Of course, many inhabitants of our planet do not even know about this disease, but pulmonary hypertension is a serious and dangerous illness that requires immediate treatment at the first “call” of this type of hypertension. This disease is a pathological condition characterized by a jump in blood pressure in the arteries of the pulmonary pool. The main causes of the disease in patients who have this type of hypertension include an anomaly in the structure of the arteries in the respiratory organs, which results in a narrowing of the lumen in one of the vessels.
In this regard, the patient experiences a constant increase in blood pressure in the pulmonary basin.
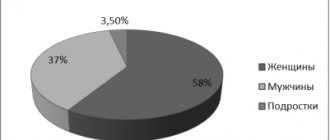
All of the above factors influence the fact that first there is a thickening of the walls of the right ventricle, and then in many patients its right ventricular failure is diagnosed, often leading to early death. Statistics say that pulmonary arterial hypertension is diagnosed more often in middle-aged women; men are one third less likely to suffer from this disease. The worst thing is that this pulmonary disease occurs without clear symptoms, so this type of hypertension is diagnosed already in advanced stages, when attacks of swelling of the respiratory organs are observed, the onset of a hypertensive crisis, or hemoptysis occurs from ruptured capillaries. Therefore, it is so important to know what it is - pulmonary hypertension and its symptoms.
Classification of the disease
Experts distinguish four types of this disease, which depend on the severity of the pathology of the above disease.
Classification of pulmonary hypertension:
- pulmonary hypertension of the 1st degree is characterized by the fact that the patient does not experience any discomfort during moderate physical activity, he does not experience shortness of breath, there is no pain in the chest area, there is no weakness or severe fatigue;
- moderate pulmonary hypertension is a picture when, with a slight increase in usual physical activity, the above signs of the disease are absent, and with a significant increase in physical activity, slight dizziness, shortness of breath appear, the patient quickly gets tired;
- in the third degree of pulmonary hypertension, even a slight load causes pain, dizziness and shortness of breath;
- The fourth degree of the disease is characterized by the fact that the above symptoms can appear in the patient even at rest.
Pulmonary hypertension is also classified according to the course of this lung disease; it is divided into acute and chronic periods. The acute form often occurs as a result of a myocardial infarction or hypertensive crisis; the acute stage can also be provoked as a result of pulmonary embolism, etc. Chronic hypertension develops against the background of increased blood pressure in the left atrium, as a result of obstructive pulmonary diseases, or for another reason that causes narrowing of the artery in the lungs.
Functional classification of pulmonary hypertension
| Class I | There is no restriction on physical activity. Ordinary physical activity does not cause shortness of breath, weakness, chest pain, or dizziness |
| Class II | some decrease in physical activity. Ordinary physical activity is accompanied by shortness of breath, weakness, chest pain, dizziness |
| Class III | severe limitation of physical activity. Little physical activity causes shortness of breath, weakness, chest pain, dizziness |
| Class IV | inability to perform any physical activity without the above clinical symptoms. Shortness of breath or weakness may be present even at rest, discomfort increases with minimal exertion |
Causes of this type of hypertension
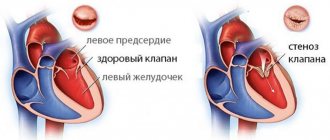
All its causes are associated with pathologies in which a sharp narrowing of the pulmonary artery occurs.
This hypertension is caused by both primary (congenital) abnormalities of the lungs and secondary ones, i.e. associated with other diseases.
Increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery can be caused for various reasons; the main factors that increase pressure in the lungs are:
- heart failure;
- severe liver disease;
- vasculitis;
- pathologies of the respiratory system;
- various congenital heart diseases;
- metabolic disorders;
- apnea;
- pulmonary hypertension disease syndrome is often observed in those living in high mountain areas;
- various pathologies of blood and blood vessels;
- some autoimmune diseases;
- HIV AIDS;
- rare genetic abnormalities.
As you can see, pulmonary hypertension develops due to various reasons.
