Make an appointment by phone: +7 (343) 355-56-57
+7
- About the disease
- Cost of services
- Sign up
- About the disease
- Prices
- Sign up
Atrial fibrillation (AF)
is the most common rhythm disorder. It is registered everywhere and occurs in almost all age groups, but the frequency of its occurrence increases with each decade of life.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, correctly selected treatment and the patient follows all the doctor’s orders, the prognosis for this disease is quite favorable and the patient’s quality of life does not suffer significantly.
This applies to patients of all age groups, including the elderly.
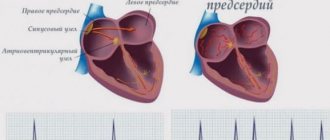
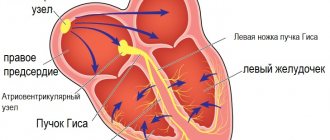
Normally, the human heart has a conducting system. It is similar to electrical wiring and its function is to conduct impulses from the sinus node located in the left atrium to the heart muscle, causing it to contract. With atrial fibrillation, the function of one “power source” (sinus node) is taken over by multiple arrhythmic foci in the atrium and the heart contracts chaotically. That is why this arrhythmia is also called delirium cordis (delirium of the heart).
These arrhythmic foci can be quite small and multiple, and then this form of AF is called atrial fibrillation
(from Latin fibrillatio - small contractions, trembling). With larger and more organized foci of arrhythmia, they speak of atrial flutter (reminiscent of the flutter of a bird or butterfly wing). Atrial fibrillation is always chaotic and absolutely arrhythmic contractions of the heart. Atrial flutter can be either regular or irregular in shape. In the first case, the rhythm is correct, but in the second, it is as chaotic as in atrial fibrillation. These forms of MA can be distinguished only by ECG. However, the methods of diagnosis and treatment, as well as prevention of these forms of the disease, are the same. Although with atrial flutter there is a greater effect from surgical treatment methods.
Like any disease, MA has its own course. It begins, as a rule, with a suddenly developing episode (paroxysm), which can end as suddenly as it began.
In this case, restoration of normal (sinus) rhythm can occur both spontaneously (on its own) and with the help of special medications - antiarrhythmic drugs.
The further course of this disease is completely unpredictable. After the first paroxysm, this ari often lasts for many years, and then it can appear at the most unexpected moment. Or, conversely, after the first episode, rhythm disturbances become more and more frequent. And, as a rule, with the increase in frequency and lengthening of paroxysms of MA, it gradually turns into a permanent form, that is, it settles in the patient’s heart forever.
In some cases, when paroxysms are repeated quite often and exhaust the patient, the transition of the arrhythmia to a permanent form brings him relief, because each episode of failure and recovery leads to complications.
In any case, you can live with this arrhythmia, you just need to master the basic principles of managing it. However, it should be understood that it is almost impossible to cure this disease once and for all, like many other diseases (bronchial asthma, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease, etc.) - you can only coexist with MA, control its symptoms and prevent the development of complications.
A special cohort consists of patients with frequent relapses of AF. In this case, we are talking about either incorrect treatment (the patient does not take the medications, or takes them in an insufficient dose, and the problem can be solved with the help of an arrhythmologist). However, in some cases, an increase in paroxysmal AF is a natural course of the disease, indicating that the paroxysmal form of AF will soon become permanent. This process can be interrupted using surgical treatments.
Causes
Pathology occurs against the background of cardiac (heart) or extracardiac (non-cardiac) diseases, as a result of previously performed surgical operations.
Atrial fibrillation can be caused by:
- arterial hypertension;
- ischemia;
- mitral stenosis;
- mitral valve insufficiency;
- cardiomyopathy;
- pericarditis;
- neoplasms in the heart;
- heart defects;
Extracardiac factors that influence the development of atrial fibrillation:
- lung diseases (pneumonia, malignant tumors, pulmonary embolism, sarcoidosis);
- obstructive sleep apnea (accompanied by snoring and partial cessation of breathing);
- obesity;
- thyroid diseases.
The main drugs for preventing stroke in AF are anticoagulants
The main drugs for patients with AF that prevent stroke are anticoagulants, the effect of which reduces blood clotting. They prevent the formation of blood clots and therefore reduce the risk of stroke. Coagulation is a normal protective reaction of the body to damage to the vascular wall. With atrial fibrillation, anticoagulants are absolutely necessary for almost everyone.
The most famous anticoagulants in Russia are Eliquis, Xarelto and Pradaxa.
Also, some patients can take Warfarin (with INR monitoring). It is prescribed for low glomerular filtration rate (or creatinine clearance - an indicator of kidney function) or for prosthetic valves.
When taking Warfarin, it is necessary to monitor the INR in the blood (International Normalized Ratio) - the indicator should be from 2.0 to 3.0.
| The main drugs for patients with AF that prevent stroke are anticoagulants, the effect of which reduces blood clotting. With atrial fibrillation, anticoagulants are absolutely necessary for almost everyone. |
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
The main symptom of atrial fibrillation is rapid heartbeat. Frequent and irregular heartbeats occur during exercise or emotional stress. It may be asymptomatic if the pathology appears against the background of another disease.
