Stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation that causes focal damage to brain cells. The disease has typical neurological symptoms that persist for a long time: painful headaches, paresis or paralysis of the facial muscles or limbs (often one-sided), impaired memory, speech, vision, and coordination of movements.
In the elderly, and especially in old age, strokes are much more severe and pose a direct threat to a person’s life. Whether a patient will be able to return to a full life after suffering a stroke or at least partially restore lost skills depends on a number of factors. In any case, this is a long process, taking months and sometimes years.
Factors influencing recovery time after stroke
Stroke is one of the main causes of disability in old age, most often occurring as a result of untimely medical care or lack of competent rehabilitation. In 80% of cases, the success of recovery after a stroke is determined by the prompt action of medical staff. It is especially important to provide assistance in the first 3-4 hours after the onset of an attack. Rehabilitation must begin as early as possible, because the quality and duration of a person’s future life depend on it.
Other factors also influence the timing of rehabilitation after a stroke:
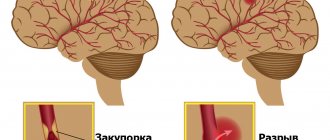
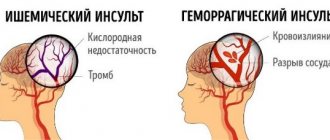
- The mechanism of stroke. There are 2 main types of strokes – ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic occurs in 80% of cases and is caused by a lack of blood supply to any part of the brain. With this type of stroke, if treatment is prescribed correctly and on time, the body has a good chance of recovery. Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by bleeding into the deep parts of the brain. The life prognosis is unfavorable, the probability of death reaches 50-70%.
- The degree of damage to brain tissue. The most serious violations of the basic functions of the body are observed with an extensive stroke affecting large areas of the cerebral cortex. In this case, if the person managed to survive, rehabilitation may take several years, and full recovery may never occur.
- Age and presence of concomitant diseases. The older a person is, the more difficult it is for him to cope with a blow, and in the presence of chronic diseases, especially the cardiovascular system, this often becomes impossible.
- What a seizure. Repeated strokes always increase the risk of death. While it takes an average of 8 months for an elderly person to recover from the first blow, it can take a year or more to recover from the second.
- Psycho-emotional state of the patient. In order to cope with such a serious illness, enormous willpower and desire to live are required, which not every patient has.
Risk factors for stroke and heart attack
Planning a preventative treatment regimen is based on addressing risk factors that are largely similar for heart attack and stroke.
Metabolic risk factors include:
- dyslipidemia (impaired lipid metabolism - organic compounds, including fats and fat-like substances);
- arterial hypertension;
- obesity;
- metabolic syndrome;
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrinopathies;
- coagulopathies (diseases that develop as a result of disorders of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems).
Common markers of heart attack and stroke are:
- previous cardiovascular diseases;
- peripheral vascular pathology;
- calcium index;
- stress test results;
- hypertrophy (thickening of the wall) of the left ventricle.
Atherosclerotic stenosis of the carotid arteries and brain tumors increase the risk of stroke. The provoking factors of a heart attack are:
- atrial fibrillation;
- dysplasia (developmental disorder) of connective tissue;
- arteritis;
- diabetes.
Although the incidence of stroke is higher in men, it is more severe in women, and about half of deaths from stroke occur in women.
Make an appointment
Periods of rehabilitation after a stroke
Modern medicine recommends starting rehabilitation of a patient who has suffered a stroke in the first hours after the attack, as soon as hemodynamic parameters (heart rate, blood pressure) return to normal. This allows not only to restore lost functions as much as possible, but also to avoid various complications that can aggravate the patient’s condition.
The recovery period can be divided into several main stages:
- acute (first 3-4 weeks after the attack);
- early recovery (first 6 months after an attack);
- late recovery (from 6 months to a year);
- remote (more than a year).
Signs of a stroke
To diagnose cerebral blood supply disorders, it is necessary to use stroke recognition techniques:
- When trying to smile, you need to pay attention to the corners of the mouth - in case of a stroke, it can be directed downwards, the smile looks crooked and asymmetrical;
- When trying to speak, it may be difficult to pronounce even the simplest words and sentences;
- When trying to raise both arms, asymmetry is observed;
- The protruding tongue falls to the side.
If at least one of the symptoms is positive, you must immediately call an ambulance. Under no circumstances should you give him water, feed him, lift him, or take him by handy transport to the nearest hospital, as this can cause harm.
