticking together in the vascular bed. Used to prevent blood clots. Some patients who have suffered an ischemic attack are prescribed antithrombotic drugs for life. Most often, low doses of Aspirin are used to prevent thrombosis - from 50 to 150 mg/day. Aspirincardio and Cardiomagnyl are used. If the patient has problems with the digestive system, Aspirin is combined with antacids - magnesium hydroxide, calcium carbonate.
- Medicines to lower cholesterol. It is known that people with blood lipid disorders are at risk of getting a stroke more often than others. To normalize indicators, statins, fibrates, and cholesterol reabsorption blockers are used. Nicotinic acid acts in several directions: it not only reduces “bad” cholesterol, but also improves blood circulation, dilates blood vessels, relieves spasms and normalizes blood pressure. The goal of therapy is to achieve cholesterol levels <4.5 mmol/L.
Cardiomagnyl
Important! The doctor selects a set of medications. The characteristics of the patient, the presence of hypertension, atherosclerosis, obesity and other risk factors are taken into account.
The first signs of a microstroke
The very first sign of a microstroke is numbness of the extremities for a short time (many patients attribute it to “numbness” of the leg or arm). Also, the first, that is, appearing earlier than others, signs of a microstroke include:
- Short painless blindness in one eye (as if a shadow had crept into the field of vision for 20-30 seconds);
- Temporary and sudden numbness of the face (the person will not be able to smile);
- Loss of the ability to speak coherently (sounds and words are confused, sometimes it is impossible to utter a word at all);
- A sharp headache (like a flash) - does not go away even if you take any medications;
- Short-term disturbances in coordination of movements are possible (objects fall from hands, the patient simply cannot lift them for some time);
- The skin becomes pale;
- Weakness appears throughout the body (a person suddenly wants to sit down or lie down);
- Sweating increases sharply for no apparent reason.
Signs of memory impairment
A patient who has suffered a stroke usually faces difficulties in self-identification and other difficulties:
- Memories from childhood, adolescence or any other period of life disappear. He may not remember people he has ever encountered, certain significant situations and events.
- Loss of motor skills and loss of coordination. It’s as if the body is returning to childhood: it doesn’t remember how to eat, take care of itself in terms of hygiene, and learns everything all over again.
At the same time, there are situations when the victim remembers everything related to his profession down to the smallest detail. For example, he knows how to drive a car, knows musical notation, remembers how he wrote his dissertation, etc. - but does not have the skills of banal household self-service.
Sometimes amnesia is not immediately noticeable and appears much later in the process of secondary complications after a stroke.
When the disease occurs, the patient’s psyche also suffers: the person does not remember the people who communicate with him. Does not understand the purpose of certain items. Can’t remember professional skills – feels extremely uncomfortable. The victim may become depressed or be in a state of increased anxiety, which negatively affects the rehabilitation process and sometimes leads to psycho-emotional breakdowns.
The first symptoms of a microstroke
In terms of symptoms, a microstroke is not very different from a traditional one. The most important difference is the duration of symptoms (usually no more than a few hours) and its intensity (signs are not as noticeable as with a stroke). Symptoms manifest themselves differently, depending on the location of the outbreak (the place where blood circulation is impaired):
- Occipital lobe of the brain (responsible for the perception of visual information): there is visual impairment to complete blindness in one or both eyes;
- Parietal lobe (responsible for tactile sensations): loss of smell, sensation of movement under the skin.
- Temporal lobe (responsible for hearing and memory): short-term memory and hearing loss.
- Frontal lobe (responsible for intelligence and muscle tone): paralysis, mood swings.
The body usually overcomes this condition on its own, and the brain is not seriously damaged.
As already noted, a micro-stroke often hardly manifests itself: the symptoms are very mild, which is why they are so easy to overlook. But it’s still worth paying attention to these first signs of the disease:
- Numbness of the whole body (or one part of it, so it may be impossible to smile or raise both arms);
- Dizziness;
- Severe headache;
- Double vision;
- Unsteady movements, weakness, desire to sit down or lie down.
To diagnose a microstroke at home, you can use the FAST test. It was developed in America for emergency doctors so that they could easily diagnose cerebral hemorrhage. This test is also suitable for a micro-stroke, since the symptoms (facial distortion, weakened arms and incoherent speech) are also present in this case, although they pass much faster. FAST is an abbreviation, but the word itself is translated from English as “quickly” - one of the main rules when diagnosing a disease.
F (face - “face”) - you need to pay attention to the victim’s face: it can be unnaturally skewed.
A (arms - “hands”) - the patient’s hands do not obey: they are weakened, trembling and do not rise up.
S (speech - “speech”) - words are confused, it is impossible to pronounce even a simple sentence without errors.