Signs of disease progression
Over time, the disease progresses, pulmonary hypertension intensifies and causes the following symptoms:
- When you cough, you produce sputum mixed with blood, which indicates swelling in the lungs.
- Attacks of angina appear, accompanied by pain in the sternum, an unreasonable feeling of fear, and severe sweating. Such symptoms indicate the development of myocardial ischemia.
- Atrial fibrillation develops.
- The patient experiences pain in the right hypochondrium. This condition occurs due to the development of a number of pathologies of the circulatory system.
- The lower extremities swell greatly.
- Ascites develops (a significant amount of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity).
At the terminal stage of the pathology, blood clots form in the arterioles, which can lead to increasing suffocation and heart attack.
Symptoms
As mentioned above, the symptoms of pulmonary hypertension are difficult to identify in the early stages of development; this lung disease can be asymptomatic and is detected after a long time. The very first symptoms are not very specific and may resemble signs of other pathologies of the respiratory or cardiovascular system.
All of these factors do not allow diagnosing it in the initial stages of development.
The main signs of pulmonary hypertension:
- the first symptom of the disease is shortness of breath, which initially occurs with increased physical activity, and as the disease progresses, it is also observed at rest;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- obsessive cough;
- frequent dizziness;
- fainting conditions;
- if pulmonary hypertension is diagnosed late, which sometimes leads to rupture of capillaries in the lungs and hemoptysis appears, severe swelling of the legs and ascites are also noted.
Interview and examination of the patient
It is necessary to find out whether the patient has had episodes of deep vein thrombosis, sudden swelling of the legs, or thrombophlebitis. Many patients have a family history of sudden death, cardiovascular disease, and an increased tendency to thrombus formation.
Objective evidence of a history of pulmonary embolism (PE) is the coincidence in time of the clinical presentation of thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities and the appearance of shortness of breath. In the coming months after PE, a period can be identified in patients when the condition remains stable and asymptomatic. This is due to the fact that the right ventricle copes with the load and allows maintaining good exercise tolerance until progressive pulmonary vascular remodeling develops. Almost the only reliable evidence of previous PE can be data from perfusion scintigraphy or computed tomography of the lungs performed during an acute episode of PE.
During a general examination of patients with CTEPH, blueness (cyanosis) may be detected. With the development of right ventricular heart failure, swollen neck veins, enlarged liver, peripheral edema, and abdominal dropsy are noted.
Disease in children
There are cases when pulmonary hypertension is diagnosed in newborns; its manifestation is caused by congenital heart defects; the hereditary factor also plays a significant role in the development of this disease in a child.
Often, pulmonary hypertension in children occurs against the background of previous diseases of the respiratory system: pneumonia, bronchitis, complications after influenza or ARVI.
The first symptom of pulmonary hypertension in newborns is the occurrence of shortness of breath; less commonly, the disease begins with fainting.
The rest of the course of the disease in a newborn is similar to the clinical picture of an adult patient.
Complications of the disease
The most common complication of pulmonary hypertension in both newborns and adults is the development of right ventricular heart failure, which is accompanied by atrial fibrillation. With a more severe course of the disease, thrombosis of the pulmonary arterioles may develop.
Also, complications from pulmonary disease increase the risk of developing a hypertensive crisis, which is accompanied by attacks of suffocation, especially at night, pulmonary edema, severe coughing with an attack of hemoptysis may develop.
In this case, a hypertensive crisis can result in involuntary emptying of the bladder or defecation.
And as a result of arterial thromboembolism, the lung may cease to perform its function, which leads to the death of the patient.
Development mechanism
The primary form of pulmonary hypertension is characterized by the following processes:
- Smooth muscle hypertrophy (accelerated growth of smooth muscle cell structures).
- Variable vasoconstriction (narrowing or spasm of blood vessels).
- Remodeling of the vascular wall (decreased elasticity, thickening of the vascular lumen, as a result of the formation of blood clots).
Changes in the anatomical structure of blood vessels lead to impaired blood circulation, which causes increased pulmonary pressure.
