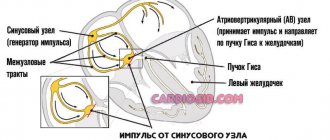
Numbness in the fingers occurs for a variety of reasons. In young people, in most cases, quickly passing numbness is a consequence of physiological causes that can be established independently; this pathology does not require specific treatment. However, loss of sensitivity in the fingers can also be an initial symptom of serious diseases, which are best treated at an early stage. Therefore, if numbness occurs frequently and for a long time, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
Main reasons
There are two large groups of causes of numbness in the fingers on the left hand, which you can learn about below.
The main ones.
- Doctors say that such symptoms cause problems with the musculoskeletal system: osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, injuries and heavy loads on the vertebrae. All this causes compression of blood vessels and nerve processes. The person feels pain and goosebumps.
- Cerebral ischemia. Due to impaired blood flow, a deficiency of oxygen appears in the cells, which a person feels as numbness.
- A non-physiological posture may also be an explanation.
- Non-pathological reasons: carrying a child or squeezing the wrist with accessories.
Additional.
When wearing backpacks and bags, at low temperatures, or with the arm positioned for a long time above chest level, the plexus of nerve processes and blood vessels is compressed, which disrupts blood circulation and causes spasm of the arteries.
Numbness as a symptom
Numbness can be caused by:
- pinched nerve. A pinched nerve can occur at the point where it exits the spinal canal ( radicular syndrome
).
Therefore, numbness is a typical symptom of osteochondrosis and other spinal diseases. The nerve can also be pinched in other areas. Pinching of a nerve in its natural canal (tunnel) is defined as tunnel syndrome
.
The most common is carpal tunnel syndrome
(a pinched nerve in the wrist).
In this case, the fingers go numb. Office work (using a keyboard and mouse) contributes to the development of the disease. Also quite common is ulnar nerve neuropathy
, the development of which is facilitated by the need for prolonged support with the elbow (typical of working at a computer).
Wearing a belt, pressing the thigh against the edge of the table, or inconvenient objects in pockets can lead to pinching of the external cutaneous nerve of the thigh ( Roth disease
) - the most common foot tunnel syndrome; - injury. Trauma can disrupt the integrity of nerve fibers, resulting in loss of sensation in the area supplied by the damaged nerve;
problems of peripheral circulation. For example, the development of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities leads to disruption of the blood supply to the legs (primarily the feet). A lack of fresh blood flow manifests itself as pale skin, a local decrease in body temperature, and numbness. Numbness may also accompany a violation of the venous outflow of blood (chronic venous insufficiency);- anemia (decreased hemoglobin in the blood). The reasons may be problems with the intake or absorption of iron, vitamins (B12, folic acid);
- polyneuropathy - multiple lesions of peripheral nerves. Polyneuropathy can be a consequence of diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, poisoning, long-term use of certain medications, autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders and other systemic pathologies;
- diseases of the central nervous system - such as brain tumors, cerebrovascular accidents, multiple sclerosis.
What is the body saying?
Suddenly my fingers lost sensitivity. If this is a rare phenomenon and it disappears after 2 - 3 minutes, then there is nothing to fear. If such sensations bother you often, then this is a signal of a developing disease.
- Little finger. Paresthesia indicates chronic heart failure and other cardiac pathologies.
- Forefinger. Goes numb with diabetes, occupational stress, inflammation in the joints.
- Thumb. Metabolic processes in the spine are clearly disrupted. You may feel pain in the forearm and weakness in the arm muscles.
- Middle finger. Raynaud's disease, hernia, articular deformity, osteochondrosis of the 7th vertebra.
- Nameless. Numbness due to the fact that the nerve endings in the bend of the elbow are compressed.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
The development of symptoms of this disease occurs gradually. The syndrome first makes itself felt at night or in the morning when a person wakes up. This is expressed in the patient's irresistible desire to shake his hands. A person can experience this state at night, and many times.
The syndrome manifests itself mainly:
- pain;
- numbness;
- tingling.
Free online intensive
Your Path to IT starts here
More details
On the hand, such manifestations occur in the thumb, index, middle fingers and half of the ring finger. Sometimes symptoms are felt throughout the entire arm, reaching up to the forearm.
