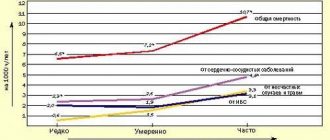
For a long time, debates have continued between doctors in different countries about the dangers and beneficial qualities of alcohol. The most heated debate is the question: does alcohol thin the blood or, conversely, thicken it? As research shows, both statements are true, but they are separated by a time period.
Considering the negative reaction of the body and the possibility of developing alcoholism, alcoholic drinks should in no case be perceived as medicines.
The effect of alcohol on the blood and on the entire body as a whole is quite multifaceted. It depends on many factors that arise when alcohol-containing drinks are in the human body.
Passage of alcohol through the body
The weak polarization of ethyl alcohol molecules allows it to easily penetrate cell membranes. The substance begins to be absorbed in small quantities in the oral cavity and esophagus, in moderate quantities in the stomach and colon, but mainly in the small intestine.
Alcoholic drinks do not have any effect on the circulatory system when inhaled or penetrated through the skin
Contraindications
According to medical recommendations, vodka and other alcoholic drinks should be strictly avoided if you have the following diseases:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- renal failure;
- liver failure;
- heart failure;
- allergy to alcohol (occurs in approximately one in 2000 people);
- age under 18 years;
- pancreatic dysfunction;
- fibrosis of the liver, pancreas;
- neuralgic disorders (for example, migraine).
You should also refrain from drinking vodka if you have diabetes or blood diseases (anemia, anemia, increased or decreased hemoglobin levels).
Decreased blood viscosity
As ethyl alcohol penetrates into the blood, the following occurs:
- relaxation of vascular muscle tissue;
- vasodilation;
- acceleration of blood flow;
- decrease in blood viscosity;
- lowering blood pressure;
- increase in heart rate.
During this period, a person feels great, becomes cheerful, sociable, relaxed, and overly self-confident. There is a slight reddening of the skin, pleasant warmth and a feeling of light heat spread throughout the body, and the frequency of urination increases.
Thickening process
After about half an hour, signs of a hangover begin to appear: the feeling of euphoria disappears, swelling and a feeling of thirst appear, and a headache begins.
This symptomatology occurs as a result of the body’s reflex action on low blood pressure in the form of increased release of norepinephrine, hypertensin, and renin. These processes help restore the tone of the muscle tissue of blood vessels, narrow them, increase blood pressure and worsen blood circulation. In addition, impaired kidney function during alcohol poisoning provokes disruptions in water and electrolyte balance.
As a result of the breakdown of ethanol, in addition to practically harmless substances, acetaldehyde is produced, which has a strong toxic effect. To get rid of poison, the body requires fluid, which is taken from the tissues, which leads to thickening of the blood and a change in its consistency.
The content of impurities in alcohol only aggravates the course of pathological processes
The effect of alcohol on the blood is also revealed in its composition:
- there is an increase in the quantitative indicators of triacylglycerols and the percentage of lactate;
- the level of hemoglobin, red blood cells, glucose, and urea concentration decreases.
Drinking alcohol also leads to platelet aggregation, which increases the risk of blood clots.
In addition to the negative effect on the blood, drinking alcohol affects the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, brain, and cardiovascular system.
Rules of use for harm reduction
The basic rule for drinking alcohol to reduce harm from it is limited cultural consumption. Each drink has guidelines for responsible consumption.
In general, for wine it will be 175-350 ml, for strong alcohol - 50-150 ml, for beer - no more than 1 liter.
The recommended dosage implies that when consuming the specified amount of alcohol, the health risk will be minimal. Accordingly, in the case of consumption of “healthy alcohol”, the benefit will be more significant than the harm caused.
In addition, there are general rules based on everyday logic. They should not be neglected, even if dosage recommendations are not followed. These include the following:
- Avoid drinking alcohol in the heat, in the sun, in stuffy rooms with insufficient fresh air;
- avoid smoking, including passive smoking, when consuming alcohol;
- drink alcohol only in pleasant company;
- have a snack - accompany drinking alcohol with tasty and healthy food;
- provide access to fresh air - for better absorption and easier removal from the body.
