Extrasystole is called untimely depolarization and contraction of the heart or its individual chambers. This is the most frequently recorded type of arrhythmia. Extrasystoles can be found in 60-70% of people. But what is the situation with the draft and are they recruited into the army with extrasystole? A note from a cardiologist about the presence of extrasystole does not yet indicate the presence of significant disruptions in the functionality of the body. Rhythm disturbances can occur even in completely healthy people; for this reason, suitability for service is determined according to certain conditions.
Are they recruited into the army with ventricular extrasystole?
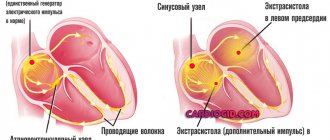
With ventricular extrasystole (one of the types of cardiac arrhythmia), untimely contractions of the ventricles of the heart occur - in other words, such contractions are called extrasystoles. This phenomenon does not always indicate certain diseases; extrasystole in some cases can also occur in absolutely healthy people.
Experts from the draft commission do not consider ventricular extrasystole as a disease. For this reason, all young men with a similar diagnostic conclusion are drafted into the army. Doctors claim that vegetative-vascular dystonia and neurosis are an unqualified diagnosis of other diseases with such symptoms, for example: diseases of the nervous system and psyche, possible heart disease, hypertension, improper functioning of the vascular system.
For this reason, doctors from the military commissariat sign up and take the young man to serve, believing that a healthy diet in the army, regular stay in the fresh air, daily routine and physical activity will cure those suffering from ventricular extrasystole.
Passing a medical examination
A rapid heart rate is not considered a pathology that exempts you from service. Therefore, it is recommended that before visiting the military registration and enlistment office you go to the hospital to obtain an extensive report. The diagnosis must comply with the Schedule of Diseases.
This list changes every year - medicine develops, new medications are produced and some pathologies cease to be dangerous. The conscript must have a package of documents (especially if he is registered with a cardiologist) confirming his inability to join the ranks of the armed forces.
Do they take into the army with cardiac extrasystole?
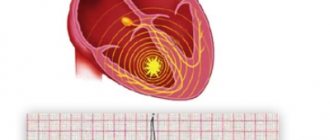
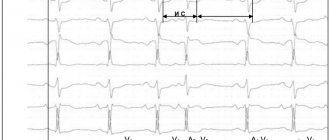
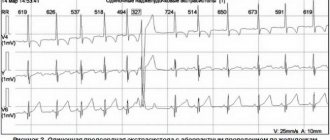
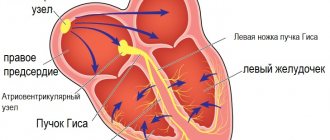
It is believed that this is the most common type of arrhythmia. Extrasystole has the characteristic of increasing the automaticity of individual zones of the myocardium (premature contractions of the heart). It is provoked by an excitation impulse that appears in the focus of heterotropic automatism. There are certain types of extrasystoles depending on the response of the atria. Before answering the question about the suitability of a conscript with extrasystole, you should understand the method of examination for such a disease. The classification is presented below.
According to the Schedule of Diseases, the classification according to Laun and Wolf is used:
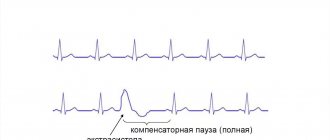
- Degree 1 – monomorphic extraordinary contractions are recorded (no more than 30 per hour of observation);
- Degree 2 – contractions occur more frequently, from one focus (more than 30 per hour);
- Degree 3 – polytopic extrasystole;
- Degree 4 – divided from the ECG rhythm pattern;
- Degree 5 – the most dangerous type “R on T” in a prognostic sense is registered, which means that the extrasystole “climbed” onto the previous normal contraction and can lead to rhythm disturbances.
In addition, a “zero” degree is allocated for people who do not have extrasystole.
The intensity of symptom expression will be personal. Typical signs of extrasystole:
- Feeling of heart sinking;
- Interruptions in rhythm;
- Strong tremors in the chest.
In addition, hot flashes, shortness of breath, weakness, feelings of anxiety and discomfort may occur. If the disease occurs in an intense form, then the internal organs will feel a lack of oxygen, especially the coronary, cerebral and renal circulation is reduced. Extrasystole can cause dizziness, angina attacks and fainting.
According to the Schedule of Diseases, Article 42, those young men who have a classification of the degree of ventricular extrasystole according to the Laun-Wolff gradation of 3-4 are exempt from service with the assignment of category “D”. This diagnostic conclusion can only be made by a cardiologist after a thorough examination of the heart’s activity. Persons with severe symptoms of extrasystole will not be hired for service due to sudden complications or cardiac arrest.
Advice for conscripts
In order to have sufficient grounds to confirm the diagnosis of extrasystole, you need to take care of collecting documents in advance, and not do it at the last moment. Therefore, it is recommended to do the following simple steps:
- if you experience a feeling of a sinking heart, interruptions in its rhythm, strong tremors in the chest, do not ignore these facts, but immediately go to a cardiologist to make a diagnosis and record it in documents;
- if symptoms recur, you need to register at the cardio-neurological center. Then you won’t have to collect certificates - the dispensary itself will send them to the military registration and enlistment office at his request with a diagnosis of “extrasystole of class 3-4.” If a young person is not registered, he may not receive category “D”, but may be sent for examination and treatment;
- When undergoing a medical examination at the military registration and enlistment office, it is important to obtain a referral for additional examination at a cardiac dispensary.
A complete diagnosis will show what awaits the patient with extrasystole - the army or liberation from it.
