Hemolysis is how the process of destruction of red blood cells is defined in medicine. This is a permanent phenomenon that is characterized by the completion of the life cycle of red blood cells, which lasts about four months. The planned destruction of oxygen transporters does not manifest itself with any symptoms, however, if hemolysis occurs under the influence of certain factors and is a forced process, then such a pathological condition can be dangerous not only for health, but also for life in general. In order to prevent pathology, you should adhere to preventive measures, and if it occurs, promptly find out the symptoms and cause of the disease, and most importantly, have an understanding of where exactly the process of destruction of red blood cells occurs.
Process characteristics
During hemolysis, red blood cells are damaged, which leads to the release of hemoglobin into the plasma. As a result, external changes in the blood occur - it becomes redder, but at the same time much more transparent.
Destruction occurs due to exposure to a bacterial toxin or antibody. The process of destruction of red blood cells occurs as follows:
- A certain irritant can affect the red blood cell, resulting in an increase in its size.
- Red blood cells do not have elasticity, so they are not designed to stretch.
- The enlarged red blood cell ruptures, and all its contents enter the plasma.
To clearly see how the destruction process occurs, you should watch the video.
Video - Hemolysis of red blood cells
“Portrait” of a middle-aged red blood cell
Cell size is determined by diameter, which is 7.5 microns (micrometers). This is 6 times smaller than the thinnest human hair. The total surface of all red blood cells is 1.5 thousand times greater than the covering of the human body. The change in size is called anisocytosis.
The shape of the cells is flat, with thickenings along the edges, forming a disk concave on both sides. The “design” of the cell is determined by the optimal distance of each surface point to the center, this increases the possibilities of contact with transported gas molecules. There is no nucleus inside the cell (fish, birds and amphibians have one), which is associated with an adaptation to binding more hemoglobin.
Disturbance in the shape of blood cells is called poikilocytosis. Up to 15% of altered cells are allowed.
Red blood cells do not synthesize their own protein; 71% of the cell mass is water, 10% is the membrane-covered membrane. Cells are economically powered by energy obtained without oxygen.
Reticulocytes are larger in size; inside there is a mesh formation containing amino acids and fats.
The plasma membrane is half composed of glycoproteins; it is capable of transmitting oxygen, carbon dioxide, electrolytes sodium and potassium, and water. This suggests that a violation of the protein-lipid composition of the blood (cholesterol levels) leads to premature wrinkling and destruction.
By weight, up to 90% is occupied by hemoglobin (a chemical compound of iron and protein).
Types of hemolysis
| View | a brief description of |
| Intravascular | The destruction of red blood cells occurs as a consequence of anemia, hemolytic gas poisoning, and autoimmune diseases. Occurs directly during blood circulation |
| Intracellular | The process of hemolysis is observed in macrophage cells and is activated due to autoimmune types of anemia, thalassemia |
Attention!
The process of destruction of red blood cells can be caused artificially under the influence of poisons, an incorrectly performed blood transfusion, as a result of the influence of certain acids.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Since red blood cells have their own mass, the blood, when drawn into a graduated tube, is stratified due to cell sedimentation. To prevent cell elements from sticking together, a special solution is added.
The result of the reaction is assessed after an hour by the height of the transparent column.
The reaction in men is considered normal - from 12 to 32 mm/hour, in women - from 18 to 23. In pregnant women, ESR increases to 60 - 70 mm/hour. The reaction is widely used in the diagnosis of diseases along with other tests.
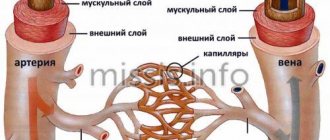
Site of destruction of red blood cells
If we consider the natural process of hemolysis, then as a result of aging of red blood cells, their elasticity is lost and they are destroyed inside the vessels. This process is defined as intravascular hemolysis. The intracellular process of hemolysis involves destruction within the Kupffer liver cells. Thus, up to 90% of old red blood cells (they contain up to seven grams of hemoglobin) can be destroyed in one day. The remaining 10% is destroyed inside the vessels, resulting in the formation of haptoglobin in the plasma.