Severity of pathological processes
After each drink, the blood thins with further thickening, as well as the expansion and contraction of blood vessels, which has an extremely negative effect on the condition of the body.
You can reduce the negative effects of alcohol by drinking diuretics or drinking plenty of fluids.
Complete breakdown of alcohol occurs within 5–36 hours. Alcohol is metabolized in the liver (90%), where it is neutralized with the help of enzymes. The remaining amount (10%) is excreted through the kidneys during urination, lungs and skin.
The strength of the effect of ethanol on the processes of thickening and thinning the blood depends on the concentration of alcohol in it, which, in turn, is influenced by:
Type of alcoholic drink
Despite the existing opinion that the highest concentration of alcohol in the blood is achieved by drinking strong drinks, it is not entirely true.
The fastest penetration into the bloodstream is observed in drinks of medium strength (alcohol content up to 30%): wine, punch, mulled wine. While drinking strong drinks (vodka, cognac, whiskey) has an irritating effect on the stomach, which delays the opening of the pyloric valve, the entry of the drink into the duodenum and its absorption.
Interesting: beer (350 ml), unfortified wine (120 ml) and port wine (40 ml) contain up to 10 g of ethyl alcohol, and vodka (500 ml) – 200 g.
Drinking speed
A short break between drinks and drinking a large amount of alcohol will lead to a higher concentration of alcohol in the body and more obvious symptoms of intoxication, compared to drinking alcohol slowly in small doses.
Consequently, drinking alcohol for a long time in small doses has a less harmful effect on the circulatory system.
Eating
Drinking an alcoholic drink on an empty stomach penetrates the blood faster, which leads to an increase in the concentration of alcohol in it.
Fatty foods increase the absorption time of alcohol by 6 times. Fat milk, drunk before a feast, or mashed potatoes will significantly reduce the rate of penetration of alcoholic beverages into the blood, which will reduce its negative impact.
Body mass
The human body is 2/3 water, in which alcohol is evenly distributed as it enters. The larger a person is, the more water is contained in his body and the lower the concentration of alcohol in him.
Excess weight in a person, caused by fat deposits, indicates less fluid compared to a person with a muscular physique. The dissolution of ethanol in fat occurs more slowly than in a liquid medium, which contributes to a higher concentration of alcohol in the blood in obese people compared to muscular athletes, when they drink alcohol in the same amount.
Consequently, the concentration of ethanol in a woman’s blood will be higher if she drinks the same amount of alcoholic beverages as a man of equal weight.
How hormonal contraception changes blood clotting
The hormones that make up oral contraceptives (like their natural analogues) work at the genetic level: they penetrate into the nuclei of cells and there directly communicate with DNA - in particular, those parts of the chain that are responsible for blood clotting. Many women will never notice this - but if someone is genetically predetermined to one day experience varicose veins or thrombosis, birth control can bring this moment closer. What do you need to know about your genetics before you start taking the pill?
Since the 1960s, oral contraceptives have been constantly improved. The first drugs contained indecently high, by modern standards, doses of hormones, which is why they quickly gained fame as rather dangerous toys. New generations of tablets are fearlessly used not only for their intended purpose, but also for medicinal purposes. The concentration of active substances in them has decreased by 5–10 times, so noticeable side effects are usually not observed: no sudden weight gain, no decrease in sexual desire, no attacks of insomnia, for which previous generations of OCs were criticized.
But contraceptives also have an invisible front of work: any hormones are needed by the body to solve many problems and cannot specifically perform only one function. For example, progesterone
(it and its analogues are part of oral contraceptives) affects not only ovulation, but also the concentration of blood clotting factors. Nature came up with this to help a woman avoid blood loss during childbirth.
