According to Rosstat, in 2010 the mortality rate in Russia from diseases of the cardiovascular system was 805.9 cases per 100 thousand people. This is 2-3 times more compared to road traffic accidents and infectious diseases.
Heart and vascular diseases are the first and main cause of mortality in the Russian population - 56.8% of all deaths. The main reason is insufficient knowledge about the dangers of this group of diseases.
September 29 is World Heart Day, which is supported by the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNESCO. Its goal is to inform society about the danger caused by the epidemic of cardiovascular diseases in the world and encourage the entire population to take preventive measures. On World Heart Day, it is customary to also talk about the culture of health: about regular medical monitoring for early detection of diseases, risk factors, developing skills to deal with stress, and how to maintain health in poor environmental conditions.
We are talking about cardiovascular diseases and how to prevent them with Bespalko Inna Arkadyevna, Doctor of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category, chief cardiologist of the multidisciplinary clinic CELT.
Our heart is constantly working - it pumps about 10,000 liters of blood per day in an adult. It is constantly under pressure: work overload, family problems, stress, bad habits. The main organ of the complex vascular web - the cardiovascular system - must serve as long as it needs. But in practice, it turns out that the heart lasts as long as you take care of it.
About risk factors and epidemics of cardiovascular diseases
Diseases of the cardiovascular system kill such a colossal number of people every year that for several decades they have been the leader in the competition for the title of “the most mass killer of the 21st century.” The World Health Organization (WHO) projects that by 2030, approximately 23.6 million people will die from cardiovascular diseases, mainly from stroke and ischemia.
The tragedy of the situation is that diseases of this group are asymptomatic: sometimes a heart attack or stroke becomes the first sign that attention needs to be paid to the condition of the heart and blood vessels. The obvious solution to the problem - early diagnosis, regular monitoring of blood pressure and heart rhythms - faces an inexorable human factor: patients, convinced that instead of a heart they have a fiery engine, brush aside medical recommendations, not wanting to waste time on prevention.
The most important risk factors for cardiovascular mortality, which had already become known by the end of the 50s, were age and family history. This is something that cannot be influenced. But there are others: smoking, arterial hypertension, cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity. You can influence them. By the forties of the twentieth century, it became clear that people began to most often die not from infections, as was the case before, but from cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, the American Heart Institute was organized, and since 1948 in Framingham, a small town near Boston, all residents of the city were included in the study, which continues today. They measure blood pressure, sugar, fibrinogen and other indicators. These data were later confirmed in large randomized controlled trials: special tables were created that allow one to estimate the risk of death within 10 years depending on factors. By the way, controlling risk factors lengthens life and improves its quality.
The problem of the century is atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is deposits of cholesterol in the wall of a vessel in the form of plaques, which can partially or completely close the lumen of the vessel. This process happens with age for everyone, but in different ways. Its development is influenced by heredity (heart attacks or strokes in close relatives at an early age), the level of cholesterol and its fractions in the blood, lifestyle (smoking, lack of physical activity, poor nutrition) and the presence of concomitant diseases (arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, kidney disease ). All these diseases and conditions contribute to faster and more intense growth of atherosclerotic plaques.
The most “popular” atherosclerosis is obliterating - when atherosclerotic plaques are deposited on the walls of blood vessels and therefore block them. It usually affects large arteries of the elastic and muscular-elastic type - for example, the terminal aorta, iliac or femoral arteries. Often these are the lower extremities. People die from this type of atherosclerosis all over the world because it ends in a stroke or heart attack. Less is known about vasodilatory atherosclerosis - when the nutrition of the vascular wall is disrupted, causing it to expand, forming a pouch. At the final stage of type 2 atherosclerosis, it is called an aortic aneurysm. An aneurysm occurs in the thoracic or abdominal aorta. Statistics show that abdominal aneurysm occurs more often. But all aneurysms are equally dangerous. At one unexpected moment, the bag bursts and the person dies. Vasodilating atherosclerosis is talked about less, but people die from it just as often as from obliterating atherosclerosis. The percentage of people dying from vasodilating atherosclerosis is quite high - up to 75%.
