general description
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the leading cause of death worldwide.
According to experts, in 2030 more than 23 million people will die from CVDs. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a disease caused by insufficient supply of the heart (myocardium) with oxygen and nutrients, which occurs due to impaired blood supply to the myocardium due to damage to the coronary arteries.
The clinical manifestations of IHD are varied: from acute manifestations in the form of myocardial infarction or sudden cardiac death to long-term chronic diseases - angina pectoris (recurrent chest pain), post-infarction cardiosclerosis, chronic heart failure.
Treatment methods for coronary heart disease
To accurately diagnose a patient with coronary artery disease, it is necessary to conduct a complete examination of the heart and blood vessels, which includes:
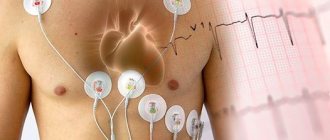
- Echocardiography (ECHO-CG).
- Electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Coronary angiography.
- Measuring blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
To treat coronary heart disease, the first step is to eliminate all negative factors that negatively affect the course of the disease: if you smoke, you need to quit smoking, limit alcohol consumption, exercise, maintain normal blood pressure levels, lose weight, reduce cholesterol levels (if it is high) and reconsider your diet (try to eat right).
In special cases, to normalize blood flow in the heart, special surgical procedures on damaged main arteries are indicated:
- Angioplasty involves installing a stent or balloon in an artery of the heart. The operation is performed under x-ray. During angioplasty, a balloon catheter is inserted into the artery and guided towards the narrowed artery. The functions of the balloon are to push through cholesterol plaques, as if “smoothing” them. If this does not happen, then a special stent is installed in this place, preventing the vascular lumen from narrowing.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting is a rather complex surgical operation that uses artificial blood circulation. Part of the blocked vessel is bypassed using a vein taken from the leg or arm. The new artery joins the aorta and coronary artery. In this way, the blocked vessel is excluded from the circulatory system. In other words, during the operation, a bypass of the blood is made, bypassing the artery in which the lumen has narrowed.
Causes
IHD occurs as a result of atherosclerosis of large (epicardial) coronary (heart) arteries of varying degrees: from a slight narrowing of the lumen in the vessel to its complete blockage by atheroma (cholesterol, fat) masses or a blood clot that has developed at the site of a “vulnerable” (damaged) atherosclerotic plaque (ASP) . Other causes of IHD are spasm of the coronary arteries and damage to the microvasculature in the myocardium. In most cases, they also develop against the background of existing atherosclerosis.
It is possible to identify the population groups most susceptible to the development of coronary artery disease: people suffering from high blood pressure, those addicted to smoking, those suffering from high cholesterol levels, diabetes mellitus, and chronic kidney diseases. . Male gender and old age are also powerful risk factors for the development of coronary artery disease.
Treatment
Depending on the type of pathology, treatment is carried out under the guidance of a cardiologist, neurologist, vascular surgeon, neurosurgeon, cardiac surgeon, phlebologist, rheumatologist. Emergency conditions require the help of a resuscitator. There are conservative and surgical methods for treating CVD.
Conservative methods include:
- drug therapy – medications are prescribed depending on the diagnosis;
- plasmapheresis, autohemotransfusion - in the treatment of rheumatic carditis;
- thrombolysis – dissolution of a blood clot during arterial embolism;
- physiotherapy – in the treatment of chronic cerebrovascular accidents, thromboangiitis obliterans.
Surgical methods for treating CVD:
- thromboembolectomy – surgical removal of a blood clot in case of ineffectiveness or contraindications to thrombolysis;
- thrombectomy – for deep vein thrombosis;
- stenting of peripheral vessels and coronary arteries – for atherosclerosis,
- heart valve replacement – for endocarditis;
- stereotactic aspiration of hematoma – for hemorrhagic stroke.
Today, open surgical interventions are rarely performed; preference is given to vascular surgery - this contributes to the speedy recovery of the patient and minimization of postoperative complications. However, after treatment of severe CVD, patients most often require long-term rehabilitation.
Symptoms
The main, but far from the only symptom of IHD is pressing or squeezing pain behind the sternum or in the region of the heart. In chronic ischemic heart disease, pain occurs initially during physical activity and causes a gradual decrease in its tolerance. In the acute form of IHD, myocardial infarction or a pre-infarction state (unstable angina) develops. During an attack, the patient may also experience:
- pain or burning in the chest, under the shoulder blade, in the back, in the upper abdomen;
- feeling of heaviness in the chest;
- sensation of uneven heartbeat, abnormal heart function, palpitations;
- feeling of a sinking heart;
- shortness of breath;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- dizziness and fainting;
- sweating
The discomfort may disappear or go away completely after completing physical activity. In case of myocardial infarction or unstable angina, the connection between complaints and physical activity is lost, and complaints can develop at rest and continue for a long time (tens of minutes, hours). Usually all of the above symptoms do not appear at the same time. In various forms of the disease, a certain feeling of discomfort dominates.
If you notice such sensations, consult a cardiologist as soon as possible. If chest pain or other symptoms described above do not disappear within 10 minutes of rest, call an ambulance. The progression of IHD can develop slowly over years. At the same time, in some patients the disease is asymptomatic or with erased or atypical symptoms. To prevent disturbances in the functioning of the heart or the development of severe forms of the disease, undergo a comprehensive heart examination in our center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency. An advanced disease is very dangerous! At a late stage, it can lead to a fatal heart attack or severe heart failure with severe disability.