A person may experience painful and unpleasant sensations throughout the day if the syndrome begins to progress. In this case, loss of strength in the hand is possible. It becomes more difficult for the patient to clench his hand into a fist or grasp small objects. Problems can also arise when you need to open a bottle, fasten a button, or type text on a computer.
Without treatment, there is a risk of muscle atrophy at the base of the thumb. This in turn will lead to a loss of the ability to sense heat and cold with the thumb and forefinger.
Symptoms of the disease may appear or intensify after the patient uses the affected arm. But even keeping the hand or the entire arm in one position for a long time can lead to tingling, burning and pain.
Treatment methods
In modern medicine, there are several effective methods for treating numbness in the fingers of the left hand.
- Drug therapy. This method involves the use of products selected by a specialist, in the form of ointments, preparations and creams. Which can relieve inflammation, swelling and pain.
- Therapeutic massage and manual therapy.
- Using ultrasound or laser. This will help restore damaged tissue and lost sensitivity.
- Special exercises and health-improving physical education. This will help improve blood circulation and the general condition of the body.
Causes of carpal tunnel syndrome
Certain areas of the brain and spinal cord are responsible for receiving information and transmitting commands to muscles and receptors. Information is transmitted to internal organs via nerves. Most of the peripheral nervous system has protective properties that protect it from physical damage:
- wave-like movements of unstressed nerves;
- elasticity of nerves;
- the location of the nerves near the joints, eliminating excessive stretching during the movement of the limbs.
Muscles, ligaments, tendons and parts of the human skeleton form natural tunnels in which the nervous system is located. If these anatomical cavities become excessively narrow, there is a predisposition to tunnel neuropathy. In this case, not only the nerves themselves can be compressed, but also all the vessels running along the nerve trunks. In such cases, neurovascular tunnel syndrome occurs.
Nowadays, activities involving prolonged static load are widespread. Office workers, IT specialists, artists, musicians and athletes, to name a few, perform much of this monotonous work. And the increase in cases of tunnel syndrome is a consequence of this situation on the labor market.
Basically, pathology in people occurs due to overstrain of the ligaments and muscles located near the affected nerve. In approximately 80% of cases, the upper extremities are affected.
How to increase your income by at least 50% by choosing the right profession
Confused by the variety of professions and don’t know where to go? Do you want to earn more or work remotely? Have you already grown up, but still don’t understand what you want to become? Do you dream of finally finding a job you love and leaving the one you don’t love?
Alexander Sagun
Chief career consultant
At GeekBrains, we train people in new professions every day and know exactly what challenges they face. Together with career building experts, we will help you decide on a new profession, find out where to start, and overcome the fear of change.
Quarry workshop is:
- List of 30 in-demand modern professions.
- A long-term plan for development in the profession that suits you.
- List of channels for job search.
- 3 tests to determine your abilities and inclinations.
- Practice in different professions on real problems.
Already 50,000 people have completed the workshop and taken a step towards a new profession!
Sign up for a free course and get closer to a new career:
A previous infection (most often viral) can also be accompanied by peripheral neuropathies of a post-traumatic nature or cause complications in the form of these neuropathies. This is the second most common cause of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Among other diseases in which neuropathy is often observed, it is worth noting diabetes mellitus, acromegaly, gout, rheumatoid arthritis and other joint problems, voluminous pathologies of the nerves themselves (neuroma, schwannoma), sarcoma, lipoma.
Causes of carpal tunnel syndrome
A significant role is played by a hereditary predisposition to paralysis from compression of nerve fibers and hormonal changes in the body against the background of ovulation, lactation and menopause. Finally, the risk of the syndrome increases with the use of oral contraceptives.
The function of the peripheral nervous system can be impaired due to injury, ischemia (primary or resulting from compression), stagnation of blood in the veins and tissue edema.
Preventing finger numbness
As with most neurological diseases, preventive measures boil down to the following:
- Maintain an active lifestyle. Do exercises and don’t forget about daily physical activity;
- Listen to your body and undergo timely medical examinations to identify pathology at an early stage;
- Periodically get tested and undergo examination of the vascular system;
- Try to eat healthy and balanced. Don't forget to take your vitamins.
