I would like to immediately make a reservation that I am against treatment over the Internet, since each patient is individual and there are no absolutely universal treatment regimens for this or that ailment.
Therefore, if you are in a metropolis or in a place where there is a relatively free access to medical services, then in case of any pronounced malfunction in the body that cannot stand waiting for an outpatient doctor’s consultation, I recommend that you do not self-medicate, but call “112” or “03” "and call a doctor or at least ask for advice on what to do in a given situation.
In this article we will discuss how, relatively safely, to reduce increases in blood pressure and heart rate at home.
The following recommendations are addressed to patients who do not have the “03” service nearby, or you know in advance that it will take a very long time to get to you...
What actions should I take?
Scheme No. 1
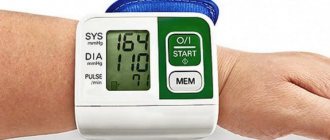
Increased blood pressure above 140 mm Hg. Art. with normal heart rate (<80 beats per minute):
- Take 1 tablet of Captopril (Capoten) 25 mg and place it under the tongue.
- We wait 1 hour. Ideally, within an hour the pressure will return to normal or be slightly lower than usual, there is nothing to worry about, since on average the effect of Captopril goes away within 4 hours after administration.
- If after 1 hour the pressure has not decreased or decreased less than 10 mm. Hg Art., then add 1 tablet of furosemide inside (not under the tongue); Within 1-2 hours, almost any increase in pressure will decrease.
Scheme No. 2
Increased blood pressure above 140 mm. Hg Art. when the pulse increases (>80 beats per minute)
We take Metoprolol (Egilok) 50 mg and put it under the tongue, for a faster effect, you can crush it with 2 dry tablespoons, wait 1 hour, then events can develop according to 2 scenarios:
- Scenario 1: a decrease in heart rate along with blood pressure - this is ideal.
- 2nd scenario: the pulse became, for example, 65 per minute, and the pressure remained as it was, for example, 160 mmHg..., in this case, we simply apply scheme No. 1 (i.e. capoten 25 mg under the tongue -we wait an hour, etc.)
Each of the drugs has contraindications and, as a rule, there are many of them, which is why there are doctors who can, without Wikipedia, select the optimal regimen for the patient, but we are now talking about situations in which it is not possible to receive this medical care.
Tachycardia due to high blood pressure: what is dangerous and what to do?
With high blood pressure, tachycardia can be observed - an increase in heart rate of more than 90 beats per minute. Olga Kononova, a methodologist at the Regional Center for Medical Prevention, spoke about the causes and possible consequences of this condition.
Various factors can provoke tachycardia with high blood pressure. These include increased body temperature, stress, physical activity, dehydration, hormonal imbalance, adverse weather conditions, and heart disease.
The combination of high blood pressure and increased heart rate is extremely dangerous for your health. Due to the destruction of red blood cells and the activation of the blood clotting process, thromboembolism can develop: a blood clot can block an artery and cause the death of the patient.
Also, if tachycardia is observed frequently, the immune system is suppressed due to metabolic disorders. In addition, the consequences of tachycardia in combination with high blood pressure can be the development of coronary heart disease and heart attack, fainting and, as a result, injury.
The prolonged course of such conditions leads to cardiogenic shock with a sharp drop in blood pressure with further death and sudden cardiac arrest.
Alarming symptoms include: palpitations, blurred vision, pounding headaches, dizziness, chest pressure, and pain radiating to the arms, back, and stomach area. In addition, dangerous manifestations include heaviness in the legs, weakness, drowsiness, disturbances in general condition, fainting, shortness of breath, numbness of the limbs and fingers.
In a condition of tachycardia in combination with high blood pressure, self-administration of drugs to lower the heart rate is not recommended, as this can lead to various consequences.
If the pulse is at the level of 90 - 120 beats per minute, a doctor's consultation is required.
However, it is important to know: if the pulse is over 120 beats per minute, you must immediately call an ambulance, especially if this condition lasts for more than two hours!
Before the ambulance team arrives, it is important to exclude any motor activity, take a sitting position, try to relax and calm down. But it is impossible to take a lying position in this state, since the blood circulation will be uneven and the risk of developing pulmonary edema will increase.
Even and slow breathing for 10 minutes, holding your breath as you exhale (5 seconds for each element of the cycle) can help. This will help not only lower your heart rate, but also your blood pressure. You can also take one sedative tablet based on herbal ingredients - motherwort or valerian, but not in alcohol form.
When you absolutely cannot capoten (captopril):
- Pregnancy (if you are pregnant and are prone to increased blood pressure and/or pulse, including other pathologies, then you, in principle, are not recommended to travel far from qualified medical care or at least very clearly understand the advice of your doctor in such situations). If there are no options to call the medical service, then you need to replace Capoten with Dopegit 250 mg. inside, not under the tongue. The standard maintenance dose of Dopegit® is 0.5-2 g/day in 2-3 doses, without further use of furosemide.
Increased blood pressure and pulse during pregnancy is, in general, a separate topic for conversation.
Captopril has other contraindications, such as severe dysfunction of the liver and/or kidneys, severe stenosis of the renal arteries, allergies (Quincke's edema), various valve stenoses, and electrolyte changes. But with a rare or one-time dose, severe harm will not occur, except for allergies (for example, Quincke's edema), but it is not realistic to predict here, the main criterion for allergic reactions is, precisely, the second time of taking the substance that causes the allergy, since the so-called sensitization or, in other words, the production of antibodies to this substance (this will not manifest itself in any way externally), but repeated exposure to the irritant provokes a number of allergic reactions, for example, urticaria, anaphylaxis, Quincke's edema, etc.