T (time - “time”) - time: so precious in the case of this disease. It is better to start diagnostics as soon as the first signs appear, because as soon as they pass (with a microstroke this usually takes no more than an hour or two), the patient will feel great again. But for emergency doctors, diagnosing the symptoms will help a lot.
Who does the disease affect?
This disease is getting younger and, if previously it was believed that it only affected older people, now this is not the case. Much depends on the person’s health status, lifestyle and chronic diseases.
Still, patients with the following problems are at risk:
- Atherosclerosis (chronic artery disease);
- Hypertension (pressure surges can trigger a minor stroke);
- Vascular lesions;
- Diabetes mellitus (high sugar content affects the walls of blood vessels);
- Alcohol abuse (the functionality of brain vessels decreases, toxins destroy tissue);
- Congenital and acquired heart diseases.
Busy people suffer a micro-stroke on their feet, that is, they do not pay attention to its symptoms and first signs, trying to maintain their usual activity. This should not be done under any circumstances, since within 24-48 hours there is a high risk of a stroke; the consequences in this case can be disability and even death. Therefore, a minor stroke is an indication for emergency hospitalization of the patient.
Types of microstroke
There are three main types of microstroke:
- Hemorrhagic stroke is hemorrhage with the formation of hematomas. Recovery takes from two weeks to several months.
- Ischemic stroke leads to blockage of blood vessels by blood clots. It differs from hemorrhagic in its increasing effect. In most cases, patients are diagnosed with this type of microstroke.
- Lacunar strokes involve damage to small arteries in the brainstem or cortex.
It is important to correctly diagnose the type of microstroke in order to provide assistance to the patient. A minor stroke is dangerous because it can recur and, without proper treatment, lead to extensive hemorrhage in the brain.
Diagnosis of microstroke
Despite the fact that this disease, compared to traditional stroke, is relatively harmless, it still needs to be diagnosed and treated. Although a microstroke occurs and passes quickly, it still causes some harm to the body and in half of the cases ends in a stroke or heart attack. That's why diagnosing the disease is so important. To make a correct diagnosis, the patient is prescribed the following examinations:
- ECG and ultrasound of the heart;
- Vascular examination;
- An echocardiogram determines any abnormalities in the heart;
- Blood test for platelet count, clotting time, sugar, etc.
- CT can detect a blood clot and determine its nature.
- REG (rheographic method for studying the vascular system of the brain) and ultrasound examination (ultrasound examination) with functional tests (for example, with turns and tilts of the head) - these methods are necessary for examining the arteries of the spine.
- MRI will allow you to detect the location of the blood clot with high accuracy.
It may be necessary to involve other specialists. For example, an ophthalmologist determines the visual field and conducts an examination of the fundus.
How to treat a microstroke
To prevent the development of severe consequences, you need to know not only the signs of a microstroke, but also the rules for providing first aid to a person in a similar condition.
First aid for microstroke
At the onset of the disease, it is almost impossible to distinguish between the condition in question and a “classic” (extensive) stroke. First aid for microstroke:
- call an ambulance;
- put the patient on a hard surface, place the head on a slight elevation - this will prevent swelling of the brain tissue;
- if the patient starts vomiting, then his head should be turned to the side - this will prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract;
- It is necessary to provide access to fresh air - unbutton your shirt, belt, collar of outerwear.
If it is possible to measure the patient’s blood pressure, then this should be done, since this data will help doctors navigate the victim’s condition.
Even if a micro-stroke occurs, first aid (pre-medical) does not imply administering medications to the patient that reduce blood pressure. Such manipulations can only be done by a specialist, since the pressure must be reduced gradually and appropriate medications administered in doses.
Treatment of microstroke
In a medical institution, doctors provide full treatment for the condition in question. And first of all, medications are administered that can lower blood pressure. Treatment for a microstroke should not only be competent, but also strictly dosed, with constant monitoring of the patient’s blood pressure. Medication prescriptions may be as follows:
- dibazole and papaverine intramuscularly;
- magnesia with saline and furosemide intravenously.
To improve cardiac activity (this will prevent a micro-stroke of the heart), the patient is prescribed corglycone, digoxin or cordiamine. It will be necessary to improve cerebral circulation and help the body restore it - citicoline, nicotinic acid, cinarizine are precisely what contribute to this development of events.
In general, the treatment of a microstroke is characterized by a long course: doctors must relieve the sharp narrowing of the small vessels of the brain and completely restore normal blood circulation. If there is a sharp narrowing of the small vessels of the brain, then you should also take care of treatment after a mini-stroke - you will need to undergo a full course of therapy under the supervision of specialists. On our website Dobrobut. com you can get complete information on how to recognize the condition in question and how to treat a microstroke of the eye and restore cerebral circulation.
