Pediatric hypertension: signs and treatment
Pediatric hypertension: signs and treatment
Arterial hypertension
- a pathology manifested by an increase in blood pressure. The increase is permanent. It can be constant or have a crisis course. In children, blood pressure depends on age, gender, weight and height. Recently, cases of hypertension in children and adolescents have been increasingly recorded. There are many factors influencing the development of pathology. The risk of developing hypertension in a child increases if close relatives have similar problems. Such pressure is a reason for dispensary monitoring of children and inclusion of them in the risk group for the hypertensive process.
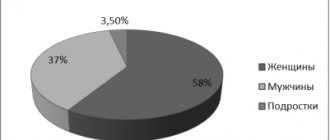
Arterial hypertension in children occurs in every tenth preschooler and every 6th schoolchild. Children in the first years of life rarely suffer from arterial hypertension. Typically, such hypertension develops as a secondary symptom of other diseases. Most often, arterial hypertension develops in adolescents during puberty. This is explained by the vegetative and hormonal disruptions that occur during this period.
There are two forms of arterial hypertension in children and adolescents:
- Primary hypertension in children:
- Secondary form of pathology:
Primary hypertension
occurs in the absence of a clear cause of the disease, develops due to many reasons:
- heredity;
- chronic stress, emotional tension;
- child's temperament;
- increased weight;
- metabolic failures;
- excess salt in food;
- dysregulation of homeostasis systems in the brain
Secondary hypertension
: the disease develops against the background of concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system, abnormalities of the thyroid gland, adrenal function and other diseases. Rare pathologies that can cause arterial hypertension: systemic vasculitis, connective tissue diseases, brain pathologies; hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome.
Moderate arterial hypertension in children is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Weak symptoms or absence of external symptoms. Parents may not be aware of their child’s illness.
- Increased blood pressure (systolic component). In children of the first year of life, up to 110 mm Hg. Art., at 10 years old up to 125 mm Hg. Art., in adolescents more than 135-140 mm Hg. Art.
- Headache, fatigue.
- Often these children have increased weight.
- Vegetative failures.
- Congenital microanomalies of the heart and kidneys.
The main risk factors for arterial hypertension in children and adolescents include:
- impressionability, emotional and psychological excitability;
- overweight, tendency to obesity, unhealthy diet;
- excessive salt intake;
- inactive lifestyle, frequent watching of TV and computer.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
The final diagnosis of arterial hypertension in children and adolescents is made after a threefold increase in blood pressure is detected. The first symptoms and signs of the disease can be detected during a regular medical examination with a doctor. Pathological changes are confirmed after daily monitoring of pressure and taking tests with physical and psycho-emotional stress.
Self-prescribing medications for children is strictly prohibited.
. The dosage and type of medicine can only be prescribed by a doctor, based on examination, test results and examinations.
Preventive measures
Prevention of arterial hypertension due to its significant prevalence should be carried out by everyone, regardless of age. The main activity in this case is the formation of the habit of leading a healthy lifestyle in children and adolescents. Parents should maintain a proper daily routine, provide a healthy and nutritious diet, good, restful sleep, an adequate work and rest schedule, and a healthy diet help avoid the occurrence of arterial hypertension. At older ages, it is necessary to exclude risk factors that influence the development of the disease. A favorable and calm emotional environment should be maintained in the family. Children and teenagers should be taught from an early age to walk in the fresh air and have an active lifestyle. Adults should supervise television viewing and computer gaming time. If there is a hereditary predisposition to the development of hypertension, it is recommended to regularly measure blood pressure in children and adolescents using a special device - a tonometer. If deviations from the norm are detected in a timely manner, the likelihood of recovery increases.
The appearance of the first symptoms of increased blood pressure in children and adolescents should not go unnoticed. Excessive nervousness, moodiness, and fatigue indicate the presence of certain health problems. If treatment is started on time, the risk of developing chronic hypertension and serious complications in older age is significantly reduced . A healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and the absence of bad habits serve as preventive measures for the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system in children and adolescents.
Monitoring blood pressure and regular examinations with a doctor will help identify problems at an early stage and successfully treat the child.
What is hypertension in children?
Hypertension in children is a condition of high blood pressure, the norm of which is determined based on:
age;
gender; child growth (based on so-called percentile grids).
Above the 95th percentile (detected at three consecutive doctor visits) is considered high blood pressure. This situation affects about 2 percent of children. Hypertension in children can be primary and secondary, the latter being more common (unlike adults).
It is difficult to determine the cause of primary hypertension, also known as essential hypertension.
Most often this condition is caused by:
overweight, obesity and lack of exercise;
hereditary factors (if a child’s parents suffer from high blood pressure, there is a high probability that he will also have problems with blood pressure). Secondary pressure, on the other hand, is associated with the presence of other diseases in the body (for example, diseases related to the kidneys, heart, or hormones).