Important! The progression of the pathological process becomes a provoking factor for right ventricular dysfunction, resulting in right ventricular failure.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing this disease, the following research methods are used:
- X-ray of the lungs allows you to detect an enlargement of the pulmonary artery and see its aneurysm;
- Ultrasound of the heart determines the thickness of its walls, and Doppler sonography can reveal circulatory disorders;
- ECG is effective in the early stages of the disease; this research method allows one to determine the first signs of right ventricular hypertrophy;
- spirography helps determine the degree of respiratory failure in a patient;
- Pulmonary tomography is also used to detect pathology;
- The studies also include a general and biochemical blood test.
Some specialists conduct a walking test for 6 minutes, so the doctor can determine how much physical activity the patient can withstand.
And to study lung tissue in patients, a biopsy is used, but this expensive research is carried out only in specialized clinics.
And in order to measure the oxygen saturation of the blood, the doctor can insert a catheter into the heart cavity; this diagnosis is carried out when secondary hypertension is detected.
Operation
If the described methods are ineffective, life-threatening pathology can be eliminated through surgical intervention performed in three ways:
- Atrial septostomy. Involves creating a small opening between the atria. As a result, the pressure in the atrium and pulmonary arteries decreases to normal.
- Thrombendarterectomy. Involves removing blood clots from blood vessels.
- Lung transplantation (lungs and heart). The main indications for such a procedure are hypertrophic changes in the muscles of the heart, insufficiency of the heart valves.
Patient survival prognosis
Now you know what pulmonary hypertension is; it is a dangerous disease, which, if its course is complicated, can lead to death. According to recent studies, experts have found that without treatment, the patient’s life expectancy is no more than 2-2.5 years. Unfortunately, even with proper therapy, the prognosis for this type of hypertension is disappointing; after drug treatment, the patient can live no more than 5-6 years; heart failure increases every year.
Patients who develop this disease against the background of congenital heart disease usually do not live beyond 35 years of age.
However, in order to extend your life years, you need to treat pulmonary hypertension; there are several ways to treat and prevent the disease.
Treatment
Before we talk about how to treat this lung disease, we list all the signs that, if detected, require urgent consultation with a pulmonologist:
- if severe shortness of breath occurs when performing physical activity in everyday life, the lack of air increases as a result of the increased volume of physical activity;
- the occurrence of pain of an unknown nature behind the sternum;
- constant feeling of drowsiness or the appearance of chronic fatigue;
- severe swelling of the lower extremities is observed.
If a detailed examination reveals pulmonary hypertension, the treatment that a doctor may prescribe includes:
- A favorable prognosis for patients who have been diagnosed with this pulmonary disease in the early stages means that the patient still has a chance to get rid of the disease forever. In such cases, the doctor prescribes a course of vasodilating drugs, the action of which is aimed at relaxing the smooth muscle layer of blood vessels. These drugs include Nifedipine, Prazosin.
- To reduce blood viscosity, drugs are prescribed: acetylsalicylic acid, dipyridamole.
- Oxygen therapy.
- Vaccination is often carried out to prevent ARVI and other infectious diseases.
- The doctor prescribes a diet for the patient, which limits salt intake, and also controls the level of fluid consumed (in all its forms), up to one and a half liters per day.
- Treatment of pulmonary hypertension in female patients involves the use of contraceptives, because Pregnancy and subsequent childbirth can greatly complicate the course of this disease, even leading to death.
- When diagnosing a disease, the doctor may prohibit any physical activity.
- Surgical treatment methods are also used, the most common being lung or heart transplantation.
As for the methods of traditional medicine, for this type of disease they are ineffective, and can only aggravate the course of the disease due to an allergic reaction to any component of the traditional recipe.
Sometimes patients can use breast tea to reduce cough, but only with extreme caution; it is better to start taking the decoction with one teaspoon.
Also, in rare cases, diuretics are used to relieve severe swelling of the legs.