The aorta delivers blood from the heart to all organs and tissues, passing through the chest and abdominal cavity. The normal diameter of the abdominal aorta is about 2 cm. When the diameter increases by 1.5-2 times, an aneurysm is formed. To prevent aneurysm rupture, endoprosthetics is performed. Aortic aneurysm is one of the most unpredictable diseases. Very often it appears and gradually increases in size unnoticed by the patient - therefore, sometimes the first clinical symptom of an aneurysm is its rupture. The incidence of aneurysms increases with age.
A ruptured aneurysm is usually fatal, regardless of treatment. The survival rate of patients after a standard aortic replacement procedure, even in a planned manner, is low; every fifth patient dies.
Prevention of hypertension
To prevent hypertension and possible complications of this disease, the cardiologist at the A-Media clinic recommends taking the following measures:
- quit smoking
- minimize alcohol consumption
- control body weight
- be sure to get eight hours of sleep
- establish proper nutrition
- engage in physical activity daily.
Contact the A-Media clinic for the treatment of hypertension, and our experienced cardiologist will help you avoid severe complications of this disease and significantly improve your quality of life.
About “good” and “bad” cholesterol
We get only a third of the necessary cholesterol from the outside, and synthesize two thirds ourselves. From cholesterol, the body produces bile salts (without them it is impossible to digest fats), steroid hormones (responsible for reproductive function), and cortisol (regulates carbohydrate metabolism). Cholesterol is necessary for kidney cells, spleen and bone marrow functions; it is responsible for the strength of cell membranes. In the skin, vitamin D is formed from cholesterol under the influence of light. In general, we need cholesterol in much the same way as fats, proteins, carbohydrates and water.
Not so long ago, a cholesterol level of 6.5 mmol/liter was considered the norm in Russia, and 3.5 mmol/liter in Japan. Now in Europe, the USA and Russia, the normal level of total cholesterol is considered to be below 5.2 mmol/l. But the main indicator is low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, popularly called “bad” cholesterol. In people with a low risk of developing coronary heart disease, it should be less than 3.0 mmol/l, in patients with a high risk - less than 2.6 mmol/l, and in those who have atherosclerosis and its complications - coronary heart disease, brain disease and other vascular zones, its target level is less than 1.8.
Causes
The main reason for the development of stage 3 disease is improper treatment of stage 2 hypertension. Congenital pathologies in the patient’s body and concomitant diseases can affect the deterioration of well-being.
If a patient is constantly exposed to stress, heavy workload, abuses alcohol and eats poorly, not a single medication will help him. His health will constantly deteriorate, and the disease will progress.
A patient diagnosed with hypertension must completely change his life in order to regain good health.
If necessary, the heart can instantly change its operating mode
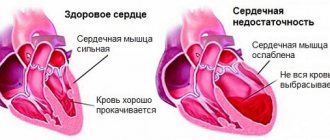
Normally, the heart is a strong muscular pump capable of pumping blood throughout the body to provide oxygen and nutrients to all organs and tissues of the body, and remove waste products. But in order to move blood through spasmodic vessels, the heart requires more effort than normal. This leads to its size becoming larger, especially the left ventricle. Because of this, weakness of the heart muscle develops. When the heart stops adequately supplying tissues and organs with oxygen and nutrients, doctors diagnose heart failure. It can be caused by irregular heartbeats (cardiac arrhythmias). It is dangerous and can lead to heart failure when the heart beats more than 140 beats per minute, since the processes of filling and ejecting blood by the heart are disrupted.