When visiting a doctor, patients note:
- cardiopalmus;
- chest pain;
- shortness of breath during exercise;
- lack of air, suffocation;
- dizziness and loss of consciousness;
Patients who have had a stroke or ischemic attack of the brain are at risk. Together with high blood pressure (BP), diabetes mellitus, heart failure and rheumatism, the risk of arrhythmia increases.
People who suffer from constant bouts of heart palpitations may stop noticing symptoms. Therefore, it is important to promptly recognize the disease and stop it. In order not to miss the development of pathology, it is necessary to be observed by a cardiologist and monitor the work of the heart. At the center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, you can undergo a comprehensive heart check, receive consultation and recommendations from a doctor.
Treatment
Conservative treatment of atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation)
Atrial fibrillation is a risk factor for ischemic stroke, which develops as a result of the formation of blood clots in the cavity of the left atrium. The first-line treatment for atrial fibrillation is drugs that prevent blood clots. They are prescribed by a doctor, because... monitoring of the blood coagulation system is required. These drugs are indicated for almost all patients who suffer from atrial fibrillation, regardless of whether the arrhythmia is constantly present or occurs in attacks (paroxysmal form of arrhythmia). The risk of stroke is the same both in the presence of a chronic form of arrhythmia and in a paroxysmal form of arrhythmia.
In patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, the issue of preventing the occurrence of arrhythmia attacks is addressed. If the attack occurs for the first time, antiarrhythmic drugs are not prescribed. Medications may be recommended to control heart rate and improve tolerance to repeated episodes of arrhythmias. Antiarrhythmic drugs are also not prescribed if the patient’s arrhythmia attacks are asymptomatic and do not reduce his quality of life. If rhythm disturbances recur and paroxysm tolerance deteriorates, the cardiologist-arrhythmologist, together with the patient, decides on the prescription of antiarrhythmic drugs or surgical treatment of arrhythmia (catheter ablation).
If a prolonged attack of atrial fibrillation develops, which does not go away on its own, it is necessary to contact a specialist cardiologist-arrhythmologist, who will choose the most suitable method for stopping the arrhythmia for the patient. A technique for medicinal restoration of normal heart rhythm has been developed, as well as a procedure for restoring rhythm using electrical cardioversion. To restore the rhythm, a certain medication preparation is necessary, the regimen of which will be determined by the doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the course of the disease. With the advent of the latest highly effective antiarrhythmic drugs, preference is given to drug restoration of rhythm.
When transforming the paroxysmal form of atrial fibrillation into a chronic form, the main task is to control the heart rate. In the presence of tachysystole (high heart rate), drugs are prescribed that reduce the heart rate, the primary of which are beta-blockers. An integral part of the treatment of atrial fibrillation is the treatment of the disease that provoked the rhythm disturbance - coronary heart disease, heart failure, arterial hypertension, disorders of the thyroid gland and others.
It is necessary to contact a cardiologist-arrhythmologist if:
- development of an attack of atrial fibrillation for the first time in life,
- development of another attack of arrhythmia that cannot be controlled by usual means,
- ineffectiveness of previously prescribed antiarrhythmic therapy.
Diagnostics
It is possible to diagnose atrial fibrillation during a physical examination. Pathology is indicated by an orderly pulse, irregular heart sounds, and significant fluctuations in their volume. Having discovered these deviations, the doctor refers the patient for instrumental studies. In the cardiology center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, diagnostics are carried out using:
- taking an ECG during an attack of arrhythmia;
- daily HM-ECG with recorded arrhythmia (ECG using the Holter method);
- data from electrophysiological studies of the heart;
- MRI or MSCT of the heart.
Atrial fibrillation classification (ESCGuidlines):
- The paroxysmal form is a sudden onset of AF, lasting from several minutes to 7 days, recovering on its own (usually within 24-48 hours).
- The persistent form is atrial fibrillation lasting from 7 days to 1 month. It does not recover on its own, but there are indications and the possibility of cardioversion.
- Long-term persistent form - atrial fibrillation lasting more than 1 month, persisting or relapsing, despite attempts at cardioversion.
- The permanent form is atrial fibrillation in which cardioversion is contraindicated, was not performed, or was unsuccessful.
The prevalence of atrial fibrillation is 6% in elderly and senile people and about 2% among the entire population. In 6-10% of patients with coronary artery disease, the disease is complicated by atrial fibrillation, and in patients with mitral heart disease who require surgical treatment, atrial fibrillation develops in 60-80% of cases. Observations indicate a significant increase in the incidence of this arrhythmia.
In patients with atrial fibrillation, mortality is approximately 2 times higher than in patients with sinus rhythm. Dissociation of the atria and ventricles leads to a decrease in cardiac output by 20-30% due to the lack of atrial contribution to cardiac output, as well as inadequate filling of the left ventricle with blood. Thus, long-term atrial fibrillation leads to the development of dilated cardiomyopathy, which is accompanied by dilation of the cavities of the heart, severe systolic dysfunction of the left ventricle (decreased ejection fraction), the occurrence of mitral and tricuspid regurgitation (reverse reflux of blood), which leads to an increase in heart failure.
