If you experience a feeling of vomiting and feel dizzy, then this is a warning bell from the body, which indicates serious illness. Only a doctor can determine the cause of a pathogenic condition. Self-examination and self-medication will not lead to results. Treatment should be carried out using comprehensive measures.
Dizziness (vertigo syndrome) is a feeling during which a person feels that all objects are spinning around him.
Nausea is the stomach's desire to vomit.
Causes of the pathogenic condition
Symptoms that are not due to disease.
If you suddenly feel dizzy and nauseous, do not be afraid. Usually the reasons for this condition are:
- a person spun on a carousel, swung on a swing, or was at a height for a long time;
- a person eats poorly, goes hungry and is on the wrong diet;
- thoughts are confused;
- stress and nervous environment;
- long stay in an unventilated and stuffy office;
- magnetic storms;
- taking medications and vitamins without consulting a doctor;
- got sick in the car;
- seasickness.
Causes of the pathogenic condition in girls.
Women have an unstable emotional and hormonal state, unlike men. They often go on diets, fast, and do fasting days to lose weight and maintain body shape.
As a result of such activities, their glucose levels decrease, frequent dizziness begins, digestive ailments worsen, and hair falls out, which leads to stress and depression.
Dizziness in women is possible only if they are pregnant, have recently been under stress, premenstrual syndrome is about to begin, or it is time for menopause.
Causes of nausea and dizziness associated with illness.
Severe dizziness and nausea lead to loss of coordination and balance. These anomalies indicate diseases:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- injuries to the head, hearing organs and spine;
- migraine;
- inflammation of the middle ear (labyrinthitis);
- episyndrome;
- Meniere's syndrome;
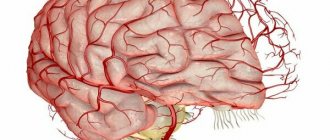
- disruption of the circulatory system of the brain;
- brain tumors;
- alcohol intoxication;
- spinal cord diseases;
- infections and meningitis;
- perilymphatic fistula;
- stroke.
An ambulance should be called if the patient, in addition to nausea and dizziness, experiences:
- fainting;
- vomit;
- elevated temperature;
- cardiopalmus;
- tingling hands;
- darkening of the eyes;
- ears began to hear poorly;
- dizzy after lying down for more than an hour;
- grainy image;
- pallor.
Pathogenic condition due to vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Staggering while walking, objects that “float”, nausea, anxiety, confusion of thoughts, a feeling of extreme hunger and lack of oxygen in the brain (the head is pressed from all sides) and dizziness are indicators of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
When you suddenly and abruptly change your body position, you begin to feel dizzy for a short period of time, and your health worsens due to the fact that the vessels do not have time to deliver a sufficient volume of blood to the brain.
Causes of pathogenic conditions that occur in the dark
. Systems such as the visual, vestibular, proprioceptive, and cerebral systems collectively regulate our balance. But if at least one of them has a disruption in the functioning of the organ, then dizziness will begin at night.
Causes of the pathogenic condition in a patient with diabetes mellitus.
During attacks, a patient with diabetes experiences chills, dizziness and nausea. This can lead to fainting or even coma. To avoid such symptoms, you need to get tested in advance, take the right amount of insulin or take medications, follow your diet and measure your sugar more often.
What to do if you feel dizzy and feel nauseous
Independent actions in case of dizziness and nausea:
- do not make quick movements, restore breathing;
- look at one specific object;
- drink cold water with a small piece of sugar;
- in case of strong emotional stress, drink a sedative or tea with oregano or chamomile;
- when your blood pressure drops, drink strong brewed black tea with chocolate (important: green tea, on the contrary, lowers blood pressure);
- if you have hypoglycemia (diabetics), eat candy with a lemon or mint flavor, or a piece of sugar, wash it down with warm tea;
- go outside or ventilate the room;
- if you start to feel very sick and everything around you is spinning, then you need to bend over and let your head go between your knees.
If the advice does not help, immediately call 003.
Arrhythmia: symptoms and treatment
The article was prepared by cardiologist Ksenia Nshanovna Borel
Arrhythmia... Perhaps the interpretation “I am worried about arrhythmia” is one of the most common complaints of cardiac patients of any age.
In fact, there is no diagnosis of arrhythmia. There is a specific disturbance in the rhythm and/or conduction of the heart, which must be recognized in time by the attending physician in order to take measures to eliminate it, if required.
I will not tire of singing the praises of my heart: this is a unique organ not only in terms of the functions it performs, but also in terms of its structural features. Did you know that the heart muscle (myocardium) is very unusual? It does not simply contract mechanically, like any other muscle in the human body.
Deep in the myocardium there are special cells of the conduction system that are capable of generating nerve charges, converting an electrical impulse into a mechanical muscle contraction:
- The main conductor of this complex composition is the sinus node (also known as the first order pacemaker), located in the wall of the right atrium. It is the power plant that reproduces charges at a frequency of 60-90 per minute, which is the normal (in terms of frequency and regularity) heart rhythm. Next, nerve impulses are transmitted to the underlying sections.
