Diabetes mellitus is common in patients with hypertension and significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, including myocardial infarction, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease. Pharmacological therapy in patients with hypertension and diabetes is controversial due to concerns about the metabolic effects of some antihypertensive agents, as well as concerns about the safety of calcium antagonists. Therefore, diet, lifestyle changes and knowledge about proper prevention of disease progression are the key to maintaining health and reducing the risk of developing cardiovascular complications.
Factors affecting blood pressure
The cause is unknown in most cases. This is called essential hypertension. The pressure in the blood vessels depends on how hard the heart pumps blood and how much resistance the blood vessels (arteries) offer. The slight narrowing of the arteries is thought to increase resistance to blood flow, which increases blood pressure.
What Causes High Blood Pressure?
Most people don't have a single reason. However, there are a number of things that increase the likelihood of its occurrence. These are the so-called risk factors:
- The influence of nicotine.
- Excessive consumption of salt or processed foods (convenience foods, canned foods, smoked foods).
- Alcohol abuse.
- Having excess weight.
- Insufficient physical activity.
- Private stress, which provokes the release of adrenaline and cortisol.
In addition, diabetic nephropathy, a complication that develops in some people with diabetes, can cause hypertension in patients with diabetes. In this condition, the kidneys are damaged, which can cause high blood pressure due to damage to the arteries, arterioles, tubules and glomeruli of the kidney tissue. It is more common in people with type 1 diabetes. In rare cases, high blood pressure is caused by other medical conditions. This is then called secondary hypertension. For example, kidney problems or hormonal imbalances can cause high blood pressure.
Possible complications
High blood pressure in diabetes significantly increases the occurrence of serious complications:
- 25 times – kidney failure;
- 20 times – non-healing gangrene and ulcers;
- 5 times – heart attack;
- 4 times – stroke;
- 15 times – sudden deterioration in the function of the visual organs.
Everyone should know why high blood pressure is dangerous in diabetes. In many patients, high blood pressure is complicated by orthostatic hypotension. The disease is characterized by a sudden decrease in blood pressure when the patient gets up from a lying position. It manifests itself as fainting, dizziness and darkening of the eyes. Vascular tone is impaired due to diabetic nephropathy.
How is blood pressure measured?
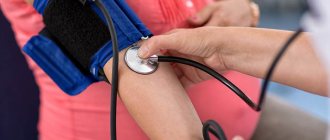
Blood pressure is measured using a device called a tonometer. A cuff (thick tape) is placed on the arm.
As air is inflated, the cuff tightens and then slowly relaxes again. During this relaxation, you can listen to the pulsation of the arteries and record the first and last tone to record blood pressure readings. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury. After the study, the result will be recorded in two numbers: the first is systolic pressure (during ventricular contraction), the second is diastolic pressure when the heart muscle is at rest. According to the principle of operation, tonometers are automatic and manual. When using a manual tonometer, air is pumped using a special bulb, and the first and last tone is heard using a stethoscope.
The automatic blood pressure monitor inflates the cuff and catches the pulse itself. Also, such devices measure heart rate and have a built-in memory for recording readings. It is much more convenient than manual ones, especially for older people.
About the types of blood pressure medications
The leading drugs are diuretics, that is, having a diuretic effect, as well as beta-type blockers, calcium antagonists, otherwise called calcium channel androgens. In addition, this category includes ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptors, which can block them.
The combination treatment includes additional types of drugs: rasilez (which is also a direct renin inhibitor), alpha adrenergic blockers, as well as agonists that provide a targeted effect on the nervous system. All these medications should be used only in accordance with medical recommendations. Otherwise, the negative impact can be very significant.
Thus, to lower blood pressure in both types of diabetes, drugs from the following groups are usually used:
- inhibitors: Enalapril, Captopril;
- diuretics: Diacarb, Furosemide;
- beta blockers: “Dilatrend”, “Trandat”, “Nebilet”;
- calcium antagonists: Verapamil, Diltiazem;
- alpha-blockers: Terazosin, Prazosin, Doxazosin;
- stimulants (agonists) of imidazoline receptors: Physiotens, Albarel.
Each group of drugs will be discussed in detail below.
Treatment and prevention of high blood pressure
To avoid a diagnosis of hypertension, patients with diabetes need to adjust their lifestyle in the following ways:
- Maintain a healthy weight. Overweight people should try to lose weight, while people of normal weight should avoid gaining weight. If you are overweight, losing just 5 kg can help prevent hypertension. Talk to your doctor about the most appropriate weight for you.
- Eat a balanced diet. Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, especially those rich in potassium, and limit your intake of excess calories, fat and sugar. Consider following the Dietary Approaches to Control Hypertension, or DASH diet, which has been shown to help control blood pressure in patients with diabetes.
- Reduce the amount of salt. A low-sodium diet can help maintain normal blood pressure. The higher your sodium intake, the higher your blood pressure. You can reduce your overall salt intake by avoiding packaged and processed foods that are high in sodium and not adding extra salt to your meals.
