What are antibodies to coronavirus?
Antibodies (also known as immunoglobulins) are special proteins that are produced and/or produced by plasma cells.
What do immunoglobulins do?
Immunoglobulins are formed in response to foreign bacteria or viruses entering the body. They interact with the antigen (specific site of the pest) and neutralize it.
Thus, our immunity guards our health.
What classes of immunoglobulins are there?
There are 5 classes of immunoglobulins
, some of which contain subclasses.
IgA - secreted on the surface of the epithelium and present in saliva, tears, and on the surface of mucous membranes.
IgM - detected upon initial exposure to antigen.
Indicates an acute infectious process in humans.
IgG is the main class of immunoglobulins that protects against viruses, bacteria, and toxins.
IgD is found on the surface of developing B lymphocytes. The function is not installed.
IgE - secreted during an immediate allergic reaction.
Interference:
- Hemoglobin. In heavy smokers due to the formation of functionally inactive HbCO.Red blood cells. Not detected. Erythrocyte indices: 1. MCV – average erythrocyte volume. Alcohol abuse, zidovudine. Drugs that provoke the development of megaloblastic anemia, including aminosalicylic acid, anticonvulsants, barbiturates, colchicine, cycloserine, estrogens, glutethimide, isoniazid, mefenamic acid, metformin, methotrexate, neomycin, nitrofurans, oral contraceptives, phenacetin, pyrimethamine, triamterene, trimet oprim . 2. MCH – average hemoglobin content in a red blood cell. No clinical interference was detected.3. MCHC is the average hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes. No clinical interference was detected. Leukocytes. Differential count of leukocytes: Neutrophils. Acetylcholine, carbon dioxide, casein, chlorpropamide, corticosteroids, corticotropin, digitalis, endotoxins, epinephrine, ethylene glycol, heparin, histamine, insecticides, lead, mercury, norepinephrine, potassium chlorate, tarpentine. Eosinophils. Eosinophilia is often a manifestation of allergic reactions to drugs, such as anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, chloramphenicol), antibiotics (erythromycin, penicillins, tetracyclines, vancomycin), sulfonamides, antituberculosis drugs, phenothiazides. Aminosalicylic acid, chlorpropamide, imipramine, mephenesin, nitrofurantoin, penicillin, sulfasalazine, sulfonamides (in all these cases, eosinophilia is part of Loeffler's syndrome); allopurinol, dapsone, etretinate, methotrexate, methyldopa, nafarelin, penicillamine, procarbazine, triamterene. Basophils. Estrogens, antithyroid drugs, desipramine. Lymphocytes. Albuterol, aminosalicylic acid, carbon disulfide (poisoning), epinephrine, griseofulvin, isoproterinol, levodopa, narcotic analgesics, niacinamide, norepinephrine, phenytoin, mephenytoin, organic arsenic compounds, lead poisoning, tetrachloroethanol poisoning, valproic acid. Monocytes. Carbon disulfide (poisoning), griseofulvin, haloperidol, mephenytoin (rare), methsuccimide, phosphorus (poisoning), prednisolone, tetrachloroethane (poisoning). Platelets. Adrenaline, metoprolol, miconazole, propranolol. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Dextran, fat emulsions, hepatitis B vaccine, oral contraceptives, vitamin A.
- Hematocrit alpha interferon, thrombolytics. Erythrocytes. Erythrocyte indices. No clinical interference was detected. Leukocytes. Differential leukocyte count. Neutrophils. Substances that act on individuals due to their individual sensitivity: analgesics, anticonvulsants, antihistamines, antimicrobials, antithyroid, antiviral, cardiovascular drugs, diuretics, hypoglycemics, etc. Substances that act on all people when used in normal doses: antitumor drugs. Eosinophils . Corticotropin, epinferin, glucocorticoids, methysergide, niacin, procainamide. Basophils. Corticosteroids, corticotropin, X-ray irradiation, chemotherapy, procainamide, thiopental. Lymphocytes. Antilymphocyte serum, asparaginase, chlorambucil, corticotropin, glucocorticoids, lithium, mechlorethamine, methylsergide, niacin, X-ray irradiation. Platelets. Antitumor drugs; other drugs in some patients due to individual sensitivity: analgesics, anticonvulsants, antihistamines, antimicrobials, antithyroid, cardiovascular, diuretics, heavy metals, hypoglycemic, psychotropic, etc. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Corticotropin, cortisone, cyclophosphamide.
