Surgeon
Bohyan
Tigran Surenovich
Experience 36 years
Surgeon of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, member of the International Association of Surgeons, Gastroenterologists and Oncologists
Make an appointment
Hemangioma is a benign vascular formation that appears due to an embryonic disorder in the development of blood vessels. The tumor appears on any part of the skin and looks like a red, purple or bluish spot rising above the surface of the skin. Most often detected at birth or formed during the first weeks of life. Treatment is surgical and conservative.
Forecast
Possible consequences of the disease
Hemangiomas can cause necrosis (death) of tissue, so the lesion becomes an entry point for infection.
The addition of a purulent process can cause sepsis. With hemangioma of bones, their destruction is possible. In addition, the process can contribute to blood clotting disorders and the formation of blood clots. Malignancy is possible - degeneration of hemangioma into cancer. With timely consultation with a doctor, the neoplasm is successfully treated in 100% of cases Source: What a pediatrician needs to know about infant hemangiomas. Zakharova I.N., Kotlukova N.P., Roginsky V.V., Sokolov Yu.Yu., Zaitseva O.V., Maykova I.D., Idrisova G.R., Pshenichnikov I.I.: Medical Council , 2021.
Diagnosis of the disease
A preliminary diagnosis is made by externally examining the patient and collecting a verbal history of the symptoms of the disease present. To clarify, the patient is prescribed additional procedures:
- blood is given for a general analysis to identify deviations in the structure of the main elements;
- ultrasound examination shows the location, shape and volume of the node;
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging provide detailed information about the structural composition of the tumor.
CT and MRI study neoplasms of internal organs and damage to skeletal bones. The examination establishes the exact volume and degree of germination in the depth of the node, and will also help determine the physical condition of the patient. Based on the diagnostic results obtained, a decision is made on the course of therapy - urgent treatment is required or control of tumor growth is sufficient.
Types of hemangiomas
There are 2 types of hemangiomas - congenital - formed during intrauterine development - and acquired;
acquired in early childhood are often called infantile. By structure, single and multiple hemangiomas (hemangiomatosis) are distinguished; by structure - capillary, arterial and venous. By education they are local and segmental. Local hemangiomas grow from one point, are distinguished by smooth edges and relatively small sizes. Segmental - large, with a “ragged” edge, often develop as part of combined pathologies of the chest, aorta, pelvis and sacrum, heart defects, etc.
Hemangiomas are classified according to their location:
- simple – formed on the surface of the skin;
- cavernous - grows under the skin;
- combined - the process involves the superficial and deep layers of the dermis;
- mixed - not only dermal, but also nervous and muscle tissues are involved in the process.
Medicinal methods
Depending on whether the patient has a particular complication, treatment tactics will be different - for example, topical corticosteroids may be prescribed. At the same time, the clinical response to even the most powerful drugs develops quite slowly—over several weeks. Therefore, this method is not suitable for vision-threatening conditions.
Injectable corticosteroids provide a faster effect: blanching of hemangiomas is observed already on days 2–3, and involution becomes noticeable after 2–4 weeks. The success rate of this therapy is about 75%.
Systemic corticosteroids are used for amblyogenic life-threatening lesions. A marked response is usually observed in 30% of patients, a moderate response in 40%, and no response in 30%.
Alpha-2a interferon is prescribed when hemangioma is resistant to corticosteroid therapy. Despite its good effectiveness, its use is associated with undesirable side effects: fever, arthralgia, retinal angiopathy.
Propranolol can be used to treat hemangiomas , although the evidence base is relatively weak and mainly consists of anecdotal cases. However, some studies indicate that propranolol may prevent loss of visual acuity in the case of periocular hemangioma.
For some superficial (and in some cases deeply located) neoplasms of a limited area, timolol .
Why do hemangiomas appear?