Treatment of microstroke
Treatment is aimed at normalizing blood supply and metabolism, preventing relapses and preventing stroke. In case of hemodynamically significant occlusion of large arteries, surgical treatment by angiosurgeons is possible. Patients with a ministroke are usually prescribed:
- Drugs aimed at restoring blood microcirculation in blood vessels;
- Drugs that dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow;
- Agents that prevent platelet accumulation;
- Drugs that improve brain activity;
- Vitamins.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient visits:
- Exercise therapy (to restore motor activity);
- Massage sessions (to stimulate motor activity in the limbs);
He also follows a diet (without fatty, spicy and salty foods) and does special breathing exercises (to ensure that sufficient volume enters the body).
But if the patient delays diagnosis and treatment, complications may arise. In this case, with a microstroke, the doctor prescribes the following groups of drugs responsible for restoring the body:
- improving blood microcirculation;
- improving metabolic processes in blood vessels;
- dilating vessels;
- preventing the formation of blood clots;
- stimulating brain activity;
- vitamins (to strengthen the immune system and improve brain activity).
The goal is to study the effect of the antihypoxant and antioxidant “Mexidol” on clinical, neurological, biochemical parameters and cerebral hemodynamics in patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke during the recovery period. Materials and methods. A comprehensive clinical and neurological examination of 20 elderly patients in the recovery period of ischemic stroke was carried out, before and after a course of taking Mexidol at a dose of 4 ml (200 mg) + 100 ml of saline intravenously 1 time per day (7 days), then 2 tablets 2 times a day for 15 days.
Results. After a course of treatment with Mexidol, the patients experienced a significant reduction in symptoms caused by circulatory failure in the vertebrobasilar system (unsteadiness when walking, dizziness), as well as headaches, which to a certain extent were caused by chronic hypoxia. Positive dynamics were also noted in the autonomic nervous system; patients became less dependent on meteorological changes and stress. After treatment, there was a decrease in irritability, sleep, memory, and mood improved. The level of depression in patients according to the Hamilton Gerontological Depression Scale decreased. An improvement in cerebral hemodynamics was also noted, which was expressed in a decrease in the thickness of the intima-media complex and an increase in the linear systolic velocity of blood flow in the vessels of the carotid and vertebrobasilar basins.
Conclusions. Taking Mexidol improves well-being (reduces headaches, dizziness, improves sleep), memory and mnestic functions (according to test results, memorizing 10 words), reduces the level of depression (according to the results of the Hamilton gerontological depression scale). In patients, the range of social and everyday activities expands, spasticity decreases, cerebral circulation improves, and the relationship between hemodynamics in the extra- and intracranial vessels of the carotid system is activated, which indicates the activation of metabolic processes in the brain.
Brain stroke is one of the main causes of morbidity and disability in the population. In Ukraine, the incidence of stroke is 2.5-3 cases per 1000 population per year, and post-stroke disability is 3.2 per 10,000 population. 20% of stroke survivors return to work. In this regard, the problem of neurorehabilitation is of great medical and social importance. In the rehabilitation therapy of stroke patients, drugs with vasoactive, nootropic and neurotrophic effects are used.
In patients with ischemic stroke (IS), a decrease in blood supply and brain metabolism is observed during the recovery period. This is due to changes in redox processes, inhibition of the antioxidant system, disturbances of phospholipid metabolism at the level of cell membranes and depression of individual neurotransmitter systems, in particular GABAergic [3, 8].
Recently, to correct these changes, the use of drugs with complex effects has become relevant. These drugs include Mexidol, an antioxidant with antihypoxic nootropic properties.
The pharmacological formula of Mexidol contains a metabolite of the tricarboxylic acid cycle - succinate. The drug has an antioxidant effect due to increased activity of antihypoxic enzymes [5], and due to the presence of succinic acid in its composition, it helps to improve energy metabolism in the cell. The power of the energy production system using succinic acid is hundreds of times greater than other energy production systems in the body [2, 9].
Mexidol has a neuroprotective effect in hypoxic-ischemic injury due to its effect on biological membranes. It improves the energy supply of the cell by optimizing the functioning of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, which helps to stabilize the cell membrane, reduce post-hypoxic metabolic acidosis, and activate macrophages by anaerobic products against the background of oxygen deficiency [4].
Antioxidant, membrane-stabilizing, antihypoxic mechanisms of action of Mexidol determine its neurotrophic effects. Due to the effect of the drug on the transport of amino acids and the modulation of receptor benzodiazepine, GABAergic, acetylcholine complexes, neurotransmitter activity increases, aimed at restoring integrative functions [1].
Mexidol also has a hypolipidemic effect, reduces the level of total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins [2].
