Lower pressure 60 mm Hg. Art., what does this mean?
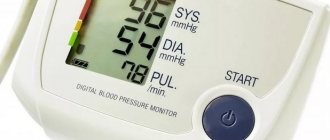
Tonometry is an important procedure that gives doctors a lot of information about a person’s condition. When measuring blood pressure, the tonometer shows two main values - upper and lower.
Upper blood pressure is called systolic (cardiac). It shows the resistance of the vascular wall of the arterioles at the time of blood ejection by the heart muscle.
The lower blood pressure is called diastolic (renal). Its indicator is the force of influence of the liquid component of blood on the walls of blood vessels when the myocardium is relaxed.
The third significant indicator of tonometry is pulse pressure, which is the difference between upper and lower blood pressure.
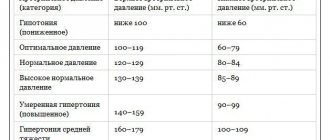
The normal level of these indicators for people after twenty years of age is determined by WHO experts within the boundaries:
- 110 -139 mm Hg. Art. – upper blood pressure;
- 70 – 89 mm Hg. Art. – lower blood pressure;
- 40 units – pulse blood pressure.
Any deviations from these figures may be interpreted as an anomaly. Whether it indicates a disease or not is determined by the doctor based on a number of specific signs after an examination, taking into account the possible influence of negative factors.
Thus, 60 mmHg. Art. for diastolic pressure, this is a downward deviation. Indicators below the officially accepted ones are usually classified as hypotension.
If systolic and diastolic pressure levels are reduced for a long time, typical hypotension is diagnosed. When only the diastolic indicator is reduced, we are talking about isolated hypotension.
Hypotension is not always a pathology that requires correction. Sometimes it is a variant of the physiological norm, or is caused by objective physiological reasons, the elimination of which will lead to normalization of the condition.
Diagnostics
Doctors of different specialties, often in tandem, study the causes of pathology and manage patients: cardiologists, neurologists, nephrologists and endocrinologists.
The full list of studies is as follows:
- Study of patient's health complaints. Equals identifying symptoms. Everything, even seemingly insignificant facts, is taken into account.
- Collection of individual and family history.
- Measuring blood pressure and heart rate on both arms.
- Daily monitoring using an automatic programmable tonometer.
- General blood test, biochemical, for hormones (T3, T4, TSH, LH, prolactin, cortisol, etc.).
- Electrocardiography. Provides comprehensive information about the functional activity of the heart. It is important to correctly interpret the results, which, unfortunately, in practice turns out to be a big problem for inexperienced doctors.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasound examination of the heart.
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck and head.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys.
Other studies are also possible. At the discretion of the physician group.
Physiological causes of diastolic hypotension
Hypotension with lower blood pressure readings of 60 mm Hg. Art. can be detected in both healthy and sick people. Experts call the physiological reasons causing the condition:
- Puberty. The hormonal characteristics of adolescents are accompanied by abnormalities in hemodynamics and heart rate. This leads to a typical or isolated form of hypotension, which occurs in thin, tall adolescents (usually girls).
- Advanced age. A slight decrease in indicators is explained by deterioration in the functioning of the heart and brain due to circulatory problems, which causes insufficient nutrition of tissues and organs.
- Changes in hormonal levels in women. A similar condition accompanies pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause. As a rule, it does not require drug correction. The exception is pathological menopause, accompanied by a serious deterioration in well-being.
- The body's need to adapt. Such hypotension is typical for professional athletes, workers in hazardous industries, and tourists visiting countries with an unusual climate.
A decrease in diastolic indicators in the above cases can occasionally affect general well-being, which requires special measures to be taken. But usually, it does not manifest itself in any way, therefore, the person feels quite healthy.
Feeling unwell due to decreased blood pressure is much more common. This is explained by the manifestations of diseases that cause hypotension.
In what case are these indicators considered normal?
Strictly speaking, this is not the norm in all cases. But it is possible for diastolic blood pressure to decrease for physiological reasons.
Such factors are not associated with pathology, and therefore do not require correction except in exceptional cases.
What cases do we mean:
- Senile age or old age. In the adult age group, physiological hypotension occurs somewhat more often than the population average.
This is explained by changes in the nature of hemodynamics (blood flow) over the years. But this is not always the case.
Much more often in elderly patients hypertension occurs, that is, the reverse process with an increase in blood pressure.
Asymmetry in tonometer readings is also explained by age and general changes in the body.
- Youth. In adolescence, hardly anyone can be surprised by low tonometer readings. Moreover, both girls and young people suffer equally often from isolated and typical forms of hypotension.
We are talking about puberty or puberty. As a result of changes in the concentration of estrogens and androgens in the body, real hormonal storms begin, accompanied by disturbances in the processes of regulation of hemodynamics and heart rate.
Hence possible problems with blood pressure. In most cases, help from doctors is not required, but you need to be observed by a cardiologist.
- Pregnancy, menstrual cycle and menopause. Classic women's problems. During all periods of peak hormonal conditions, disturbances in the regulation of vascular tone are possible. This is most noticeable in pregnant women.