You can live with heart failure for many years without a diagnosis. This is not an independent disease, but the outcome of various heart diseases. It signals itself in the form of increased fatigue, swelling of the legs, shortness of breath, asthma attacks, and causeless weight loss. These symptoms, if noticed individually, appear in a wide variety of diseases. Therefore, the correct diagnosis is rarely made and usually in later stages. Significant weight loss, which is typical of severe heart failure, is often mistaken for a sign of cancer. And harmless swelling of the legs caused by stagnation of lymph is diagnosed as “heart failure.” With some primary symptoms (for example, pulmonary edema), there is an immediate risk of death. Within 3-5 years, 50% of patients die from heart failure, and after 9 years, only 2 people out of 1000 patients remain alive - of course, provided that appropriate treatment is not carried out. There is a radical way to help - a new heart transplant. But restrictions - an age limit, an expensive operation, few donor hearts - make it unrealistic for most.
In recent years, medical science, pharmacology and medical experience have helped to achieve amazing success in treating even severe forms of heart failure. Patients can not only save their lives, but also restore their quality. Moreover, treatment can take place on an outpatient basis, without a hospital stay.
Treatment of people with cardiovascular diseases requires effort, time and great pedantry. The speed and accuracy of diagnosis of the underlying disease that caused heart failure plays a huge role. In 50% of cases, this is coronary heart disease, which can be identified and treated with coronary angiography and angioplasty. The earliest, they are called preclinical (that is, before the onset of complaints), forms of heart failure can be treated only by using instrumental research methods: echocardiography, Holter monitoring, stress tests.
CHF: symptoms
The clinical picture of CHF is quite diverse and depends on the severity and duration of its course. The disease develops slowly over several years. Lack of treatment threatens serious deterioration of the patient's condition.
Most often, chronic heart failure is manifested by the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath during physical exertion, when the patient moves to a supine position, and later at rest;
- dizziness, fatigue and weakness;
- nausea and lack of appetite;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- development of ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity);
- weight gain due to swelling;
- fast or irregular heartbeat;
- dry cough with pinkish sputum;
- decreased intelligence and attention.
The science of the marathon runner or how running affects the cardiovascular system
While running, your heart rate increases and your blood pressure rises. The heart works under increased load. Therefore, with moderate intensity loads, a positive training effect on the cardiovascular system is noted. But with too intense and frequent exercise, there is a negative effect on the cardiovascular system. And if there are pronounced atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels, then such loads can lead to insufficient vasodilation and ischemia (reduced blood supply) in organs and tissues, or even to rupture of plaques with subsequent thrombus formation.
Therefore, before running intensively, especially after 40 years, if you smoke or have smoked before (even 15 years ago), if you have high blood pressure or blood glucose, you must first be examined by a cardiologist who will conduct stress tests.
It is a myth that you either need to run regularly or it is better not to engage in physical activity at all, because sudden exercise is harmful to the heart. It is always better to practice some physical activity than not to do any physical activity at all. For example, the clinical guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology for the prevention of coronary heart disease (September 2021) recommend aerobic (dynamic) exercise of 150 minutes per week (30 minutes per day, 5 days a week). Best: Walking until mildly tired, or 75 minutes per week of vigorous aerobic activity (15 minutes 5 times a week - such as jogging or a combination of these activities) and oxygenating aerobic activity (this could be cycling, swimming or tennis). At any age, walking 2 times a week for 1.5-2 hours (8-10 km) is useful, but not in strong winds and cold. There is no need to suddenly start exercising very intensively; the load is usually increased gradually.
Getting a disability
Due to the fact that stage 3 hypertension is associated with severe dysfunction of vital organs and entails a limitation in the ability to self-care, patients are assigned group 1 disability.
It can only be obtained after a medical and social examination. It is carried out on the basis of a medical institution in which hypertensive patients are observed.
When a disability is assigned, they are shown pension payments and corresponding benefits.
People in the first group are completely disabled or can only work in specially created conditions.
Everyone needs cardiology
Many people have a strong opinion that cardiology is a field of science for those “over 50.” But according to estimates from the National Research Institute, in Russia 59% of women and 54% of men over 20 years of age are overweight, and 15% and 28.5% are obese. That is, every third Russian of working age is overweight or obese - risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. An unhealthy lifestyle, which leads to the development of cardiovascular diseases, most often develops in childhood and adolescence, and over time, the risk of cardiovascular diseases only increases. Therefore, prevention should begin from childhood.