Complications of CVD
According to WHO, cardiovascular pathologies are the main cause of death and often lead to disability. Death is not uncommon with large heart attacks and strokes, massive pulmonary embolism, heart failure complicated by pulmonary edema, and cardiogenic shock. A stroke can lead to a wide range of neurological disorders, and chronic cerebrovascular accident can lead to progressive cognitive impairment. Peripheral arterial pathologies are dangerous due to the development of gangrene with subsequent amputation of the limb (often at a young age). CVDs have a detrimental effect on the state of the reproductive sphere: impotence is often registered in men, and infertility and childlessness in women.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of coronary artery disease is carried out by cardiologists in several stages. When interviewing the patient, complaints are clarified and symptoms that may be characteristic of the disease are clarified. Examination of the patient helps to note visual changes - swelling and changed skin color (cyanosis); listening to the heart helps to identify murmurs and rhythm disturbances. Next, the patient undergoes laboratory tests for certain indicators in the blood, which may indicate pathology. Standard biochemical analysis is also important, as well as determination of glucose and cholesterol levels. But the most accurate diagnostic method is instrumental:
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- stress tests with physical activity or drug stimulation of the heart;
- Holter ECG monitoring;
- angiography of the coronary arteries (coronary angiography).
Timely examination helps to avoid serious consequences and the development of irreversible pathology. Spend a few hours on your health, because this time will help maintain your quality of life in the future.
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP) is a clinical and morphological syndrome characterized by special morphological signs: damage to the respiratory bronchioles and alveoli, the development of chronic inflammation around the alveoli, the predominance of changes in the alveoli (organizing pneumonia) over damage to the bronchioles (bronchiolitis).
Synonyms for COP are: bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia and proliferative bronchiolitis.
The morphological basis is productive inflammation with damage to the epithelium, proliferation of granulation and then connective tissue in the respiratory bronchioles and alveoli, and the formation of Masson's bodies.
The frequency of occurrence is unknown. There are no gender differences. The average age of onset of the disease is 55-60 years. In 70% of cases, cryptogenic organizing pneumonia is an idiopathic disease.
In other cases, the reasons may be:
- post-transplant complications (lung transplant, heart-lung complex, bone marrow transplant),
- systemic connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic scleroderma, Schoengren's syndrome),
- infections (Mycoplasma pneumonia, RSV, CMV, adenovirus, HIV, etc.).
- complications of drug therapy (amiodarone, D-penicillamine, gold drugs, sulfasalazine),
- inhalation of toxic substances (sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, phosgene, etc.),
- complications of radiation therapy,
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Apparently, organizing pneumonia is a nonspecific stereotypical reaction to various damaging agents.
Among the most common manifestations of the pathology: weakness, fever (60%), weight loss (50%), myalgia (50%), cough (90%), shortness of breath 80%. When auscultating the lungs, end-inspiratory crepitus is heard, and less often, dry wheezing along with crepitus.
Among the laboratory data, attention is drawn to peripheral blood leukocytosis, increased levels of ESR and C-reactive protein. Spirometry indicates a restrictive type of breathing disorder (decrease in VC, FVC and Tiffno index).
Computed tomography is the leading method for diagnosing COP. There is no evidence base for treatment. All recommendations correspond to evidence class C and D. The first line of drugs is glucocorticosteroids (GCS), treatment is effective in 70% of cases. In case of insufficient response to GCS therapy. Cytostatic agents (azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine) are introduced into the arsenal. Of course, in the latter case, all the pros and cons of drug therapy are weighed.
Prevention
Preventing a disease is much easier than curing it. To maintain healthy arteries and blood vessels, it is necessary to eliminate risk factors that negatively affect your health:
- To give up smoking;
- Monitoring blood pressure levels
- Normalization of the level of “bad” cholesterol (low-density lipoproteins)
- Fighting stress and depression
- Minimize alcohol consumption;
- Refusal of smoked, fatty, fried and salty foods.
Spend more time on an active lifestyle: moderate physical activity, therapeutic exercises, morning exercises, walking, swimming, dancing. Physical activity will help strengthen the walls of blood vessels and maintain normal weight, and if necessary, reduce it.
The most important thing in prevention is timely observation by a specialist. In order not to visit medical institutions several times to undergo all the necessary tests and examinations, contact our cardiology center. Federal Research Center FMBA offers patients several programs for comprehensive heart research. You can find them here.
Preventive measures
Patients with coronary artery disease are advised to change their lifestyle:
- reduce weight in case of obesity;
- include active sports;
- adhere to proper nutrition;
- stop smoking;
- comply with night sleep standards.
Preventing the development of a disease is easier than treating it. To prevent narrowing of the arteries, doctors recommend monitoring blood pressure, reducing stress levels, and not triggering depression. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of alcohol, fried, fatty, smoked and salty foods. It is advisable to walk more, do exercise therapy, exercise, and swimming. Physical activity strengthens the walls of blood vessels and reduces the risk of weight gain.
An important measure for the prevention of coronary heart disease is regular visits to a cardiologist to prevent the development of pathological processes. In our center you can undergo all the necessary examinations and tests to determine the state of your cardiovascular system.