Usually the process goes away on its own after delivery. The same applies to the menstrual cycle, but with menopause everything is more complicated.
Medication correction is required, although the attenuation of reproductive function is not considered a pathology.
- Long stays in hot and humid climates, work in hot enterprises. Such patients develop a protective mechanism. Reducing blood pressure is vital and cannot be corrected.
- Professional sports, especially running. Accompanied by hypertrophy (growth) of the heart and the body's fitness.
In professional athletes, blood pressure is consistently low, as is the heart rate.
But such preparedness and adaptation of the body to peak loads can play a cruel joke: in the absence of physical activity of the same intensity, spontaneous cardiac arrest, the development of coronary artery disease, congestive failure and even a heart attack are possible.
- Acclimatization. Most often observed among tourists who come to unusual environmental conditions.
This is not a complete list. Physiological factors are common; a lower pressure of 60 is also possible for pathological reasons.
Pathological causes of decreased blood pressure
Some diseases and pathological conditions can become factors causing a decrease in diastolic pressure to 60 mmHg. Art. and below. Among them:
- kidney disease with insufficiency of renin synthesis (more often, this is typical hypotension);
- adrenal gland problems with insufficient cortisol synthesis (Addison syndrome);
- pathologies of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism), pituitary gland;
- early period of a heart attack, stroke;
- TBI;
- disorders of the musculoskeletal system, cervical muscles (fibrosis, myositis, intervertebral hernia);
- anemia;
- massive bleeding;
- tumors of different locations;
- cardiomyopathy;
- severe infections (tuberculosis, syphilis);
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (prolonged diarrhea, vomiting);
- mental instability (neuroses, depression).
Hypotension can occur as a consequence of prolonged use of drugs to lower blood pressure prescribed for hypertensive patients, diuretics. This especially often occurs due to self-medication or exceeding prescribed doses.
Why is this condition dangerous?
Figuratively speaking, a pressure of 60 mmHg is the edge of a knife. A slight downward movement is enough for a critical moment to occur.
The dangers of excessively low diastolic pressure include:
- Fainting. They may occur at a dangerous moment: while driving a vehicle, when working with machinery, climbing stairs, etc.
- Heart attack. A sharp disturbance in the trophism (nutrition) of the myocardium. Accompanied by a decrease in cardiac output and tissue necrosis. Possible death or disability, at a minimum. Read about the symptoms of a pre-infarction condition in this article.
- Stroke. The process of ischemia of brain tissue. Often leads to the formation of a persistent neurological defect, depending on the focus of the process (in the occipital lobe of the brain - cortical blindness, etc.). Read a detailed description of the symptoms of a pre-stroke condition here.
- Congestive heart failure.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Persistent arrhythmias. That is, heart rhythm disturbances, often of the bradycardia type.
- Early dementia, decreased cognitive function.
- Cardiac arrest (asystole).
Attention:
According to some data, patients with hypotension, including the isolated type, are more susceptible to organic changes in the brain: schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
A decrease in blood pressure is not always asymptomatic. Sometimes it is accompanied by unpleasant or painful symptoms that require consultation with a specialist. These include:
- prolonged throbbing headaches;
- dizziness, coordination problems;
- deterioration in sleep quality;
- exhaustion;
- irritability, apathy;
- menstrual dysfunction;
- decreased sex drive;
- blurred vision;
- fainting;
- extraneous noises in the head or ears.
With a sharp drop in indicators to critical levels, a symptom complex very similar to the consequences of a stroke may occur:
- unilateral paresis (face, limbs);
- sensation of goosebumps;
- speech disorders;
- passing blindness (partial or complete).
This condition is considered an emergency. It requires immediate hospitalization of the patient and intensive care.
Forecast
The prognosis is favorable if early treatment is started. The duration of the process is associated with resistance (immunity) to therapy and an unfavorable prognosis.
Everything needs to be done on time before it’s too late. In particularly difficult cases, there is still hope for a complete cure and getting rid of the problem.
Blood pressure with a diastolic reading of 55-60 is hypotension. There is no talk about the norm. The doctor decides how to deal with it, but only after an examination.
It is important not to miss the moment and follow all the recommendations of specialists. You also need to be patient.
What to do: treatment features
Treatment of hypotension with a lower pressure of 60 mm Hg. It is necessary only if your health deteriorates significantly or if unpleasant or painful symptoms appear.
The first step to recovery should be a visit to a general practitioner. He will be able to refer you to more specialized specialists - a cardiologist, endocrinologist, urologist, neurologist. You should also prepare to undergo detailed diagnostics and undergo laboratory tests.
To relieve the symptoms of hypotension, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease that caused it. To alleviate the condition, symptomatic drug therapy is prescribed. Can be used:
- analeptics;
- alpha adrenergic agonists;
- adaptogens;
Also prescribed are medications that include caffeine and can help in a very short time - Citramon, Caffetamine, Saparal. The drugs are recommended in limited dosages so as not to provoke the onset of hypertension.
To stabilize the level of lower pressure, physiotherapy may be recommended - massage, electro-, water- and magnetic therapy, aromatherapy.
In some cases, professional psychological help is necessary.