The exact causes of hemangiomas have not yet been identified; It is generally accepted that their appearance can provoke disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus due to a viral illness of the mother or oxygen starvation. Additional risk factors for the formation of congenital hemangioma:
- multiple and/or late pregnancy;
- increased amount of estrogen in the mother;
- her sedentary lifestyle;
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol or nicotine intoxication of the fetus;
- his low birth weight.
In adults, the cause of neoplasm can be a hereditary predisposition, diseases of the cardiovascular system, excessive ultraviolet radiation, and increased levels of the female hormones estrogen.
Possible complications
With combined hemangiomas, deep ulcerations occur in 16% of cases. Ulcers are localized in the skin folds, groin, and lips, since the skin moisture is increased in these areas. After healing it is possible:
- scar formation;
- change in the shape of the lip, ear;
- partial destruction of cartilage.
Due to trauma to the tumor, bleeding occurs. In some cases it is difficult to stop them. Another common complication is dysfunction of the organ next to which the formation is located. When localized in such areas, hemangioma must be treated (most often with its removal) to avoid the risk of complications.
The most dangerous tumor is located:
- in the eye area - threatens the development of strabismus or partial loss of vision;
- neck - can compress the larynx, trachea and interfere with breathing;
- spine - causes acute pain;
- nose and ears - possible destruction of the nasal and ear cartilages;
- in the perineum, armpits - due to constant friction of the skin, the tumor may bleed;
- in the sacral area - a complication may be damage to the spinal cord with atrophy of the muscles in the legs, disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, and the genitourinary system.
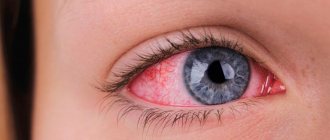
The eyes are a dangerous location for hemangioma. Photo: JOVR / ResearchGate (Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported)
Signs of hemangioma and pathogenesis
Hemangioma is a red spot, in the center of which there is a point, and from it comes a network of small vessels.
Usually the neoplasm is smooth and can protrude 1-2 cm above the skin. When pressed, it turns pale, but quickly returns to its normal appearance. A characteristic symptom is temperature unevenness: upon palpation, the hemangioma is noticeably warmer than the surrounding areas of the body. It may not manifest itself clinically and may be discovered by chance during examination. The disease occurs in phases: growth, stabilization, and optionally spontaneous regression. Complications are possible during the growth and stabilization phases of hemangioma. If a neoplasm grows near a functional organ, its function may deteriorate - for example, in the periorbital zone it can contribute to decreased vision, and on the laryngeal mucosa - obstruction of breathing.
If the hemangioma is localized near the nerve ending, as it grows, weakness and numbness of the limbs, disruption of the bladder and gastrointestinal tract are possible. Large spinal hemangiomas can cause pain and increase the risk of compression fractures. New growths are easily injured, so they can cause bleeding.
Are red moles dangerous?
In themselves, these formations are harmless and are not precancers.
If you have a lot of red moles on your body, the cause may be a serious liver or pancreas disease. Pay attention to this - this is a reason for examination.
Problems may arise in case of traumatization of hemangiomas. Even fairly small formations threaten heavy bleeding, which is not easy to stop.
Clinical case
Patient L, 26 years old, presented with a traumatized mass in the axillary region. According to her, she tore off a convex hemnagioma with the edge of a rigid corset of a wedding dress almost a few minutes before the start of the wedding ceremony. The hemangioma bled very heavily and a large blood stain appeared on her white dress. She had to wear the witness's jacket over her wedding dress. It was in such a strange outfit that the wedding took place.
How are hemangiomas treated?
The main method of treatment is surgical. In addition to cosmetic reasons, there are medical indications for this:
- rapid growth and threat of malignancy of the tumor;
- disruption of the normal functioning of organs - for example, if there is a tumor on the eyelid or tongue;
- impaired blood circulation – if the tumor is on a large vessel;
- infection and bleeding – for example, when on the genitals.
The priority is gentle, minimally invasive methods for removing hemangioma or vascular surgery methods to reduce blood flow in it. The excised tissue is sent for histological analysis.