However, experts recommend not using traditional healing for this type of hypertension. After all, if you do not make a diagnosis on time and miss the initial stages of the disease, you can forever lose the chance of recovery. Therefore, at the first signs of pulmonary hypertension, you must immediately contact a competent pulmonologist.
Modern drugs
Macitentan
Macitentan is a drug belonging to the group of endothelial receptor antagonists. It is prescribed as an antihypertensive agent, that is, to lower blood pressure in patients with pulmonary hypertension.
The drug is recommended for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary hypertension, for the treatment of PAH, which develops against the background of heart disease and connective tissue pathologies. The drug is aimed at relieving the symptoms of the disease and improving the quality of life of patients.
Macitentan reduced the risk of hospitalization associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension by 51.6%. The cost of the medicine is quite high and amounts to 2800 euros.
Ventavis
Ventavis is an inhalation solution in which the main active ingredient is iloprost. Ventavis is a drug with antiplatelet properties. It prevents the formation of blood clots in the pulmonary arteries by inhibiting platelet aggregation.
Another effect of using the drug Ventavis is a vasodilating effect on the arteries of the lungs. That is, the drug expands their lumen, thereby relieving the load on the heart muscle.
Ventavis is the only drug for inhalation from the prostanoid group that is available in the Russian Federation. It is inhaled 6 to 9 times a day using a nebulizer.
Ventavis therapy has proven effectiveness, which has been confirmed in scientific studies. They involved 203 patients with PAH who received monotherapy with the drug for 12 weeks. This reduced dyspnea and improved NYHA functional class in 16.5% of patients. The average increase in 6-MX distance during treatment was 36.4 m.
The drug can also be used as a drug in the complex therapy of pulmonary arterial hypertension. The STEP study on this issue lasted 12 weeks and included 67 patients with PAH. Therapy was supplemented with the drug Bosentan. It was found that the patients' physical performance significantly increased, and other symptoms of the disease began to decline.
The Opitiz study involved 6 people who received the drug for 5 years. At the same time, the survival rate of people increased from 32% to 49% compared to patients who did not receive similar treatment.
There was also the AIR 1 study, in which people received therapy for one year and three years. At one year, survival rates were 83%, at 2 years 78%, and at 5 years 58%.
Therefore, it can be argued that the drug not only improves the quality of life of patients with PAH, but also prolongs it. At the same time, the cost of Ventavis is about 100,000 rubles per package.
Truckleer
Tracleer is a drug whose main active ingredient is bosentan. The drug is available in tablet form. Its main effect is to dilate the pulmonary arteries by removing vascular resistance from them. This allows you to reduce the load on the heart, lower blood pressure, improve the well-being of patients and increase the body’s tolerance to physical activity.
With the help of this drug, life expectancy can be increased in patients with idiopathic PAH, as well as with secondary PAH. Tracleer is prescribed to patients with pulmonary hypertension due to heart defects. It can be used by both adults and children.
The cost of the medicine is 200,000 rubles per package.
Revatio
Revatio is a prescription drug whose main active ingredient is sildenafil. The leading effect of taking the drug is the removal of spasm from the pulmonary arteries, as well as the expansion of their lumen. In addition, Revatio allows you to reduce blood pressure and reduce the load on the heart muscle. The patient's body becomes tolerant to physical activity, even in cases of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. The drug has been proven to improve survival of patients with PAH.
Revatio can be used in a complex treatment regimen for pulmonary hypertension. It is used to treat all forms of the disease. The average price for a package of the drug is 50,000 rubles.
Volibris (Ambrisentan)
Volibris is a drug from the group of endothelin receptor antagonists. Its main active ingredient is Ambrisentan. Taking the drug can reduce the clinical symptoms of pulmonary arterial hypertension, increase the level of tolerance to physical activity, and improve hemodynamic parameters. The effect of using the drug Volibris is stable throughout the year.
The average price for a package of medicine is 60,000 -75,000 rubles.
Adempas (Riociguat)
The drug Adempas with the main active ingredient Riociguat. This drug belongs to the pharmacological group of antihypertensive drugs, guanylate cyclase stimulators.
