03 Jun 2021 at 09:50 MRI of the heart in Tushino 12066
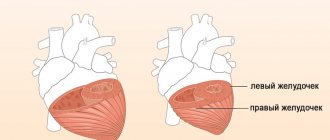
Left ventricular hypertrophy is a fairly common heart disorder. The disease in most cases begins to develop in patients suffering from hypertension. Hypertrophy provokes an increase in the size of the wall of the left ventricle. The disease can provoke a change in the size of the septum, which is located between the left and right ventricles. The development of hypertrophy in most cases occurs over several years.
Left ventricular hypertrophy: causes
The myocardium can increase in size under the influence of certain factors that force it to work harder. In this way, the heart cells try to compensate for the increased load. These factors include:
- High blood pressure. One of the most common causes of left ventricular hypertrophy.
- Aortic valve stenosis. It is located between the left muscular chamber and the aorta. If it narrows, the muscle has to work harder, causing it to increase in size.
- Intense physical exercise. During prolonged cardio and strength exercises, thickening of the myocardium is considered as an adaptation of the body to increased loads.
Sometimes left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart develops due to a genetic disease that causes structural changes in heart cells - hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Another possible cause may be amyloidosis, which is accompanied by abnormal protein deposits in all organs, including the heart.
Prevention of hypertrophy
Lifestyle changes will help not only prevent the development of hypertrophy, but also improve the condition of an already enlarged ventricle. Since hypertrophy is common in people suffering from obesity, maintaining an ideal body mass index will be the best prevention of the disease. It is also worth limiting the amount of salt in your diet to normalize blood pressure. If hypertrophy is suspected, it is recommended to drink alcohol in moderation, and if treatment is prescribed, then it is better to avoid strong drinks altogether.
Despite the fact that one of the reasons for an enlarged ventricle of the heart is heavy physical activity, you should not give up sports. Regular physical exercise, such as walking, Pilates, yoga, will not only do no harm, but, on the contrary, will strengthen the heart. If a diagnosis of hypertrophy has already been made, it is necessary to ask a physiotherapist to select the optimal exercise program. 30 minutes of moderate physical activity will strengthen weakened heart muscle and prevent its enlargement.
A healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition will allow you to forget about problems with the left ventricle for a long time.
Diagnosis of the disease
At the first stage, the doctor will listen to the patient's complaints, take a medical history and conduct a thorough physical examination, including measuring blood pressure and a preliminary assessment of heart function (auscultation or auscultation). Further additional studies will be prescribed:
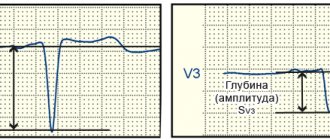
- Electrocardiogram (ECG). Thickening of the wall of the left heart chamber can lead to disruption of the electrical activity of the heart, which is reflected in the results of the ECG.
- Echocardiogram. Allows you to evaluate blood flow, detect myocardial hypertrophy and identify the causes that caused it, for example, aortic valve stenosis.
- MRI. It has a high discriminative ability when assessing soft tissues, including the heart muscle.
Laboratory tests and, in some cases, invasive tests such as coronary angiography and myocardial biopsy may also be performed.
Causes leading to illness
The following diseases and conditions are considered to be the causes of myocardial hypertrophy:
- arterial hypertension;
- heart disease;
- idiopathic hypertrophy;
- excessive physical activity;
- sleep apnea (or otherwise - snoring). This is caused by involuntary cessation of breathing for a few seconds during sleep and a delay in oxygen supply.
Sign up for a consultation
The development of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy usually occurs against the background of hypertension, but can be a consequence of excessive physical stress on the body. Therefore, heavy professions (masons, loaders) are called the reasons for the development of hypertrophy.
Attention! Active smokers and those people who lead a sedentary lifestyle are at particular risk.
Drugs for left ventricular hypertrophy
Medicines for high blood pressure help prevent further enlargement of the myocardium and, in some cases, reverse it. For this purpose, the following may be prescribed:
- ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme). They lower blood pressure and reduce the load on the heart by dilating blood vessels and improving blood flow. Examples: Captopril, Enalapril, Lisinopril, Ramipril.
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). Drugs such as Lozap, Closart, Sentor also relax blood vessels, reducing blood pressure.
- Calcium channel blockers. These drugs inhibit the penetration of calcium ions from the intercellular space into the muscle cells of the heart and blood vessels. The blood vessels relax, blood pressure decreases. Examples: Amlodipine, Diltiazem, Verapamil, Lercanidipine.
- Diuretics. Diuretics used for left ventricular hypertrophy are called thiazide diuretics. They work by decreasing the kidneys' ability to reabsorb salt and water from urine, thereby increasing urine production and output (diuresis). Also, diuretics of this type directly help relax the smooth muscles of blood vessels. Examples: Tonorma, Hypothiazide, Hydrochlorothiazide.
- Beta blockers. Drugs such as Metoprolol, Atenolol, Lokren, Betak help reduce heart rate and blood pressure, as well as prevent the negative effects of stress hormones. Beta blockers are generally not prescribed as the primary treatment for hypertension. Your doctor may recommend them if therapy with other drugs has not been successful.
In cases where the disease is caused by aortic valve stenosis, surgery may be required. The decision on the advisability of the operation is made by the doctor after a thorough diagnostic examination of the patient.