Thus, the mechanism of action of Mexidol is determined by its antioxidant properties, the ability to stabilize cell biomembranes, activate the energy-synthesizing functions of mitochondria, modulate the functioning of neuroreceptors and the passage of ionic currents, improve synaptic transmission and interstructural connections of the brain [6].
In recent years, Mexidol has been used in the treatment of patients with various forms of vascular diseases of the brain, partial epilepsy, parkinsonism, hereditary forms of neuromuscular diseases, and traumatic brain injuries [5, 7, 9].
The purpose of the study was to study the effect of the antihypoxant and antioxidant “Mexidol” on clinical, neurological, biochemical parameters and cerebral hemodynamics in patients who had suffered ischemic stroke during the recovery period.
Materials and methods
We examined 20 patients aged from 59 to 75 years who had suffered atherothrombotic stroke in the carotid system (up to 1 year after the acute period) without significant cardiac pathology, who were in the rehabilitation department of patients who had suffered cerebrovascular accident, Institute of Gerontology of the Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine. According to the TOAST classification, the patients suffered an atherothrombotic pathogenetic variant of stroke. The course of taking Mexidol was carried out according to the following scheme: 4 ml (200 mg) + 100 ml of physiological solution intravenously once a day (7 days), then 2 tablets 2 times a day for 15 days.
All patients underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain (to verify and localize the size and nature of the lesion) using a 1.5 T Magnetom vision plus device (Siemens). MRI of the brain revealed encephalopathy of vascular origin with foci of ischemia in all patients.
The clinical examination included a neurological examination and analysis of complaints.
The volume of social and everyday activity was assessed using the Barthel scale. The Hamilton Depression Scale was used to assess the level of depression. Memory was assessed using a 10-word memory test.
Changes in cerebral hemodynamics were studied using duplex ultrasound scanning of the vessels of the head and neck on a Philips EnVisor ultrasound machine before and after a course of Mexidol.
Results and discussion
Before treatment, patients who underwent IS in the internal carotid artery complained of headaches, dizziness, and fatigue. During treatment with Mexidol, the intensity and number of complaints decreased significantly (table).
After a course of treatment with Mexidol, the patients experienced a significant reduction in symptoms caused by circulatory failure in the vertebral-basilar system (unsteadiness when walking, dizziness), as well as headaches, which to a certain extent were caused by chronic hypoxia. Positive dynamics were also noted in the autonomic nervous system; patients became less dependent on meteorological changes and stress. After treatment, a decrease in irritability, improvement in sleep, memory, and mood were observed. The level of depression in patients according to the Hamilton gerontological depression scale decreased (before treatment - 11.33 ± 0.03, after - 7.53 ± 0.02, p < 0.01). Under the influence of Mexidol, patients noted an activation of mnestic processes. Thus, an initial and moderate decline in cognitive functions was observed in 75% of patients before treatment, and in 61% after treatment. Data from quantitative determination of the degree of reduction (memorization test for 10 words) also indicated an improvement in memory (before treatment - 77.72 ± 0.1, after - 91.86 + 0.3, p < 0.01). When analyzing the dynamics of neurological symptoms during the period of treatment with Mexidol, a tendency towards a decrease in spasticity in paretic limbs, a decrease in the severity of pyramidal insufficiency, a slight increase in muscle strength and an expansion in the range of social and everyday activities was noted (Barthel index increased from 81.2 ± 3.51 to 93 .1 ± 3.01; p < 0.01).
Analysis of the state of cerebral hemodynamics in patients before treatment showed an increase in the thickness of the intima-media complex (IMC) in the common carotid artery (CCA), a decrease in linear systolic blood flow velocity (LSVV) and an increase in resistance and peripheral resistance indices (RI and PI) in individual vessels carotid and vertebrobasilar (VBB) basins. Under the influence of a course of Mexidol, patients who underwent IS experienced an improvement in cerebral hemodynamics, which was expressed in a decrease in the IMT thickness, as in the ipsilateral one (before treatment - 0.97 + 0.01, after - 0.89 ± 0.02) , and in heterolateral OSA (before treatment - 1.04 ± 0.01, after - 0.98 ± 0.02); an increase in LSCV in the vessels of the carotid system and VBB. Thus, LSCV increased in the ipsilateral CCA (73.89 ± 0.14 - before treatment, 77.91 ± 0.2 - after treatment; p < 0.05), in heterolateral VA (respectively 36.57 ± 0.17 and 40.24 ± 0.2; p < 0.05) and posterior cerebral artery (49.95 ± 0.21 and 58.90 ± 0.18; p < 0.05, respectively). The patients also showed a decrease in resistance and peripheral resistance indices in the ipsilateral CCA (RI before treatment - 0.76 + 0.01, after - 0.72 + 0.015; PI - 1.65 ± 0.14 and 1.51 ± 0, respectively ,15).