Acute stage of the disease
Rehabilitation in the acute period takes place in a medical institution under the guidance of doctors. It is advisable to begin rehabilitation treatment as soon as the patient’s condition stabilizes, optimally 3-4 days after the stroke. The main tasks at this stage are: restoration of simple motor and speech functions, prevention of complications and relapses, assessment of the degree of damage to the body and development of a rehabilitation program.
To restore the motor system, passive gymnastics, massage and treatment by changing body position are used, when the patient’s limbs are placed in various positions to prevent the development of muscle hypertonicity. The return of lost speech skills begins with simple articulation exercises, gymnastics of the tongue, cheeks, and lips. Speech is more actively restored 3-6 months after a stroke, but full recovery requires 2-3 years of work with the patient.
An important condition that accelerates rehabilitation in the acute period is the use of medications and physiotherapeutic pain-relieving procedures - magnetic, electro- and laser therapy.
Fatigue
Fatigue is one of the most common symptoms of stroke. This symptom affects most people who have had a stroke, regardless of its severity, and is usually most noticeable when they return home from the hospital.
This type of fatigue is different from the usual and usual fatigue for us, and it does not depend on your activity or activity. Each of us sometimes feels tired, but this feeling often goes away after rest. However, after a stroke, the fatigue you feel may make you feel like you don't have the energy to do anything. Often you may feel that the feeling of fatigue comes completely unexpectedly and at this moment the only thing you can do is rest until this feeling passes.
Sometimes it takes months or even years for this symptom to go away. Many people after a stroke say they have good days and bad days - days when they feel they can do more things and days when they need to rest more because they feel tired. During the recovery process, good days tend to increase and bad days decrease. Often this fatigue is invisible to other people, so it can be difficult for them to understand what you are feeling. Despite this, you can help yourself in various ways. The key to success is to realize that it is not your fault and it is not your fault. You need to accept the fact that it takes a long time to overcome this symptom of fatigue.
Rehabilitation after stroke in the early recovery period
The early recovery stage is crucial for the patient and should ideally take place in a sanatorium or rehabilitation center. When deciding to leave the victim at home, you should remember that successful recovery after a stroke is impossible without the active participation of specialized specialists who will have to be invited to the home.
The first three months after the onset of the disease are especially productive and favorable for rehabilitation. At this stage, they move from the simplest exercises to more complex ones - they teach a person to roll over, rise, sit down, and stand up independently. Next, elements of active physical therapy are gradually introduced, physiotherapy, massage, speech work are continued, and complexes are performed to restore vision and eye movements, cognitive functions (memory, thinking, attention).
A common consequence of a stroke is complete or partial loss of vision, dysfunction of the eyelid, presbyopia, when a person cannot distinguish small print or small objects at close range. All these disorders require qualified assistance from an ophthalmologist, who will prescribe either medication or surgical treatment. In mild cases, they can do with therapeutic exercises for the eyes.
To restore attention, memory, and intellectual abilities, there are many exercises: memorization tasks, memorizing poetry, solving riddles, rebuses, putting together puzzles, chess, checkers. However, for complete rehabilitation of cognitive functions, psychological and correctional classes are necessary individually or in groups. Additional stimulation is provided by medications that should be prescribed by a doctor.
Types of brain strokes
The most common ischemic stroke (infarction) of the brain - 85% of cases, hemorrhagic stroke occurs in 15% of cases. Strokes can be caused by several reasons:
- formation of thromboembolism in heart diseases;
- acute circulatory disorders in the cervical and large cerebral arteries;
- disturbance of blood circulation in the small arteries of the brain during the acute course of the process.
Late and remote periods
At a later stage, the body’s potential for rehabilitation after a stroke gradually decreases, but the patient must continue to study and train self-care skills. This period already passes at home, so responsibility for the health and mental state of the patient falls entirely on his loved ones.
You can change your usual exercise therapy complex by adding new exercises and classes with simple exercise equipment, for example, an expander. It is recommended to talk with the patient as often as possible, ask questions, thereby encouraging him to be vocal.
A year after the stroke, the exercises no longer have a pronounced effect, so in the long-term recovery period, the main attention should be paid to consolidating skills and periodic visits to the doctor for follow-up examinations.