How does a red blood cell participate in respiration?
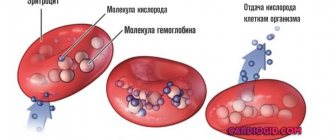
Red blood cells are responsible for saturating the blood with oxygen and removing unnecessary carbon dioxide accumulations. To achieve this, most of the cell mass is occupied by hemoglobin (globin protein + 4 heme/iron molecules). It is called "blood pigment" because heme is what gives blood its color. Depending on the sequence of amino acids, different types of pigment are distinguished in globin.
The oxyhemoglobin complex is formed by combining with oxygen. It is created in the pulmonary capillaries, and in the tissues it breaks down again and releases free oxygen to the cells.
The appearance of methemoglobin or carboxyhemoglobin in the blood during poisoning and intoxication disrupts the process of oxygen transfer and leads to tissue hypoxia.
Mechanisms of hemolysis
The process of destruction of red blood cells in the body can occur in several ways.
| Mechanism of hemolysis | Characteristic |
| Natural | This is a continuous natural process, which is a completely normal phenomenon that is typical for the completion of the life cycle of oxygen transporters |
| Osmotic | The development of the process occurs in a hypotonic environment under the influence of substances that have a negative effect directly on the cell membrane |
| Thermal | When conditions arise with a temperature effect on the blood, red blood cells begin to disintegrate |
| Biological | Biological toxins or improper blood transfusion can have a negative effect on red blood cells. |
| Mechanical | Hemolysis is triggered by mechanical stress, which leads to damage to the cell membrane |
Tasks and functions
The main functions of red blood cells are related to:
- with the transfer of oxygen from the pulmonary lobes to the tissues, and carbon dioxide in the opposite direction;
- representation of the species antigenic specificity of human blood (the AB0 blood group determination system is based specifically on the properties of erythrocyte agglutinogens);
- supporting the acid-base ratio (balance) and osmotic pressure necessary for the course of biological processes in the body;
- simultaneous transfer of fatty organic acids into tissues.
Red blood cells carry oxygen molecules
Root causes and symptoms
In medicine, there are several reasons why the destructive processes of red blood cells can be activated, the main ones include:
- if heavy metal compounds enter the blood;
- in case of human poisoning with arsenic;
- when exposed to acetic acid;
- for chronic illnesses;
- for acute sepsis;
- if DIC syndrome develops;
- as a consequence of severe burns;
- with unsuitable Rh factors, when blood is mixed during transfusion.
The initial stages of hemolysis are absolutely not characterized by anything, so the pathological process must be determined by a specialist. Manifestations noticeable to the patient themselves occur during the acute stage. This stage occurs very quickly, so it is necessary to react in time. Clinical characteristics of the process of destruction of red blood cells appear as follows:
- There is a feeling of nausea, which often ends in vomiting.
- Painful sensations in the abdomen.
- Change in skin color.
A crisis occurs when the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- the person has a fever;
- nausea occurs, which is accompanied by vomiting;
- the temperature rises;
- shortness of breath becomes worse;
- painful syndrome in the form of pain in the abdomen and lower back;
- tachycardia.
A more severe form leads to the development of anuria, and first, a significant decrease in blood pressure.
It is important!
During the acute period, a significant enlargement of the spleen will be observed.
What is considered normal
The total number of these cells in the body is determined by the figure 25 × 1012. Laboratory calculations are based on the cell content in one cubic mm of blood.
According to the rules, the analysis is taken from capillary or venous blood in the morning after a quiet rest and before meals. The level of red blood cells is influenced by external conditions and the nature of nutrition.
The norm changes throughout life. There is a dependence on a person’s age, gender and climate zone where people live.
In a child during the neonatal period, the maximum number of erythrocyte cells is observed (within the range of 4.3 - 7.6 x 10¹²/l). The destruction of the mother's red blood cells immediately after birth and their replacement with her own causes yellowing of the skin. By the year the amount decreases to 3.6 - 4.9 x 10¹² / l, and in adolescence it increases slightly to “adult” levels (3.6 - 5.1 x 10¹² / l).