Taking the drug Adempas allows you to reduce pulmonary vascular resistance, improve hemodynamics, reduce the severity of shortness of breath, and reduce the clinical manifestations of the disease. The drug used in complex therapy makes it possible to increase the one-year survival rate of patients to 96%. The drug is prescribed to patients with PAH accompanied by the formation of blood clots, with idiopathic, hereditary PAH and with PAH associated with connective tissue pathologies.
Aptravi (Selexipag)
Aptravi is a drug from the group of selective agonists of the non-prostacyclin receptor. It is worth noting that the drug is not registered in Russia. Its main effect is the expansion of spasmodic pulmonary vessels and a decrease in blood pressure. The drug is used in a complex treatment regimen for PAH, and also as an independent remedy. The average cost of one package of Aptravy is 5,200 euros.
Author of the article:
Molchanov Sergey Nikolaevich |
Cardiologist Education: Diploma in Cardiology received from Perm State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenova (2015). Here I completed my postgraduate studies and received a diploma in Cardiology. Our authors
Prevention
Every person can significantly reduce their risk of developing this lung disease. To do this, patients with varying degrees of pulmonary hypertension need to follow several rules:
- give up bad habits (smoking, excessive alcohol consumption), adhere to healthy eating rules;
- perform light exercise every morning;
- undergo regular preventive examinations with a pulmonologist;
- if a person has chronic diseases of the respiratory system, it is necessary to strictly monitor their course;
- there should be regular physical activity in a moderate mode;
- It is also necessary to exclude situations that can expose a person to severe and prolonged stress (conflicts in the family, at work).
But the most important thing that any patient should remember is that the causes of pulmonary hypertension are very diverse, and at the very first “bells” of this insidious disease, you need to urgently contact a qualified specialist to undergo a detailed examination. After all, only when the disease is diagnosed in the early stages there is a high chance of successful recovery; when the disease is detected in the later stages, in 50% of cases it leads to death within 5 years after the onset of this type of hypertension. And in no case do not self-medicate; only a doctor can select competent comprehensive treatment; the dosage of certain medications depends on the severity of the disease and the type of concomitant pathologies.
Why is it developing?
Pulmonary arterial hypertension occurs in two types, depending on the cause of its occurrence.
Primary or idiopathic
The etiology of the disease has not yet been precisely established, and the form of the pathology is quite rare. Severe idiopathic hypertension is first diagnosed in newborns, having a hereditary form. Pathology can be transmitted not only in a direct line from the mother or father, but also from grandparents or even great-grandparents.
During diagnosis, children with a similar diagnosis are found to have atherosclerotic changes in the cavity of the pulmonary artery and an increase in the mass of the right cardiac ventricle. If a child or adult who first develops pulmonary hypertension syndrome is not given immediate assistance, he will remain disabled, and complete ignorance of the symptoms can lead to the death of the patient.
Secondary
It develops more often in adults against the background of concomitant diseases. Secondary pulmonary hypertension is observed in pathologies occurring against the background of insufficient functioning of the left ventricle, HIV infection and heart defects of congenital etiology. The risk of developing the disease increases for people with connective tissue pathologies - lupus erythematosus, systemic scleroderma.
With acquired heart defects, after thromboembolism has been transferred to the pulmonary artery cavity, there is also a high risk of signs of increased blood pressure in the vascular bed of the pulmonary arteries. In lung diseases, pathology can also manifest itself, but usually does not reach an advanced stage. Potential dangers are those conditions that increase the risk of developing pulmonary hypertension.
This is taking drugs from certain drug groups (Aminorex, Amphetamines, Cocaine, Fenfluramine, Chemotherapy drugs); oral contraceptives, antidepressants, and estrogen drugs are considered less dangerous in this regard. Diseases that increase the chances of developing pulmonary hypertension are HIV infection, the presence of congenital shunts located between the systemic and pulmonary capillaries, severe diseases of the thyroid gland and liver, genetic mutations and metabolic disorders.
No ads 1