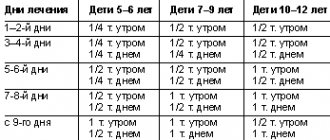
Astheno-neurotic syndrome is a complex disorder of higher nervous activity and cannot be ignored. Treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome with sleep disturbance and a feeling of weakness and constant fatigue has its own characteristics. For this purpose, the Transfiguration Clinic uses modernized neurometabolic rehabilitation programs. Therapy is selected and carried out individually, depending on the specifics of the formation and functioning of the body.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome has a cumulative property and occurs as a result of serious psychological and physical stress. The clinic’s specialists effectively combat problems by conducting individual rehabilitation therapy based on identified cause-and-effect relationships.
We select methods for treating astheno-neurotic syndrome strictly individually, so the effectiveness reaches 100%, and the duration of therapy is reduced several times, unlike other methods.
Signs and symptoms of astheno-neurotic syndrome
The syndrome is manifested by physical fatigue, weakness, inability to engage in long-term physical and mental exercise, and increased irritability. A diagnosis can be suspected if the following clinical picture is observed: pronounced disorders of the autonomic nervous system; nonspecific subjective complaints about disturbances in the functioning of various organs; in some cases, in reality, there may be minor changes in their functions (for example, flatulence, hiccups). However, in general, the functioning of organs and systems is preserved. People of a hysterical disposition are especially susceptible to the manifestation of the syndrome.
In general, the symptoms of astheno-neurotic syndrome can be divided into:
- Somatovegetative disorders: dizziness, rapid heartbeat, chest pain, shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air or a lump in the throat, hand tremors, muscle spasms, sweating, nausea, stomach discomfort, frequent urge to urinate. These manifestations are often combined with phobias and anxiety.
- Somatoform disorders: complaints of various symptoms of diseases (short-term pain, burning, etc.), craving for new medical examinations in the absence of real pathologies.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies are used as an auxiliary method of treating neurasthenia. Herbal sedatives can be used to help reduce irritability and other symptoms. However, it is important to remember that any folk remedies may have certain contraindications. Therefore, it is better to consult your doctor first.
- Herbal teas . They can be prepared from chamomile, peppermint, and lemon balm. You can drink them separately or prepare a collection. To prepare tea, take 1 tbsp. l. mixture in 250 ml of boiling water, leave for 10 minutes. You need to drink this tea 2-3 times a day, 150 ml. You can also add rose hips and oregano to this tea. It is recommended to drink herbal tea with honey.
- Motherwort . Helps reduce the severity of symptoms of neurasthenia. To prepare the product you need 2 tsp. pour 200 ml of boiling water over the raw material and leave for 8 hours. Strain and drink throughout the day. Similarly, you can prepare an infusion of St. John's wort.
- Hawthorn . 3 tbsp. l of hawthorn fruit, pour 250 g of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Drink 150 ml half an hour before meals three times a day.
- Celery greens. It is recommended to add it to salads and soups. You can also prepare an infusion, pour 3 tbsp. l. celery 250 g boiling water. Fresh dill is similarly useful for neurasthenia.
- Beetroot juice . Fresh beet juice is mixed with natural honey in a 1:1 ratio. You need to drink 100 g 3 times a day for a month.
- Valerian root . 1 tbsp. l of the product, pour 250 ml of boiling water into a thermos and leave overnight. Drink 70 g three times a day for 1-2 months.
Forms, stages and types of astheno-neurotic syndrome
The disease develops in acute or chronic form. The first is of a functional nature; it appears after severe stress, an infectious or other severe somatic disease. The second (usually organic in nature) has a long course. This form also includes chronic fatigue syndrome.
The disease has several stages, depending on the strength, duration and nature of mental trauma:
- The hypersthenic stage is characterized by hyperexcitability, irritability, fatigue, and excessive reaction to minor stimuli. Over time, symptoms become more frequent and persist for a long time.
- The hyposthenic stage is characterized by physical and nervous exhaustion, depression, drowsiness, passivity, and decreased performance. Possible tachycardia, cardialgia, dizziness, intestinal dysfunction, disorders of the genitourinary system, loss of appetite.
From the point of view of etiology, a distinction is made between reactive neurasthenia, which occurs against the background of stress, excessive emotions, and secondary (somatogenic, organic).