The main thing to remember is that the body always warns in advance about changes, and does not suddenly get sick. Few people notice problems that are just beginning; most often they do not pay attention to it, hoping that everything will go away on its own. Lack of time, fear of doctors and injections, reduction of the importance of what is happening ultimately lead to the disease becoming much worse, treatment time taking much longer, or the consequences can cost lives.
General description of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome can occur when the median nerve in the wrist is compressed and is characterized by certain symptoms. This disease is listed in ICD-10 under code G56.0.
Among the characteristic symptoms, numbness in the hand, paresthesia, and pain in the area of innervation of the median nerve should be noted. Symptoms may also affect hand sensation and strength.
The syndrome develops as a complication of diseases of various origins or as a consequence of ligamentous and ligamentous overstrain that occurs around nerve fibers. In this case, the nerves are either compressed or stretched. The median and ulnar nerves are most often affected. The latter, in turn, can be pinched in the joint area or on the wrist inside Guyon's canal.
General description of carpal tunnel syndrome
There are several types of tunnel syndrome, depending on the degree of participation of anatomical structures in the development of pathology. To date, experts have identified 30 such options.
Medications for carpal tunnel syndrome
To reduce inflammation, patients are recommended to receive corticosteroid injections (usually into the carpal tunnel). Tablets are less effective in relieving inflammation, although they are also available in pharmacies. The effect does not occur immediately - the pain begins to subside only after 2 days, and before that it can, on the contrary, intensify.
But even with a positive result of treatment, symptoms sometimes reappear after a few months. If this happens, a new dose of corticosteroids is prescribed. Subsequent use of these drugs may cause long-term side effects, so further use is not recommended.
Aspirin, ibuprofen and similar non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can reduce short-term pain. Their use is advisable only when the syndrome occurs due to an inflammatory process. If the cause of the disease is excessive activity of the hand, this option will not help.
Other treatment methods include Botox injections and special exercises.
Treatment of hand tunnel syndrome
There is reliable evidence of the effectiveness of aerobic exercise with body weight control. At the same time, exercise bikes and cycling should be avoided in case of tunnel neuropathy, since here the arms are constantly tense.
Physiotherapy methods (for example, ultrasound treatment) can help relieve symptoms temporarily.
Treatment of hand tunnel syndrome
If electroneuromyography has revealed carpal tunnel syndrome in the early stages, in many cases applying a night splint to fix the hand in a neutral position during sleep is helpful. This procedure must be done for at least three weeks.
Sometimes conservative methods do not allow you to completely get rid of carpal tunnel syndrome. How to treat the disease in this case? An injection of, for example, glucocorticoids with diprospan gives a good effect. In other cases, as well as in severe cases of the disease, surgery is prescribed.
Surgery for compression neuropathy of the wrist involves cutting the palmar ligament that compresses the median nerve. In 9 out of 10 cases, the outcome of the operation is favorable with a minimal likelihood of complications. Moreover, almost always the patient no longer encounters relapses of this disease in the operated area. If, as a result of ENMG, no pathologies were identified, the likelihood of success of surgical intervention is reduced.
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
Usually, to make a diagnosis, the doctor needs to know the characteristic symptoms of the patient. In this case, it is convenient to use a set of special tests that make it possible to identify different types of tunnel neuropathies.
If a number of signs suggest that a patient has compression-ischemic damage to the peripheral nervous system, standard testing is performed. It includes the following activities:
- general somatic examination with identification of basic vital functions;
- neurological diagnostics using special tests;
- radiography of the affected area to identify additional ribs, bone processes or calluses, fractures, dislocations, etc.;
- neuroimaging using MRI and CT techniques of the affected areas of the nerve trunk, spine, etc.;
- electrophysiological diagnostics using the results of electroneuromyography, which makes it possible to determine the speed of the impulse in the nerve canal and clarify the degree of damage to this nerve;
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the extremities with flexion-extension tests;
- Ultrasound of the affected area, which allows us to identify pathologies that in turn lead to carpal tunnel syndrome.
Also during diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude concomitant somatic pathologies, which are often caused by progressive tunnel neuropathy. To do this, a number of additional examinations are carried out:
- clinical blood test;
- determination of blood glucose levels;
- determination of thyroid-stimulating hormones;
- rheumatoid factor analysis;
- determination of C-reactive protein;
- determination of the antistreptolysin-O indicator;
- analysis of circulating immune complexes.