What to choose – qualitative or semi-quantitative analysis?
Why is qualitative and quantitative analysis carried out?
Qualitative analysis allows us to answer 2 questions:
- Were you sick or not?
- How long have you been sick?
A semi-quantitative test can answer these questions and also determine the amount of immunoglobulins in the body.
Why determine the amount of immunoglobulins?
Determining the amount of antibodies allows you to determine whether long-term immunity has been formed. It is what protects the body from re-infection with coronavirus.
Decoding the results of the test for antibodies to coronavirus
How to decipher a qualitative coronavirus antibody test
| Yes/No | Ig G (Eat) | Ig G (No) |
| Ig M (Yes) | 1 option | Option 2 |
| 5-10 weeks have passed since infection. IgM is still present in the blood, but IgG is already being formed | Acute phase of the disease. 1-3 weeks have passed since infection | |
| Ig M (No) | Option 3 | Option 4 |
| Several months have passed since the illness. You may have had the disease asymptomatically | You have not encountered any viruses or no more than 7 days have passed since infection |
Antibodies to coronavirus - table with interpretation of results
In the 2nd and 4th version
(if there are suspicious symptoms), it is recommended to take a PCR test for coronavirus to identify the pest.
The complete absence of immunoglobulins may also mean that:
1) The preparation conditions were not met and the result was distorted
2) The symptoms of influenza or ARVI were similar to the symptoms of coronavirus,
3) The patient suffered a mild form of the disease and did not develop antibodies.
4) The patient suffered a severe form of the disease, and the antibodies quickly disappeared.
When is an immunological blood test prescribed?
Immunological research is carried out:
Immunological blood test
- in case of recurring infectious diseases;
- if the infectious disease is severe and protracted;
- if you suspect congenital or acquired immunodeficiency;
- if an autoimmune disease is suspected;
- for allergic reactions;
- before major surgical interventions;
- if the postoperative period occurs with complications;
- in order to monitor the progress of treatment with certain groups of medications (immunosuppressants, immunomodulators, etc.).
Ig G - interpretation of the test for antibodies to coronavirus
To determine class G immunoglobulins in the blood, a qualitative and quantitative method for determining antibodies is used. Below is a table with a breakdown of the enzyme immunoassay for coronavirus (igG indicator for coronavirus).
Coronavirus antibody index - transcript of captions
| Result | Index | Meaning |
| Negative | Less than 0.8 | The patient either did not encounter the disease or underwent the procedure in the acute phase. |
| Border | 0,8-1,1 | You need to do a repeat test after 14 days. Perhaps the test was done at the onset of the disease or during the recovery process. |
| Positive | More than 1.1 | This level of antibodies to coronavirus in adults is normal. The person had coronavirus infection several months ago, and humoral immunity had time to develop. |
Class G antibodies to coronavirus - interpretation of results
An antibody titer to coronavirus of 1,800 (positive result) is normal. In this case, immunoglobulins of class A and M should be absent in the blood. Their presence indicates the stage of recovery.
Decoding and data of normal indicators
The result of the analysis is a conclusion, which is usually a table about the content of chemicals and biological agents in the blood. The first column indicates the indicator, the second - the identified value, and the third - the normal range. Only a specialist, assessing the indicators, can determine the presence of disturbances in water-salt metabolism, identify inflammatory processes and infections, and also assess the performance status of all the patient’s organs.