In 80% of patients before treatment, venous discirculation in the intracranial veins and dilatation of the jugular or vertebral venous plexuses were detected to varying degrees of severity. Mexidol reduced the linear velocity of blood flow through the veins of Galen (before treatment - 38.2 ± 2.64, after - 26.7 ± 3.15).
Analysis of indicators of lipid metabolism and the blood coagulation system in patients who underwent IS before and after taking Mexidol indicated only a statistically significant decrease in fibrinogen (before treatment - 3.31 ± 0.04, after - 3.07 + 0.07) and prothrombin index (before treatment - 83.03 + 0.21, after - 75.21 + 0.19). The content of total cholesterol and low- and very low-density lipoproteins had only a slight tendency to decrease.
Considering that the range of relationship between the level of hemodynamics in extracranial carotid vessels and hemodynamics in intracranial vessels to a certain extent characterizes the activity of metabolic processes in the central nervous system [10], to assess the effect of Mexidol on metabolic processes, an analysis of the structural relationship between hemodynamic parameters in the CCA and intracranial vessels of the carotid basin and VBB. An increase in LVSC was noted in the ipsilateral CCA, as well as in the heterolateral VA and posterior cerebral atreria. The figure shows the structure of correlations between hemodynamic parameters in extra- and intracranial vessels in patients who have undergone IS, before and after a course of taking Mexidol. The results obtained indicate that under the influence of Mexidol in patients, the number of correlations between hemodynamic parameters in the CCA and in the intracranial vessels of the carotid system significantly increases. Thus, before taking the drug, the background structure of correlations was characterized by the presence of only positive correlations between indicators of peripheral resistance (PI) in the hetero- and homolateral CCA and LSCC in both posterior cerebral arteries. After a course of treatment with Mexidol, the number of correlations more than doubled and the range of relationships between hemodynamics in the intracranial vessels (in the anterior and middle cerebral arteries) and hemodynamics in the CCA expanded. The type of increase in correlation relationships indicates that a course of Mexidol increases blood supply to the brain due to the carotid system.
conclusions
In patients with IS during the recovery period, Mexidol reduces the manifestations of diffuse and focal cerebrovascular insufficiency, which is characterized by a decrease in the intensity and frequency of headaches, dizziness, improved sleep, memory, increased emotional level and mnestic functions. Patients have an expanded range of social and everyday activities,
spasticity decreases, cerebral circulation improves and the relationships between hemodynamic parameters in the extra- and intracranial vessels of the carotid system are activated, which indicates the activation of metabolic processes in the brain. Considering the multicomponent regulatory effect of Mexidol on emotional and mnestic functions, the level of social and everyday activity, the use of this drug in the rehabilitation system for elderly patients who have suffered ischemic stroke is advisable.
CM. Kuznetsova, V.V. Kuznetsov, F.V. Yurchenko
Literature:
1. Astakhov S.V. Possibilities of antioxidant therapy in limiting secondary brain damage in neurocritical care patients. Bull. experiment, biol. and med. M.: Medicine, 2006. pp. 176-178.
2. Voronina T.A. Mexidol. Domestic drug of a new generation, main effects, mechanism of action, application. Journal Neurology and Psychiatry 2003; 5: 34-38.
3. Gusev E.I., Skvortsova V.I. Cerebral ischemia. M.: Medicine, 2001. 586 p.
4. Dyumayev K.M., Voronina T.A., Smirnov L.D. Antioxidants in the prevention and treatment of central nervous system pathologies. Institute of Biol. honey. Chemistry RAMS 1995; T. 4: 2: 73-85.
5. Zhulev N.M., Pustozerov V.G., Saykova L.A. The use of Mexidol in the treatment of patients with hereditary neuromuscular diseases. Bull. experiment. biol. and honey M.: Medicine, 2006. pp. 22-27.
6. Kravtsova E.Yu., Martynova G.A. Mexidol in the complex treatment of stroke in working-age streets. Mater, scientific-practical conf. in neurology. M., 2005. T. 1. P. 215-224.
7. Lyubashina O.V., Bobakho V.V. Antioxidant therapy of stroke in the prehospital and hospital stages. Mater, scientific-practitioner. conf. in neurology. M., 2000. T. 1. P. 148-154.
8. Skvortsova V.I., Stakhovskaya L.V. et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the effectiveness and safety of Mexidol in the complex treatment of ischemic stroke in the acute period. Journal Neurology and Psychiatry 2006; 18: 47-54.