- From the sinus node, the nerve impulse runs along three highways to the atrioventricular node. It is a kind of gateway with selective throughput and provides a physiological delay in the conduction of charges formed in the sinus node. The atrioventricular node is capable of generating nerve impulses with a frequency of 40-60 per minute (this is a second order pacemaker).
- This is followed by the His bundle (third order pacemaker) with the right and left legs, which generate nerve impulses with a frequency of 20-40 per minute.
- Well, the most extreme branches of the conduction system of the heart are Purkinje fibers, operating at a frequency of 15-20 impulses per minute.
A peculiarity of the conduction system of the heart is that its normal operation is regulated by the sinus node: nerve impulses “born” in it spread from top to bottom, occupying all conduction tracts, leaving no chance for other pacemakers to generate their own nerve impulses, suppressing their activity . Thus, if a patient develops arrhythmia, it means that either the formation of a nerve impulse in the sinus node is disrupted, or so-called ectopic (not from the conduction system) foci of nerve impulse formation appear, or the conduction of a nerve impulse in various parts of the conduction system is disrupted (aka blockades) .
How does a patient suffering from rhythm disturbances feel?
Very often we hear various metaphors from patients when describing their condition when they feel an arrhythmia. They often say that the heart “gurgles”, “turns over”, “quivers”, “freezes”, “shakes like jellied meat”, “beats like a bird in a cage”, “pounds” and many others. Remember the words from the song of the group “Spleen”? “My heart stopped, my heart froze...” Sasha Vasiliev sang about arrhythmia.
In a conversation with the patient, it is very important to find out several factors that will help to predict the nature of the arrhythmia and determine its potential danger to life. So, if you are worried about arrhythmia, try to characterize it using the following parameters:
- What causes arrhythmia? What is the cause of arrhythmia?
- Does the arrhythmia begin paroxysmally or gradually, with a “warm-up” period?
- What is the heart rate for arrhythmia?
- How long does the arrhythmia last?
- During an arrhythmia, do you feel pain in the heart area, shortness of breath, dizziness, or decreased blood pressure? Or maybe you even develop a fainting state or briefly lose consciousness?
- Does the arrhythmia stop spontaneously? Or does it stop only after using certain medications or when performing specific manipulations?
- How often does arrhythmia bother you? Is there a frequency of its repetition?
As you already understand, arrhythmias can be classified into paroxysmal (non-paroxysmal and paroxysmal) and constant. In addition, arrhythmias can be with an increase (more than 90 per minute) or a decrease (less than 60 per minute) of the heart rate.
We must not forget that changes in heart rhythm can be normal. For example, sinus tachycardia in response to emotional experiences or physical activity. And, conversely, sinus bradycardia during sleep under the influence of the vagus nerve or in professional athletes. In addition, the presence of up to 20 extrasystoles per hour is not considered a pathology when performing daily ECG monitoring.
What are the causes of arrhythmias?
The reasons are varied, but they can be standardized into 2 large groups, which often determine the patient’s management tactics: a distinction is made between organic (associated with anatomical defects in the structure of the heart and blood vessels) and functional (due to changes in the tone of the autonomic nervous system).
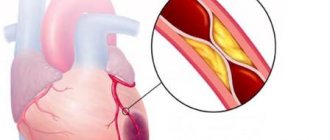
Among the organic causes, the main ones are coronary heart disease and previous myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, previous myocarditis, heart failure with low ejection fraction, left ventricular hypertrophy (due to hypertension or valve defects). Functional arrhythmias are more common in young patients and usually manifest as sinus tachycardia or sinus (respiratory) arrhythmia.
In addition, it is important to separately identify the so-called channelopathies, or electrical heart diseases, which, as a rule, are congenital pathologies in which the normal content of ions and electrolytes changes at the biochemical level.
There are a huge number of types of arrhythmias. Despite this, they are quite easy to diagnose. You just need to register an ECG. As a rule, major difficulties may arise here: it is not always possible to record an ECG at the moment when the patient feels an arrhythmia.
It often happens that the ECG outside an attack of arrhythmia is absolutely normal and uninformative for diagnosing the nature of the heart rhythm disturbance. I always recommend to my patients to call an ambulance or go to the nearest medical facility where they could record an ECG while the patient is experiencing arrhythmic sensations.
But it also happens that the arrhythmia persists for a very short time, or the heart rhythm returns to normal before the ambulance arrives. In such situations, it is necessary to recommend that the patient perform Holter (24-hour) ECG monitoring, in which the heart rhythm is recorded throughout the day. But even here there can be a catch: in the absence of daily frequency of arrhythmia, monitoring may be uninformative. Then it is necessary to carry out transesophageal pacing to actively provoke arrhythmia.
Treatment of arrhythmia directly depends on its nature and the reasons that caused it.
- For organic arrhythmias, treatment of the underlying disease is necessary. For example, in patients with a history of myocardial infarction, the appearance of ventricular extrasystoles is an unfavorable sign and may be associated with atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries.
