Oncological diseases are the scourge of humanity. Today, oncology ranks second in the list of causes of mortality in the population after cardiovascular diseases. The situation is complicated by the fact that a method for treating malignant neoplasms has not yet been developed, although the global scientific community is making every effort to solve this problem.
And although a diagnosis of cancer sounds like a death sentence, in some cases it can be successfully treated, especially if the tumor is detected in the early stages. But there is also a stumbling block here: it is often not possible to determine the onset of the disease, since it can be completely asymptomatic.
Symptoms indicating the presence of cancer:
Symptoms largely depend on the location, size and type of tumor and, as mentioned above, may not appear at all if we are talking about the early stages. Therefore, the key point in diagnosing cancer is timely preventive examinations by a specialist.
The following common symptoms will help you suspect the presence of a tumor:
- Frequent cough;
- Bleeding;
- Color and size changes in moles;
- Disorders of the excretory system;
- Lumps and swelling on the body;
- Unexplained weight loss;
- Increased fatigue.
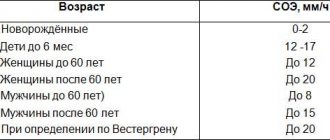
What does ESR show?
ESR is not a specific indicator for any particular disease, that is, it is impossible to establish a specific diagnosis based on its increase.
This test is considered useful for identifying hidden forms of various diseases and determining the activity of chronic inflammatory conditions. ESR can also serve as an indicator of the effectiveness of therapy.
However, measuring ESR is in no way used to diagnose cancer.
Prevention of cancer
Unfortunately, at this point in time it is not possible to completely prevent the development of cancer. But following some preventive rules can reduce the risk of disease to a minimum:
- Complete cessation of smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Diet;
- Sports activities;
- Maintaining a daily routine;
- Reducing time spent in direct sunlight;
- Annual follow-up with a doctor, especially for those at risk.
What are the reasons for increased ESR?
An elevated ESR is a sign of any disease associated with significant tissue damage, inflammation, infection, or malignant cancer.
In all infectious and inflammatory diseases, the immune system responds by increasing the production of immunoglobulins. This in turn increases the tendency of red blood cells to aggregate and form red blood cell columns. Repeated studies of ESR make it possible to evaluate the dynamics of the infectious process and the effectiveness of treatment.
Also, the ESR is influenced by many other factors that determine the physicochemical state of the plasma: viscosity, electrolyte composition of the plasma, the ratio between cholesterol and lecithin in the plasma, the content of acids in it, etc.
The main reasons for increasing ESR:
- Any inflammatory process in the body, for example, arthritis, accelerates ESR due to the production of large amounts of “acute phase proteins of inflammation.”
- A number of diseases in which tissue damage occurs - myocardial infarction, destructive pancreatitis, etc.
- Surgical interventions are also accompanied by an increase in ESR.
- A decrease in the number of red blood cells in patients with anemia also leads to an increase in ESR.
- All infectious diseases are usually accompanied by an acceleration of ESR.
- Obesity.
- An error during a blood test, for example, incorrect temperature conditions.
- An increase in ESR is observed in elderly patients.
Cytological examination
This is the most informative type of laboratory examination, which accurately determines the presence or absence of malignant cells.
The analysis consists of taking a tiny section of tissue in which the presence of a cancerous tumor is suspected, with further examination under a microscope. Modern endoscopic technologies make it possible to collect biomaterial from any organ - skin, liver, lungs, bone marrow, lymph nodes.
Cytology is the study of cellular structure and function. The cells of a cancerous tumor differ significantly from the cells of healthy tissues, so laboratory testing can accurately determine the malignancy of the neoplasm.
The following biomaterials are used for cytological examination:
- imprints from the skin, mucous membranes;
- liquids in the form of urine, sputum;
- swabs from internal organs obtained during endoscopy;
- tissue samples obtained by puncture with a thin needle.
This diagnostic method is used for preventive examinations, clarifying the diagnosis, planning and monitoring treatment, and identifying relapses. It is simple, safe for the patient, and results can be obtained within 24 hours.
How to calculate the individual ESR norm in elderly patients?
The easiest way is to use Miller's formula:
For example, the permissible ESR limit for a 60-year-old woman is: (60 years + 10): 2 = 35 mm/hour
When changes are detected in a clinical blood test, the first thing the patient does is go to a general practitioner. A useful point is that ESR is included in the Clinical Blood Test, which means that the doctor simultaneously sees the level of leukocytes, platelets, and hemoglobin. When making a diagnosis, the doctor first chooses between three groups: infections, immune diseases and conditions, and malignant diseases. The doctor interviews and examines the patient, after which, based on symptoms, examination and diagnostic data, he determines further tactics.