- Exercise regularly. Get moving to prevent hypertension. Physical activity is critical. The more you exercise, the better, but even light exercise can help control your blood pressure. Moderate exercise for 30 minutes three times a week is a good start.
- Limit your alcohol intake. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to high blood pressure.
- Check your blood pressure regularly. If your doctor detects early signs of hypertension (prehypertension), additional precautions may be needed to correct the condition.
Take a look at your lifestyle and decide where you can make changes to prevent hypertension. Achieve small goals, like snacking on fruits and vegetables instead of junk food, and continue to practice these healthy habits until they become part of your daily life.
ACE inhibitors
They block an enzyme involved in the synthesis of angiotensin, which causes an increase in blood pressure. Medicines prevent complications in the heart and kidneys. During administration, the sugar content does not increase.
ACE inhibitors have a mild hypotensive effect; after two weeks a persistent decrease in blood pressure is achieved. In both types of diabetes, these medications are prohibited if renal artery stenosis and hyperkalemia have been diagnosed. It must be taken into account that in severe hypertension, ACE inhibitors will not have a therapeutic effect. In some patients they cause cough.
What other medicine for blood pressure in diabetes mellitus is effective?
Treatment with medications
If you have diabetes, the use of antihypertensive therapy is recommended in cases where blood pressure remains at 140/80 mmHg. even when adjusting your lifestyle through diet, exercise, etc. Target blood pressure is below 130/80 mm Hg. Art. is mandatory if the patient has complications such as damage to the retina, kidney (nephropathy) or brain tissue (stroke).
There are several different medications that can lower blood pressure readings. The choice depends on things like:
- Do you have other health problems?
- Are you taking other medications?
- Possible side effects of the medicine.
- Patient's age and ethnicity.
The first group of drugs that is most often used is a drug called an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. ACE inhibitors protect against kidney damage and also help control blood pressure.
One drug lowers blood pressure to target less than half the time. Therefore, this means that two or more different medications are usually required to achieve the target level (140/80 mmHg or below). In about a third of cases, three or more medications are needed to lower blood pressure to target levels. Therefore, patients with a combination of diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension need regular consultations with doctors to monitor their health status and adjust treatment.
Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
The following methods and tests have been established for diagnosing diabetes mellitus:
- measuring blood glucose levels (determination of glycemia);
- measurement of daily fluctuations in glycemic levels (glycemic profile);
- measuring insulin levels in the blood;
- glucose tolerance test;
- blood test for the concentration of glycosylated hemoglobin;
- blood chemistry;
- urine test to determine white blood cell, glucose and protein levels;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- Rehberg's test.
In addition, if necessary, carry out:
- study of blood electrolyte composition;
- urine test to determine the presence of acetone;
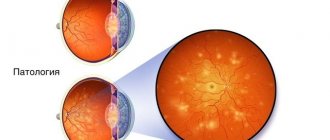
- fundus examination;
- electrocardiography (ECG).
Calcium antagonists
They slow down the flow of calcium into cells, which dilates blood vessels and reduces pressure. The following groups are distinguished:
- non-dihydropyridine - reduce heart rate, can be used to treat hypertension, which appears with nephropathy, and help avoid renal damage in diabetes;
- dihydropyridine - increase heart rate, reducing the likelihood of a heart attack.
Both are allowed to be used along with diuretics and ACE inhibitors. Prohibited for use in cases of unstable angina and heart failure.
Non-dihydropyridine blockers should not be prescribed along with beta blockers. Many people are interested in what blood pressure pills to take for diabetes.
Diagnosis of hypotension and hypertension
The diagnosis of hypertension or hypotension is made if incorrect pressure numbers were recorded three times within 2-3 weeks at approximately the same time of day. This rule applies to everyone.
Considering the danger of arterial hypertension in diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2, doctors resort to a more reliable diagnostic method - daily blood pressure monitoring. The method makes it possible to identify incipient hypertension and hypotension and determine disturbances in the daily rhythm of blood pressure fluctuations.
A special device is attached to the patient’s body with which he goes about his usual activities throughout the day. The pressure is measured approximately every hour, and some devices are equipped with sensitivity sensors that record changes in numbers. The doctor receives reliable information and has the opportunity to detect hypertension early, prescribe antihypertensive treatment, and determine the correct time to take medications.
Why is low blood pressure dangerous in diabetes?
Low blood pressure in diabetes is sometimes more dangerous than high blood pressure. Under normal conditions, a decrease in pressure causes a compensatory spasm, which helps maintain blood supply to the tissues. Due to microangiopathy caused by diabetes, the vessels of the kidneys and microvasculature cannot contract, so the blood supply to all tissues suffers.
Constant oxygen starvation leads to the development and worsening of diabetic encephalopathy, impairs vision and contributes to the formation of trophic ulcers on the extremities. The condition of the kidneys worsens and renal failure develops.
A sharp decrease in blood pressure in type 1 and type 2 diabetes can lead to cardiogenic shock - an urgent condition that requires emergency medical intervention. If signs of low blood pressure appear suddenly, you should call an ambulance to prevent acute renal failure and cardiogenic shock.