The coagulation system is needed not only for this case: if the vessels are damaged for any reason, it changes the consistency of the blood and turns part of the liquid into a dense clot - a thrombus of protein threads and cells adhered to them, which can be used as a patch.
To prevent the blood from clotting when it is not needed, the system is divided into two camps: coagulation proteins
start the process of blood clot formation, and
anticoagulant proteins
, on the contrary, stop it. Normally, they are in a balanced state: this allows the blood to remain liquid, but at the same time quickly respond to any malfunctions. Disruption of this balance can lead to serious consequences: internal hemorrhages or thrombophilia (increased clotting, due to which blood clots form in unplanned places - for example, among the vessels that supply the brain with oxygen).
In most people, the clotting system regularly experiences pressure:
- due to caffeine, which is found not only in coffee beans and tea leaves, but also in soda cans;
- nicotine coming from tobacco (and hookah tobacco too);
- sports activities, during which water loss inevitably occurs and the blood naturally becomes thicker;
- certain medications (for example, diuretics and fat burners).
The coagulation system can withstand individual blows of fate quite steadfastly, but if negative factors begin to add up, it becomes difficult for the body to thin the blood. At first he will report this with a feeling of heaviness in his legs. Later – varicose veins and hemorrhoids. In the worst case, such disorders will lead to thromboembolism - a sudden blockage of blood vessels in the brain, heart or other organs.
Some people have an imbalanced clotting system from birth. This is due to a slight change in the DNA structure - polymorphisms in genes
, which are called
F2
and
F5
. The F2 gene encodes information about coagulation factor II - prothrombin, a protein precursor that directly affects the formation of the filamentous basis of a blood clot. Due to a genetic failure, too much of it is produced, which means the risk of blood clots increases. The F5 gene encodes coagulation factor V – proaccelerin. A change in the sequence of the gene code makes this protein insensitive to protein C, an anticoagulant that limits excessive blood clotting.
Oral contraceptives affect the same genes: penetrating into the cell nucleus, hormones bind to DNA sections responsible for the production of clotting factors and change them. If, against the background of a genetic breakdown, it is already difficult for the body to maintain balance, the risk of blocking blood vessels with blood clots increases tenfold. Because of this, the World Health Organization calls the prescription of oral contraceptives to women with polymorphisms in the F2 and F5 genes an unacceptable health risk - and this is even without combination with other negative factors.
Polymorphisms in the necessary genes can be identified using tests - DNA does not change with age, so it is enough to take them once in a lifetime. Usually, before prescribing hormonal drugs, gynecologists ask patients to bring the results of such tests to make sure that there are no risks to their health. If for some reason this does not happen, you should check yourself and discuss the results of the study with your doctor. It is especially important to get tested if there are other risk factors:
- Cases of varicose veins, strokes or heart attacks in relatives
- Phlebeurysm
- Smoking
- Regular coffee consumption
- Active physical activity
You can read more about the analysis here.
Types of alcohol and their effect on blood condition
Alcohol contained in any alcoholic beverages always thins the blood and subsequently thickens it. However, the effects of different types of alcohol may differ from one another.
Drinking any alcoholic beverages in excessive quantities has a negative effect on the blood.
So, use:
- Vodka provokes a strong thickening of the blood and a change in its composition. The drink promotes the formation of blood clots and increases the risk of thrombosis;
- Beer in large quantities leads to surges in blood pressure, dilation of blood vessels and thinning of the blood. Subsequently, blood pressure rises and kidney function fails;
- red wine in moderation leads to blood thinning and reduces the risk of blood clots;
- champagne causes destruction of red blood cells, changes in blood consistency, and also provokes oxygen starvation of tissues;
- cognac leads to an increase or decrease in blood pressure. In moderate quantities it lowers cholesterol levels, in large quantities it provokes a rapid deterioration in well-being.
Don't forget about the quality of alcohol. Drinking alcoholic beverages purchased from dubious manufacturers can lead to unpredictable consequences both for the condition of the blood and for the entire body as a whole.