The syndrome can manifest itself with a predominance of symptoms of mental fatigue - inability to concentrate, lack of concentration, absent-mindedness, weakening of memory, or physical ill health - general weakness, muscle pain, inability to relax. However, both forms are characterized by the following common symptoms: dizziness, headache, irritability, anxiety, sleep disturbance.
Types according to ICD10
The international classification defines two main options for the development of pathology:
- Hyperdynamic. With this nature of the disease, increased excitability, absent-mindedness, disinhibition, and loss of attention are manifested. Also obvious signs are emotional instability and insomnia.
- Hypodynamic. Provokes reduced activity, bad mood, excessive calmness. The child exists inside his own world; he reacts weakly to the changing reality. There may be problems with speech development, inadequate perception of smells and extraneous sounds.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome in children
Children are characterized by lability of neuropsychic processes and rapid fatigue, so any somatic or infectious diseases can be accompanied by symptoms of asthenia. The longer the disease lasts, the higher the likelihood of developing a neurotic syndrome.
Prerequisites for asthenia include increased stress at school and in extracurricular activities (clubs, sections). The risk of developing neurotic syndrome is increased in those who have an unhealthy microclimate in the family, school, and problems in relationships with peers.
A special category consists of children who had lesions of the central nervous system during fetal development, during childbirth or in the early neonatal period. This may become an additional risk factor for the development of astheno-neurotic syndrome.
Pathogenesis
The basis of neurasthenia is a psychological conflict, the essence of which is the contradiction between desires and capabilities.
In the pathogenesis of neurasthenia, both somatic and mental factors are important. The main role is played by the individual’s reaction to psychotrauma. In this case, not only objective life circumstances are important, but also how the patient relates to them. With neurasthenia, there is a contradiction between the individual’s capabilities and his demands on himself. This discrepancy is covered by internal resources and mobilization of efforts, which ultimately leads to disorganization of the body.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of astheno-neurotic syndrome is established by a qualified specialist - a neurologist or psychotherapist after a clinical and anamnestic examination. Pathopsychological research is carried out by a medical psychologist, recording deviations from the norm by conducting special tests on the way of thinking, memory, and concentration.
To identify the causes of this condition and exclude organic lesions of the central nervous system, echoencephalography, electroencephalography, computer and magnetic resonance therapy are performed. If necessary, a consultation with specialists is prescribed - a neurologist, sexologist, psychiatrist.
Forecast
Asthenoneurosis is not a serious disease if treated promptly. People with asthenia need to be registered with a neurologist, follow all his recommendations and take the necessary medications. A healthy active lifestyle, good mood and a positive outlook on the world also play a decisive role in the treatment of the syndrome. The main thing is not to start the course of the disease, which can lead to memory deterioration, decreased concentration and the development of depression or neurasthenia.
How to treat astheno-neurotic syndrome?
The goal of treatment is to achieve stable remission. It is carried out in three main areas:
- etiopathological treatment;
- nonspecific, restorative and immunocorrective therapy;
- symptomatic therapy.
Drug therapy supplemented with psychotherapeutic methods has a positive effect. A psychotherapist helps to find out and understand the causes of the disease, to form the right attitude towards it through individual and group classes, trainings, art therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, etc.
The basis for the treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome in children is non-drug methods aimed at normalizing the child’s lifestyle. Parents must monitor not only the child’s compliance with the daily routine, diet, and avoid overload, but also the preservation of psychological comfort in the family and educational institution (sometimes it may be necessary to change schools). The diet should consist of foods rich in B vitamins (offal, whole grain bread, eggs), tryptophan (lean meat, cheeses). It is recommended to exclude carbonated drinks, chips, and crackers. Additional conversations should be held with teenagers about the harm of alcoholic drinks and energy drinks, which give a feeling of cheerfulness for a short time, but generally worsen the patient’s condition. To resolve internal conflicts, eliminate traumatic situations or change attitudes towards them, long-term work with psychologists is indicated.
MY RECOMMENDATIONS
Children facing neurotic disorders need sessions with a psychologist. The duration of the course is 3–6 months. This is necessary to develop adequate self-esteem in children and prevent relapse of the disease.
Children with asthenia need to be taught the rules of interpersonal interaction and group work. Therefore, during psychological rehabilitation, both individual classes and group trainings are conducted.
Art therapy classes help children find hobbies. Having gained the opportunity for self-realization, children find something to do - creativity has a healing effect on them.