The level in women (3.7 - 4.7 x 10¹² /l) is lower than in men (4.0 - 5.1 x 10¹² /l). This is due to physiological blood loss during menstruation. During pregnancy, a woman’s body begins to increase the consumption of iron, and with it red blood cells. Mild anemia (anemia) indicates this feature.
A decrease in red blood cell levels is called anemia. The degree and form of the disease are influenced by various reasons.
An increase in the number of red blood cells (erythrocytosis) is possible with significant dehydration or with blood pathology associated with increased synthesis of red blood cells and impaired utilization.
Hemolytic anemia and the process of hemolysis
In most cases, these concepts are interconnected. This is explained by the fact that with hemolytic anemia, an immediate breakdown of red blood cells occurs with the release of bilirubin. When a person suffers from anemia, the life cycle of oxygen transporters decreases and the process of their destructive action accelerates.
There are two types of anemia:
- Congenital. A person is born with an abnormal structure of red blood cell membranes or with an incorrect hemoglobin formula.
- Acquired. Occurs as a consequence of exposure to toxic substances.
If the pathology is acquired, the following symptoms develop:
- the temperature rises sharply;
- pain in the stomach;
- the skin turns yellow;
- dizziness;
- painful syndrome in the joints;
- feeling of weakness;
- increased heart rate.
Reference!
In the toxic form of anemia, one of the internal organs suffers - the liver or one of the kidneys. The autoimmune form is characterized by increased sensitivity to too low temperatures.
Increased quantity
A large number of red blood cells is provoked by dehydration, chronic leukemia and other factors. Erythrocytosis is divided into:
- primary – refers to genetic pathologies with attacks of dizziness, loss of strength, darkening of the mucous membrane;
- secondary - provoked by certain pathologies, occurs when smoking, visiting mountainous areas, and is caused by persistent oxygen starvation.
The source of elevated red blood cells is represented by:
- dehydration – insufficient intake of fluid into the body leads to an artificial increase in blood cells in percentage terms;
- insufficient oxygen supply - the deficiency is compensated by the active production of red blood cells;
- congenital heart defects - in the absence of effective blood pumping, hypoxia develops, elements are necessary to compensate for it;
- genetic prerequisites - in some patients, altered sensitivity to oxygen was recorded, disturbances - with the release of gas by hemoglobin;
- Polycythemia vera is a rare pathology associated with a constantly high production of red blood cells.
Active production of red cells threatens a subsequent slowdown in blood circulation, its increased density and the occurrence of associated symptoms: cephalgia, dizziness, decreased visual acuity, accelerated blood clotting. Sometimes the deviation occurs against the background of heat, severe stress, heavy loads. The pathological form of an increase in the number of red blood cells occurs in exceptional cases.
The process of breakdown of red blood cells in newborns
Already in the first hours of life, the baby may experience the process of breakdown of red blood cells. The root cause of this pathology is the negativity of the Rh factor with the maternal one. This condition is accompanied by yellowing of the skin, anemia and swelling. The danger of this pathological condition is a possible death, since excessive amounts of bilirubin are released into the blood plasma.
The baby is worried about cramps, reluctance to take the breast, and a lethargic state. If a complicated form of the disease is observed, then swelling will be noted on the skin, as well as an enlarged liver.
Attention!
Modern medicine methods reduce the risks of jaundice to a minimum and prevent complications in the form of developmental delays.
You can learn about the structure and functionality of red blood cells in the video. Is it possible for a person to live without a spleen? Read on our website.
How does agglutination occur?
Agglutination of erythrocytes is the reaction of interaction of agglutinogens (antigens) located on the surface of the cell membrane with specific plasma agglutinins. The result of the interaction can be seen when determining the blood group on a white plate - the formation of small sticky lumps.
In a healthy person, this process is reversible and is possible when the cells lose their electrical charge. In pathological conditions, agglutination promotes thrombus formation. At the same time, the number of free red blood cells in the blood decreases.
Below shows agglutination of red blood cells with slow blood flow