9. Suslina Z.A., Smirnova I.I. and others. Treatment of nervous diseases 2002; T. 3: 3: 28-34.
10. Alexandrov AV Cerebrovascular ultrasound in stroke prevention and treatment. NY: Blackwell Publishing, 2003. 267 p.
Forecast of microstroke
If the disease was diagnosed on time, no serious consequences are observed in patients after a mini-stroke. In young patients, the rehabilitation period can take only a few days; in older patients it usually takes up to a month. If a person begins to pay due attention to his health and follow the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis is favorable, but if not, he should expect a recurrence of the attack, including an increased possibility of a stroke.
During the rehabilitation period, patients may experience the following disorders:
- Men at a young age experience memory loss, erectile dysfunction, frequent headaches, seizures, and mood swings.
- In women, the consequences usually affect the nervous system and are associated with frequent mood swings and even possible depression.
- In the elderly: difficulty in motor activity, decreased vision, epileptic attacks, decreased memory and mental activity, speech impairment, sclerosis.
If the patient does not receive timely treatment, the microstroke may return within two to three days, and 50% of patients subsequently develop an ischemic stroke. In this case, mortality increases from 10 to 40%.
Symptoms
Signs of a microstroke come in acute form and are felt immediately, in just two to three hours. What a person may feel during a microstroke:
- Acute weakness, fatigue, feeling very sleepy.
- Arms and legs go numb, simultaneously or alternately.
- The face becomes numb and the facial muscles are paralyzed.
- Paralyzes the right or left side of the body, limbs cannot be felt.
- A migraine attack begins.
- Memory lapses occur.
- Speech is unclear.
- Throws from hot to cold and back.
- Unable to tolerate loud sounds or bright lights.
A microstroke occurs against the background of stressful situations, attacks of hypertension, or hard work. At the first symptoms of a mini-stroke, you should immediately call an ambulance, since there may be repeated attacks, and the consequences may be severe, including partial paralysis. By the way, the first symptoms of a microstroke in women are often similar to the signs of premenstrual syndrome. Therefore, they need to be especially attentive to their health and not ignore warning signs.
How to recover after a mini-stroke?
The following principles that patients adhere to contribute to rehabilitation and speedy recovery:
- A doctor is a specialist. And you need to trust specialists. If the patient is incompetent in matters of treatment and rehabilitation, it is worth following the doctor’s recommendations and taking the medications he prescribed;
- Don’t put it off until tomorrow... If a patient needs to do exercise therapy every day, this means that classes cannot be missed, otherwise the desired effect will not be achieved;
- The importance of support. After a ministroke or, worse, a stroke, the support of loved ones is very important for the patient. Sometimes they simply give up, patients become depressed, and only family and friends are able to influence and help a person they know well. You can accompany the patient to a massage or exercise therapy, help him prepare food so that it fits the diet, and just talk. Feelings of loneliness should not be present in rehabilitation.
- Systematicity. This means that if a patient is prescribed exercise therapy, he should not miss a single day; if he has a diet, then he needs to strictly follow it. In terms of timing, rehabilitation after a mini-stroke is an individual process, since everything depends on the degree of impairment and the patient’s condition.
- Gradualism. This means that the body does not recover immediately, it needs time. This means that it is better to leave the usual active workouts for later, and immediately after a micro-stroke go for a massage or exercise therapy.
Also, recovery and rehabilitation after a mini-stroke imply the following actions:
- Drug treatment
- Restoration of motor functions
- Vision restoration
- Restoration of speech function
- Normalization of psychological state
A ministroke usually affects the lower and upper extremities, and motor function is impaired. The grasping reflex may disappear, weakness in the arms and legs may appear (symptoms may intensify and then it will be impossible to move at all).
The following methods are used to restore motor functions:
- Exercise therapy. Therapeutic exercise is designed to normalize muscle tone and restore strength to the muscles.
- Massage. This procedure relaxes, stimulates blood circulation and normalizes muscle tone. In this case, a massage session can be carried out both by a specialist and by the patient himself, if he is ready to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. You can also combine a procedure with a specialist and a home massage. This approach will speed up the recovery process.
- Physiotherapy. After a micro-stroke, the patient is usually prescribed warming, which allows the body to regain lost sensitivity.
Vision restoration
Frequent symptoms of a microstroke are double vision, darkening, spots, and even temporary blindness in one or two eyes at once. While the patient is undergoing treatment, the issue of vision restoration is dealt with by an ophthalmologist, and less often by a surgeon (if it is impossible to avoid surgical intervention).
During the rehabilitation period, the patient is usually prescribed pills that normalize vision function, and is also recommended to perform special exercises that stimulate the work of the oculomotor nerve. To record progress or regression, it is recommended to visit a doctor regularly.