You can strengthen family relationships and normalize the psychological climate at home through joint leisure time between children and parents, visiting the theater and cinema. However, when organizing meaningful leisure time, you should remember that an excess of vivid impressions is also a load on the nervous system, which may be too much for an exhausted body.
Cure for astheno-neurotic syndrome
The treatment strategy can be divided into three basic areas:
- etiopathogenetic treatment of the underlying disease;
- nonspecific, restorative and immunocorrective therapy;
- symptomatic therapy.
For psychopharmacological therapy, drugs of different groups are used: vitamin-mineral complexes, antidepressants, nootropics, tranquilizers and antipsychotics.
During the treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome, vitamins, macro- and microelements are recommended. In particular, the patient’s body needs a greater supply of vitamin C, which is typical for the recovery period after serious illnesses or prolonged stay in stressful situations. A lack of B vitamins is recorded in the case of somatogenic asthenia. And vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) is generally called an anti-stress vitamin. Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) is involved in energy metabolism, which is also important for increasing the patient’s tone. Iron, phosphorus, manganese are indispensable for the normal functioning of enzymes involved in energy processes. Potassium and magnesium also play a significant role in the treatment of manifestations of astheno-neurotic syndrome.
Basic therapy for astheno-neurotic syndrome is tranquilizers and antidepressants. If the syndrome is combined with expressive hysterical, hypochondriacal manifestations, or phobias, low doses of antipsychotics are added to the basic therapy. The choice of drug, dose and course of treatment is determined by the doctor.
Among over-the-counter drugs, homeopathic remedies (Hepel) and sedative herbal medicines (valerian extract, Persen, Novo-Passit) have proven themselves well.
Non-drug methods of treating the disease (as well as its prevention) include: a healthy lifestyle, moderate physical activity, adequate sleep, and giving up bad habits.
Causes
Neurasthenia develops in people against the background of mental and physical overload, which, in turn, provokes overwork of the body. The reason for the development of this condition can be internal conflicts, a weak psyche, long-term adherence to a very strict diet, etc.
The occurrence of neurasthenia is influenced by predisposing and provoking factors. Predisposing ones include:
- increased anxiety;
- tendency towards perfectionism;
- period of recovery after somatic illnesses.
Provoking include :
- severe stress;
- conflict situations in the family and at work;
- lack of normal rest for a long time;
- previous traumas, including birth injuries;
- previous surgical interventions;
- infectious diseases;
- poor nutrition and, as a result, deficiency of vitamins and other important substances;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- lack of physical activity;
- lack of sleep;
- intoxication;
- endocrinological disorders;
- unfavorable psychosocial conditions;
- severe weather conditions, etc.
List of used literature
- Grishchenko E.V. Methods for correcting asthenic syndrome in outpatient practice // “medical council”, 2012 - p. 36-37
- Kolyutskaya E. V. Modern approaches to psychopharmacotherapy of anxiety disorders // Pharmaceutical Bulletin: information and analytical newspaper. 2005. - p. 112-116
- Vein L. M., Voznesenskaya T. G., Vorobyova O. V. et al. Autonomic disorders: clinical picture, treatment, diagnosis / ed. A. M. Veina. M.: medical information agency. - 1998. - 752 p.
Popular questions about astheno-neurotic syndrome
How dangerous is astheno-neurotic syndrome?
If not treated in time, it can cause hormonal disorders, disorders in the digestive tract (stomach ulcer), cardiovascular system (up to the development of heart attacks and strokes), the development of depressive states, and the appearance of suicidal thoughts.
How long to treat astheno-neurotic syndrome?
The drug and course of treatment are determined by the patient’s condition and concomitant pathologies, and therefore are prescribed by the doctor individually.
Which doctor treats astheno-neurotic syndrome?
Neurologist, psychotherapist.
Diet
Diet for the nervous system
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 2 months
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of food: 1700-1800 rubles per week
A very important point is proper nutrition for neurasthenia. The diet should be enriched with vitamins and minerals, as well as all nutrients important for the body. It is recommended to include the following foods and dishes in your diet:
- whole grain cereals;
- honey, dried fruits;
- fresh vegetables and fruits - bananas, greens, cabbage, asparagus, citrus fruits, sea buckthorn, currants;
- liver;
- Brewer's yeast;
- Fish and seafood;
- cheese, dairy products.
The following should be completely removed from the menu:
- fat meat;
- sugar and confectionery;
- spicy dishes;
- nuts, seeds;
- sauerkraut;
- alcohol.