Principles of treatment
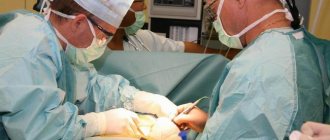
Aneurysm treatment is carried out by a neurologist. The operation is performed only by a neurosurgeon. Surgical methods are aimed primarily at preventing aneurysm rupture, which can result in the death of the patient. Conservative therapy for this pathology is used to slow the progression of the disease.
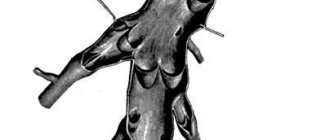
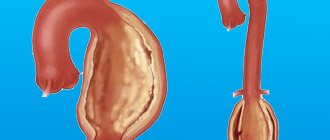
Surgical treatment of a cerebral aneurysm involves two types of main operations: clipping and endovascular occlusion. Surgery prevents the aneurysm from rupturing. A radical method of treatment is the removal of arteriovenous malformation during a microsurgical operation.
Aneurysm clipping
Aneurysm clipping is an open operation during which the neurosurgeon blocks blood flow in a certain area of the vessel and applies a clip. At the stage of preparation for surgery, specialists prescribe a procedure that allows them to stabilize the patient’s condition and minimize the risk of possible complications. Preventive examination makes it possible to identify possible disorders and diseases that can lead to adverse consequences of surgical intervention.
The operation is performed using modern microsurgical techniques through a small trepanation hole. During surgery, the neurosurgeon prevents rupture of the wall of the malformation.
After isolating the neck of the aneurysm, the specialist places a clip on it. Additional control with Doppler ultrasound allows you to assess the state of blood flow and ensure the effectiveness of the operation.
Treatment of an aneurysm using the clipping method is considered quite complex and should only be performed by an experienced neurosurgeon. A qualified specialist will do everything possible to ensure accurate and technically correct application of the clip. Otherwise, dangerous complications and a long rehabilitation period cannot be avoided.
The clip is applied to the neck of the aneurysm vessel. The accuracy of the neurosurgeon’s actions is confirmed by conducting high-quality diagnostics (Dopplerography) during the procedure.
Endovascular occlusion
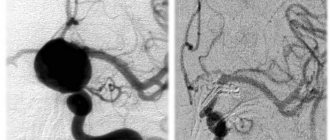
During endovascular occlusion of an aneurysm, the neurosurgeon blocks the lumen of the dilated vessel with a special implant. The operation is used when clipping is not possible, for example, when the aneurysm is spindle-shaped. During surgery, a specialist inserts a catheter balloon through the femoral artery using angiographic control. It closes the lumen of the aneurysm. You can also use a microspiral to perform thrombosis. The choice remains with the attending physician. The microspiral in the cavity of the affected vascular area forms blood clots, which clog the lumen of the vessel and shut off the aneurysms from the blood circulation.
Causes of the disease
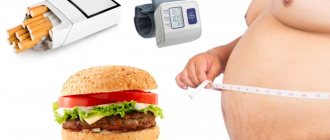
A cerebral aneurysm can be either a congenital pathology or acquired during life. Usually congenital are combined with many other developmental defects: coarctation of the aorta, polycystic kidney disease, connective tissue diseases. The main causes of aneurysm:
- genetic abnormalities in the structure of the walls of brain vessels;
- pathological infectious processes;
- injuries and tumors;
- development of atherosclerosis and high blood pressure;
- thromboembolism;
- bad habits.
Scientists have not fully studied the causes of the disease and the theory of their occurrence.
Symptoms
More than half of the patients do not know about the existence of the disease, because for a long time the pathology may not manifest itself in any way, especially if the expansion is insignificant and does not compress the surrounding tissues. In rare cases, headaches of varying intensity may be present. The main symptoms of cerebral aneurysm:
- frequent disturbances in speech and coordination of movements;
- vision problems (double vision, blurred vision), of varying severity;
- strabismus and pain in the eye area;
- short-term memory, distracted attention;
- hearing impairment and taste perception;
- pronounced changes in the patient’s mood and behavior;
- signs of fatigue.
All of these symptoms are characteristic not only of this disease. Therefore, for the correct diagnosis and timely treatment of cerebral aneurysm, it is necessary to carry out a set of diagnostic measures to identify the pathology.
Methods for diagnosing aneurysm
In German clinics, extensive diagnostics are carried out in order to provide qualified and effective treatment.
The latest computer technologies are used:
- Angiography. The technique is used by specialists to accurately diagnose possible circulatory disorders and makes it easy to detect an aneurysm or a vessel that has burst.
- Computed tomography (CT) of the head. Using this technique, cerebral aneurysm is diagnosed quickly and completely painlessly. Through diagnostics, the doctor can easily detect the presence of an aneurysm, and if the formation ruptures, the exact location of the hemorrhage in the brain is determined.
- Computed angiography (CT angiography). A technique with which a specialist can quickly and thoroughly examine the vessels of the head.
- Electroencephalogram.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The technique is used by specialists to obtain detailed images of the vessels of the head and brain.
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). The study helps German specialists carry out detailed diagnostics of the condition of the walls of blood vessels. The specialist is able to view detailed cross-sectional images of the brain and its blood vessels, both two-dimensional and three-dimensional.
- Positron emission tomography of the brain.
- Dopleography.
- Cerebrospinal fluid examination is a study of the cerebrospinal fluid of the brain and spinal cord for inflammatory processes, brain and spinal bleeding, infections and tumors.