To drink or not to drink?
Whether alcohol thins the blood or, conversely, thickens it is a very controversial issue.
The results of numerous studies show that drinking alcoholic beverages in acceptable quantities has a thinning effect on the blood, which prevents blood clots, atherosclerosis, blockage of blood vessels, and the development of heart attacks and strokes. Ethyl alcohol also prevents the production of homocysteine, which has a negative effect on blood vessels, increasing the risk of blood clots.
A striking example of a positive effect on the blood is drinking red wine. The drink is made from grapes, the skin of which contains large quantities of antioxidants, catechin, resveratrol and other beneficial substances that have a beneficial effect on the blood.
However, the blood-thinning effect can be achieved by consuming products that do not contain alcohol, such as natural grape juice or berries.
How does the body lose water?
Due to the fact that water leaves the blood, but the number of red blood cells remains the same, there is an increased risk of thrombosis, especially in small vessels. It is due to hemoconcentration that in the morning, in a state of hangover, a person experiences severe thirst.
It is known that in order to avoid this state of hangover, immediately during and after drinking alcohol, drink a large amount of clean water, which prevents the process of blood thickening.
It is necessary to remember the insidiousness of alcohol intoxication. Everyone knows the phenomenon that in a state of mild to moderate alcoholic intoxication, a person wants to go to the toilet quite often for minor needs, and not only when he has drunk a lot of beer.
We are not talking about any special thinning or thickening properties of alcohol - it’s just that the body that has experienced an “osmotic shock” is able to excrete ethanol only along with water, which is necessary for life.
Being in an elevated state of alcoholic intoxication, a person quickly hurries from the toilet to the feast and back to good company, and does not realize that he is gradually losing the necessary fluid. Strong alcohol works especially hard. Those people who do not understand whether vodka thins or thickens the blood, let them remember their condition the next morning, during a severe hangover.
Naturally, at this time you are constantly thirsty, and there is no desire to run around for minor needs. Moreover, it does not matter what was consumed in large doses - vodka, beer or cognac, there is no difference. Ethanol processing products, under-oxidized acetaldehyde and fusel oils, or high-atomic alcohols, cause severe intoxication syndrome, drowsiness, and headache. And, of course, the constant desire to drink water, brine, eliminating the “dry wood” is disturbing.
Eliminating the negative effects of alcohol
We cannot exclude the possibility that the situation gets out of control and the person drinks a large amount of alcohol. The main thing is not to cross a threshold that leads to difficult reversible consequences.
You can reduce blood viscosity during a hangover with the help of medications: Aspirin, Cardiomagnyl, Aspecard, previously approved by a doctor. It is also recommended to include fermented milk products, eggs, citrus fruits, grapes, plums, cherries, and oatmeal in the diet.
Drinking tea, decoctions and infusions from horse chestnut, white willow, sweet clover, and dry nettle is beneficial.
Despite the fact that alcoholic drinks have a short-term thinning effect on the blood, its overall effect on the circulatory system is negative. It is advisable to minimize alcohol consumption to prevent harmful consequences for the entire body.
Doctors' opinions on alcohol
If previously the belief about the benefits of a glass of wine and a glass of vodka was popular among doctors, now everyone is actively disowning these beliefs. Recent scientific studies have proven 100% negative effects of alcohol on the body. Today, the safest and healthiest solution is to give up alcoholic beverages or reduce them in your diet to a minimum.
There is not a single medical recommendation on alcohol consumption in the world. No disease can be cured or prevented by this dangerous substance. The heart and blood vessels should be treated with medications and physical activity, and flu and coronavirus should be prevented by vaccination.
Alcoholism is a serious disease that destroys a person both physically and socially. It always starts with “safe” doses—a glass of wine on Friday night, a can of beer after work—and ends with dire consequences. Control yourself and try to limit your drinking to holidays and special events.
Take care of your health!