Conditions for successful rehabilitation after a stroke
A stroke is a difficult ordeal, especially for older people, who can suffer from it with unpredictable consequences. How long it will take to recover - even doctors cannot answer this question for sure. But in order to shorten the rehabilitation period after a stroke, the patient must provide a number of conditions:
- rehabilitation should take place under the strict guidance of a qualified doctor according to an individually developed program;
- the rehabilitation process must be continuous and comprehensive. This means that it is necessary to work on restoring all body functions simultaneously and sequentially;
- in the home environment, it is necessary to create all the conditions for the successful rehabilitation of the patient: equip the sleeping place with an anti-decubitus mattress, allocate a place for doing therapeutic exercises and purchase the necessary exercise equipment, as well as additional equipment - walkers, wheelchairs, canes, special personal hygiene products;
- provide a balanced diet throughout the entire period of rehabilitation;
- take care to create a favorable home atmosphere, sensitive and caring attitude towards the sick person.
Features of stroke in older people
Age is one of the significant factors in the development of acute vascular pathologies of the brain that impair blood circulation. Diseases of the blood vessels in older people are much more severe than in young people. This is due to physiological changes in the body, and in particular in the central nervous system, such as:
- reduction in brain volume and weight;
- thinning of the leptomeningeal membranes;
- senile neuronal atrophy;
- degenerative changes in white matter;
- decreased functional activity of neurons;
- neuronal death caused by electrolyte imbalance;
- reduction of the blood-brain barrier;
- pathological changes in the cerebral ventricles.
About 80% of stroke cases are diagnosed in people over 70 years of age. And, unfortunately, the prognosis for recovery is very often unfavorable. The consequences of stroke in older people are difficult to predict, since it is difficult for such patients to choose effective therapy.
Causes of stroke in older people
Among the causes of stroke in older people, etiological factors and risk factors are distinguished. The former cause the disease itself, while the latter increase the likelihood of pathology occurring. The main causes of acute disorders of blood flow in the brain include:
- arterial hypertension;
- vasculitis and angiopathy;
- improper use of drugs that affect blood clotting;
- neoplasms in the cells of nerve or connective tissues;
- changes in heart rate;
- atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries;
- hormonal imbalance, which increases the risk of blood clots.
The main risk factors for stroke in older people include:
- gender (statistically, men are more susceptible to extensive bleeding into the brain);
- presence of cardiovascular diseases;
- increased cholesterol levels in the blood;
- history of micro-strokes.
As a rule, a stroke is preceded by certain vascular and cardiac diseases. Some of them are systemic atherosclerosis and atrial fibrillation, which develop at the age of 85 years.
Systemic vascular atherosclerosis
This disease is heterogeneous plaques that form in medium and large arteries, including the brain. Elderly and senile age are the main risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis.
Frequent atrial fibrillation after 85 years
Heart rhythm disturbances that lead to an irregular heartbeat indicate the presence of atrial fibrillation. The sinus node cannot cope with the coordination of the heart rhythm, which is why the upper chambers flicker chaotically. As a result, insufficient blood enters the ventricles. The main symptoms of atrial fibrillation are:
- trembling in the chest;
- cardiopalmus;
- irregular heart rhythm;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the chest;
- dizziness;
- fatigue, drowsiness;
- increased anxiety and restlessness.
Many people live with this disease for decades. It is not a direct threat to life, but when a person reaches old age it leads to a number of complications, including stroke.
Stroke in people over 70 years of age
With age, cerebral circulation deteriorates. These disorders are explained by natural aging changes, due to which the body's compensatory reserves decrease. As a result, the walls of blood vessels become brittle, the inner lining of the arteries is affected by atherosclerotic plaques, and cases of sudden jumps in blood pressure become more frequent.
The consequences of a stroke in elderly patients (over 70 years of age) are very life-threatening and radically change it. The first episode of cerebral vessel rupture leads to coma in more than half of the cases. The recovery process after an acute cerebral circulatory disorder is difficult and lengthy.
Signs of stroke in older people
In most cases, the disease manifests itself almost immediately. Deprived of normal blood supply, brain cells die, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe headache;
- dizziness;
- fainting, short-term loss of consciousness;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- deterioration of speech and pronunciation (slowness, deterioration of diction, inability to reproduce sounds);
- decreased vision, darkening of the eyes, blurred and unclear images;
- confusion, absent-mindedness;
- disorientation in space.