If the neoplasm is small, it is possible to use electrocoagulation, radio wave or laser surgery, or cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen. For some forms of hemangiomas, sclerotherapy is effective - “gluing” damaged capillaries by injecting special solutions Source: Hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Modern theories and therapeutic tactics. Goncharova Y.A.: Child’s health, 2013.
For slow-growing tumors with a low risk of malignancy, conservative drug therapy with drugs from the group of beta-adrenergic receptor blockers is possible Source: Wong A., Hardy K., Kitajewsky A. Propranolol causes functional changes in hemangioma stem cells and hemangioma endothelial cells // Abstract book. ISSVA the 19th International Workshop on Vascular Anomalies. — 2012. – p. 245.. In some cases (if the tumor does not grow, does not bother, or there is a tendency towards its reverse development), they resort to wait-and-see tactics.
To ensure the effectiveness of treatment, after its completion, a control study is prescribed - ultrasound, tomography or dermatoscopy. To consult with a specialized specialist in St. Petersburg, fill out the online form.
Sources:
- What a pediatrician needs to know about infantile hemangiomas. Zakharova I.N., Kotlukova N.P., Roginsky V.V., Sokolov Yu.Yu., Zaitseva O.V., Maykova I.D., Idrisova G.R., Pshenichnikov I.I.: Medical Council , 2016
- Infantile hemangioma: classification, clinical picture and methods of correction. Sheptiy O.V., Kruglova L.S.: Russian Journal of Skin and Venereal Diseases, 2021.
- Hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Modern theories and therapeutic tactics. Goncharova Y.A.: Child’s health, 2013.
- Sires V. Systemic corticosteroid use in orbital lymphangioma /V. Sires, C. Goins, R. Anderson // Ophthal. Plast.Reconstr.Surg. — 2001. Mar. - Vol. 17(2). — P. 85 — 90.
- Wong A., Hardy K., Kitajewsky A. Propranolol causes functional changes in hemangioma stem cells and hemangioma endothelial cells // Abstract book. ISSVA the 19th International Workshop on Vascular Anomalies. — 2012. – p. 245.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment information
Previously, when a hemangioma was detected in childhood, a wait-and-see approach was adopted; doctors hoped that the tumor would resolve on its own before reaching puberty. Over time, this statement became irrelevant due to the low frequency of reverse development. In only 5% of cases, hemangioma in children disappears from the skin without consequences, in 2% of cases this occurs before the age of 5.
Today, hemangioma is treated using the following methods:
- physical removal;
- surgical resection;
- drug therapy.
The list of popular methods of physical removal includes cryodestruction, laser irradiation, sclerotherapy and electrocoagulation. The described methods allow you to painlessly remove soft tissue tumors. Complete disappearance takes from several months to several years. Scars may remain on the skin.
The surgical method is rarely used in modern practice. It is used for small hemangiomas in adult patients. Most often, tumors located in invisible areas of the body are excised. The cosmetic effect is questionable; scars remain on the surface of the skin.
Drug therapy is based on the use of hormonal and antitumor drugs. It is often used at the preparatory stage to reduce the area of hemangioma. Complete resorption due to drug therapy occurs rarely, in no more than 2% of cases.
Our clinic specialists will help you choose an effective treatment method and get rid of hemangioma on the skin. Doctors will conduct an examination and determine the most effective treatment regimen, and establish a prognosis for the possibility of self-relief. Examination using new equipment is the key to successful therapy. The experience of doctors will allow you to choose the best scheme for eliminating hemangioma, allowing you not to fear possible consequences.
What can cause a pathological phenomenon
To date, it has not been precisely established why hemangioma appears on the head of an infant. Presumably this may be due to:
- with a reaction to certain medications that a woman took in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- with the consequences of infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother;
- with hormonal imbalance;
- with accommodation during pregnancy in a contaminated ecological zone;
- with bad habits (alcohol, smoking) of the expectant mother while carrying a child.
Interesting! The pathology is gender-selective - it is diagnosed several times more often in girls.