Fitness category with extrasystole
The fitness category is determined by the Schedule of Diseases. A conscript whose complaints are determined by the state of ventricular extrasystole by the commission may not be allowed to serve. However, for this purpose, it is required at the time of passing the medical commission to have in hand the appropriate documentation that will prove this diagnosis.
With problems of this type, according to the Schedule of Diseases and Article 42 of the army, a conscript will be released with fitness category “D”.
Extrasystole and the army
According to Article 42 of the “Schedule of Diseases”, the army and extrasystole are compatible in most cases. Patients with functional extrasystole after drug treatment are recruited for military service on a general basis.
If there is evidence of the stability of the pathology and manifestations of extrasystole of an organic nature, then conscripts with heart rhythm disturbances can receive an exemption from military duty in accordance with the severity of the anomaly.
If you have doubts whether you can count on exemption from the army or service without restrictions due to health conditions, it is better to consult with an experienced military lawyer who will help you understand the nuances and develop the right course of action.
How does the military medical commission make a decision on the fitness of a conscript?
Cardiologists distinguish 2 types of extrasystole: functional and organic. Often young people have type 1 disorder. In this case, arrhythmia is caused by stress, emotional and physical stress, and drinking alcohol, coffee or energy drinks. The pathology of heart contractions, as a rule, does not pose a danger to young men and in most situations does not require therapy: as soon as the condition that provoked the syndrome is eliminated, the heart rhythm will return to normal. Organic type disorders appear with significant cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction, ischemic disease, cardiac muscle dystrophy. As a rule, this type of disease is typical for the population over 40-60 years of age.
The second criterion that determines the relationship between extrasystoles and service is whether the extrasystoles are amenable to therapy. They will accept service if the disorder can be easily eliminated with the help of medications or goes away on its own. In order to be released from the army, one must also prove that the violation is of a persistent nature.
Another factor on which the future of a conscript citizen depends is the classification of the violation. The decision on suitability is made after comparing the specialist with the Lown-Wolf characteristics, which were given above in the article.
About pathology
Tachycardia is an increase in heart rate caused by vigorous activity, taking tonic drinks, emotional outbursts, exposure to climatic factors or taking certain medications. The heart rate exceeds 90 beats per minute and can reach 150 beats or higher.
It will be difficult for a guy with cardiac tachycardia to perform all physical activities at the same level as his colleagues. An intensive training program can worsen health conditions, even being life-threatening. However, tachycardia is not a guarantee of exemption from the army, since conscription is not carried out for specific types of disease, and natural processes are often mistaken for tachycardia.
Depending on the type of tachycardia, a verdict will be made on accepting the conscript into the ranks of the armed forces, issuing a deferment, or assigning category “D” (not fit). There are 2 main types:
- Physiological – is the body’s natural reaction to an external stimulus (fear, anxiety, overexcitation). It is not considered dangerous and does not require medical intervention.
- Pathological is not a full-fledged disease, but is a consequence of some more serious, sometimes difficult to diagnose disease.
Pathological tachycardia is divided into 3 types depending on the location and cause of occurrence:
- sinus - occurs more often than other types. In the sinus node there is a focus that affects the increase in heart rate, while the heart rate remains normal. In a calm state of the body, there are no symptoms. Appears after physical exertion, emotional surges;
- supraventricular paroxysmal - manifests itself in attacks of a sharp increase in heart rate up to 250 beats. Treatable, requires immediate medical intervention;
- ventricular – a severe form of pathology that poses a threat to life. Develops against the background of a heart attack or drug intoxication. Does not tolerate physical exertion.
The question of whether someone with tachycardia will be accepted into the army remains open, since tachycardia is not an independent disease, but often indicates the presence of another disease that needs diagnosis. Depending on the complexity of this disease (and syndromes), a conclusion is drawn up by a military medical commission (MMC).
How to increase extrasystoles?
For those who are trying to avoid the army with such a disease and are wondering how to increase extrasystoles, it is worth keeping in mind that it is not always possible to increase them. But the following methods can help:
- Physical activity (before the examination it is good to run, jump, stress your body).
- Stressful situations.
- Emotional and physical stress.
- Drinking alcohol (not the best option, since you won’t be able to come to the medical examination drunk).
- Coffee or energy drinks.
Reviews
Dear readers, you can leave your feedback on whether they will serve in the army with extrasystole in the comments, your opinion will be useful to other users of the site!
Yaroslav:
They take it with such a disease. Medical commission specialists do not even consider this disorder to be a disease. Well, naturally, if there are already serious pathologies, but they are mainly found in old people.
Andrey:
I was diagnosed with such a disorder, but they accepted me into the army anyway, since my stage was mild. The doctors explained it to me, but I didn’t really understand it. I wasn't going to quit the army.
Who is eligible for service?
Conscripts with sinus tachycardia without related pathologies are serving. It is impossible to fully complete all tasks, so the young man is assigned a restrictive category “B” or “D”, which implies a delay for treatment and restoration of indicators. Sedatives can bring your heart function back to normal.
They recruit conscripts with tachycardia into the army if:
- there are no serious diseases;
- ailments have been identified that do not pose a threat to service;
- Heart rate increased slightly;
- tachycardia is provoked by physiological reasons (heavy active loads, adrenaline release, poor lifestyle).
A recruit with acceptable heart rate abnormalities may be referred:
- to the Marine Corps;
- Airborne Forces;
- border troops;
- Special Forces;
- fleet;
- driver of cars and tanks.