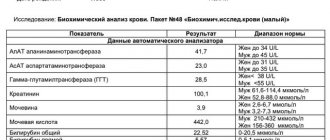
As for normal indicators, the data for adults looks like this:
| Analysis | Men | Women |
| Total protein | 64-84 g/l. | 64-84 g/l. |
| Hemoglobin | 130-160 g/l | 120-150 g/l. |
| Haptoglobin | 150-2000 mg/l | 150-2000 mg/l |
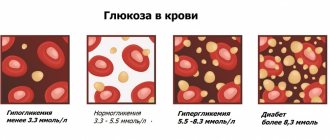
| Glucose | 3.30-5.50 mmol/l. | 3.30-5.50 mmol/l. |
| Urea | 2.5-8.3 mmol/l. | 2.5-8.3 mmol/l. |
| Creatinine | 62-115 µmol/l | 53-97 µmol/l. |
| Cholesterol | 3.5-6.5 mmol/l. | 3.5-6.5 mmol/l. |
| Bilirubin | 5-20 µmol/l. | 5-20 µmol/l. |
| AlAT (ALT) | up to 45 units/l. | up to 31 units/l. |
| ASAT (AST) | up to 45 units/l. | up to 31 units/l. |
| Lipase | 0-190 units/l. | 0-190 units/l. |
| Alpha amylase | 28-100 units/l. | 28-100 units/l. |
| Pancreatic amylase | 0-50 units/l. | 0-50 units/l. |
Decoding the main indicators of the LHC
Total protein.
A biochemical blood test determines the total concentration of various proteins, which consist of amino acids. Protein takes an active part in the processes of coagulation, processing and transport of nutrients to organs and tissues.
Hemoglobin.
This specific protein from the red blood cell system is responsible for transporting oxygen in the body
Haptoglobin.
A blood plasma protein that binds hemoglobin and is responsible for preserving iron in the body. Also involved in the control of local inflammatory processes.
Glucose.
An important component responsible for carbohydrate metabolism. Its content in arterial blood is higher than in venous blood.
Urea.
This is the main product of protein breakdown, in which nitrogen unnecessary by the body is removed in the urine.
Creatinine.
This, like urea, is the end product of protein metabolism. The content of creatinine in the blood depends on gender, age, and muscle mass.
Cholesterol
. A component of fat metabolism, which is also involved in the construction of cell membranes and the synthesis of vitamin D and sex hormones. Another name is cholesterol. There are: total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.
Bilirubin
. The breakdown product of hemoglobin, a toxic substance of two types: direct and indirect. They form a “general” one and the norm when deciphering a biochemical blood test is indicated specifically for it.
AlAT (ALT).
Alanine aminotransferase is an enzyme contained in the cells of the liver, kidneys and heart, so its presence in the blood indicates the destruction of the cells of these organs.
AST (AST).
Aspartate aminotransferase is a cellular enzyme that is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and is found in the liver cells of the heart and kidneys.
Lipase.
An enzyme that promotes the breakdown of fats.
Amylase.
It breaks down carbohydrates from food and ensures their digestion. There are alpha-amylase (diastase) and pancreatic amylase.
It is important to remember that only a specialist can evaluate the results of a blood test, decipher a biochemical analysis, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment!
BAU/ml - new interpretation of the test for antibodies to coronavirus
The World Health Organization has approved a new international standard for the determination of immunoglobulins for coronavirus, with the unit of measurement BAU (translated as “binding antibody coefficient”).
Interpretation of quantitative analysis for antibodies to coronavirus
Laboratory diagnostics
the level of immunity protection against coronavirus is carried out by studying immunoglobulins to the S-protein of the virus. To facilitate the interpretation of the study results, it was proposed to use a universal measurement system.
Conversion table for antibody test results from different manufacturers in BAU/ml
| Manufacturer | Conversion factor to BAU/ml |
| Abbott ARCHITECT | 0,142 |
| Roche | 1 |
Immunological blood test at the "Family Doctor"
For the study, blood is taken from the ulnar vein. You can donate blood for an immunological test at any of the Family Doctor clinics.
The results are interpreted by an immunologist, who takes into account examination data, patient complaints and the results of other studies. The greatest attention is paid to significant deviations from the norm (more than 20%), smaller deviations can be caused by random factors - diet, stress, physical activity, as well as individual characteristics of the body.