Signs of stroke in older people have some peculiarities. A vascular accident in the brain occurs regardless of the time of day, but more often develops in the early morning or evening. In older patients, the condition often worsens gradually over several days. This is due to the fact that cerebral hemorrhage occurs quite slowly.
Where to go for help?
It is impossible to provide complete rehabilitation after a stroke in the home environment. Therefore, the most reasonable option for the family of an elderly person who has suffered an attack would be to enter into an agreement with a specialized institution, where he can receive help from highly qualified specialists and undergo a comprehensive rehabilitation program developed taking into account his diagnosis and characteristics of the body.
The Trust boarding house network has been providing care and rehabilitation to stroke victims for the past 5 years. The staff consists of highly qualified doctors and nurses with medical education. The boarding houses have all the conditions for a comfortable stay and full recovery after a stroke:
- Individual rehabilitation programs aimed at adaptation after a stroke and prevention of a recurrent attack.
- Regular medical examination of the patient.
- A full range of rehabilitation procedures: exercise therapy classes, exercises for the rehabilitation of speech and cognitive functions.
- Drug therapy.
- Social and psychological assistance, warm and attentive attitude towards each ward.
- Cozy rooms equipped with functional beds, wheelchairs, orthopedic mattresses.
- Prevention of bedsores and daily hygiene.
- Specialized 6 meals a day, rich in vitamins and microelements.
- Organization of leisure and communication.
By entrusting us with the care of your loved ones, you create decent conditions for life and restoration of their health, thereby reducing the recovery time after a stroke. To find out more details about our programs, leave a request on the website, and we will call you back at a time convenient for you.
What should you expect when you return home?
When you are discharged from the rehabilitation center, you will be given a discharge summary. It will cover all the necessary guidelines for caring for you at home, as well as the necessary equipment and supplies you may need. Returning home can be initially scary. You may not fully recover and will need to continue rehabilitation on an outpatient basis. You may also have many questions about how you can continue living a full life after a stroke.
Restoration of motor functions
Often, after suffering an apoplexy, the patient loses his previous motor activity in full or in part. For example, hand motor skills suffer, movement coordination is impaired, and limbs do not move. Doctors also strongly recommend that you strictly adhere to bed rest for the first time and not get up, even if you have the strength to do so. The best option would be to sit on a special bed or use pillows to warm up your arms and legs.
It is useful to use therapeutic massage , which can only be performed by a qualified master. It can be general and complex in nature or affect a specific muscle group. It is also important to develop muscles, which will be an excellent barrier to the appearance of spasms and pain. If the client is unable to move parts of the body, then a passive version of gymnastics is used.
It is important to understand that physical therapy, massage sessions and feasible physical activity alone will not be enough to restore lost motor activity. It is important, along with them, to use professional equipment. For example, by applying current pulses, it is possible to stimulate the affected areas and bring them back into active tone.
Baths and applications are also used as additional measures to improve blood circulation. The doctor may prescribe medications to relax muscles, eliminate pain and spasms. Pay special attention to the person’s face and facial expressions. In case of pinched nerves or paralysis, facial expressions change noticeably. You can cope with its restoration with the help of simple exercises. You should do gymnastics for your eyes and mouth, make a wide smile, pronounce various sounds, squint your eyes tightly and relax your eyelids.
Restoring everyday skills
All everyday skills should be developed under the supervision of a loved one, an assistant who will control the patient’s movements and, if necessary, support and guide his hand.
Nutrition
To prevent spoons and forks from slipping out of the patient’s hand, you can wrap their handles with thin foam rubber. If paralysis/paresis affects the leading hand, then when eating, you should help the patient - support and guide his hand towards the mouth.
Using the tap and washing your face
A chair should be placed in front of the sink so that the patient can wash while sitting. He should open the tap with the affected hand and, if necessary, should be assisted by guiding his hand towards the tap. In this case, the patient should check the temperature of the water with a healthy hand with preserved sensitivity. Once a comfortable temperature has been established, the patient should attempt to wash the affected hand.
Combing
You should choose combs made from non-slip materials, or wrap the comb handle with thin foam rubber. If possible, you should try to comb your hair with the hand with impaired function.
Dressing
Clothes (jacket, shirt) should be loose, fastened with buttons. It is placed on the knees, between which the sleeve for the affected arm is lightly fixed. With the help of the healthy one, she gradually moves into the sleeve.