Restoration of speech function
Confusion of speech is another symptom of a mini-stroke, which can be cured with proper treatment. But, if after treatment the speech function is not completely restored, special classes are conducted with the patient aimed at its restoration. They are usually carried out by a speech therapist or neuropsychologist. In case of complications and serious speech disorders, all basic speech skills are studied with the patient from scratch: listening (understanding what is heard), reading, writing, speaking.
The process of speech restoration will accelerate if the patient’s relatives continue to study with him at home. For the process to be effective, in addition to training with the victim, you just need to talk (ask him simple questions, patiently waiting for an answer; tell the news; share opinions, etc.), even if this seems useless at first glance. But we must remember that a person can only speak in a linguistic environment (that is, he must constantly hear speech in order to begin to produce it), which is the task of family and friends to create during the rehabilitation period.
Normalization of psychological state
Patients who have suffered a mini-stroke often experience depression (people with a fine mental organization and women are especially prone to it due to their physiology and psyche). Relatives need to try to understand this condition: the patient suddenly lost some abilities, is forced to take pills and regularly visit the doctor. His life has completely changed. To help him overcome this condition it is necessary:
- Interact and communicate with him more often;
- Go for walks, which will provide him with physical activity;
- Help you find a new hobby or return to an old one, if possible.
As soon as rehabilitation is over, it is better for a person to return to work: to the old one or, if this is not possible, to find a new one as soon as possible.
Any activity requires a certain amount of effort and time, therefore, by getting busy, the patient will think less about problems and, accordingly, will quickly overcome a depressive state.
Where and how to undergo rehabilitation and how long will it take to recover after a mini-stroke? These are the most frequently asked questions by patients. Of course, everyone wants to return to normal life as soon as possible, go to work or go on a trip.
Rehabilitation is possible both at home and in a hospital setting. In the first case, success will depend on those who surround the patient: on their willingness to communicate, care and support. Secondly, it depends on the literacy of specialists and the development of the rehabilitation program.
Expert opinion
Author: Tatyana Aleksandrovna Kosova
Head of the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, neurologist, reflexologist
According to statistics, the number of cases of first-time transient cerebrovascular accident is increasing every year. A microstroke is provoked by various factors. It has been noted that the disease is most common among men of working age. According to clinical studies, in 10-15% of cases, myocardial infarction develops after a transient cerebrovascular accident. 30-40% of patients experience a major stroke over the next 5 years. Therefore, it is important to seek medical help on time and undergo preventive examinations.
Diagnosis of microstroke at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using modern medical equipment. European CT and MRI installations make it possible to accurately determine the location of the lesion and its extent. An individual treatment and rehabilitation program is developed for each patient. The recovery period takes place under the supervision of experienced neurologists, massage therapists, exercise therapy instructors and physiotherapists. A personal approach can reduce the time of hospital stay and reduce the risk of recurrent microstroke.
Nutrition for microstroke of the brain
After an acute cerebrovascular accident, patients need a nutritious diet that ensures the body receives a balanced amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. A necessary component of a healthy diet is a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals in the food consumed. After a mini-stroke, it is important to maintain a water regime.
When selecting products from which to prepare dishes, nutritionists recommend giving preference to whole grains or products made from them. After a micro-stroke, you should eat orange and dark green foods, peas and beans. The menu should include a sufficient amount of fresh, frozen or dried fruits and berries every day.
Diet after a stroke is aimed at reducing the risk of another attack. When selecting food products, you should pay attention to the following criteria:
- nutritional value (calorie content);
- presence of fat;
- the presence of saturated and trans fats;
- do you have cholesterol?
- content of table salt and fiber.
Limiting your intake of trans fats will reduce blood cholesterol, which is of great importance in cases of brain damage.
The diet after a microstroke should contain vitamins and minerals. Vitamin B6 is present in the following foods:
- carrot;
- sunflower seeds;
- walnuts;
- spinach;
- peas;
- herring;
- salmon.
Legumes and whole grains are rich in potassium, and α-pinoleic acid is found in sea fish. An important component of the menu after a microstroke are fruits and vegetables, seeds and nuts. The energy value of foods consumed per day should not exceed 2.5 thousand kilocalories.
Why is memory impaired after a stroke?
The moment when a vessel in the brain becomes clogged or ruptures, a person may not notice, because... there may be no consequences of circulatory disorders. However, in situations where the circulatory system is significantly damaged and the blood does not deliver oxygen to one or another part of the brain, its cells stop functioning with proper efficiency and gradually die.
Cell necrosis is the main reason why various complications occur after a stroke: paralysis, speech dysfunction, memory loss.
Timely medical care and intensive rehabilitation sessions provide a chance to eliminate the negative consequences. Cells in a healthy area can take over the functions of those affected.
Scientists, based on cutting-edge brain research, view human memory in the light of three integral components that are involved in its formation and functioning:
- Short-term. The ability to store material in a short time period and small volume - about 20 seconds and several elements.