If the reason for the increase in ESR has not been identified, the analysis should be repeated after 1-3 months. Normalization of the indicator is observed in almost 80% of cases.
Tumor markers
Tumor markers are specific proteins produced by malignant tumor cells. Normally, humans do not have such proteins or contain them in small quantities. Each organ has its own tumor marker; let’s look at the most frequently identified ones:
Tumor marker CA 12 , normal -
Okomarker CA 15-3 , normal
Tumor marker PSA , norm 0 - 4 ng/ml. Detects prostate cancer.
The tumor marker AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) is a marker of liver cancer. Also used in gynecology to determine fetal malformations. The norm for men and non-pregnant women is: 0.5 – 5.5 IU/ml.
Tumor marker Ca 19-9 , normal
Tests for tumor markers are carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach. Blood for analysis is taken from a vein.
ESR and oncology
In the absence of an inflammatory and infectious disease, a significant increase in ESR should raise suspicion regarding the presence of a malignant tumor. At the first suspicion of its presence, a consultation with an oncologist and a thorough additional examination using high-tech equipment and competent specialists are necessary.
Oncology is a multifactorial disease, accompanied by both inflammatory processes and anemia, metabolic disorders, and therefore causing the body to release a large amount of active substances and proteins. Therefore, most patients with various forms of malignant tumors have an elevated ESR.
For example, ESR in lung cancer may increase in the presence of pneumonia near the tumor. With colon or stomach cancer, severe anemia occurs, which leads to an increase in ESR.
There is no specific level for each tumor; most often, the increase is due to a combination of many factors.
The highest level of ESR (80-90 mm/h or more) associated with oncology is usually determined in diseases grouped as “paraproteinemias” (myeloma, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia). With these diseases, structurally abnormal and functionally defective proteins appear in the blood, which leads to changes in the blood.
Stool analysis
Blood may also be present in the stool, and it is almost impossible to notice it visually. Laboratory analysis will help determine its presence.
The presence of blood in the stool is a sign of intestinal cancer (most often colon), but it is also a symptom of many benign gastrointestinal diseases. Polyps in the intestines can bleed. Moreover, it should be remembered that polyps tend to degenerate into a malignant tumor. In any case, the presence of blood in the stool is a reason to undergo a more in-depth diagnosis and take tests to detect cancer.
Feces are also collected in a sterile container in the morning.
Symptoms of oncology in children
Common symptoms of the first signs of cancer in children include:
- fatigue without good reason;
- irritability (the child constantly cries, is capricious for no reason);
- the skin becomes pale (a feeling of intoxication occurs);
- poor sleep, development of insomnia;
- increase in body temperature (it will stabilize itself, then rise sharply and fall again);
- nausea and vomiting;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The child will be afraid of everything, stop communicating with strangers, and become withdrawn. Each type of disease has its own symptoms, let’s look at the main ones.
Leukemia
If the level of certain cells in the blood decreases, this leads to pathological growths of the bone marrow. Symptoms:
- poor appetite;
- irritability;
- the skin becomes pale;
- weight loss;
- dyspnea;
- vomit.
This problem occurs in up to 35% of children. Some patients experience loss of coordination, symptoms are accompanied by bleeding and enlarged lymph nodes. Redness and hematomas may appear on the skin.
Brain tumor
The cerebellum and brainstem are the first to be at risk. Symptoms:
- headache;
- loss of coordination;
- insomnia;
- visual impairment;
- hearing impairment.
The child’s handwriting changes, especially headaches, which torment the baby in the morning. Movements such as rubbing the head against the wall may appear, as the baby tries to get rid of the discomfort. Severe headaches occur when tilting your head back and forth. The disease is also accompanied by convulsions, hallucinations, and vomiting in the morning.
Nephroblastoma
Kidney damage is typical for children under 3 years of age. Symptoms:
- hard breathing;
- increased body temperature;
- loss of appetite;
- the appearance of pain.
Parents can feel changes in the area of the celiac cavity themselves; when the first signs appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Another sign is diarrhea, which is initially assessed by parents as a common stomach upset.
Neuroblastoma
Signs are typical for both newborns and children under 9 years of age. Symptoms:
- increase in abdominal volume;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- bone damage.
Pain sensations are concentrated only in one place - in the abdomen; the disease does not spread to other organs and areas. The child may have swollen limbs; during palpation, the doctor can determine the source of the disease; there is a malfunction in the gastrointestinal tract and bladder.
Retinoblastoma
This is a malignant tumor that affects the eye area. Symptoms:
- loss of vision;
- pain in the eye area;
- redness of the eyes (the disease is accompanied by frequent hemorrhages);
- bulging eyes.