Returning to work
A stroke will be a real challenge for you if you have previously worked. It can leave a big imprint on your life and change your role in the family and society. Many people do not look at the situation realistically and try to do many things in a short period of time. Fatigue, cognitive complications such as memory loss, and difficulty concentrating may mean you will not be able to return to work. It is important to have an honest conversation with your employer so that you can consider on-the-job adaptation. Part-time work and a reduced workload may be a viable option. Don't be too hard on yourself if things don't work out or aren't going as well as they did before you had your stroke. A lot of people are returning to work. Many see this as an opportunity to try something new, such as working from home or taking on new responsibilities.
Memory training
Memory and intellectual function training occurs simultaneously with speech restoration. The patient should try to repeat the syllables, words, phrases spoken by the assistant, gradually increasing the interval between pronouncing the word and repetition.
Board games, composing stories based on pictures, solving crossword puzzles, and even simple conversations help restore thinking abilities. Near each item in the room you can put a card with its name. As cognitive functions are restored, the patient can read, watch films, and discuss their content.
Speech rehabilitation
To restore speech skills, the patient will need to consult a speech therapist, who will prescribe exercises for training facial muscles, language, as well as help and certain behavior from loved ones.
The patient's relatives should constantly communicate with him, while pronouncing words slowly and clearly, avoiding complex long sentences. The patient must first train the pronunciation of individual sounds, gradually moving on to syllables and words. Sometimes it is easier for a person to pronounce words in a sing-song manner than in the usual way.
Recommended exercises:
- stretch out your lips like a tube and “bar your teeth”;
- lick and lightly bite lips;
- stick your tongue out of your mouth, stroke your cheeks with your tongue, “click” your tongue;
- puff out one's cheeks;
- smile, trying to use both sides of the mouth symmetrically.
Relearn to speak, eat, understand and remember
— How should you prepare a home for a patient after a stroke? And what additional equipment will he need?
— While the patient is regaining the daily skills necessary to independently care for himself, while he has difficulty moving, it is necessary to ensure that he can move safely. For this:
- remove carpets and wires on the floor to prevent the patient from tripping. Make sure all paths the patient uses are clear and well lit.
- equip the bed with rails so he can sit down
- in the bathroom, attach special vertical railings that the patient can hold on to,
Special devices - a toilet chair, a bath seat - will make the patient’s life easier at home.
- install a seat in the bathtub or shower so that the patient can wash while sitting,
- raise the height of the toilet using a bedside chair,
- when the patient learns to walk, buy him a walker, and later a cane.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
— After a stroke, people often have speech impairments. Can it be restored?
— Yes, articulation gymnastics, which I mentioned above, as well as classes with a speech therapist, help restore speech functions, but the main thing is communication with loved ones, that is, daily speech practice. Speech disorders can be of two types - aphasia (the patient has difficulty understanding words and expressing his thoughts) and dysarthria (there is understanding, but pronunciation and fluency and clarity of speech are impaired). General rules:
- Ask questions that the patient can answer “yes” or “no.”
- speak slowly and clearly, give the patient time to respond, do not speak for him.
- be patient and consistent. With regular exercise, improvement will definitely come over time.
— What should a person be fed after a stroke?
- Patients with stroke often have a problem with impaired swallowing - dysphagia, and there is a risk of obstruction of the esophagus and aspiration (penetration of foreign bodies into the lungs). It can cause suffocation, infectious diseases, and pneumonia. Such patients need to be fed, strictly following the recommendations: only in a sitting position with support under their back, turning to the healthy side at the time of swallowing, only with a small amount of food.
Semi-hard foods are best tolerated - casserole, thick yogurt, pureed vegetables and fruits, watery porridge.
Give solid and liquid foods at different times. Eliminate from your diet foods that often cause choking - bread, cookies, nuts, etc.
— What other disorders does a stroke lead to?
— During a stroke, areas of the brain that are responsible for the processes of learning, understanding, and communication can be damaged. Memory deterioration and problems with perception are often observed: a person does not realize that the functions of his body are impaired, he does not recognize familiar objects or people, he may ignore some part of the body. Over time, with proper therapy, lost skills will be restored, but this is a slow process.
At home, you can and should exercise your memory and attention: ask the patient about what he did/saw yesterday, look at a family album, solve riddles, remember similar objects by shape, color, etc.