- Long-term. Unlimited in time and volume. Provides long-term storage of information.
- Operational. The ability to hold any amount of information and perform various operations with it in a short period of time.
Recording, storing and reproducing information is one of the main functions that makes a person capable and ensures his normal functioning. Each new source contributes to the formation of new neural connections. In a situation where a person needs to use the knowledge he has ever acquired, the neural connection is activated.
However, after a cerebrovascular accident, countless neurons die, and the connections that were formed between them are destroyed. This is how the process of memory loss occurs. Together with the killed neurons, a lot of material that a person has managed to accumulate during his life goes away.
The nature of the disorders depends on which area was destroyed and in which hemisphere of the brain critical changes occurred. The hemispheres work together, exchanging millions of impulses with each other every second. Their normal operation is impossible without the use of memory mechanisms. Therefore, it is very difficult to specify and accurately state what changes will be entailed by the death of one or another part of memory, and how this will affect a person.
In any situation, a patient with a stroke requires immediate medical attention and a long recovery process.
Prevention of micro-stroke
Prevention is always simpler and more effective than treatment, and preventive measures are usually the same, so by following simple rules, you can eliminate many diseases from your life. What should be done?
- Maintain normal blood pressure. Any stroke is a surge in pressure, so just measure your blood pressure at least once a day using a home blood pressure monitor;
- Give up bad habits: for example, coffee and alcohol increase blood pressure, smoking thins the walls of blood vessels. All this provokes strokes of varying severity;
- Follow the diet recommended by your doctor: it is aimed at reducing cholesterol levels and, accordingly, preventing the appearance of plaques;
- Exercise regularly: physical activity keeps all body systems in good shape;
- Monitor your sleep status, sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- Monitor hormonal levels;
- Seek help for head injuries;
- Visit doctors periodically and promptly treat vascular diseases.
Prevention
To avoid a second attack, you need to completely change your habits and lifestyle. In this case, you will be able to maintain your health for many years and avoid unpleasant consequences. Preventive measures:
- Complete exclusion of alcohol and tobacco
- Daily physical activity (gymnastics, Nordic walking, swimming)
- Get up and go to bed at the same time, sleep at least 8 hours
- Follow a diet, drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day.
- Constantly monitor your blood pressure levels
- Get a medical examination 2 times a year
- Avoid stress
If a micro-stroke did not leave significant consequences for your health, this does not mean that it passed without a trace. If you do not follow the doctor's instructions, the probability of relapse is up to 80%. Repeated rehabilitation is more complex and time-consuming, and in some cases it is impossible.
Main conclusions
A minor stroke is small because it is often followed by a large one and this can only be avoided if the disease is diagnosed in time. The fact that the symptoms were there but went away is not a reason to put off going to the doctor, not even a trip, but a trip by ambulance, because if a micro-stroke is diagnosed, doctors have only three hours to start treatment and reduce all risks to a minimum. The longer the disease goes undiagnosed, the greater the likelihood of complications.
It is also important to understand that if a person, for example, has incoherent speech, this does not mean that he has a minor stroke: at least 4-5 of the symptoms described above must be observed. Do not forget about the most effective diagnostic methods: what could be simpler than smiling or raising your hands up - but not for a victim of a mini-stroke. The results of these two exercises will be enough to call an ambulance and speed up competent treatment.
Treatment of heart diseases of any complexity is carried out at the Yusupov Hospital: top-class specialists work here, only modern methods of examining and restoring patients after illnesses are used.
Other treatments
Many people with vascular pathology lead a sedentary lifestyle, but it is the lack of activity that affects the condition of the blood vessels. The patient, immediately after a mini-stroke, is recommended to exercise daily for 5 to 10 minutes. They start with simple exercises - raising arms and legs, rotating the body, bending to the sides. In the future, the complex becomes more complicated, and the duration of classes increases.
If you feel better, walking is recommended - 30 minutes daily or 3-5 hours a week. Easy running and swimming are shown.
The rehabilitation program includes physiotherapeutic treatment:
- electrophoresis,
- darsonval,
- electrosleep,
- manitotherapy.
Aeroionization of the facial and collar zones has a good effect. To raise muscle tone, thermal procedures are used - paraffin wraps, therapeutic mud, ozokerite applications. A combination of thermal effects and electrical procedures (galvanization, ultrasound) is effective.
Restoring emotional health is an important part of rehabilitation efforts. If a person has a speech disorder, sessions with a speech therapist will help. The psychotherapist will identify hidden problems and set you up for successful treatment.
A person who regularly faces stressful situations should learn relaxation techniques - breathing exercises, auto-training. It is important to get a good night's sleep - at least 7-8 hours. Annual vacation and weekends are best used for active recreation.