Symptoms are typical for children under 6-7 years of age. The last stage of the disease is expressed in complete loss of vision. Children develop strabismus and develop the impression of a “cat’s eye” – a glow in the pupil that parents and doctors cannot notice.
Osteosarcoma
Bone damage, the disease is typical for adolescent children. Symptoms:
- pain;
- slight swelling;
- insomnia.
The pain is especially intensified at night, the early stage of the disease does not last long, pain symptoms and swelling at the site disappear on their own, but then appear in a more acute form.
Ewing's sarcoma
Children under 16 years of age can get this disease. In the affected area are the scapula and collarbone. Symptoms:
- pain in the affected area;
- increased body temperature;
- sweating (especially at night);
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The child will become irritable, aggressive, get tired quickly, and exhibit causeless mood swings.
Khodzhikin's lymphoma
The disease is typical for adolescence. The main symptoms include:
- increased body temperature;
- excessive sweating;
- weakness;
- fatigue.
The child's lymph nodes will enlarge; this syndrome is expressed painlessly, may disappear over time, and then reappear.
Diagnosis of cancer in children at early stages of development
Early diagnosis of cancer in children helps to promptly pay attention to the disease, provide medical care and get rid of the disease. The main role is assigned to parents; they must monitor the baby’s health, respond to all changes in a timely manner, and contact specialists for any need. You also need to listen to the child’s complaints and not let things take their course. There are cases when the first symptoms are characteristic of other diseases, for example, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache.
Parents do not fully appreciate the severity, accepting the symptoms as a mild disorder of the body. Do not self-medicate, show your child to a doctor. The specialist will conduct an examination and, if signs of cancer appear, will prescribe an examination. It could be:
- inspection;
- palpation of the place where the baby hurts;
- X-ray;
- ultrasonography;
- MRI;
- CT;
- taking tests.
The doctor’s task is to determine the cause of the symptoms, to understand why the child complains of pain and other changes. If pain bothers you in the abdominal area, endoscopy of the stomach, esophagus, and duodenum is prescribed. To better study the condition of the internal organs, scintigraphy with radioisotopes is performed, thanks to which it is possible to study the organs and see all changes in a two-dimensional position.
A blood test is required to help determine whether there are changes in the composition of the cellular ratio. If surgery is required, in most cases young patients are prescribed a biopsy, and this can also be a separate additional type of examination.
FAQ
When deciphering blood tests, patients often ask questions about how this or that indicator can change with cancer and what this can mean. Let's look at the most common of them.
Can a good blood test be detected in cancer patients?
Yes, it can if the disease is detected in the initial stages or at the compensation stage. In addition, do not forget that there are a huge number of types of blood tests and a situation may arise that there are no changes in the general analysis, and tumor markers were not detected.
However, the situation when a general blood test for cancer does not have any abnormalities does not occur so often
Is it possible to determine the stage of cancer using a blood test?
Oncology is staged based on many criteria, and most of them are purely clinical - the spread of the primary tumor, the presence of metastases in the lymph nodes and nearby organs, and so on. Therefore, if it is possible to draw a parallel with the stage using a blood test, then it is very approximately, and such an analysis should be highly specific, such as genetic tests or determination of tumor markers.
Is there a specific test to detect stomach cancer?
Stomach tumors cannot be detected by analyzing general blood tests. However, today there are innovative molecular tests that make it possible to determine gastric cancer and its antigenic set. This is the detection of PEA-1 tumor markers and the Foundation One genetic test, which completely determines the antigenic profile of a cancer cell. This test will show the cancer itself and determine its aggressiveness.
These tests are not carried out in all clinics in the world and are expensive. At the First Tel Aviv Medical Center, the patient has the opportunity to order all the latest genetic and molecular tests.
Can a blood test detect cancer?
Most often, even general and biochemical blood tests will show changes in indicators in the presence of cancer. However, this does not always happen and these changes may be associated with other reasons - infections, stress, and so on.
Identification of specific tumor markers is a more specific criterion, but they can also be elevated in related pathologies. But innovative genetic tests will always give an answer - what type of tumor led to the changes, whether it is treatable and show the degree of aggressiveness of atypical cells.
However, such tests are not performed in the CIS countries, so the answer to the question is no, there is no general test that determines cancer in the blood.
What tests should I take for blood cancer?
For hemoblastoses, the most effective will be a general blood test with a formula of cellular elements and a detailed biochemical analysis with the identification of tumor markers NSE and CEA-5
Deciphering a blood test for bone marrow cancer
In this situation, the general analysis will include immature cells and progenitor cells that are not normally found in the blood. During a tumor process in the bone marrow, they do not have time to develop to mature forms, enter the bloodstream and cease to perform their function