Another important point is the patient’s mood. A person experiences despondency, emptiness and hopelessness due to the fact that he cannot fulfill his previous social functions (work, take care of his family), a feeling of humiliation due to lost basic skills, and may refuse to communicate. Sudden mood swings, aggression, anger, laughter and tears for no reason are possible.
In such cases, the patient may need treatment with antidepressants, and relatives may need to be calm and refrain from criticism.
Both the patient and his family need to remember that all of these are consequences of a stroke, which will go away as they recover.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
Daily routine
A daily home routine can be helpful. Your day will be less monotonous and this will allow you to learn to listen to yourself and determine when you feel active and do some housework accordingly. The daily routine is based on your needs and the needs of your loved ones. Think about what chores you need to do every day, what you can do on your own, what you need help with, and what you will need to learn to do again. Think about how much time you will need to complete all this work. If you feel yourself getting tired, try to perform the most difficult and tiring tasks that require more energy during the day or week when you feel more energized, making sure to take time to rest. It is very important to be as active as possible. Try to continue your hobbies, social activities and other activities as much as possible. And if you can, try to breathe fresh air every day!
General rules of care
The recovery period after a stroke is divided into early (up to 6 months), late (6-12 months) and residual effects (after 1 year). Ideally, in the early recovery period, the patient is recommended to be treated in palliative hospitals, sanatoriums, in the late recovery period and during the period of residual effects - in a day hospital, rehabilitation department, or by a visiting team at home. In reality, most often patients are at home after an acute period of stroke, and the main question that arises among their loved ones is where to begin rehabilitation. One of the main tasks of the rehabilitation process is to create comfortable conditions that promote relief and speedy recovery.
Preparing the premises
To exclude the impact of external traumatic factors (light, sound, temperature stimuli) on the patient’s psyche, he should be placed in a bright, well-ventilated room, where no extraneous noise can be heard from the street. The room should maintain a comfortable temperature within +18-22 °C.
The room should not be cluttered with furniture or objects that are easily moved out of place. A good alternative to a regular bed would be a functional one - with adjustable height and backrest position, side rails, and lockable wheels. Near the bed you need to place a bedside table with hygiene items, a blood pressure monitor, other necessary things, a wheelchair or other mobility aids (walkers, canes), a portable toilet or a bedpan.
If the person caring for the patient is not always with him, you can equip the room with a call button that the patient can easily reach, or replace it with a regular bell. Patients who can move independently or are beginning to train the skill of walking will find handrails along the walls very useful, and anti-slip mats in the bathroom will prevent injuries.
Body hygiene and bedsore prevention
Adequate prevention of bedsores can prevent their occurrence in 80% of cases.
Preventive measures:
- a special anti-bedsore or foam mattress with a thickness of at least 10 cm;
- soft bed linen without wrinkles;
- special cushions or pads made of foam rubber for vulnerable parts of the body (back of the head, shoulder blades, elbows, sacrum, heels, ankles);
- changing body position every 2-3 hours;
- comfortable underwear;
- prevention of skin trauma - carefully moving or turning over the patient.
It is important to carry out proper hygiene measures and skin care. At least once a day, during hygienic procedures, you should examine the entire surface of the patient’s body, vulnerable areas - every time you turn over. You should use waterproof diapers and diapers and change them as needed. It is necessary to wash the patient with warm water without soap after each bowel movement, washing with soap - no more than once a day, it is better to use liquid soap. After washing, the skin is thoroughly dried with a soft towel. For dry skin, moisturizing and nourishing creams are used; for diaper rash, powders without talc are used.
Nutrition
Food should be comfortable to swallow and easily digestible. The patient needs a sufficient amount of fluid - at least 1.5 liters. in the absence of restrictions. Drinking should not be limited even with urinary incontinence, since with a lack of fluid, urine becomes concentrated and irritates the skin.
The patient's diet should contain a sufficient amount of protein. It can be a soufflé, minced chicken, beef, rabbit, or fish. Patients who have difficulty chewing or swallowing semi-solid foods may be given meat or fish broth.
The menu should include dishes rich in vitamin C, iron, zinc, fermented milk products, fruits and vegetables.
Food is prepared boiled or baked and must be freshly prepared. You should not eat fried foods, pickles, smoked foods, spicy foods, canned food, fast food, carbonated and sweet drinks. You need to eat 4-5 times a day, in small portions.