- For functional arrhythmias, normalization of the work and rest regime is sufficient.
- For arrhythmias with a low pulse rate, which are accompanied by poor health (weakness, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, dizziness, loss of consciousness), implantation of a pacemaker is indicated.
- For arrhythmias with a high pulse rate, the prescription of tableted antiarrhythmic drugs or, if they are ineffective, radiofrequency ablation (laser cauterization) of the heart rhythm disturbance is indicated.
- If the arrhythmia is life-threatening, then patients are advised to undergo implantation of a cardioverter defibrillator.
- For some arrhythmias, so-called vagal tests are effective: holding your breath with straining at the height of inspiration for 5-10 seconds, reproducing the gag reflex by pressing on the root of the tongue with your fingers, immersing your face in a basin of ice water (“diving reflex”). But these tests are not a way to treat arrhythmias, but more often serve as assistants in their diagnosis.
The topic of arrhythmia is quite extensive. In each specific case, the approach is very individual. The patient’s task is to consult a cardiologist in a timely manner.
Take care of your health, and then the melody of your heart will always be rhythmic.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT WITH A CARDIOLOGIST
Diagnostics
The doctor clarifies all the symptoms, their frequency, asks about your diet and sleep patterns, and how often you are in stressful situations. Asks about head, hearing, and vision injuries; do you take vitamins and medications, drink alcohol, and about the pace of life.
After all clarifications, the doctor refers to:
- blood analysis;
- echocardiography;
- electrocardiography;
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRI of the brain (magnetic resonance imaging);
- radiography;
- vestibulometry;
- audiography;
- electroencephalogram;
- Ultrasound.
What to do if you have causeless anxiety and worry
It's hard to live in constant stress. If you are experiencing causeless anxiety and fear, the following list will tell you what to do:
- Talk to someone you trust. This could be a relative, a close friend, a psychotherapist or a helpline employee. People are social creatures, so communication is a good way to relieve internal stress.
- Find a way to calm down quickly. There is not always someone nearby with whom you can share. Therefore, it is important to find a suitable method that will help you relax: breathing techniques, soothing music, aromatherapy, self-massage and more. If you cannot independently choose a technique that quickly helps with anxiety for no reason, a specialist will tell you what to do.
- Add physical activity to your life. It is a natural and effective remedy for anxiety. Moderate exercise relieves tension, reduces stress hormones and strengthens the nervous system. Get at least 30 minutes of exercise every day.
- Normalization of lifestyle. Get enough sleep, eat well, give up bad habits. This stabilizes physical performance and neurotransmitter levels, which helps maintain emotional balance.
- Start keeping a journal. Taking notes can help you identify patterns of anxiety flare-ups, understand the causes, and spot early signs of them. Also, thanks to this, you will begin to focus more on positive events that you may not have noticed before.
When worried for no reason, everyone who regularly encounters this wants to know what to do. There is no universal method, but the 5 steps listed above are recommended for every person with increased anxiety. This may be enough to alleviate symptoms. But if self-help techniques do not give the desired effect, then if you regularly experience anxiety for no reason, you need to find out what to do from a specialist.
Signs of stress
According to statistics, in Russia women are more susceptible to stress due to their increased emotionality and sensitivity. In 2021, people of all professions experienced strong negative experiences, but especially teachers, entrepreneurs and, of course, doctors.
This year has been difficult for many, so the number of people with chronic stress has increased many times over. At the same time, people began to consider their depressed state as the norm. But even in the most difficult times, it is important not to let the situation get worse and fight back the disease.
Stress changes the entire body, so you should pay attention to different symptoms.
Behavioral signs of stress:
- conflict;
- aggressiveness;
- irritability;
- loss of interest in life, friends, appearance;
- decreased self-esteem;
- suspicion;
- frequent attacks of anger and feelings of helplessness.
Lifestyle changes:
- sleep disturbance;
- the emergence of bad habits;
- increased fatigue;
- decreased performance.
Intellectual traits:
- poor concentration;
- excessive distractibility;
- decrease in attention.
Changes in thinking:
- decreased creativity and memory;
- violation of logic;
- common spelling errors.
Physiological signs:
- frequent headaches;
- cardiopalmus;
- decreased immunity;
- sudden weight loss or, conversely, rapid weight gain;
- deterioration of organ function.
call me back
Treatment of stress
Do not delay making an appointment with a specialist if you feel that you cannot cope with stress on your own. Based on the patient's complaints, a treatment plan is prescribed.
An approximate treatment regimen looks like this:
- Therapeutic practice with a psychologist. At the moment, there are many psychological techniques that will help you cope with stress and return to normal life. The specialist will choose the one you need based on the patient’s condition and personal characteristics.
- Collection of analyses. Since stress can affect many organs, it is important to identify the problem early.
- Drug therapy. If the stress is not prolonged, then mild sedatives are prescribed that will reduce anxiety and anxiety. In more severe cases, patients are recommended to take tranquilizers and antidepressants.
- Relaxation. Healthy relaxation techniques include breathing techniques, massage and yoga.