How is hypertension diagnosed in children?
The diagnosis of high blood pressure in a child is made by measuring the blood pressure. For a doctor to determine this, blood pressure must be above the 95th percentile for at least three doctor visits. It is also worth measuring your blood pressure at home, especially if the above or other alarming symptoms are present.
Blood pressure is measured using a cuff that is narrower than that used for testing adults. It is better to take the measurement on the right hand, the elbow should be located at the level of the heart. Before the examination, the child needs to be calmed down; it is advisable for him to sit or lie down for 5-10 minutes.
If a child has hypertension, it is necessary to diagnose the underlying disease that caused the situation, or identify factors that could contribute to the increase in blood pressure. To do this, the doctor must carefully take a history and prescribe additional tests, including blood and urine tests, and, if necessary, ultrasound of the kidneys, echocardiography and fundus examination.
Symptoms of hypertension in children
Hypertension in children very often does not produce any symptoms. However, symptoms such as:
headache;
dizziness; vomit; nausea; lack of appetite; growth retardation; d hyperactivity or, conversely, apathy and impaired consciousness.
Conversely, signs such as bedwetting, frequent trips to the toilet or difficulty urinating, and swelling of the face and limbs may indicate high blood pressure due to kidney disease.
Diagnosis of the disease
Recognition and treatment of hyperkinetic behavior disorder in children requires a comprehensive approach. The diagnosis is made based on a number of studies, which include:
- determination of neurological and psychological status using various techniques;
- assessment of the child’s medical history, environment, environment and living conditions;
- consultation with an ophthalmologist, psychiatrist, geneticist;
- electroneurophysiological examination;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography of the brain;
- complex of laboratory tests.
The main task at the diagnostic stage is not only to identify the characteristic signs of hyperkinesis, but also to exclude other pathologies that may give a similar clinical picture, for example, epilepsy, Schilder-Addison syndrome.
Treatment of childhood hyperkinesis
The key condition of therapy is to eliminate the root cause of the disease, after which the symptoms gradually disappear on their own.
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to achieve this goal, and the main treatment measures are symptomatic techniques that improve the child’s quality of life. These include anticonvulsants, which reduce involuntary motor activity of the muscle structure; in some cases, botulinum therapy is used to help block neuromuscular transmission. Auxiliary techniques may include:
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- water procedures.
Unfortunately, hyperkinetic disorder is often lifelong. An important role in the treatment of hyperkinesis is played by adequate psychological assistance aimed at stabilizing the emotional state of the child and his parents, awareness and acceptance of the disease.
Causes of high blood pressure in children
Depending on what type of hypertension a child has, the factors that cause it will be different. When secondary pressure occurs more often in children and adolescents, it may be caused by an underlying medical condition.
Very often this group includes:
kidney diseases (including renal parenchyma and vessels);
thyroid diseases; heart diseases. In children suffering from hypertension, the most common reasons for this are: excess weight; obesity; poor nutrition; low physical activity.
To counteract this type of hypertension, it is necessary to take care of proper nutrition (exclude sweets, unhealthy snacks, salt, sugary carbonated drinks, etc.) from the menu, as well as provide the child with sufficient physical activity.
Genes may also be responsible for high blood pressure in children. If there is a history of high blood pressure in immediate family, this may also affect the child.
How to treat hypertension in children?
Hypertension in children is treated whenever possible without medications or using minimal doses.
If it is possible to lower blood pressure through non-medical measures, such as lifestyle changes or diet, such measures are recommended.
If another condition, such as one related to the kidneys, heart, or hormones, is causing hypertension, appropriate treatment should be started immediately. And when it becomes necessary to include antihypertensive drugs, it is recommended to take them in the lowest possible doses and in the smallest amount, if possible and reasonable.
A child diagnosed with arterial hypertension should be under the supervision of a medical specialist, and after treatment, his condition must be constantly monitored.
Prevention
There are no specific agents that can prevent the development of pathology. The following will help reduce the likelihood of your child developing hyperkinetic disorder:
- careful planning and monitoring of pregnancy;
- prevention of household injuries in infancy;
- timely vaccination against diseases affecting the central nervous system;
- maintaining a friendly atmosphere around the child.
With timely detection of pathology and adequate assistance, there is a real chance that by the age of 17–20, the manifestations of hyperkinesis will significantly decrease, giving the child the opportunity to live and develop fully in society.
If your child suffers from hyperkinetic disorder, do not delay a visit to the experienced specialists of the SM-Doctor clinic. At your service are comprehensive methods for diagnosing and treating disorders, assistance from experienced psychologists and neurologists, group and individual recovery programs.