There are no nerve endings in the vessels, they do not hurt. Therefore, their defeat occurs gradually and symptoms appear only when complications develop: ischemia or infarction of organs, more often after 50 years in men and after 60 years in women. But the processes that cause irreversible changes begin much earlier and are easier to prevent. Therefore, all men after 40 years of age and women after 50 years of age need to undergo preventive examinations by a cardiologist with ultrasound examinations, biochemical markers and stress tests.
If there is a family history of early heart attacks or strokes, if the patient is a smoker or suffers from diabetes, if he has high blood pressure or chronic kidney disease, if the person simply does not tolerate physical activity, then you should definitely come to a cardiologist at an earlier age than 50 or 40 years. And the sooner the better.
How is diagnosis carried out?
To make a diagnosis of stage 3 hypertension, risk 3, regular blood pressure measurements are required, as well as laboratory tests of the patient’s blood and urine. You cannot do without instrumental diagnostic techniques, such as ultrasound, Dopplerography, ECG.
And also read on our website: What is hypertension, stage 1, risk 2, what are the causes and symptoms, and how to treat?
All these measures allow the doctor to assess the condition of the target organs and determine the extent of their damage. Sometimes I need additional consultation with an ophthalmologist and endocrinologist.
Evidence-based medicine and myths of cardiology
Until the 90s, Russian cardiologists treated based on the opinions or views of different medical schools, which often did not agree with each other on scientific research. When the massive advent of computers helped to introduce the principles of evidence-based medicine everywhere, uniform requirements for conducting scientific research were formulated. When evaluating drugs, double-blind randomized studies have begun to be used, which are highly accurate and impartial. We created a unified knowledge base and assessment of all research conducted in the world that corresponds to a high scientific and technical level. As a result, the efficiency and safety of diagnosing and treating patients has dramatically increased.
A myth that all doctors face, but which is especially dangerous in cardiology, can be expressed in one common phrase: “Don’t take medicine, you’ll destroy your liver.” Medicines are metabolized in the liver and eliminated through the liver or kidneys, but they do not destroy them. Canceling the selected therapy can lead to a sharp increase in blood pressure, cholesterol levels and other indicators. This aggravates diseases from heart attack and stroke to diabetic coma. Surprisingly, patients are not afraid to take dietary supplements (dietary supplements) or alcohol in any quantity.
The second common myth in the practice of a cardiologist is the erroneous opinion about the dangers of cholesterol-lowering drugs - statins. A large number of studies based on the principles of evidence-based medicine confirm the high effectiveness of this group of drugs in preventing the development of atherosclerosis and its consequences (heart attack, stroke, damage to the arteries of the legs, intestines); these drugs are included in all generally accepted recommendations. Statins require constant, simple laboratory monitoring in order to avoid fairly rare side effects. Individual intolerance occurs when using any medicine or even food product. When using statins too, but rarely.
About medical examination
Clinical examination in the field of cardiology is one of the main measures to reduce mortality from cardiovascular diseases. There is a clearly defined concept of risk factors that must be controlled and treated for a long and fulfilling life. Therefore, clinical examination including cardiac examination is indicated for all men over 40 years of age and women over 50 years of age.
“Smart” gadgets are an assistant in heart control
I really like modern devices that allow you to assess how much work a person did during the day, how many steps and kilometers he walked, and what his heart rate was. This is useful, since the load level is often calculated based on the pulse. I also like devices that allow you to evaluate the duration and quality of sleep (by sleep phases). This is a very useful feature for people living in the modern world, when both pleasure and work are prolonged due to sleep. Meanwhile, only in sleep the body is restored, healed and absorbs daytime information. “Smart” gadgets are my favorite gift to everyone who is dear to me.