About cardiomyopathies
Pathological processes in myocardial cells are based on hereditary predisposition (idiopathic cardiopathy) or dystrophy and sclerosis. The latter are caused by myocarditis, allergies and toxic damage to heart cells, endocrine pathologies (excess catecholamines and somatotropic hormone), and immune disorders.
Types of cardiomyopathies occurring with LVH:
Hypertrophic form
It may produce diffuse or limited symmetrical or asymmetrical thickening of the muscle layer of the left ventricle. At the same time, the volume of the heart chambers decreases. The disease most often affects men and is inherited.
Clinical manifestations depend on the severity of obstruction of the heart chambers. The obstructive variant gives the clinical picture of aortic stenosis: heart pain, dizziness, fainting, weakness, pallor, shortness of breath. Arrhythmias may be detected. As the disease progresses, signs of heart failure develop.
The boundaries of the heart expand (mainly due to the left sections). There is a downward displacement of the apical impulse and dullness of heart sounds. A functional systolic murmur is characteristic, heard after the first heart sound.
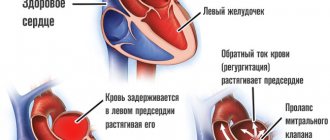
Dilated form
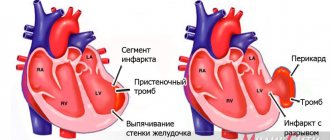
It is manifested by expansion of the chambers of the heart and hypertrophy of the myocardium of all its parts. At the same time, the contractile capabilities of the myocardium decrease. Only 10% of all cases of this cardiomyopathy occur in hereditary forms. In other cases, inflammatory and toxic factors are to blame. Dilated cardiopathy often manifests itself at a young age (30-35 years).
The most typical manifestation is the clinical picture of left ventricular failure: bluish lips, shortness of breath, cardiac asthma or pulmonary edema. The right ventricle also suffers, which is expressed in cyanosis of the hands, enlarged liver, accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, peripheral edema, and swelling of the neck veins. Severe rhythm disorders are also observed: paroxysms of tachycardia, atrial fibrillation. Patients may die due to ventricular fibrillation or asystole.
Hypertrophy of the left ventricular myocardium is diffuse. The expansion of the cardiac cavities prevails over the thickening of the myocardium. Learn more about the symptoms and treatment of cardiomyopathy.
Is left ventricular hypertrophy dangerous?
Without effective treatment, pathological thickening of the wall of the heart chamber can lead to serious complications such as:
- weakening of the blood supply to the heart;
- pumping dysfunction (heart failure);
- heart rhythm disturbance (arrhythmia);
- insufficient oxygen supply to the myocardium (ischemic disease);
- stroke and heart attack.
Timely consultation with a doctor and properly prescribed therapy can avoid serious consequences of the disease.
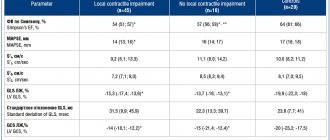
Differences between different types of LVH
Cardiomyopathy | Arterial hypertension | Sports heart | |
| Age | under 35 | over 35 | from 30 |
| Floor | both sexes | both sexes | more often men |
| Heredity | burdened with hypertension | burdened with cardiomyopathy | not burdened |
| Complaints | dizziness, shortness of breath, fainting, heart pain, rhythm disturbances | headaches, less often shortness of breath | stabbing pain in the heart, bradycardia |
| Type of LVH | asymmetrical | uniform | symmetrical |
| Myocardial thickness | more than 1.5 cm | less than 1.5 cm | decreases when the load stops |
| LV dilatation | rarely, more often a decrease | Maybe | more than 5.5 cm |
Popular questions about left ventricular hypertrophy
What medications should I take for left ventricular hypertrophy?
The choice of medications primarily depends on the causes of LVH. Therefore, drug therapy should be prescribed by a doctor. Most often, it includes taking ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, calcium channel blockers, thiazide diuretics and beta blockers.
Why is left ventricular hypertrophy dangerous?
If the patient does not receive proper treatment for severe LVH, this can lead to the development of complications such as acute heart failure, arrhythmia, coronary artery disease, heart attack and stroke.
Is it possible to cure left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart?
You can achieve good results by eliminating the underlying cause of the disease, namely high blood pressure. Correctly selected antihypertensive therapy in many cases makes it possible to stop the progression of the pathology, and sometimes leads to a reduction in the hypertrophied heart wall.
What is concentric left ventricular hypertrophy?
It is a disease that occurs as a result of stressors on the heart, such as hypertension, congenital heart defects (such as tetralogy of Fallot), valve defects (narrowing of the aorta or stenosis), and primary myocardial defects that directly cause hypertrophy (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy). It is characterized by thickening of the myocardium without a corresponding increase in the size of the ventricles, and is often accompanied by symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath on exertion, general fatigue, syncope and palpitations.
Symptoms of the development of an abnormal condition
Dilatation of the left ventricle in most cases develops very slowly. The patient may not experience any unpleasant signs or symptoms, especially in the early stages of the disease. But as hypertrophy develops, the following may occur:
- shortness of breath;
- unexplained fatigue;
- chest pain, especially after exercise;
- sensation of fast, fluttering heartbeats;
- dizziness or fainting.
You should seek medical help if:
- there is a feeling of pain in the chest that lasts longer than a few minutes;
- there are serious breathing difficulties that interfere with daily activities;
- have severe, recurring memory problems;
- there are loss of consciousness;
- shortness of breath combined with rapid heartbeat is troubling.