The presence of atrial fibrillation leads to blood stagnation and thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage with a high risk of blockage of the arteries of the brain, the main arteries of the upper and lower extremities (systemic circulation), and the vessels supplying internal organs. Every sixth stroke occurs in a patient with atrial fibrillation. The risk of such a complication in patients with atrial fibrillation is 5 to 7 times higher than in people without arrhythmia. In patients with heart defects of rheumatic etiology, complicated by atrial fibrillation, the risk of developing acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA) is 17 times higher than in patients without atrial fibrillation.
Diagnostics
The main method for diagnosing atrial fibrillation is electrocardiography (ECG) and Holter monitoring - continuous long-term (for 1 - 7 days) ECG recording.
If the diagnosis of AF is confirmed and indications for endovascular catheter ablation of AF are determined, the patient undergoes an electrophysiological study (EPS) to identify zones of ectopic foci and construct a map of these zones.
Prevention of atrial fibrillation
The main goal of disease prevention is the treatment of arrhythmia in order to prevent its development and progression. People with a confirmed diagnosis need to visit a doctor in a timely manner and follow his prescriptions and recommendations. Additional measures include adjustments to your usual lifestyle:
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- active lifestyle and moderate physical activity;
- relieving emotional stress;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol and tonic drinks, overeating).
To maintain good health, we also recommend visiting your doctor and cardiologist annually. You can find out about heart screening programs in our center here. Timely diagnosis of the problem will help to quickly take measures to treat the disease and prevent its occurrence. Specialists from the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center FMBA will definitely give their recommendations, help you choose a cardiac diet and choose treatment tactics.
Anticoagulants can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor.
Standard dosage: Xarelto 20 mg / once a day Eliquis 5 mg / 2 times a day Pradaxa 150 mg / 2 times a day
Studies show that patients are more comfortable taking Xarelto - taking it once a day is easier to remember, especially for older people.
"Wafarin": take one tablet in the evening, take the INR test after 3-4 days. If the INR does not reach 2.0, then the doctor should increase the dosage. The INR should be taken every 3-4 days until the desired level is reached. Then you need to take an INR test every 3 weeks.
Important: all medications and their dosage are prescribed strictly during an in-person consultation with a doctor! This information is for informational purposes only and cannot be a guide to action. Self-medication for arrhythmia is unacceptable and can have serious health consequences.
| Reducing the dosage of anticoagulants mainly depends on only three parameters: — Creatinine clearance is less than 50. — The patient’s weight is less than 65 kg. — The patient’s age is over 85 years. In other cases, reducing the dosage risks a stroke. |
Why is the heart rhythm disrupted?
The normal heart rate is between 70-80 beats per minute at rest. It can increase with physical activity, various emotional experiences, exposure to medications, and alcohol.
A slowdown in heart rate is observed with general weakness, severe fatigue, in old age, in athletes or during sleep. In addition, various types of disorders can be caused by side effects of medications or diseases of internal organs (for example, pathologies of the nervous system).
Also, arrhythmias can occur due to cardiovascular diseases, among which the main role is played by:
- myocardial damage caused by atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, inflammatory processes, injuries and other factors;
- lesions of the sinus node in the heart caused by congenital or acquired factors;
- tumors of the heart muscle;
- pericardial lesions. We are talking about pericarditis, adhesions, metastases and other problems;
- disturbed balance of electrolytes (deficiency of Mg, K, Ca and Na);
- catheterization, angiography, surgical interventions that irritate the heart.
In addition, the problem in question can also occur in completely healthy people. For example, the loss of one or more beats - in other words, extrasystole - happens to any person from time to time.
Such cardiac failures do not cause inconvenience and are not accompanied by a risk to life and health, unless they become permanent.
Anticoagulants thin the blood - is it dangerous?
Like any blood thinners, anticoagulants can cause bleeding. However, the risk of bleeding is 10 times lower than the risk of stroke. If a person has spontaneous bruises, nosebleeds, heavy menstruation, or blood in the urine, this is not an indication that the dosage needs to be reduced. Minor bleeding does not cause death, unlike a stroke. If you have the above symptoms of bleeding, you need to come for an examination to your attending physician - a gynecologist, urologist and, of course, a cardiologist.
| If a person takes anticoagulants, he must take a general blood test, creatinine, glomerular filtration rate (creatinine clearance), potassium, sodium, ALT, AST every 6 months. |
Dangerous or useless drugs
● 50% of strokes in AF are associated with the fact that a person takes aspirin. Neither aspirin, nor Clopidogrel, nor their combination protects a person from the development of ischemic stroke. ● Many people take blood-thinning drugs when there is no reason for this, others are ready to replace anticoagulants with Cardiomagnyl, Mildronate, Riboxin - this cannot be done. ● “Preductal” can cause extrasystole and increase arrhythmia; it is used only for coronary heart disease. ● The heart cannot be “nourished” with anything; there are no “vitamins for the heart.” The heart is a reflection of your lifestyle - nutrition, movement, sleep.