Drugs for the treatment of hypertension
Hypertension has many causes, which are explained by breakdowns in different organs and at different levels.
Pharmacologists are trying to find points of influence for each of them, so there are several classes of drugs for the treatment of hypertension. However, they should not always be used together, and some should absolutely not be combined.
Groups of drugs for hypertension
There are five main classes of medications for treating hypertension. Probably the most famous are β-blockers
(propranolol, carvedilol, metaprolol, nebivolol). They reduce the body's sensitivity to adrenaline and norepinephrine - hormones responsible for saving from danger and therefore increasing blood pressure and heart rate. Therefore, when taking β-blockers, blood pressure and heart rate (HR) decrease.
When is furosemide strictly forbidden?
- Renal failure with anuria (complete absence or urine output less than 50 ml per day)
- Pregnancy
- A pronounced disturbance of the outflow of urine of any etiology (including unilateral damage to the urinary tract), note: in the presence of kidney stones (if there is a history of urolithiasis), but at the time of increased blood pressure there are no signs of renal colic - furosemide is not contraindicated
- Decompensated mitral or aortic stenosis
- Severe electrolyte imbalance (including severe hypokalemia and hyponatremia)
- Severe liver failure, hepatic coma and precoma
When is it absolutely forbidden to take metoprolol (egilok)?
- AV blockade of the II and III degrees, sinoatrial block, in other words, pauses in heart contraction, usually more than 2 seconds (the presence of these abbreviations in your diagnosis or in the conclusion on the ECG and/or 24-hour monitor)
- severe sinus bradycardia (heart rate less than 50 beats/min)
Also note: metoprolol, unlike, for example, anaprilin, is allowed for bronchial asthma in small dosages.
And also, even in the presence of the above contraindications, but during an attack of severe tachycardia, above 100 beats per minute. (for example, with Tachy-Brady syndrome), anyway, B-blockers are often used, in particular metoprolol.
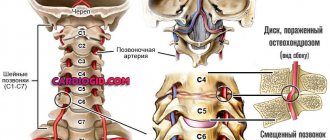
How is osteochondrosis related to tachycardia?
Today, every second inhabitant of the planet has problems with the spine. One of them is osteochondrosis, when the vessels of the spinal column are pinched, and the vertebrae sag and crumble. So it’s not far from a hernia. Therefore, it is important not only to make a correct diagnosis, but also to treat the cause of all problems.
How to determine the disease
Osteochondrosis is a destructive disease of the spine, when the vertebrae sag and the intervertebral discs become thinner. If previously it was believed that pathology occurs only in older people, after fifty years, that it was associated with a violation of the hormonal surge, now even twenty-year-old young people suffer.
The problem lies in a sedentary lifestyle, unbalanced diet, and lack of physical exercise. For treatment, in addition to medications, frequent walks are used, jogging is practiced at a convenient time of the day. Warm-up of the spine, in particular, bends and turns of both the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions. Proper nutrition. The food must contain calcium and phosphorus.
People who do not train the musculoskeletal system are at risk, since the muscular corset weakens, stooping develops, leading to curvature of the column, and this is how a problem arises.
We distinguish three types of disease:
- Cervical spine;
- Thoracic department;
- Lumbar.
The clinical manifestation is different, but the symptoms are approximately the same. This is soreness, muscle tension.
How it manifests itself
Each type has its own characteristics. Let us pay attention to the cervical and thoracic regions, since this is where tachycardia develops, around which this article is built. The curvature of the spine is to blame.
Cervical osteochondrosis is accompanied by headaches, migraines, pressure surges, tachycardia, and thoracic osteochondrosis disrupts the functioning of organs located in the thoracic region. Pain in the heart is frequent, it radiates to the shoulder blade and left arm, tachycardia occurs, the swallowing process is disrupted, shortness of breath appears, and breathing is difficult.
Since not everyone is aware that tachycardia and back pain are connected, they treat the symptoms, but not the disease itself.
Why does the heart beat faster?
Tachycardia is a consequence of the development of osteochondrosis in the cervical and thoracic spine. Often people do not understand that it is their back that needs to be treated. They think that the pulse increases only because the body is not trained. But, over time, the heart rate increases even with a sedentary lifestyle.
Tachycardia means an increase in heart rate, that is, the heart beats more than ninety beats per minute. What does the spine have to do with it? Let's look at it now.
Since back disease causes the discs between the vertebrae to wear out, the distance between them becomes smaller. When the disease is advanced, the distance is so small that the nerve endings and blood vessels are simply pinched. It is this process that causes back pain, as well as tachycardia.
Moreover, cervical osteochondrosis most often leads to increased heart rate, because this is where a large accumulation of blood vessels and nerve endings is located.
How to deal with the problem?
If your doctor has diagnosed you with tachycardia due to osteochondrosis, then you should be treated not only with medications, but also with physical exercise.
You can lower your heart rate by taking certain pills. We are talking about cinnarizine, piracetam, nitroglycerin, theobromine. To make your heart rate slower, you can take bisprolol or metoprolol. These drugs do not affect blood pressure in any way.
To address the root cause of the disease, you should think about your neck. So it would be right to make improvements in three areas:
- Loosen the spine, reducing the infringement;
- Establish blood circulation in the cervical region;
- Direct blood to the affected discs.
To do this, it is important to do massages, exercises, turns and head rotations.
Move more, taking breaks from sedentary work. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr