It is believed that heart rate (HR) and pulse are the same concepts. But it is not so. Heart rate shows the contractions per minute of the lower parts of the heart, its ventricles, and the pulse rate is the number of dilations of the artery at the moment of blood ejection from the heart. As the blood passes through the vessels, it creates a bulge in the arteries, which can be determined by touch and, by placing two fingers on the wrist or neck, the number of beats per minute can be checked. Correspondence between heart rate and pulse rate can only be found in healthy people.
What is arrhythmia?
Arrhythmia is a general name for cardiac diseases accompanied by a violation of the frequency or coordination of contractions of the heart - its atria and ventricles.
Depending on the specific changes in the functioning of the heart, arrhythmias are divided into:
- Tachyarrhythmias. Disorders in which all parts of the heart contract too quickly, that is, with a frequency of more than 100 beats per minute at rest.
- Bradyarrhythmias. Slowing the heart rate to less than 60 beats per minute.
- Extrasystoles. A group of arrhythmias in which an extraordinary, additional contraction occurs in parts of the heart.
- Fibrillations and flutters. A type of rhythm disorder in which the atria and/or ventricles begin to contract at a high frequency (from 300 beats/min or more). In this case, the coordination of work between the parts of the heart is disrupted.
- Blockades. Cardiac conduction disorders, in which, out of general ri, cardiac contractions of certain parts of the myocardium.
What can the pulse be like during arrhythmia?
The pulse with arrhythmia may be slow and rapid. Too fast a pulse is tachycardia, which is characterized by:
- pulse exceeds 90 beats per minute;
- an insufficient amount of nutrients reaches the heart tissues;
- the ventricles of the heart do not have time to fill with blood in sufficient volume;
- the performance and functionality of all organs and systems deteriorate.
Bradycardia, or slow pulse, is the number of beats no more than 50 per minute. This condition is considered less dangerous to human life, although it indicates an excess of potassium in the body.
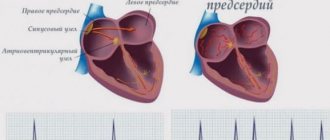
Atrial fibrillation is the most dangerous condition in which the pulse rate can reach 700 beats per minute and be completely irregular. This condition is a consequence of erratic contraction of the heart muscles - the work of the atria is not consistent with the activity of the ventricles. Atrial fibrillation is a direct path to vascular thromboembolism.
Indicator 60
A pulse rate of 60 beats per minute is considered the lower limit of normal; some doctors classify this condition as incipient bradycardia. It does not pose a danger to the health, much less the life of the patient. Experts generally do not consider such indicators as deviations from the norm.
Elevated
An increased pulse during arrhythmia occurs for the following reasons:
- atrial extrasystole - the heart contracts prematurely because impulses from the atria arrive at the wrong time, symptoms: severe pallor of the skin, a feeling of lack of air, darkening in the eyes;
- atrial tachycardia - the rhythm increases in short-term attacks, characteristic of heart defects, hypertension and obesity, symptoms: dizziness, shortness of breath, panic attacks;
- atrial flutter - a pulse rate of more than 200 beats per minute, this is associated with a sharp rise in pressure and heart disease, symptoms: pain in the chest, shortness of breath, a feeling of anxiety.
The most harmless condition is atrial tachycardia, while the other two can lead to a heart attack, acute disturbance of blood flow and cardiac arrest.
Can this happen with a normal heart rate?
With an absolutely normal pulse, arrhythmia can also occur, but it is always associated with physiological reasons:
- measurements are taken immediately after eating;
- the person recently drank a cup of strong coffee;
- shortly before the measurements there was consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- the person is worried and stressed;
- relatively recently there have been physical activities.
Normal pulse
In the vast majority of observations, the heart of an adult at rest beats at a rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute. However, there are also other variants of the norm, for example, in people involved in aerobic sports (long-distance running, cycling, swimming), there is a tendency to bradycardia - a slow heartbeat.
In children, the normal heart rate differs significantly depending on age (Fig. 1):
- Newborns and children up to 3 months - 100-150 beats per minute.
- From 3 to 6 months - 90-120 beats/min.
- From 6 months to 1 year - 80-120 beats/min.
- Children aged 1 to 10 years - 70-130 beats/min.
Figure 1. What pulse is considered normal. Source: MedPortal
How to measure your pulse?
The pulse can be determined independently on any of the arteries, but the most convenient for this are: the radial, carotid and dorsal arteries of the foot (Fig. 2).
The radial artery is located on the inside of the forearm, closer to the thumb. The carotid artery runs along the lateral surface of the neck, 2-3 cm away from the midline, along the inner edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The dorsalis pedis artery can be felt on the back of the foot, along a line running from the space between the first and second toes.
To count the pulse, you need to slightly press the corresponding artery and count its pulsations for 1 minute.
Figure 2. Places of pulse measurement: radial, carotid artery, dorsal artery of the foot. Source: MedPortal
Causes of arrhythmia in women and men
Arrhythmias, in most cases, develop against the background of other myocardial lesions and concomitant disruption of the conduction system of the heart. In this case, dysfunction of both the cells that generate the impulse and those that conduct it through various parts of the organ is possible. Most often this is:
- Coronary heart disease and its complication in the form of myocardial infarction.
- Cardiomyopathy - thickening or thinning of the walls of the heart, their deformation, excessive expansion of the atria or ventricles.
- Congenital defects of the heart and its valves.
- Inflammation of the heart and its membranes - myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis.
- Previously undergone heart surgery.
Separately, provoking factors are identified that directly or indirectly contribute to the occurrence of heart rhythm disturbances. These include:
- Arterial hypertension and heart failure.
- Severe infectious diseases that can affect the heart: diphtheria, streptococcal tonsillitis, etc.
- Endocrine diseases: hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism (excessive and insufficient production of thyroid hormones), diabetes mellitus.
- Chronic stress and psycho-emotional stress.
- Bad habits: abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products.
- Taking certain medications from the antidepressant group, including antipsychotics and antiarrhythmic drugs.
- Hereditary tendency to arrhythmias.
In women, arrhythmias can be associated with sharp hormonal fluctuations, for example, during the first menstruation, pregnancy, transition to menopause, as well as with uncontrolled, improper use of oral contraceptives.
Diagnosis of arrhythmia
Diagnostics allows the doctor to study the patient’s condition, determine the type of arrhythmia and prescribe the necessary treatment. If arrhythmia is suspected, a comprehensive examination is carried out, the main stages of which are the following diagnostic methods:
- echocardiography
- general blood tests, urine tests, biochemical blood tests, including thyroid hormone tests
- 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring
- electrocardiography at rest and during exercise
- general examination of the patient, questioning the patient regarding complaints, time of onset of the first attack, concomitant diseases, medications taken
The doctor may prescribe other tests depending on the presence of the underlying and concomitant diseases. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by cardiologists, but consultation with other specialists - an endocrinologist, neurologist or cardiac surgeon - may also be necessary.
First signs of heart problems
Often the first signs of heart rhythm disturbances are invisible to a person or are associated with other disorders or conditions, for example, fatigue after a working day.
Photo: Koldunov / Depositphotos
Early signs of arrhythmias may include:
- More frequent headache attacks.
- Chest discomfort and shortness of breath during exercise.
- Insomnia and sudden awakening in the middle of the night with shortness of breath.
- Tremor in the extremities - slight tremors in the fingers and hands.
Measurement Rules
You can measure the pulse rate and detect arrhythmia using an ECG or tonometer, but the easiest way to do this is as follows:
- Find the point on the inside of the wrist where the pulse beats are especially pronounced.
- Press the 2nd and 3rd fingers of your free hand to this place, wrap your thumb around the hand.
- Count the number of beats in 60 seconds.
Measurements must be taken taking into account the following nuances:
- After eating, at least an hour and a half should pass;
- the person must be in a sitting or lying position;
- you need to relax and restore your breathing;
- any physical activity (even walking) is excluded 30-40 minutes before measurements.
How to recognize an attack of arrhythmia?
During an attack of arrhythmia, as a rule, there is an inability of the heart to provide normal blood circulation in the body. Therefore, its manifestations are more noticeable, and most often they are the reason for visiting a doctor.
Arrhythmia attacks can occur spontaneously, but quite often they are associated with external influences: prolonged and/or intense physical activity, stress or emotional shock, an episode of smoking or drinking alcohol, a long period of lack of sleep, etc.
The main signs of an arrhythmia attack are:
- Unreasonable feelings of weakness, anxiety, fear.
- Severe weakness, dizziness, feeling of “woolly” legs.
- Discomfort or moderate pain in the heart area, behind the sternum. Often attacks are accompanied by distinct sensations of rapid heartbeat and interruptions in heart function.
- Presyncope or loss of consciousness.
What to do if you have an arrhythmia attack?
First of all, you should take medications previously recommended by your doctor for such cases, while continuing to monitor your condition. If normal heart rhythm is not restored within 1-2 days, you should seek help from a medical facility on an empty stomach. In the absence of previously received recommendations and a significant deterioration in general condition, you should immediately contact emergency medical services.
How to treat to stabilize the heart
The easiest way to restore the pulse rhythm is at a reduced frequency - bradycardia is corrected by drinking a cup of strong coffee or applying mustard plaster to the chest area. But it is strictly forbidden to use mustard plaster on the area of the anatomical location of the heart - this is fraught with a sharp increase in heart rate and ventricular fibrillation.
An increase in heart rate can be adjusted independently only if it happened spontaneously and literally for the first time. You can stop an attack of arrhythmia:
- tincture of peony, valerian or motherwort;
- breathing exercises;
- neck massage on both sides in the area where the carotid arteries are located;
- by relaxing in a lying position with your eyes closed.
In case of repeated attacks of arrhythmia, regular occurrences, it is necessary to undergo examination by a cardiologist and receive medication prescriptions. Most often, doctors recommend taking Bisoprolol or Cordarone as a course, but these drugs are strictly contraindicated for self-administration.
There are different types of arrhythmia, not all of them are dangerous to human health and life. Bradycardia is considered the most harmless, and tachycardia and atrial flutter must be monitored by specialists and treated.
Symptoms of arrhythmia
The clinical manifestations of arrhythmia are quite varied and largely depend on the specific form of cardiac arrhythmia. In men and women, the signs of arrhythmia, as a rule, do not differ from each other. Also, during the periods between attacks, symptoms of the disease may be completely absent.
Most often, the main signs of arrhythmia are:
- Attacks of weakness and decreased performance.
- Inability to perform physical work due to shortness of breath and discomfort, pressure behind the chest.
- Frequent headaches and dizziness.
- A feeling of spontaneous acceleration or deceleration of the heartbeat, episodes of “fading” of the heart.
When to see a doctor?
The reason to contact a cardiologist or therapist should be the first attack of arrhythmia or the previously described first signs of cardiac dysfunction.
You should also sign up for a consultation if you have risk factors, independently identify pulse anomalies: its increase over 100 beats per minute, slowdown less than 60 beats per minute, the phenomenon of “pulse deficiency” - a discrepancy in heart rate (which can be felt by placing your palm on the area heart) and contractions of the peripheral artery.
Photo: zinkevych / freepik.com
BY THE WAY
Experts give the following advice on preventing arrhythmia:
- To keep your heart working smoothly, include oranges, pears, raspberries, and currants in your diet. In winter, let it be frozen berries, it’s still good. The diet should also include red sweet peppers, tomatoes, beets, parsley, apples, and corn;
- a very healthy mixture of honey, walnuts, lemon, dried apricots and raisins. These products contain a lot of potassium, magnesium, calcium, which are needed for normal heart function;
— for arrhythmia and cardiovascular diseases, it is better to drink mint tea. Mint relieves irritability and calms. In this case, you should keep the liquid in your mouth longer and drink it in small sips. You could also take a mint candy before bed;
- An infusion of viburnum berries is also useful. It contains a large amount of vitamin K, which has a beneficial effect on the heart and blood vessels and normalizes cardiac activity. Viburnum is also rich in vitamin C, which strengthens the immune system, and vitamin P, which is necessary for the body to absorb ascorbic acid. This is why viburnum is indispensable for high blood pressure. The recipe is simple:
Pour 1 cup of fruit with 1 liter of hot water, put on low heat and let boil for 10 minutes. Then strain and cool. Drink half a glass three times a day;
— what about coffee? Scientists have come to the following conclusion: if a strong coffee overdose can lead to arrhythmia, then a couple of cups of good grain coffee a day, as it turns out, for some reason stabilize the heart rhythm. This mainly concerns atrial fibrillation.
#diseases #heart #health
The material was published in the newspaper “St. Petersburg Vedomosti” No. 094 (6692) dated 06/03/2020 under the title “If the heart beats out of sync.”
Share on VKontakte Facebook
Cool
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmia
Before starting treatment, a comprehensive examination is always carried out, since not only the tactics of doctors, but also the feasibility of restoring normal heart rhythm in general may depend on the presence of certain individual characteristics of a person and concomitant diseases.
The diagnosis of arrhythmias and other cardiac diseases is based on: electrocardiography (ECG) (Fig. 3), 24-hour Holter monitoring, ultrasound of the heart and a number of laboratory tests (lipidogram, coagulogram, etc.).
Figure 3. Arrhythmia on the electrocardiogram. Source: MedPortal
Drug therapy
Depending on the form of rhythm disturbance, the patient is prescribed various classes of antiarrhythmic drugs, as well as β-blockers, calcium antagonists, cardiac glycosides, etc. They are used both for drug cardioversion (restoring normal heart rhythm) and for the prevention of new attacks.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is resorted to when it is impossible to restore the heart rhythm with medications or there are contraindications to the use of necessary drugs.
The purpose of surgical intervention for extrasystoles and fibrillations is to remove a section of the myocardium that creates pathological impulses that disrupt the normal sequence of contractions of sections of the heart.
Another option for operations that are used for blockades is the installation of an artificial pacemaker - a pacemaker. Its function is to compensate or replace the cells that normally generate the impulse that triggers heart contraction.
Additional drugs
Depending on the existing diseases and disorders, the treatment regimen for arrhythmia may include:
- herbal sedatives,
- vitamin complexes,
- antihypertensive drugs.
Also, for arrhythmias, anticoagulants are often used - a group of medications that prevent the formation of blood clots, protecting against strokes and heart attacks.
Arrhythmia - symptoms and treatment
First aid for an arrhythmia attack
First aid measures depend on the specific arrhythmia, and its type can only be determined by a doctor. Therefore, you should not self-medicate, you need to seek medical help.
Is it possible to cure arrhythmia?
Cardiac arrhythmias vary greatly in prognosis. Some are completely harmless, and some are dangerous. Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias is not always required. First, treatment is appropriate when arrhythmia reduces quality of life. Secondly, it makes sense to treat those arrhythmias that worsen the prognosis, that is, they can lead to premature death or other complications (and the reality of such complications must be proven in clinical studies). Accordingly, asymptomatic cardiac arrhythmias that do not lead to any sensations are not treated in most cases.
In addition, the doctor must try to establish what caused the arrhythmia, and then prove the connection between the suspected causative factor and the arrhythmia itself.
When the decision about the need to treat a particular cardiac arrhythmia is made, the question arises of how to treat it.
Surgery
For many decades, the doctor had no other treatment options for heart rhythm disorders other than medication. Rare exceptions include electrical shock therapy, which delivers a shock using an external defibrillator in a critical situation to eliminate a life-threatening arrhythmia, and transesophageal electrical stimulation of the heart to eliminate some supraventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Since the 90s of the last century, and in Russia since the 2000s, a new treatment method has appeared that is effective for many cardiac arrhythmias - radiofrequency ablation (RFA). The method allows in many cases to permanently relieve the patient of the need to take medications to treat arrhythmias. The essence of the method is a local radiofrequency effect on the source of arrhythmia or on the pathological path of electrical impulse circulation in the heart. The procedure is carried out using a catheter passed to a specific area in the heart through a puncture in a vessel (usually in the thigh). Due to the effect through the tip of the catheter, local heating of the heart muscle area occurs up to 70 °C. As a result, in this place there is a local death of cells involved in the unwanted generation of impulses or in their unwanted conduction. Thus, the conditions for the occurrence and maintenance of certain cardiac arrhythmias, for example, ventricular tachycardia, disappear.
Almost all supraventricular tachyarrhythmias can be treated with RFA: atrioventricular nodal tachycardia, tachycardias involving accessory pathways, atrial flutter, focal atrial tachycardia, and, with less success, atrial fibrillation.[9] In addition, this method treats many types of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular extrasystoles, if it is very frequent (tens of thousands of extrasystoles per day) and comes from one focus.[10]
Another high-tech treatment for potentially fatal ventricular arrhythmias is implantation of a cardioverter defibrillator.[10] This device is capable of eliminating already developed ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation in two ways: by electrical stimulation of the ventricles at a rhythm exceeding the tachycardia rhythm, or by applying a fairly powerful electrical discharge, which is quite painful, but saves lives. Thus, a cardioverter-defibrillator is used in cases where there is a real risk of sudden death due to ventricular arrhythmias.[13]
Electrocardioversion
Electrical cardioversion (defibrillation) is used when the arrhythmia sharply worsens the patient's condition and is accompanied by a significant drop in blood pressure. It is also sometimes performed routinely to restore sinus rhythm if atrial fibrillation persists.
Pharmacotherapy
However, in many cases, cardiac arrhythmias are treated with medications. Most often, antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed in the case of atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation), in which case the effectiveness of RFA is not so high. Another situation in which antiarrhythmic drugs are often used is frequent premature beats (thousands or tens of thousands of untimely heartbeats per day) accompanied by symptoms. Less commonly, the drug method is used to treat other arrhythmias - for example, ventricular tachycardia, supraventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Unfortunately, few antiarrhythmic drugs are registered in Russia compared to Europe or the USA. Available in our country are “Novocainamide” (still used for intravenous administration in the emergency treatment of paroxysms of atrial fibrillation and rarely ventricular tachycardia), “Lidocaine” (for intravenous administration for ventricular tachycardia), “Etatsizin”, “Allapinin” and “Propafenone”. " These drugs exist in the form of tablets and are prescribed for long-term use in order to prevent the occurrence of a wide range of ari in the form of tablets and solution is also used to eliminate paroxysms of atrial fibrillation - a universal antiarrhythmic drug, but is used mainly as a backup antiarrhythmic. But it can be prescribed for organic damage to the heart (previous myocardial infarction, low cardiac contractility, severe left ventricular hypertrophy, etc.), while Etatsizin, Propafenone and Allapinin cannot be used in these conditions.[11]
Sotalol is an antiarrhythmic drug to prevent attacks of atrial fibrillation, as well as ventricular arrhythmias. Available in tablets.
Another class of drugs for arrhythmia are calcium antagonists - Verapamil and Diltiazem. They are used for some supraventricular tachyarrhythmias, both for long-term use in tablets and to eliminate developed attacks of arrhythmias with a high heart rate.
Beta-blockers form an independent class of antiarrhythmic drugs, although their direct antiarrhythmic activity is low. Their main effect is their ability to reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death, mainly in people with low cardiac contractility and associated heart failure.[11] The most studied in this regard are Metoprolol succinate, Bisoprolol, Carvedilol and Nebivolol.
In the treatment of atrial fibrillation and flutter, the most important place is occupied by antithrombotic drugs, which reduce blood clotting and thereby reduce the risk of blood clots (in these cardiac arrhythmias it is increased). These are Warfarin, Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban, Apixaban, Edoxaban. Accordingly, taking these medications reduces the risk of stroke associated with thromboembolism.
Lifestyle
Some arrhythmias are provoked by stress, abuse of coffee and caffeine-containing drinks, smoking, lack of sleep, physical activity and taking certain medications. Therefore, the doctor first of all looks for a cause-and-effect relationship between lifestyle factors and the occurrence of arrhythmia. Sometimes the patient himself notices this connection. In such cases, if you eliminate the provoking factor, you can get rid of the arrhythmia. However, it is not always possible to detect such a connection.
Folk remedies
If you suspect an arrhythmia, you should consult a doctor, get diagnosed and adhere to the prescribed treatment. Traditional methods of therapy are not scientifically substantiated and can be hazardous to health. Without adequate treatment, arrhythmia can cause serious complications: angina pectoris, myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke.
Contraindications to restoring heart rhythm
In a number of situations, the risks associated with restoring normal heart rhythm outweigh the benefits that will ultimately be gained. In such situations, maintenance therapy is carried out aimed at preventing complications and controlling the heart rate within certain limits.
Contraindications to restoring normal heart rhythm are:
- Persistent forms of atrial fibrillation and a high risk of thromboembolism.
- Severe concomitant heart diseases, for example, a previous myocardial infarction.
- Liver and kidney failure, complicating drug treatment.
- Severe arterial hypertension.
- Severe heart failure.
- Elderly age.
- Heart defects.
Prevention
Photo: stangro / freepik.com
Prevention of arrhythmia includes early treatment of diseases of the heart, cardiovascular system and related pathologies. This also includes avoiding or minimizing exposure to risk factors.
- Healthy sleep and adherence to work and rest schedule.
- Quitting the use of alcohol and tobacco products.
- Regular, moderate physical activity.
- Compliance with the dosage and frequency of taking previously prescribed medications. Refusal to self-use medications.
- Regular preventive examinations with a cardiologist or therapist.